HashMap是线程不安全的,在多线程的情况下,可以用以下三种方式来代替HashMap:
- 使用Collections.synchronizedMap(Map)来创建
- HashTable
- ConcurrentHashMap
Collections.synchronizedMap(Map)
synchronizedMap在内部维护了一个map对象和一个排斥锁mutex。
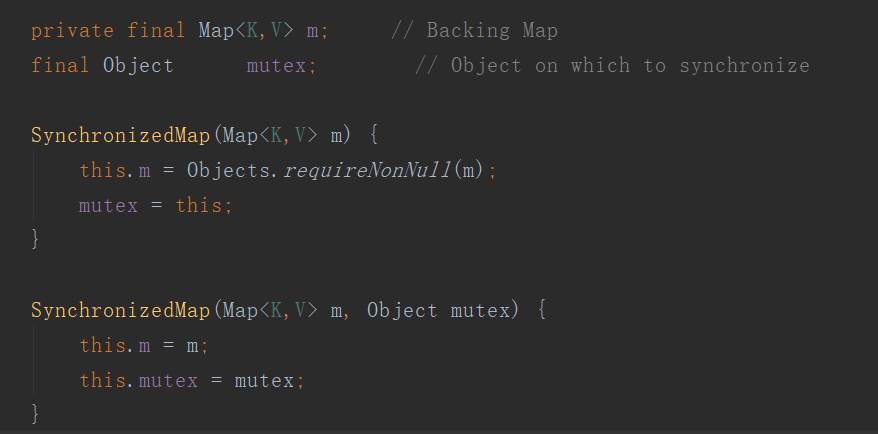
在调用这个方法创建map后,在使用这个map的时候,就会对方法上锁,从而达到线程安全的目的。
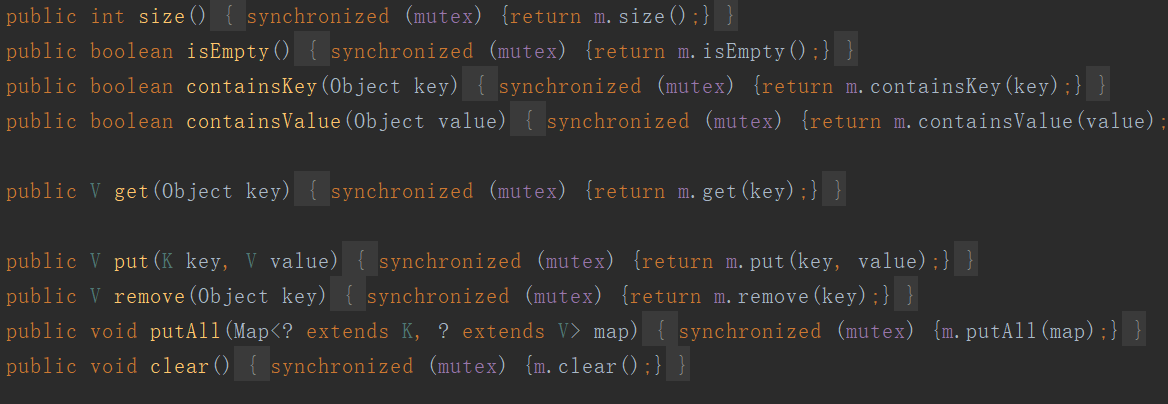
HashTable
HashTable通过加锁的方式来实现线程安全。它的方法都是由synchronized关键字来修饰的。由于它的这种实现方法,并发度不够,性能较低。
HashTable与HashMap的区别:
- HashMap的键值都可以为null,HashTable不允许为null
- HashMap的默认容量为16,HashTable为11。负载因子都是0.75。在构建时设置了大小,HashMap会将其变成2的倍数,HashTable不做处理。
- HashMap继承AbstractMap,HashTable继承Dictionary。
- HashMap扩容是,长度变为原来的两倍。HashTable扩容时,长度便来原来的两倍+1
ConcurrentHashMap
在jdk1.8中,ConcurrentHashMap的底层数据结构和HashMap一样,都是数组加链表,数组中存放Node。 ConcurrentHashMap使用volatile来修饰Node的value和next,来保证可见性。
ConcurrentHashMap在进行put操作时,大概分为以下几个步骤:
- 计算key的hash值。
- 判断是否需要初始化数组。
- 以key的hash值作为数组下标插入,若该位置没有值,则直接插入。通过cas和自旋的方式确保插入成功。
- 如果当前位置的hashcode等于-1,则进行扩容
- 如果都不满足,则通过synchronized加锁,写入数据。当链表长度大于等于8,转化为红黑树。
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 计算hash值
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
// 判断是否需要初始化数组
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
// 若当前位置为null,插入数据
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
// 扩容
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
// 使用synchronized加锁,插入数据
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
...
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
...
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
// 若链表长度大于等于8,转化为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
注意,ConcurrentHashMap的键值都不能为null。
ConcurrentHashMap的get操作和HashMap类似,首先通过key的hash值寻址。如果找到的节点只有一个值,则返回。如果是链表或红黑树,则遍历,用equals方法比较key的值,返回对应的value。