简述
关于go的web开发框架,主要是两大类。一类以beego为主,功能全,配置多,大而全;一类是以gin为主的,基于httprouter进行开发,轻而快。这个无所谓好坏,全看个人选择。今天主要说httprouter是如何实现。
-
httprouter支持参数类型的URL(
/user/:id)也支持*的通配符URL(/static/*file)。 -
httprouter使用radix tree(前缀树)对请求的URL进行管理,最差时间复杂度为O(n),n为URL长度。
-
httprouter对每种请求方法都会建立一个tree进行管理。例如所有的GET请求会都用一个tree,所有的POST用一个tree,所有的PUT一个tree......
-
当同时使用GET方式添加路由
/ff/:id和/ff/kk时,会抛出panic: 'kk' in new path '/ff/kk' conflicts with existing wildcard ':id' in existing prefix '/ff/:id'。是因为在GET的tree上面,前缀都是/ff的情况下,参数类型的:id和具体的路由字段kk冲突。
关于httprouter目录
项目总共三个文件router.go、tree.go、path.go,其中router.go是主文件,路由的添加、异常路由的处理等基本设置在此完成,调用httprouter.New() 返回一个Router结构的指针。tree.go负责前缀树的操作,包括将路由添加到前缀树中,从树中查询到URL对应的handler。path.go主要包含CleanPath方法,返回一个符合规范的URL。
关于router.go 中的 Router结构
type Router struct {
//前缀树的结构
trees map[string]*node
paramsPool sync.Pool
maxParams uint16
//如果无法匹配到当前路由,但是存在带有(不带)尾部斜杠的路由时,是否自动重定向
//例如,如果请求了/foo/,但是只存在/foo的路由,那么将301重定向到 /foo
RedirectTrailingSlash bool
//是否修正路径,主要依靠path.go 的 CleanPath 方法
RedirectFixedPath bool
//如果无法匹配到当前路由, 那么检查是否有其他方法能否拼配到当前的路由
HandleMethodNotAllowed bool
//是否允许路由自动拼配到options
HandleOPTIONS bool
//全局的options操作,可以设置CORS时调用
GlobalOPTIONS http.Handler
globalAllowed string
//当没有匹配到路由的时候, 执行这个handler. 如果没有配置,那么返回NotFound
NotFound http.Handler
//当没有匹配到路由并且HandleMethodNotAllowed=true的时候,这个函数被使用
MethodNotAllowed http.Handler
PanicHandler func(http.ResponseWriter, *http.Request, interface{})
}
这其中最重要的就是trees节点,路由的添加、查找都是通过这个操作完成。
关于node的结构
type node struct {
//当前node 的路径
path string
// children对应的索引,保存的是分裂分支的第一个字符
indices string
//判断子节点是否为通配节点,(包括:param、catchAll)
wildChild bool
//节点类型。
//root: 第一个插入的节点
//catchAll: 有* 匹配的节点
//param:参数节点 :id
//static: 静态节点,前几个剩下的都是静态节点
nType nodeType
// 优先级
priority uint32
//子节点
children []*node
//当前节点的处理函数
handle Handle
}
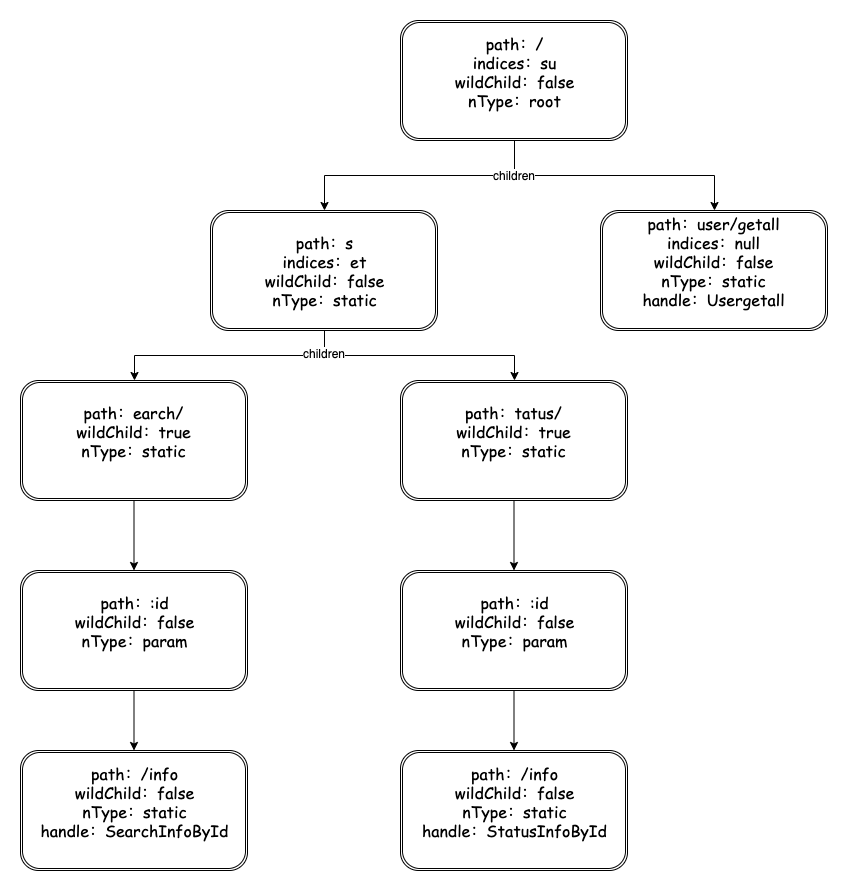
node示意图
例如GET请求,/search/:id/info、/status/:id/info、/user/getall
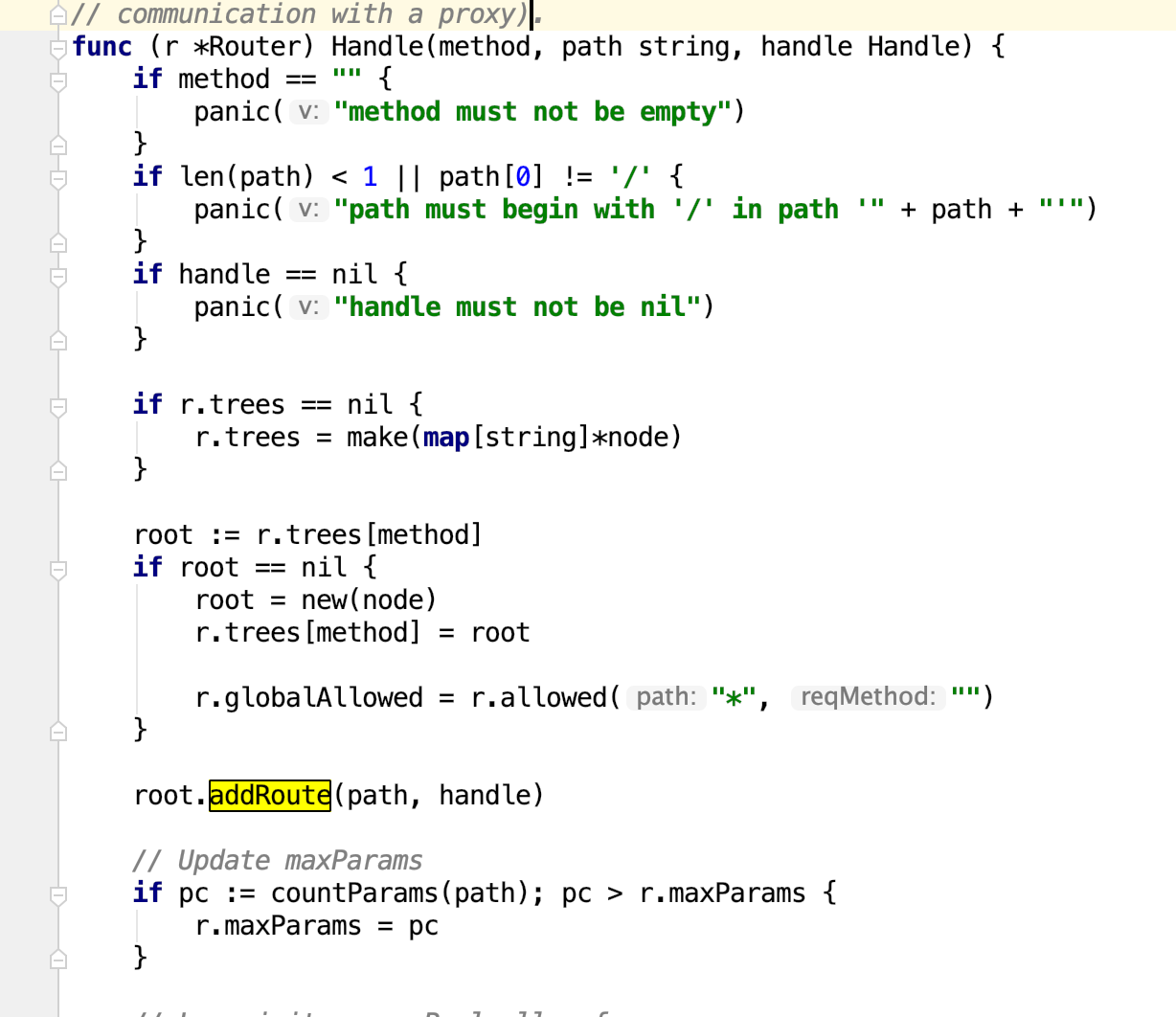
关于addRoute

当调用GET添加路由时,走的是Router的Handle方法。同样,post、put、delete等也是一样
addRoute 的基本思路就是先寻找路由的最长公共前缀,找到对应的节点位置,然后调用insertChild,插入到对应的node中。
- tree是一个空树时,那么当前URL直接插入path,nType为root
- tree不为空时,如果匹配的最长前缀小于当前节点path的长度,那么说明当前节点需要进行调整。最长公共前缀作为节点的path,原先节点成为最长公共前缀的子节点。
- tree不为空时,如果匹配的最长前缀小于传入的path的长度,说明需要在当前节点下,添加一个新的子节点。当然这里可能会有循环递归。
- tree不为空时,如果匹配的最长前缀等于path,那么就是在此节点直接添加handler操作。
代码说明
// addRoute adds a node with the given handle to the path.
// Not concurrency-safe!
func (n *node) addRoute(path string, handle Handle) {
fullPath := path
n.priority++
// Empty tree
if len(n.path) == 0 && len(n.indices) == 0 {
n.insertChild(path, fullPath, handle)
n.nType = root
return
}
walk:
for {
// Find the longest common prefix.
// This also implies that the common prefix contains no ':' or '*'
// since the existing key can't contain those chars.
// 寻找传入的路由与节点的最长公共前缀
i := longestCommonPrefix(path, n.path)
// Split edge--分割 边际
// 如果最长前缀的长度 < 节点长度
if i < len(n.path) {
//那么当前节点的path就应该是最长前缀,原先的节点是最长前缀的子节点
child := node{
//节点的路径就是 当前节点后段字符串
path: n.path[i:],
wildChild: n.wildChild,
nType: static,
indices: n.indices,
children: n.children,
handle: n.handle,
priority: n.priority - 1,
}
//刚分裂的节点,作为新节点的子节点
n.children = []*node{&child}
// []byte for proper unicode char conversion, see #65
n.indices = string([]byte{n.path[i]})
n.path = path[:i]
n.handle = nil
n.wildChild = false
}
// Make new node a child of this node ----为当前节点创建一个新的子节点
//如果最长前缀 < 路径的长度
//除了tree为空的情况外,只有在这个判断下才会走 insertChild ,创建新节点
if i < len(path) {
path = path[i:]
//如果子节点是参数节点
if n.wildChild {
n = n.children[0]
n.priority++
// Check if the wildcard matches
// 如果子节点是通配节点,需要验证合法性
if len(path) >= len(n.path) && n.path == path[:len(n.path)] &&
// Adding a child to a catchAll is not possible
n.nType != catchAll &&
// Check for longer wildcard, e.g. :name and :names
(len(n.path) >= len(path) || path[len(n.path)] == '/') {
continue walk
} else {
// Wildcard conflict
// 通配符冲突
pathSeg := path
if n.nType != catchAll {
// SplitN 根据/分割字符串,最多2个
pathSeg = strings.SplitN(pathSeg, "/", 2)[0]
}
prefix := fullPath[:strings.Index(fullPath, pathSeg)] + n.path
panic("'" + pathSeg +
"' in new path '" + fullPath +
"' conflicts with existing wildcard '" + n.path +
"' in existing prefix '" + prefix +
"'")
}
}
idxc := path[0]
// '/' after param --
if n.nType == param && idxc == '/' && len(n.children) == 1 {
n = n.children[0]
n.priority++
continue walk
}
// Check if a child with the next path byte exists
//判断当前节点的 indices 索引中是否存在当前path的首字母
for i, c := range []byte(n.indices) {
if c == idxc {
i = n.incrementChildPrio(i)
n = n.children[i]
continue walk
}
}
// Otherwise insert it ---否则直接插入
if idxc != ':' && idxc != '*' {
// []byte for proper unicode char conversion, see #65
n.indices += string([]byte{idxc})
child := &node{}
n.children = append(n.children, child)
n.incrementChildPrio(len(n.indices) - 1)
n = child
}
n.insertChild(path, fullPath, handle)
return
}
// Otherwise add handle to current node
//如果最长前缀 == 传入的path,就直接在这个节点添加handle
if n.handle != nil {
panic("a handle is already registered for path '" + fullPath + "'")
}
n.handle = handle
return
}
}