断点跟踪的三种方式
- ctrl + debug调试栏中的下一步按钮
- 添加Symbolic BreakPoint,Symbol选项中填写跟踪的方法:alloc/[NSObject alloc]
- 查看汇编,选中Xcode --> Debug --> Debug Workflow --> Always show Disassembly,并在代码出添加断点
调试技巧
在debug时,有时会用到register read指令查看内存,其中register代表寄存器,在寄存器中,x0中存放的是,函数的第一个参数或者返回值。
x指令,以16进制打印对象
x/x4g指令,以16进制打印4段数据,每段都是作为一个整体
(lldb) register read
General Purpose Registers:
x0 = 0x00000001006646c8 (void *)0x0000000100664a88: OS_voucher
x1 = 0x0000000000000048
x2 = 0x000000016f93a690
...
x28 = 0x0000000000000000
fp = 0x000000016f93a680
lr = 0x0000000100606474 libdispatch.dylib`_os_object_alloc_realized + 40
sp = 0x000000016f93a670
pc = 0x00000001aa39f950 libobjc.A.dylib`class_createInstance
cpsr = 0x20000000
(lldb) register read x0 //可以将x0换做想要查看的寄存器标志
x0 = 0x00000001f226b3e0 (void *)0x00000001f226b408: __NSArrayM
x0~x7存放的是程序的参数。
iOS中,每个函数都包含了两个默认参数id self、SEL cmd,其中self就存在x0中。
查看Xcode LLDB常用指令,了解更多指令。
alloc流程分析
[[NSObject alloc] init]是日常开发中最常用的对象初始化方法,现在我们对alloc和init的流程进行分析。
先上一张alloc的流程图
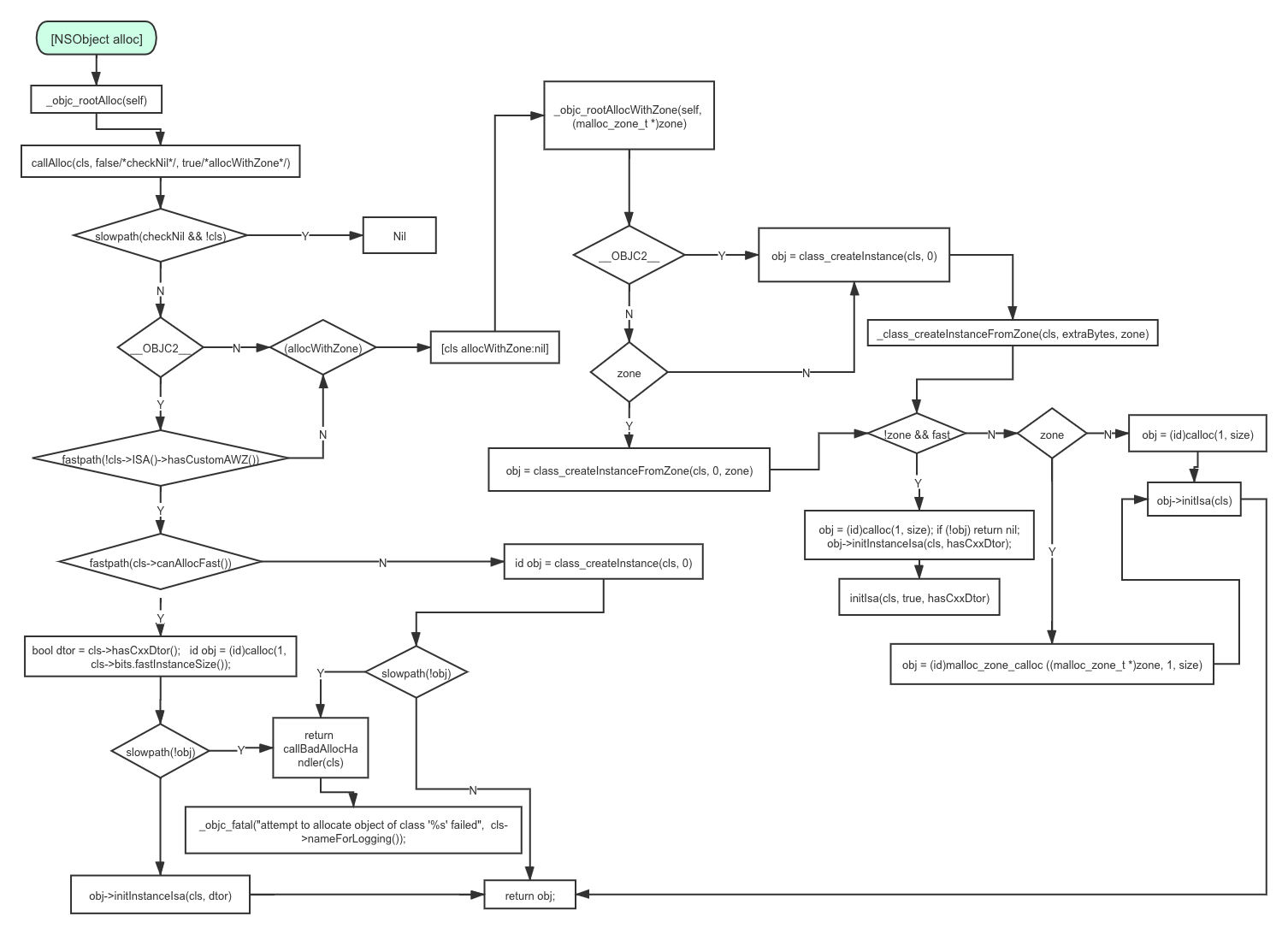
配置过程自行百度或参考 Cooci的 iOS_objc4-756.2最新源码编译调试
在 main.m 中写入初始化代码就开始对 alloc 流程的探索
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
// insert code here...
NSObject *object = [[NSObject alloc] init];
NSLog(@"Hello, World! %@",object);
}
return 0;
}
command点击alloc,进入源码查看
+ (id)alloc {
return _objc_rootAlloc(self);
}
继续深入
id
_objc_rootAlloc(Class cls)
{
return callAlloc(cls, false/*checkNil*/, true/*allocWithZone*/);
}
该方法的参数是一个object_class类型的结构体Class,该结构体存放了对象的各种信息
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
struct objc_class : objc_object {
// Class ISA;
Class superclass;
cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtable
class_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags
class_rw_t *data() {
return bits.data();
}
void setData(class_rw_t *newData) {
bits.setData(newData);
}
void setInfo(uint32_t set) {
assert(isFuture() || isRealized());
data()->setFlags(set);
}
//...
可以看出 objc_class 继承自 objc_object
struct objc_object {
private:
isa_t isa;
public:
// ISA() assumes this is NOT a tagged pointer object
Class ISA();
// getIsa() allows this to be a tagged pointer object
Class getIsa();
// initIsa() should be used to init the isa of new objects only.
// If this object already has an isa, use changeIsa() for correctness.
// initInstanceIsa(): objects with no custom RR/AWZ
// initClassIsa(): class objects
// initProtocolIsa(): protocol objects
// initIsa(): other objects
void initIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=false*/);
void initClassIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=maybe*/);
void initProtocolIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=maybe*/);
void initInstanceIsa(Class cls, bool hasCxxDtor);
// changeIsa() should be used to change the isa of existing objects.
// If this is a new object, use initIsa() for performance.
Class changeIsa(Class newCls);
//...
继续进入callAlloc函数
static ALWAYS_INLINE id
callAlloc(Class cls, bool checkNil, bool allocWithZone=false)
{
if (slowpath(checkNil && !cls)) return nil;
#if __OBJC2__
if (fastpath(!cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ())) {
// No alloc/allocWithZone implementation. Go straight to the allocator.
// fixme store hasCustomAWZ in the non-meta class and
// add it to canAllocFast summary
if (fastpath(cls->canAllocFast())) {
// No ctors, raw isa, etc. Go straight to the metal.
bool dtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
id obj = (id)calloc(1, cls->bits.fastInstanceSize());
if (slowpath(!obj)) return callBadAllocHandler(cls);
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, dtor);
return obj;
}
else {
// Has ctor or raw isa or something. Use the slower path.
id obj = class_createInstance(cls, 0);
if (slowpath(!obj)) return callBadAllocHandler(cls);
return obj;
}
}
#endif
// No shortcuts available.
if (allocWithZone) return [cls allocWithZone:nil];
return [cls alloc];
}
函数中存在4个判断,我们逐个分析判断的内容
1、slowpath
#define fastpath(x) (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 1))//表示x的值为真的可能性更大,if 下的代码执行的可能性更高
#define slowpath(x) (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 0))//表示x的值为假的可能性更大,else下的代码执行的可能性更高
if (slowpath(checkNil && !cls)) return nil; 其实就是判断了当前 cls 是否存在。
2、hasCustomAWZ()
hasCustomAWZ 其中AWZ为allocWithZone的缩写。
bool hasCustomAWZ() {
return ! bits.hasDefaultAWZ();
}
void setHasDefaultAWZ() {
assert(isInitializing());
bits.setHasDefaultAWZ();
}
void setHasCustomAWZ(bool inherited = false);
可以看出默认返回的是YES
3、canAllocFast()
bool canAllocFast() {
return false;
}
由此可见这个判断永远返回false,只能执行else中的代码
else {
// Has ctor or raw isa or something. Use the slower path.
id obj = class_createInstance(cls, 0);
if (slowpath(!obj)) return callBadAllocHandler(cls);
return obj;
}
这时,通过class_createInstance(cls, 0)方法,正式进入创建过程。
继续深入class_createInstance(cls, 0)方法进入_class_createInstanceFromZone,该方法包含了alloc的所有执行操作,包括类大小的获取,类的堆空间开辟,isa 指针的指向。截取重要部分如下
bool hasCxxCtor = cls->hasCxxCtor();
bool hasCxxDtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
bool fast = cls->canAllocNonpointer();
size_t size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes);
if (outAllocatedSize) *outAllocatedSize = size;
id obj;
if (!zone && fast) {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size); //开辟内存空间
if (!obj) return nil;
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor); //对象初始化
}
else {
if (zone) {
obj = (id)malloc_zone_calloc ((malloc_zone_t *)zone, 1, size);
} else {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
}
if (!obj) return nil;
// Use raw pointer isa on the assumption that they might be
// doing something weird with the zone or RR.
obj->initIsa(cls);
}
- static attribute 的标识代表 OC 中 C++ 的全局构造函数。
- hasCxxCtor() 判断当前 class 或者 superclass是否有
.cxx_construct方法的实现。
- hasCxxDtor() 判断判断当前 class 或者 superclass 是否有
.cxx_destruct方法的实现。
- canAllocNonpointer() 具体标记某个类是否支持优化的isa。
- instanceSize(extraBytes) 获取类的大小,最小16byte。 最后调用objc_object的initIsa方法进行初始化。
字节对齐 instanceSize(extraBytes)
size_t instanceSize(size_t extraBytes) {
size_t size = alignedInstanceSize() + extraBytes;
// CF requires all objects be at least 16 bytes.
if (size < 16) size = 16;
return size;
}
通过源码可以看出,对象申请的空间,最少为16个字节。
alignedInstanceSize()
// Class's ivar size rounded up to a pointer-size boundary.
uint32_t alignedInstanceSize() {
return word_align(unalignedInstanceSize());
}
word_align()函数是一个进行对齐的算法
static inline uint32_t word_align(uint32_t x) {
return (x + WORD_MASK) & ~WORD_MASK;
}
static inline size_t word_align(size_t x) {
return (x + WORD_MASK) & ~WORD_MASK;
}
其中WORD_MASK为7,通过二进制的& ~ 运算,即代表该算法为8字节对齐,即所计算出的内存为8的倍数,代表对象实际根据属性数来申请内存的话,其实是以8的倍数来进行申请的。
4、allocWithZone
入参默认为false,所以不执行。
init
// Replaced by CF (throws an NSException)
+ (id)init {
return (id)self;
}
- (id)init {
return _objc_rootInit(self);
}
id
_objc_rootInit(id obj)
{
// In practice, it will be hard to rely on this function.
// Many classes do not properly chain -init calls.
return obj;
}
可见,init什么都没做。 init存在的意义只是方便开发者在init中进行自定义初始化赋值。
至此,alloc、init流程就完全结束了。
new
+ (id)new {
return [callAlloc(self, false/*checkNil*/) init];
}
所以[NSObject new]等价于[[NSObject alloc] init]。