上两个分享中,从写SQL语句到直接用Sequelize编译帮我们写好执行SQL,现在到了我们前端最有兴趣的这块了,此处实现数据的增删改查已经对常用的代码封装以及编写接口。
mongodb 的基本使用
我们现在最新安装都是4以上的版本,所以不需要自己启动,他都会自动启动了
mongodb 原生驱动
安装mysql: npm i mongodb --save
连接mongodb操作
const MongoClient = require("mongodb").MongoClient;
const url = "mongodb://localhost:27017";
const dbName = "test";
(async function() {
//创建客户端
const client = new MongoClient(url,{useNewUrlParser:true}); //配置项,新的url解释器作用连接的时候会报老的错误信息 https://mongoosejs.com/docs/connections.html
await client.connect();
console.log("连接成功");
const db = client.db(dbName)
//获取集合
const fruitsColl = db.collection('fruits');
//插入文档,返回Promise
let obj = [
{name:'芒果1',price: 20},
{name:'芒果2',price: 20},
{name:'芒果3',price: 20},
{name:'芒果4',price: 20},
]
let r = await fruitsColl.insertMany(obj); //插入多条数据,insertOne()插入一条
console.log("插入成功",r.result);
// 查询文档
r= await fruitsColl.findOne();
console.log('查询结果',r);
r = await fruitsColl.updateOne({name: '芒果1'},{$set: {name: '苹果2'}});
console.log("更新成功",r.result)
r=await fruitsColl.deleteOne({name: '苹果'});
console.log('删除成功',r.result);
} catch(error) {
console.error(error);
}
client.close(); //关闭
})();
// 运行: nodemon 文件名称
// 连接成功
// 插入成功 { ok: 1, n: 4 }
// 查询结果 { _id: 5e09ad07a100d551bcf10152, name: '芒果1', price: 20 }
// 更新成功 { n: 1, nModified: 1, ok: 1 }
封装,接口
进入正题编辑数据接口,常用封装。每次连接我们都需要声明数据库连接的配置项,会很费时,则我们可以根据这个进行封装相应的配置文件,即MVC结构的M层配置
Node 是先走同步的代码,再走异步的代码,所以在封装的时候,导入配置项确保是同步代码anscy .. await,或是运用通信机制,事件派发器EventEmiter
模型式连接配置
//配置连接 conf.js
module.exports = {
url: 'mongodb://localhost:27017',
dbName: 'test'
}
模型式db调用封装
每次都需要db连接获取集合,则进行封装,此处如有不明白可以看下上一块的原型驱动。此处的实现是对db的和collection调用的封装,以及事件的派发监听。
- 通过构造函数constructor的方法构造出集合,继而连接客户端。
- 其二解决的事collection调用的封装
//获取集合方法 const fruitsColl = db.collection('fruits');
col(colName,dbName=this.conf.dbName) { //集合名称;尝试获取不同数据库,如果不传则放入默认数据库
return this.client.db(dbName).collection(colName);
}
- 由于node的特性,我们需要引入事件派发器,进行实例化派发器,当在连接数据库成功后emit派发成功通知,其次封装一个监听事件的方法,进行函数的回调
const EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter; //导入事件派发器
this.emitter = new EventEmitter(); //实例化
this.emitter.emit('connect');//连接成功后进行派发成功通知
//监听事件的方法(只听一次)
once(event,cb) {//事件,回调函数
this.emitter.once(event,cb)
}
继而我们只需要抛出方法即可,以下是全部封装db的函数
//db封装
const conf = require('./conf')
const MongoClient = require("mongodb").MongoClient;
const EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter; //导入事件派发器
class Mongodb{
constructor(conf) {
//保存conf
this.conf=conf //成员变量
this.emitter = new EventEmitter(); //实例化
//连接
this.client = new MongoClient(conf.url,{useNewUrlParser: true})
this.client.connect( err => { //有自动重连的机制
if(err) {
throw err
}
console.log('连接数据库成功');
this.emitter.emit('connect');//连接成功后进行派发通知
});
}
//监听事件的方法(只听一次)
once(event,cb) {
this.emitter.once(event,cb)
}
//获取集合方法
col(colName,dbName=this.conf.dbName) {
return this.client.db(dbName).collection(colName);
}
}
module.exports = new Mongodb(conf);
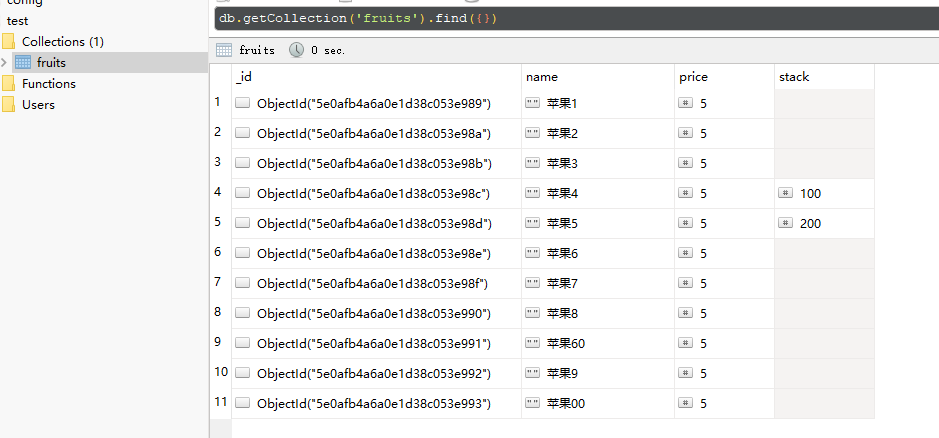
测试数据编写
此处包括如何once监听方法的使用,此处你会发现插入的数据即使是不对称的还是可以随意编入
//testdata.js
const mongodb = require('./db');
mongodb.once('connect',async ()=> { //进行监听方法
const col = mongodb.col('fruits');
try {
//删除已存在
await col.deleteMany();
//插入测试数据
await col.insertMany([
{name: '苹果1',price:5},
{name: '苹果2',price:5},
{name: '苹果3',price:5},
{name: '苹果4',price:5,stack: 100},
{name: '苹果5',price:5,stack: 200},
{name: '苹果6',price:5},
{name: '苹果7',price:5},
{name: '苹果8',price:5},
{name: '苹果60',price:5},
{name: '苹果9',price:5},
{name: '苹果00',price:5},
])
console.log('测试数据插入成功')
} catch (error) {
console.log('测试数据插入失败');
console.log(error);
}
})
运行数据文件
//fruit-market.js
const mongodb = require('./db');
const testdata = require('./testdata');
// nodemon fruit-market.js
// 连接数据库成功
// 测试数据插入成功
接口编写
有了上述的测试数据后,我们再基于//fruit-market.js中编写服务器端口和请求接口的编写
//服务器
const mongo = require('./db');
const testdata = require('./testdata');
const path = require('path')
const express = require('express')
const app = express();
app.get('/fruit-market',(req,res)=> { //检测路由地址匹配
res.sendFile(path.resolve('./fruit-market/fruit-market.html'))
})
//分页查询
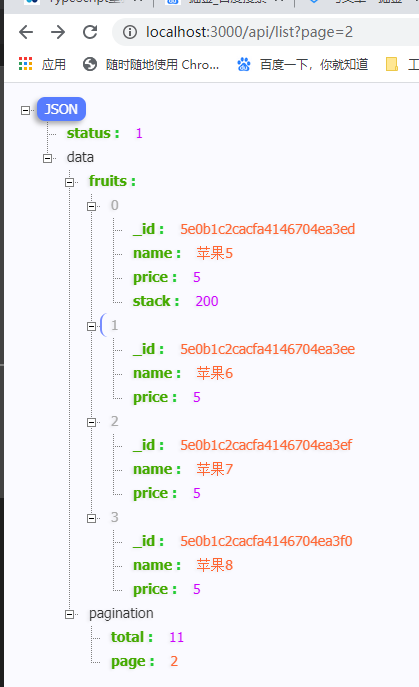
app.get('/api/list',async(req,res)=>{//定义接口
//分页数据
const {page} = req.query; //api/list?page=3
//查询
try {
const col = mongo.col('fruits')
const fruits = await col.find().skip((page-1)*4).limit(4).toArray(); //游标转成数组
//查询总条数 聚合操作
const total = await col.find().count();
res.json({status: 1,data: {fruits,pagination:{total,page}}})//请求到的JSON
} catch (error) {
}
})
app.listen(3000); //端口
前端数据遍历
getData() {
axios
.get(`/api/list?page=${this.page}`)
.then(res => res.data)
.then(({ data }) => {
this.fruits = data.fruits;
this.total = data.pagination.total;
});
}
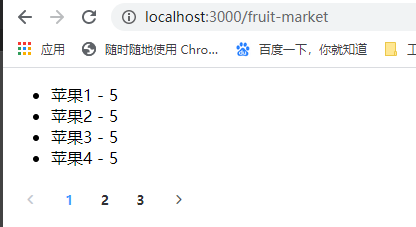
类别查询
//分类查询
app.get('/api/category',async(req,res)=>{
const col = mongo.col("fruits");
const data =await col.distinct("category");
res.json({status: 1,data})
})
//结果
{
"status": 1,
"data": [
"其他",
"家居",
"水果",
"蔬菜"
]
}
分类查询接口
此处跟分页类似的,只是这块多做一个操作,那么就是将类别的数据进行添加到一个数组当中,让find在数组中找到我们想要的数据结构
app.get('/api/list',async(req,res)=>{//定义接口
//分页数据
const {page,category} = req.query; //http://localhost:3000/api/list?page=1&category=蔬菜
//查询
try {
const col = mongo.col('fruits')
const condition={} //过了条件,构造条件
if(category) {
condition.category = category
}
const fruits = await col.find(condition).skip((page-1)*4).limit(4).toArray(); //游标转成数组 find--查询条件
//查询总条数 聚合操作
const total = await col.find(condition).count();
res.json({status: 1,data: {fruits,pagination:{total,page}}})//请求到的JSON
} catch (error) {
}
})
拓展 操作符
r = await fruitsColl.findOne({
// $or:[{price:{$gte:20}},{price:{$lte:10}}] //或,大于20或小于10
price:{$gte:20,$lte:10}
name: {$regex: /果/} //适用模糊搜索
})
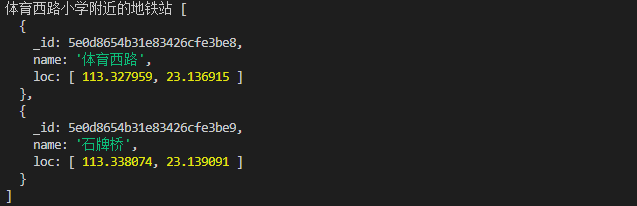
球面式的位置查询
实现的需求地图1公里内的地铁站
//查询1公里内的地铁站
const stations = db.collection('stations')
await stations.insertMany([
{name: '体育西路',loc:[113.327959,23.136915]},
{name: '石牌桥',loc:[113.338074,23.139091]},
{name: '林和西',loc:[113.330241,23.1471]},
{name: '动物园',loc:[113.313784,23.140828]},
])
await stations.createIndex({loc:'2dsphere'}) //设置索引 --概念:球面地理位置索引
r = await stations.find({ //指定查询字段,千米与弧度为单位,
loc: {
$nearSphere: {
$geometry: { //地理定位
type: 'Point', //类型,点
coordinates:[113.332666,23.135195] //指定坐标 体育西路小学
},
$maxDistance: 1000//接受最远的距离 1公里
}
}
}).toArray();
console.log('体育西路小学附近的地铁站',r)
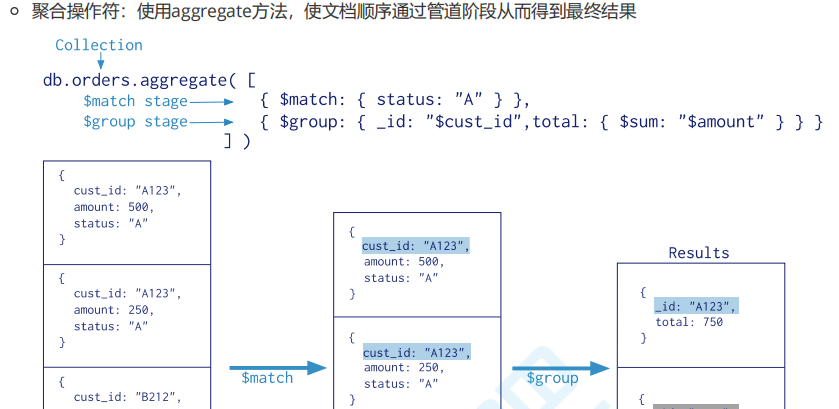
聚合操作符,使文档顺序通过管道阶段而得出
//获取集合
const fruitsColl = db.collection('fruits');
//插入文档,返回Promise
let obj = [
{name:'芒果',price: 20},
{name:'芒果',price: 15},
{name:'葡萄',price: 20},
{name:'苹果',price: 20},
]
let r = await fruitsColl.insertMany(obj);
//分组,求和 主要是实现对列表数据重复部分进行合并,比如在实现电商购物车的时候,我们可以根据group对同一个多商品进行合并成一个计算
//聚合管道操作 $group,$count,$sort,$skip,$limit,$project
r = await fruitsColl.aggregate([
{$match:{name: '芒果'}} ,//查询出芒果
{$group:{_id:'$name',total:{$sum:'$price'}}} //按照名称进行分类
]).toArray();
console.log(r);
//[ [ { _id: '芒果', total: 35 } ]