前言:
什么是二叉树?
树是一种比较重要的数据结构,二叉树是一种特殊的树,是每个结点最多有两个子树的树结构。通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree),二叉树常被用于实现二叉查找树和二叉堆。
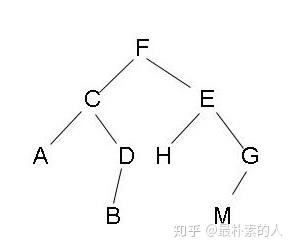
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),(又:二叉搜索树,二叉排序树)它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值。
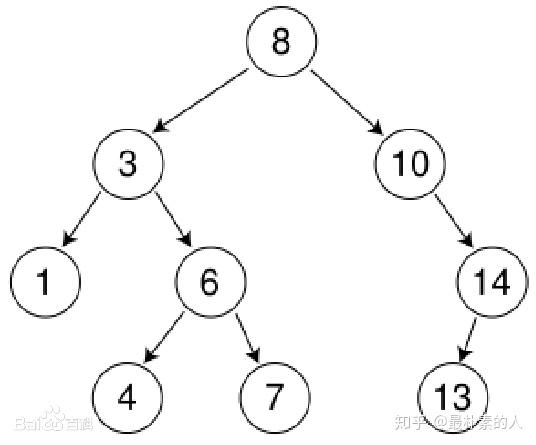
二叉树的遍历算法:二叉树的遍历可分为三种:先序遍历,中序遍历和后序遍历
先序遍历:简单说其遍历顺序就是:根--左--右
中序遍历:简单说其遍历顺序就是:左--根--右
后序遍历:简单说其遍历顺序就是:左--右--根
实现
二叉搜索树
解释完二叉树的基本知识,下面我们来定义一个二叉树对象,想要的效果就是传入一个无序number数组能生成一个 二叉搜索树
class BinaryTree {
constructor (arr = ['请输入正确的数组']) {
this.dataSource = arr; //原数组
this.binaryTree = {}; // 二叉搜索树
this.addToTree(this.dataSource); //生成二叉树
return this;
}
createNode(key) {
return {
key,
left:'',
right:''
}
}
addToTree(dataSource) {
for(let item of dataSource) {
JSON.stringify(this.binaryTree)==='{}' ?
(this.binaryTree=this.createNode(dataSource[0])) :
this.insertNode(this.binaryTree, item);
}
return this;
}
insertNode(tempBinaryTree, key) {
if(key<=tempBinaryTree.key){
if(tempBinaryTree.left==''){
tempBinaryTree.left=this.createNode(key)
return;
}
this.insertNode(tempBinaryTree.left, key);
}else{
if(tempBinaryTree.right==''){
tempBinaryTree.right=this.createNode(key)
return;
}
this.insertNode(tempBinaryTree.right, key);
}
}
}
createNode的作用是将每一个传入的值,将其包装成最小的树单元,有左右子节点。
insertNode的作用是根据规则组合成一个二叉搜索树
如果传入的key值小于现在节点的key值,且当前节点的左子数为空,就将传入的key包装成树单元插入到这个节点左节点上,如果左节点有值了就继续递归下去
如果传入的key值小于现在节点的key值,且当前节点的右子数为空,就将传入的key包装成树单元插入到这个节点右节点上,如果右节点有值了就继续递归下去
let result = new BinaryTree([6,4,2,6,74,6]).binaryTree
console.log(result)
//执行结果
result = {
"key": 6,
"left": {
"key": 4,
"left": {
"key": 2,
"left": "",
"right": ""
},
"right": {
"key": 6,
"left": {
"key": 6,
"left": "",
"right": ""
},
"right": ""
}
},
"right": {
"key": 74,
"left": "",
"right": ""
}
}
先序遍历
class BinaryTree {
constructor (arr = ['请输入正确的数组']) {
this.dataSource = arr; //数组
this.binaryTree = {}; //树对象
this.preOderArr = []; //先序数组
this.addToTree(this.dataSource); //生成二叉树
this.preOrder(this.binaryTree, this.preOderArr) //先序
}
createNode(key) {
}
addToTree(dataSource) {
}
insertNode(tempBinaryTree, key) {
}
//先序排序:根--左--右
preOrder(binaryTree, arr) {
if(!!binaryTree) {
arr.push(binaryTree.key);
this.preOrder(binaryTree.left, arr);
this.preOrder(binaryTree.right, arr);
}
}
}
可以看到实现代码非常的简洁明了,运用递归实现,准备一个数组容器,先将跟节点push到容器中,再递归遍历其左节点,然后递归其右节点,简单说其遍历顺序就是:根--左--右
执行:
let tree = new BinaryTree([6,4,2,6,74,6]);
let preOderArr = tree.preOderArr;
console.log(preOderArr)
//执行结果
[ 6, 4, 2, 6, 6, 74 ]
中序遍历
class BinaryTree {
constructor (arr = ['请输入正确的数组']) {
this.dataSource = arr; //数组
this.binaryTree = {}; //树对象
this.inOderArr = []; //中序数组
this.addToTree(this.dataSource); //生成二叉树
this.inOrder(this.binaryTree, this.inOderArr) //中序
}
createNode(key) {
}
addToTree(dataSource) {
}
insertNode(tempBinaryTree, key) {
}
//中序排序:左--根--右
inOrder(binaryTree, arr) {
if(!!binaryTree) {
this.inOrder(binaryTree.left, arr);
arr.push(binaryTree.key);
this.inOrder(binaryTree.right, arr);
}
}
}
可以看到实现代码非常的简洁明了,运用递归实现,准备一个数组容器,先遍历左节点,然后将当前节点的key值push到容器中,最后遍历右节点,简单说其遍历顺序就是:左--根--右
执行:
let tree = new BinaryTree([6,4,2,6,74,6]);
let inOderArr = tree.inOderArr;
console.log(inOderArr)
//执行结果
[ 2, 4, 6, 6, 6, 74 ]
后序遍历
class BinaryTree {
constructor (arr = ['请输入正确的数组']) {
this.dataSource = arr; //数组
this.binaryTree = {}; //树对象
this.behindOderArr = []; //后序数组
this.addToTree(this.dataSource); //生成二叉树
this.behindOrder(this.binaryTree, this.behindOderArr) //后序
}
createNode(key) {
}
addToTree(dataSource) {
}
insertNode(tempBinaryTree, key) {
}
//后序排序:左--右--根
behindOrder(binaryTree, arr) {
if(!!binaryTree) {
this.behindOrder(binaryTree.left, arr);
this.behindOrder(binaryTree.right, arr);
arr.push(binaryTree.key);
}
}
}
可以看到实现代码非常的简洁明了,运用递归实现,准备一个数组容器,先遍历左节点,后遍历右节点,然后将当前节点的key值push到容器中,简单说其遍历顺序就是:左--右--根
执行:
let tree = new BinaryTree([6,4,2,6,74,6]);
let behindOderArr = tree.behindOderArr;
console.log(behindOderArr)
//执行结果
[ 2, 6, 6, 4, 74, 6 ]
非递归的中序算法
用非递归实现的中序算法,其他可以以此类推
inOrder(binaryTree, arr) {
let temp = [binaryTree];
while(temp.length!==0){
let item = temp.pop();
if(item instanceof Object){
item.left&&temp.push(item.left);
temp.push(item.key)
item.right&&temp.push(item.right);
}else{
arr.push(item)
}
}
arr = arr.reverse();
}
要非递归的完成排序,排序有个特点就是朝一个方向一直深入下去,那自然想到我们要准备一个temp栈,栈的特点是先进先出,当temp的长度为0表示排序结束。根据中序的规则,左中右的顺序入栈。最后进行arr.reverse(),就能得到正确的排序顺序了;
完整源码
class BinaryTree {
constructor (arr = ['请输入正确的数组']) {
this.dataSource = arr; //数组
this.binaryTree = {}; //树对象
this.preOderArr = []; //先序数组
this.behindOderArr = []; //后序数组
this.inOderArr = []; //中序数组
this.addToTree(this.dataSource); //生成二叉树
this.preOrder(this.binaryTree, this.preOderArr) //先序
this.inOrder(this.binaryTree, this.inOderArr) //中序
this.behindOrder(this.binaryTree, this.behindOderArr) //后序
}
createNode(key) {
return {
key,
left:'',
right:''
}
}
addToTree(dataSource) {
for(let item of dataSource) {
JSON.stringify(this.binaryTree)==='{}' ?
(this.binaryTree=this.createNode(dataSource[0])) :
this.insertNode(this.binaryTree, item);
}
return this;
}
insertNode(tempBinaryTree, key) {
if(key<=tempBinaryTree.key){
if(tempBinaryTree.left==''){
tempBinaryTree.left=this.createNode(key)
return;
}
this.insertNode(tempBinaryTree.left, key);
}else{
if(tempBinaryTree.right==''){
tempBinaryTree.right=this.createNode(key)
return;
}
this.insertNode(tempBinaryTree.right, key);
}
}
getBinaryTree() {
return {
binaryTree: this.binaryTree,
preOderArr: this.preOderArr,
behindOderArr: this.behindOderArr,
inOderArr: this.inOderArr
}
}
//中序排序^
inOrder(binaryTree, arr) {
if(!!binaryTree) {
this.inOrder(binaryTree.left, arr);
arr.push(binaryTree.key);
this.inOrder(binaryTree.right, arr);
}
}
//先序排序<
preOrder(binaryTree, arr) {
if(!!binaryTree) {
arr.push(binaryTree.key);
this.preOrder(binaryTree.left, arr);
this.preOrder(binaryTree.right, arr);
}
}
//后序排序>
behindOrder(binaryTree, arr) {
if(!!binaryTree) {
this.behindOrder(binaryTree.left, arr);
this.behindOrder(binaryTree.right, arr);
arr.push(binaryTree.key);
}
}
}
let tree = new BinaryTree([6,4,2,6,74,6]).getBinaryTree();
console.log(tree)