本文主要内容为BAT面试过程中设计到的redis知识。理解原理最重要,切勿死记硬背。作者语言组织不行,所以大部分都是复制的,已标明出处!!!
RDB(快照) 和 AOF(追加文件) 持久化得区别与优缺点
-
RDB会定时生成快照临时文件,然后替换旧的快照。所以可能会丢失最后一次生成快照以后的数据
-
AOF会在redis启动后记录每一个写操作,以追加命令的方式持久化。当AOF文件过大的时候会进行重写
-
进行数据恢复时,Redis优先使用AOF,但RDB的性能会好于AOF(可能是AOF保存的数据较完整)
参考 Redis持久化
过期淘汰策略
redis 支持三种过期淘汰策略
- 惰性过期:redis会记录key的过期时间,当访问这个key时判断是否过期,进行删除操作。节省cpu浪费内存。
- 定时过期:每个设置过期时间的key会添加定时器,到时去自动清理。 浪费大量的cpu
- 定期过期:redis的expires字典保存了所有设置了过期时间的key信息,定期扫描一定数量的key,并清理过期的key。cpu和内存相对较友好
redis 同时使用了定期过期和惰性过期策略
redis 内存淘汰策略
- redis启动时可以设置最大内存使用量,redis使用以下6种淘汰策略保证内存
- noeviction:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,新写入操作会报错。
- allkeys-lru:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在键空间中,移除最近最少使用的key。
- allkeys-random:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在键空间中,随机移除某个key。
- volatile-lru:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在设置了过期时间的键空间中,移除最近最少使用的key。
- volatile-random:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在设置了过期时间的键空间中,随机移除某个key。
- volatile-ttl:当内存不足以容纳新写入数据时,在设置了过期时间的键空间中,有更早过期时间的key优先移除。
有序集合
因为有序集合涉及到的数据结构比较多,且不常用,所以一般考redis数据结构时会问此处。 有序集合的编码可以是 ziplist 或者 skiplist 。
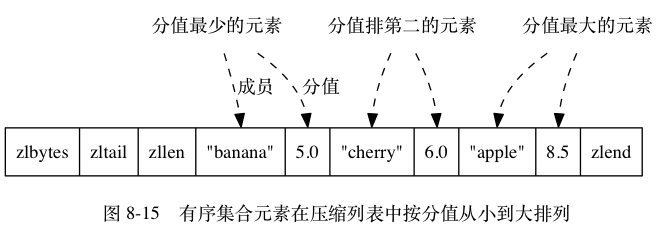
压缩列表 ziplist
ziplist 编码的有序集合对象使用压缩列表作为底层实现,每个集合元素使用两个紧挨在一起的压缩列表节点来保存,第一个节点保存元素的成员(member),而第二个元素则保存元素的分值(score)。
压缩列表内的集合元素按分值从小到大进行排序,分值较小的元素被放置在靠近表头的方向, 而分值较大的元素则被放置在靠近表尾的方向。
跳表 skiplist
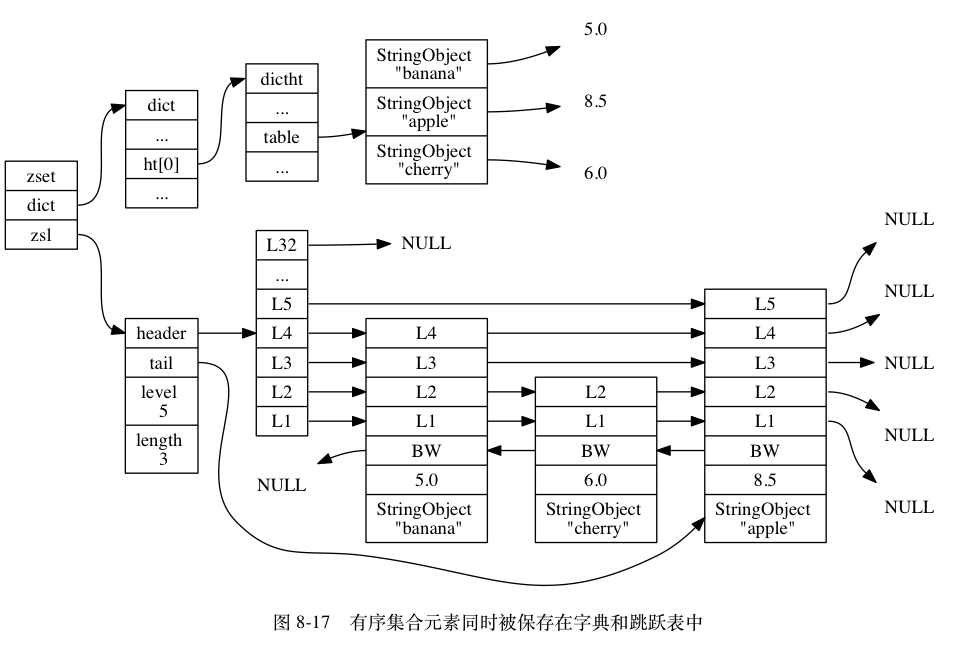
skiplist 编码的有序集合对象使用 zset 结构作为底层实现, 一个 zset 结构同时包含一个字典和一个跳跃表:
typedef struct zset {
zskiplist *zsl;
dict *dict;
} zset;
字典表保证了查找单个member的时候O(1)复杂度的操作,有序集合保证了范围查找的时间复杂度
存储示意图
实现难度不大,有兴趣可以自己撸下算法。随机插入性能很好,但顺序插入性能差的不行。抽空写的一个golang版本
package skiplist
import (
"log"
"math"
"math/rand"
"time"
)
const DefaultSkipListDepth = 32
type slNode struct {
score int
forward []*slNode
}
func (sln *slNode) Score() int {
return sln.score
}
type SkipList struct {
Head *slNode
Tail *slNode
MaxDepth int
depth int
}
func (sl *SkipList) randDepth() int {
var depth = 1
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
for rand.Intn(2)%2 == 0 {
depth++
}
if depth > sl.depth{
depth = sl.depth + 1
}
return int(math.Min(float64(depth), float64(sl.MaxDepth)))
}
func (sl *SkipList) newNode(score int, depth int) slNode {
node := slNode{
score: score,
forward: make([]*slNode, depth+1),
}
return node
}
func (sl *SkipList) Search(score int) *slNode {
startNode := sl.Head
for i := sl.depth - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
for p := startNode; p.forward[i] != sl.Tail; p = p.forward[i] {
if p.forward[i].score < score {
continue
} else if p.forward[i].score > score {
startNode = p
break
} else {
return p.forward[i]
}
}
}
return nil
}
func (sl *SkipList) Delete(score int) {
startNode := sl.Head
for i := sl.MaxDepth - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
for p := startNode; p.forward[i] != sl.Tail; p = p.forward[i] {
if p.forward[i].score < score {
continue
} else if p.forward[i].score > score {
startNode = p
break
} else {
p.forward[i] = p.forward[i].forward[i]
break
}
}
}
}
func (sl *SkipList) Insert(score int) *slNode {
depth := sl.randDepth()
updates := make([]*slNode, depth+1)
startNode := sl.Head
for i:=sl.depth ; i < depth ; i++{
updates[i] = sl.Head
}
for i := sl.depth - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
for p := startNode; ; p = p.forward[i] {
//log.Println("insert", "score",score, "depth",depth, "sl depth",sl.depth, "level",i,"next", p.forward[i].score)
if p.forward[i] == sl.Tail || p.forward[i].score > score{
if depth > i{
updates[i] = p
}
startNode = p
break
}else if p.forward[i].score == score{
return p.forward[i]
}
}
}
node := sl.newNode(score, depth)
for i := 0; i < depth; i++ {
node.forward[i] = updates[i].forward[i]
updates[i].forward[i] = &node
}
if sl.depth < depth{
sl.depth = depth
}
return &node
}
func (sl *SkipList) Display() {
for i := sl.MaxDepth - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
var values []int
for p := sl.Head; p.forward[i] != sl.Tail; p = p.forward[i] {
values = append(values, p.forward[i].score)
}
log.Println("level", i, values)
}
}
func NewSkipList(depth int) *SkipList {
sl := &SkipList{
MaxDepth: depth,
Head: &slNode{
forward: make([]*slNode, depth),
},
Tail: &slNode{},
}
for i := 0; i < depth; i++ {
sl.Head.forward[i] = sl.Tail
}
return sl
}
参考 有序集合对象
缓存穿透
当接口被恶意访问的时候,缓存命中率降低,大量请求会落到DB上,应用直接挂掉,通过BloomFilter布隆过滤器拦截非法请求
布隆过滤器使用多个hash函数将k映射到一个足够大内存中,如果判断某个key不存在,则一定不存在,如果判断某个key存在,则有一定概率不存在。