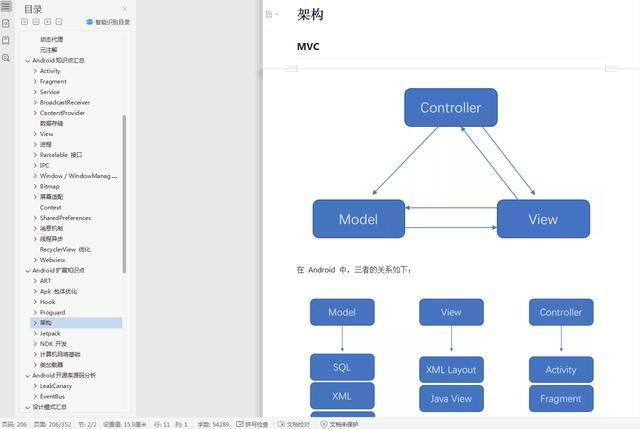
前言
LruCache 是我们经常使用的缓存机制,也叫 “最近最少使用的” 缓存策略。其本质原理是通过历史访问记录来 倒序淘汰数据,它认为刚刚访问的数据,将来被访问的可能性较大,因此将该类数据维护到相对安全的区域,防止被淘汰。此时如果超过设定的内存瓶颈,将优先淘汰最老的数据。

- 比如你在玩一款游戏,游戏里有一个仓库,有 20 个位置可以存放装备。
- 1-20 件装备都可以正常存放,并根据时间顺序进行了排序,最晚存放的装备排在最后。
- 当你使用其中任意一件装备的时候,这件装备的排序就变成了最后。
- 有一天你又获得了一件装备,但是你的仓库已经满了,只能扔一件才能存储刚刚获得的,扔的顺序是从头开始扔。新装备存储后,排序为最后。依次类推。
1. 分析源码
接下来我们通过正常的使用来分析源码的逻辑,以下所有源码均来自 API 28。
通过 LruCache 提供的每一个方法进行一对一分析,首先我们看一段正常使用 LruCache 的代码
private void lruTest() {
LruCache<Integer, Integer> lruCache = new LruCache<>(5);
lruCache.put(1, 1);
lruCache.put(2, 2);
lruCache.put(3, 3);
lruCache.put(4, 4);
lruCache.put(5, 5);
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : lruCache.snapshot().entrySet()) {
Log.e("LRU", entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
Log.e("LRU", "超出设定存储容量后");
lruCache.put(6, 6);
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : lruCache.snapshot().entrySet()) {
Log.e("LRU", entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}
---日志输出---
2019-11-18 18:21:03.624 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 1:1
2019-11-18 18:21:03.624 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 2:2
2019-11-18 18:21:03.624 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 3:3
2019-11-18 18:21:03.624 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 4:4
2019-11-18 18:21:03.624 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 5:5
2019-11-18 18:21:03.624 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 超出设定存储容量后
2019-11-18 18:21:03.624 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 2:2
2019-11-18 18:21:03.624 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 3:3
2019-11-18 18:21:03.624 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 4:4
2019-11-18 18:21:03.625 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 5:5
2019-11-18 18:21:03.625 24293-24293/com.we.we E/LRU: 6:6
以上的例子的流程比较简单,初始化一个容量为 5 的 LruCache。
调用 put 方法添加数据,最后通过 snapshot () 方法获取 Map 然后遍历打印。
但是超出设定容量后再进行 put 数据,会将最先 put 的数据顶替掉,我们记住这个特性往下看。
2. LruCache 构造函数
如果有特殊需求可以通过重写 sizeOf()方法设定每条缓存数据的大小
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
//初始化一个负载因子为0.75,启动访问顺序排序的LinkedHashMap对象。至于LinkedHashMap是什么东西,我们后续分析。
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}
put () 方法源码解析
/**
* 对于 key,缓存其相应的 value,key-value 条目放置于队尾
*
* @return 返回先前 key 对应的 value 值
*/
public final V put(K key, V value) {
//如果键值有一个为空,则抛空指针异常。
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
//先给 size +1, safeSizeOf()方法返回值默认是1
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
//map.put()方法返被替换的值,如果没有被替换,则返回null。(只有当前key在put之前就已经有数据,这种情况存储才会被替换)
previous = map.put(key, value);
if (previous != null) {
//如果是被顶替的数据,那size需要-1,因为没有新增数据。
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
//当多线程中一个线程调用到了create方法,另一个线程调用到了put,此时一个key可能生成了两个值,因此需要通过重写这个方法进行处理。该方法默认为空方法。
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
//判断是否超出设定容量,如果超出,则循环删除最早数据,直到容量<=设定值。
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
3. put () 方法小结
- 首先会进行 K/V 的 null 判断,如果为 null 则抛出异常。
- 加锁并自增元素条目计数器,通过 LinkedHashMap.put 方法将 K/V 添加到 LinkedHashMap 对象中,如果 put 方法返回值不为 null,则说明原来该 key 下有数据,因此只是更新 key 对应的数据并没有新增数据,所以此时 size 需 -1。
- 如果 previous!=null,说明当前的 put 操作替换了之前的一个值,如果重写了 entryRemoved () 方法,则会回调到该方法中进行处理,如果没重写 entryRemoved (),该方法默认不做任何处理。
- 调用 trimToSize (maxSize) 进行容量检测和处理。
4. trimToSize () 方法源码解析,以及 bug 发现
/**
*删除最旧的元素,直到剩余数据总数 <= maxSize。
*/
private void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
//如果当前元素数<=设定的最大值,则直接break退出循环。
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
// BEGIN LAYOUTLIB CHANGE
// get the last item in the linked list.
// This is not efficient, the goal here is to minimize the changes
// compared to the platform version.
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = null;
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : map.entrySet()) {
//获取最少使用的数据元素,此处的写法是源码的一个bug,后续我会详细说明。
toEvict = entry;
}
// END LAYOUTLIB CHANGE
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
//移除元素
map.remove(key);
//计数长度size -1;
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
//缓存移除的次数 +1
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
5. trimToSize () 方法小结
- 该方法主要用于容量检测,和容量超出后的元素移除操作。
- 首先开启循序,并加锁,判断当前数据量 <= 设定的阀值 maxSize 则 break 跳出循环。
- 获取当前 LinkedHashMap 对象中的最老数据(最不常用的数据),但是源码中通过 for 循环去循环赋值,实际上循环完获取到的是最新的数据。
3.1. 举例说明,可通过以下例子和日志输出判断 for 循环后的最终赋值。
LruCache<Integer, Integer> lruCache = new LruCache<>(5);
lruCache.put(1, 1);
lruCache.put(2, 2);
lruCache.put(3, 3);
lruCache.put(4, 4);
lruCache.put(5, 5);
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : lruCache.snapshot().entrySet()) {
Log.e("LRU", entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
2019-11-19 16:22:54.299 31747-31747/com.we.we E/LRU: 1:1
2019-11-19 16:22:54.299 31747-31747/com.we.we E/LRU: 2:2
2019-11-19 16:22:54.300 31747-31747/com.we.we E/LRU: 3:3
2019-11-19 16:22:54.300 31747-31747/com.we.we E/LRU: 4:4
2019-11-19 16:22:54.300 31747-31747/com.we.we E/LRU: 5:5
3.2. 通过以上例子的日志打印,可以看到最后打印的也就是最后循环的数据为 5, 而 5 是最新插入的数据,那这个逻辑删除的不是最新插入的数据了么?那对 LRU 而言不是有问题了么?我又翻看了以前 SDK 版本的源码,接下来我们对比下 API 27 和 API 28 中该段逻辑的差异。
API 27
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
//...
//eldest是被标记隐藏的. 实现如下:
public Entry<K, V> eldest() {
LinkedEntry<K, V> eldest = header.nxt;
return eldest != header ? eldest : null;
}
API 28
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = null;
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : map.entrySet()) {
toEvict = entry;
}
3.3. 通过对比因此这段逻辑是源码中的一个 bug,但是我们使用过程中并不影响正常的功能,这是为什么?其实是 Framework 实现和 SDK 源码不一致,而 SDK 中是一份带 bug 版本的 LruCache.
4. 移除数据并 size -1, 缓存移除的次数 +1
6. get () 方法源码解析
/**
* 指定 key 对应的 value 值存在时返回,否则通过 create 方法创建相应的 key-value 对。
* 如果对应的 value 值被返回,那么这个 key-value 对将被移到队尾。
* 当返回 null 时,表明没有对应的 value 值并且也无法被创建
*/
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
//通过LinkedHashMap对象获取当前key对应的value
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
//缓存命中的次数+1
hitCount++;
//并return返回结束
return mapValue;
}
//缓存未命中的次数+1
missCount++;
}
/*
* 尝试创建一个value值,但是可能消耗很长时间,当create方法返回时,哈希表有几率发生变化
* 如果再哈希表中添加了一个有冲突的值,那么将保留原有的值,替换刚刚生成的value
*/
//create()是需要重写的方法,如果不重写默认返回null
V creaweValue = create(key);
if (creaweValue == null) {
return null;
}
synchronized (this) {
//创建 key 对应的 value 的次数+1
createCount++;
//map.put方法返回的是该key下原来的值,如果该key下原来没有值则返回null
mapValue = map.put(key, creaweValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
//mapValue不为null说明该key原来有对应的值,因此需要使用原来值替代刚刚生成的value。
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
//如果原来key没有对应的值,说明新增了一对键值对,因此需要size+1
size += safeSizeOf(key, creaweValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, creaweValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return creaweValue;
}
}
7. get () 方法小结
- get () 放中除了正常的判 null 以为,进行了加锁并通过 LinkedHashMap.get (key) 获取该 key 下的 value。
- 如果 LinkedHashMap.get (key) 没有获取到 value,则通过 create () 方法创建对应的 value 值,但 create () 默认返回 null,需要重写进行创建处理。
- 如果重写了 create () 方法并且生成了 value,则加锁通过 LinkedHashMap.put () 进行插入,并根据 put 方法的返回值判断该 key 之前是否有对应的 value,如果有则重新将原有的值 put 替换刚刚生成的值。
注
以上逻辑中 create (key) 方法其实是未加锁的,如果该方法是有使用的,可能会出现多线程调用同一个 key,而生成多个 value 的情况。或者当一个线程调用 put 而另一个线程调用了 create 方法为其创建值时这种情况下,在后续逻辑中会调用 entryRemoved () 方法进行处理。而 entryRemoved () 方法也需要重写实现。可根据 entryRemoved () 方法的参数值判断当前调用是由 put 或 remove 引起的还是为了腾空间由 trimToSize () 引起的。
@param evicwe true 表明条目正在被删除以腾出空间,false 表明删除是由 put 或 remove 引起的(并非是为了腾出空间)
@param newValue key 的新值。如果非 null,则此删除是由 put 引起的。否则它是由 remove 引起的
8. remove () 源码解析
/**
* 删除key对应的value
*
* 返回key对应的value值
*/
public final V remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
previous = map.remove(key);
if (previous != null) {
//数据删除后需要将数据计数器size -1
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}
9. remove () 方法小结
1. 判空,并加锁调用 LinkedHashMap.remove () 方法移除该 key 对应的 value,并通过返回值判断 size -1;
2. 调用 entryRemoved () 方法
总结
通篇下来发现 LruCache 有以下几个特点。
- 其实 LruCache 类中方法数量不多,大部分都依赖于 LinkedHashMap 的方法,而 LruCache 只是在维护一个内部 LinkedHashMap 对象。
- LruCache 使用并不是线程安全的,因此提供了 entryRemoved () 方法用来重写解决异常情况。
- LruCache 的大部分方法中都进行了 K/V 判空,因此 LruCache 不支持空 K 和空 V。
感谢大家能耐着性子看完啰里啰嗦的文章
在这里我也分享一份私货,自己收录整理的Android学习PDF+架构视频+面试文档+源码笔记,还有高级架构技术进阶脑图、Android开发面试专题资料,高级进阶架构资料帮助大家学习提升进阶,也节省大家在网上搜索资料的时间来学习,也可以分享给身边好友一起学习
如果你有需要的话,可以点赞+评论,关注我,点击这里领取 Android学习PDF+架构视频+面试文档+源码笔记