tomcat支持的请求处理方式
Tomcat请求支持三种请求处理方式:AIO、NIO、APR
BIO模式:阻塞式I/O操作,表示Tomcat使用的是传统Java。I/O操作(即Java.io包及其子包)。Tomcat7以下版本默认情况下是以bio模式运行的,由于每个请求都要创建一个线程来处理,线程开销较大,不能处理高并发的场景,在三种模式中性能也最低。
NIO模式:
同步非阻塞I/O操作,是一个基于缓冲区、并能提供非阻塞I/O操作的API,它拥有比传统I/O操作具有更好的并发性能。tomcat8之前server.xml配置参数
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"connectionTimeout="20000"redirectPort="8443" />
<Connector port="8080" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"connectionTimeout="20000"redirectPort="8443" />
APR模式:简单理解,从操作系统解决异步IO问题,大幅度的提高服务器的处理和响应性能,也是tomcat运行高并发应用的首选模式。
tomcat的NioEndpoint
我们先来简单回顾一下一般的Nio服务器实现,借鉴infoq上的一篇文章Netty系列之netty的acceptor多线程模型。
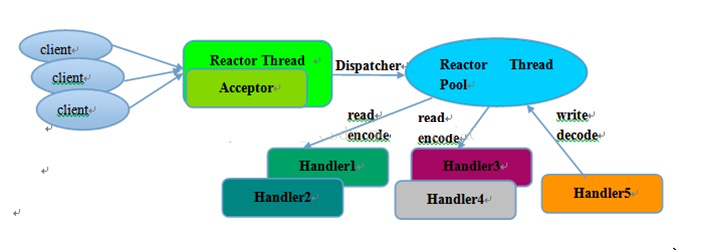
一个或多个Acceptor,每个线程都有自己的Selector,Acceptor只负责accept的线程连接,一旦连接建立之后将连接注册到其他Worker线程中。worker线程池有多个线程,也可以称为I/O线程,就是专门负责I/O读写的。一种实现方式就是像Netty一样,每个Worker线程都有自己的Selector,可以负责多个连接的IO读写事件,每个连接归属于某个线程。另一种实现方式有专门的线程负责IO事件监听的,这些线程都有自己的Selector,一旦监听到IO读写事件,并不是像第一种实现方式那样,而是将IO操作封装成Runnable交给Worker线程池来执行,这种情况每个连接可能会被多个线程同时操作,相比第一种并发性提高了,但是也可能引来多线程问题。
这里要借鉴断网故障时Mtop触发tomcat高并发场景下的BUG排查和修复(已被apache采纳)上面有对NIO模式下的有更详细的说明。
一个典型的请求处理如图:
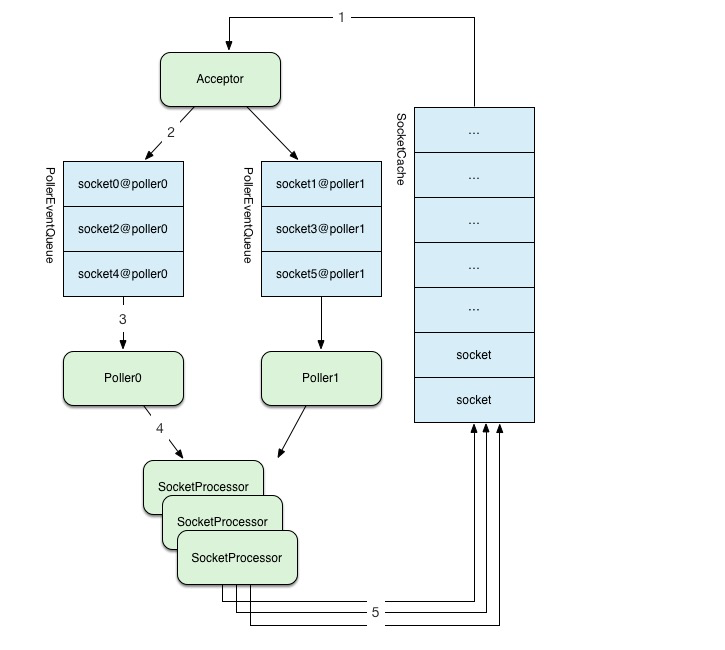
Acceptor负责处理线程请求,从SocketCache里面拿出socket对象(没有的话会创建,缓存的目的是避免对象的开销)。
Acceptor线程标记好Poller对象,组装成PollerEvent,放入该PollerEvent队列。
Poller线程从事件队列里面拿到PollerEvent,将其中的socket注册到其自身的selector上,Poller等到有IO事件发生时,分发给SocketProcessor线程去实际处理请求,SocketProceesor处理完请求,socket对象被回收,放入socketCache。
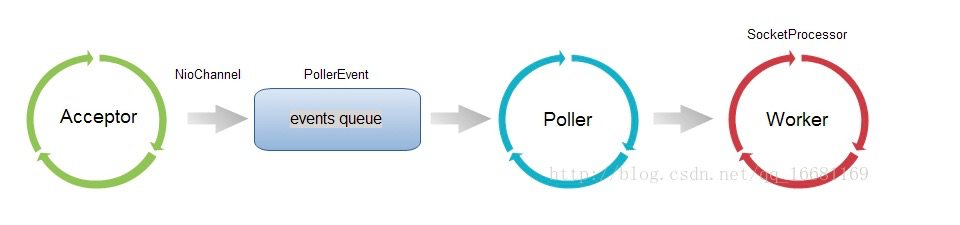
整个处理线程模型如下:
tomcat8并发配置参数
1、acceptCount
The maximum queue length for incoming connection requests when all possible request processing threads are in use. Any requests received when the queue is full will be refused. The default value is 100.
这个参数就立马牵涉出一块大内容:TCP三次握手的详细过程,这个之后再详细探讨。这里可以简单理解为:连接在被ServerSocketChannel accept之前就暂存在这个队列中,acceptCount就是这个队列的最大长度。ServerSocketChannel accept就是从这个队列中不断取出已经建立连接的的请求。所以当ServerSocketChannel accept取出不及时就有可能造成该队列积压,一旦满了连接就被拒绝了。
2、acceptorThreadCount
The number of threads to be used to accept connections. Increase this value on a multi CPU machine, although you would never really need more than 2. Also, with a lot of non keep alive connections, you might want to increase this value as well. Default value is 1.
Acceptor线程只负责从上述队列中取出已经建立连接的请求。在启动的时候使用一个ServerSocketChannel监听一个连接端口如8080,可以有多个Acceptor线程并发不断调用上述ServerSocketChannel的accept方法来获取新的连接。参数acceptorThreadCount其实使用的Acceptor线程的个数。
3、maxConnections
The maximum number of connections that the server will accept and process at any given time. When this number has been reached, the server will accept, but not process, one further connection. This additional connection be blocked until the number of connections being processed falls below maxConnections at which point the server will start accepting and processing new connections again. Note that once the limit has been reached, the operating system may still accept connections based on the acceptCount setting. The default value varies by connector type. For NIO and NIO2 the default is 10000. For APR/native, the default is 8192.
Note that for APR/native on Windows, the configured value will be reduced to the highest multiple of 1024 that is less than or equal to maxConnections. This is done for performance reasons. If set to a value of -1, the maxConnections feature is disabled and connections are not counted.
这里就是tomcat对于连接数的一个控制,即最大连接数限制。一旦发现当前连接数已经超过了一定的数量(NIO默认是10000),上述的Acceptor线程就被阻塞了,即不再执行ServerSocketChannel的accept方法从队列中获取已经建立的连接。但是它并不阻止新的连接的建立,新的连接的建立过程不是Acceptor控制的,Acceptor仅仅是从队列中获取新建立的连接。所以当连接数已经超过maxConnections后,仍然是可以建立新的连接的,存放在上述acceptCount大小的队列中,这个队列里面的连接没有被Acceptor获取,就处于连接建立了但是不被处理的状态。当连接数低于maxConnections之后,Acceptor线程就不再阻塞,继续调用ServerSocketChannel的accept方法从acceptCount大小的队列中继续获取新的连接,之后就开始处理这些新的连接的IO事件了。
4、maxThreads
The maximum number of request processing threads to be created by this Connector, which therefore determines the maximum number of simultaneous requests that can be handled. If not specified, this attribute is set to 200. If an executor is associated with this connector, this attribute is ignored as the connector will execute tasks using the executor rather than an internal thread pool。
这个简单理解就算是上述worker的线程数。他们专门用于处理IO事件,默认是200。