地图投影
这里使用的是 topoJSON 而非是 geoJSON 数据。网站也有许多网站能够转化文件。
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
path {
fill: #ccc;
stroke: #fff;
stroke-width: .5px;
}
.state:hover {
fill: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script src="../d3.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/topojson@3"></script>
<script>
const width = 960,
height = 500
const path = d3.geoPath().projection(d3.geoAlbersUsa())
const svg = d3.select('body').append('svg')
.attr('width', width)
.attr('height', height)
const g = svg.append('g').call(d3.zoom().scaleExtent([1, 10]).on('zoom', zoomHandle))
function zoomHandle() {
const transform = d3.event.transform
svg.select('g').attr('transform', `translate(${transform.x}, ${transform.y}) scale(${transform.k})`)
}
d3.json('./us.json').then(data => {
g.selectAll('path.state')
.data(topojson.feature(data, data.objects.states).features)
.enter()
.append('path')
.attr('class', 'state')
.attr('d', d => path(d))
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
topoJSON 文档见:github.com/topojson/to…
我们先给 svg 定义了平移缩放,然后通过以下关键代码渲染了地图:
const path = d3.geoPath().projection(d3.geoAlbersUsa())
g.selectAll('path.state')
.data(topojson.feature(data, data.objects.states).features)
.enter()
.append('path')
.attr('class', 'state')
.attr('d', d => path(d))
我们定义了一个地图的 path 生成器,通过 projection 方法设置生成器的投影方式。然后我们通过 topojson 拿到 地图数据中各个州的数据,通过 path 元素和生成器渲染到页面上。
d3 中常见的投影方式见下例。
投影方式
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body {
background: #fcfcfa;
}
.map {
float: left;
margin: 20px;
text-align: center;
}
.land {
fill: #222;
}
.boundary {
fill: none;
stroke: #fff;
stroke-width: .5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script src="../d3.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/topojson@3"></script>
<script>
const width = 300,
height = 300,
translate = [width / 2, height / 2],
projections = [
{name: 'geoAzimuthalEqualArea', fn: d3.geoAzimuthalEqualArea().scale(60).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoAzimuthalEquidistant', fn: d3.geoAzimuthalEquidistant().scale(50).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoGnomonic', fn: d3.geoGnomonic().scale(60).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoOrthographic', fn: d3.geoOrthographic().scale(80).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoStereographic', fn: d3.geoStereographic().scale(50).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoAlbers', fn: d3.geoAlbers().scale(50).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoConicConformal', fn: d3.geoConicConformal().scale(40).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoConicEqualArea', fn: d3.geoConicEqualArea().scale(50).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoConicEquidistant', fn: d3.geoConicEquidistant().scale(35).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoEquirectangular', fn: d3.geoEquirectangular().scale(50).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoMercator', fn: d3.geoMercator().scale(50).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoTransverseMercator', fn: d3.geoTransverseMercator().scale(50).translate(translate)},
{name: 'geoNaturalEarth1', fn: d3.geoNaturalEarth1().scale(80).translate(translate)}
]
d3.json('./world-50m.json').then(data => {
projections.forEach(projection => {
const path = d3.geoPath().projection(projection.fn)
const div = d3.select('body')
.append('div')
.attr('class', 'map')
const svg = div.append('svg')
.attr('width', width)
.attr('height', height)
svg.append('path')
.datum(topojson.feature(data, data.objects.land))
.attr('class', 'land')
.attr('d', d => path(d))
svg.append('path')
.datum(topojson.mesh(data, data.objects.countries))
.attr('class', 'boundary')
.attr('d', path)
div.append('h3').text(projection.name)
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
各投影方式的效果如下:
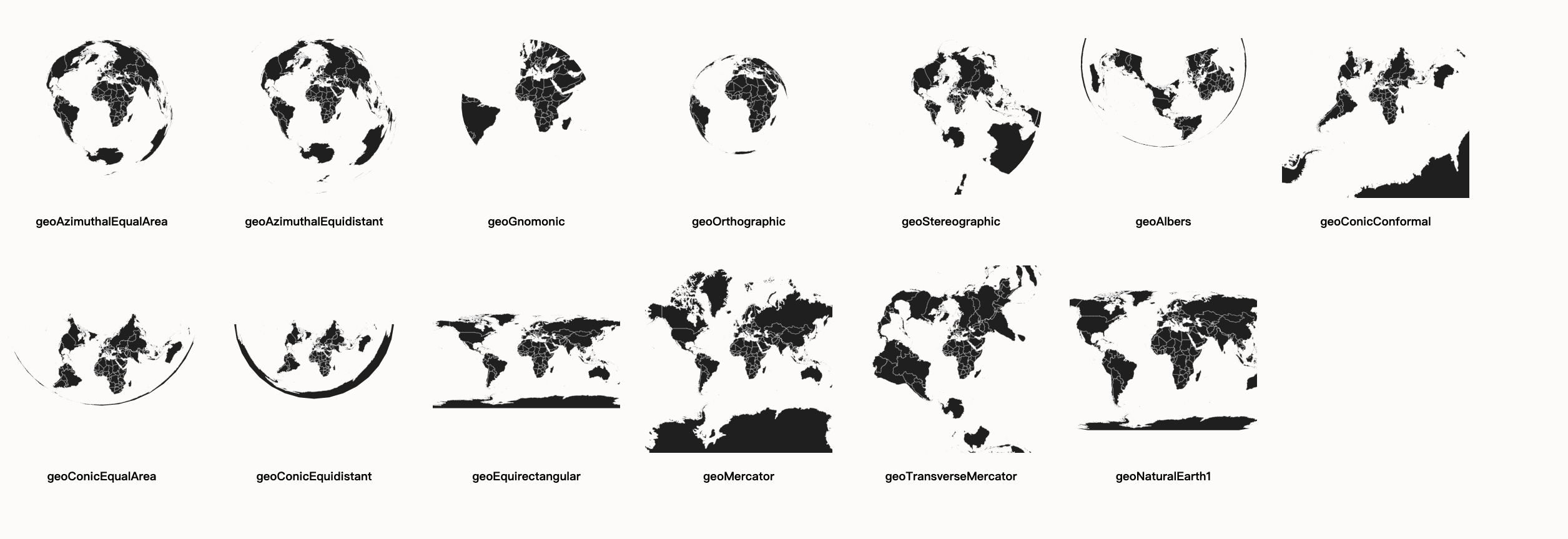
等值区域图(热度地图)
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.states {
fill: none;
stroke: #fff;
stroke-width: .5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script src="../d3.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/topojson@3"></script>
<script>
const width = 960,
height = 600,
colors = d3.scaleLinear()
.domain([0.02, 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.10])
.range(d3.schemeRdBu[6].reverse()),
path = d3.geoPath().projection(d3.geoAlbersUsa()),
svg = d3.select('body').append('svg')
.attr('width', width)
.attr('height', height),
g = svg.append('g').call(
d3.zoom()
.scaleExtent([1, 10])
.on('zoom', zoomHandle)
)
function zoomHandle() {
const transform = d3.event.transform
g.attr('transform', `translate(${transform.x}, ${transform.y}) scale(${transform.k})`)
}
svg.append('text').text('2008年美国失业热度图').attr('transform', 'translate(400, 550)')
d3.json('./us.json').then(us => {
d3.tsv('./unemployment.tsv').then(unemployment => {
const map = new Map()
unemployment.forEach(d => {
map.set(Number(d.id), Number(d.rate))
})
g.append('g').selectAll('path')
.data(topojson.feature(us, us.objects.counties).features)
.enter()
.append('path')
.attr('d', d => path(d))
.attr('fill', d => colors(map.get(d.id)))
g.append('path')
.datum(topojson.mesh(us, us.objects.states))
.attr('class', 'states')
.attr('d', d => path(d))
})
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
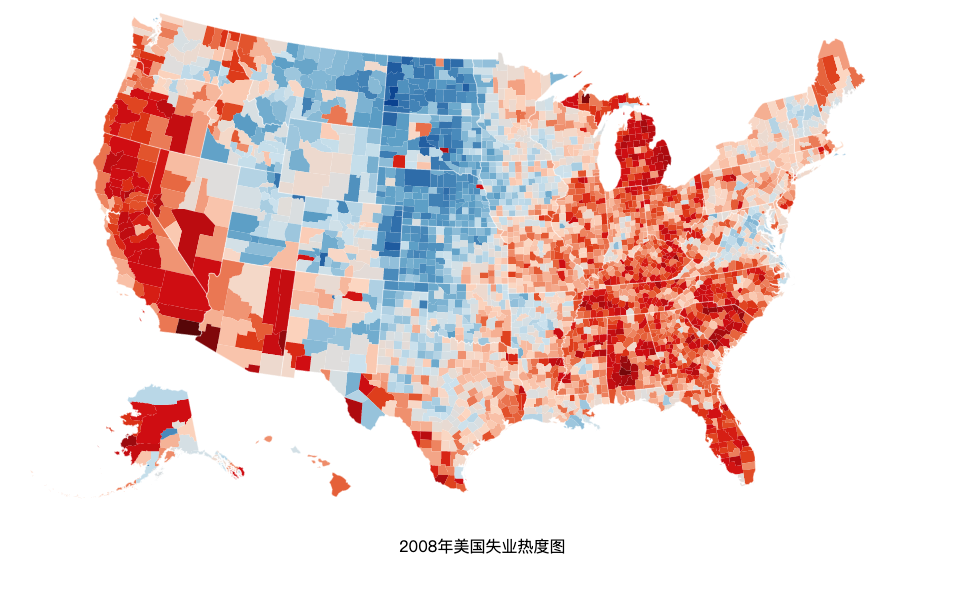
在请求到地图数据和每个区域的失业值后,我们先是把失业数据置入一个 map 中,
const map = new Map()
unemployment.forEach(d => {
map.set(Number(d.id), Number(d.rate))
})
这便于我们通过每个区域的 id 值找到其对应的失业率。
我们先通过
g.append('g').selectAll('path')
.data(topojson.feature(us, us.objects.counties).features)
.enter()
.append('path')
.attr('d', d => path(d))
.attr('fill', d => colors(map.get(d.id)))
绘制出各个区,并以失业率值对应的颜色填充,然后再通过下面的代码绘制出各个州的轮廓:
g.append('path')
.datum(topojson.mesh(us, us.objects.states))
.attr('class', 'states')
.attr('d', d => path(d))