前言
使用 javascript 来学习了解数据结构
栈数据结构
栈是一种遵从
后进先出原则的有序集合。新添加或待删除的元素都保存在栈的同一段,称做栈顶,另一端叫栈底。类比叠书取书的过程。
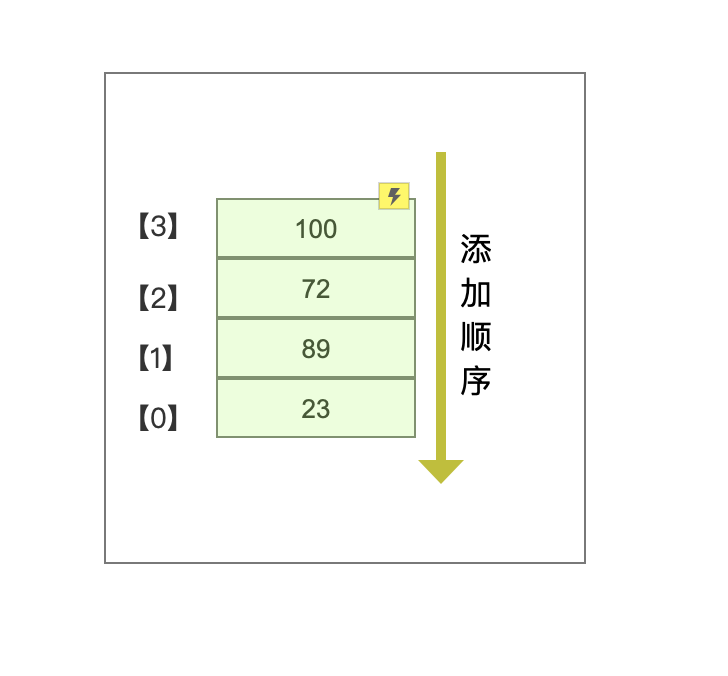
使用对象来模拟栈
下面代码声明了一个 Stack 类,items 用于存储栈内所有的元素,count 记录了当前元素的个数。并且在原型上添加了 push,pop,peek,isEmpty,string 这些方法。在模拟队列和链表的时候都会去实现这些方法。
// Stack 类
class Stack{
constructor(){
this.items = {}
this.count = 0
}
push(element){
this.items[this.count] = element
this.count++
}
pop(){
if(this.isEmpty())return undefined
let remove = this.items[this.count-1]
delete this.items[this.count-1]
this.count--
return remove
}
// 返回栈顶的元素
peek(){
if(this.isEmpty())return undefined
return this.items[this.count-1]
}
isEmpty(){
return this.count === 0
}
string(){
let list = []
for(let i=0;i<this.count;i++){
list.push(this.items[i])
}
return list.join()
}
clear(){
this.items = {}
this.count = 0
}
size(){
return this.count
}
}
十进制转二进制
使用 Stack 类来实现十进制转二进制的功能。下面代码模拟了,往栈内存数据以及通过 pop 取出最近的数据体现了先进后出的概念。
const stack = new Stack()
let number = 32
// 将所有数据存入栈中
while(number>0){
stack.push(number%2)
number = parseInt(number / 2)
}
let arr = []
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
// 每次取出栈顶上的数据
arr.push(stack.pop())
}
let result = arr.join('')
console.log('result',result);
// 100000
队列数据结构
队列是遵循先进先出原则的一组有序的项。队列
在尾部添加新元素,并从顶部移除元素。类比排队取号,先到先得。
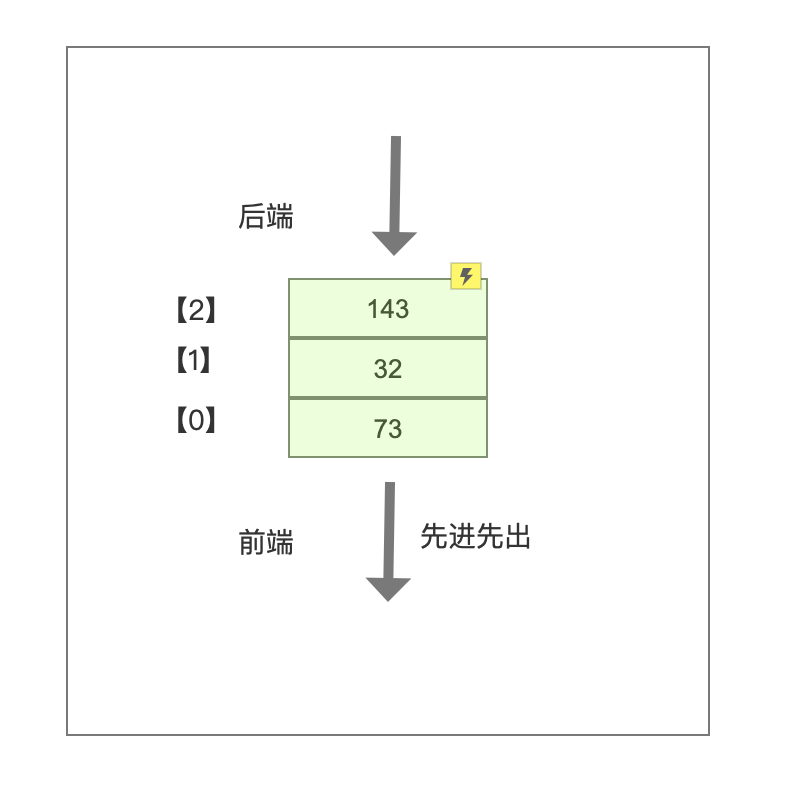
使用对象来模拟队列
Queue 和 Stack 很类似不同点在于添加和移除元素点规则,下面代码 还是通过 items,count 来记录队列所有项和项数最大序号。由于队列移除元素是先进先出所以需要lowestCount来记录当前最小序号。注意的是当前队列有多少项是通过 count - lowestCount 来计算得到。
class Queue {
constructor(){
this.items = {}
this.count = 0
this.lowestCount = 0
}
// 入队列
enqueue(element){
this.items[this.count] = element
this.count++
}
toString(){
let arr = []
for(let i=this.lowestCount;i<this.count;i++){
arr.push(this.items[i])
}
return arr.join()
}
isEmpty(){
return this.size()=== 0
}
// 出队列,先进先出
dequeue(){
if(this.isEmpty())return
let count = this.lowestCount
let last = this.items[count]
delete this.items[count]
this.lowestCount++
return last
}
}
双端队列
是一种允许我们同时从前端和后端添加和移除元素的特殊队列
constructor(){
this.count = 0
this.items = {}
this.lowestCount = 0
}
addBack(element){
this.items[this.count] = element
this.count++
}
addFront(element){
if(this.isEmpty()){
this.addBack(element)
}else{
this.items[this.lowestCount - 1] = element
this.lowestCount--
}
}
reMoveFront(){
if(this.isEmpty())return
let remove = this.items[this.lowestCount]
this.lowestCount++
return remove
}
reMoveAfter(){
if(this.isEmpty())return
let count = this.count -1
let remove = this.items[count]
this.count--
return remove
}
使用双端队列实现回文检查器
回文是正反都能读通的字符如
madam和racecar
双端队列判断当前字符串是否为回文
let deque = new Deque()
let str = '1madam1'
// 将字符串的所有想添加到队列中
for(let item of str){
deque.addBack(item)
}
let isTrue = true
while (deque.size()>1) {
// 从首位同时取出一位来判断是否相同
isTrue = deque.reMoveAfter() === deque.reMoveFront()
}
console.log(isTrue);
链表数据结构
链表数据结构如下,每个元素有 value和next 两个属性,可以通过 next 来指定下一个元素,所以相比与数组这类的数据结构优势在于能够灵活地插入或移除元素而不用遍历数组每项。
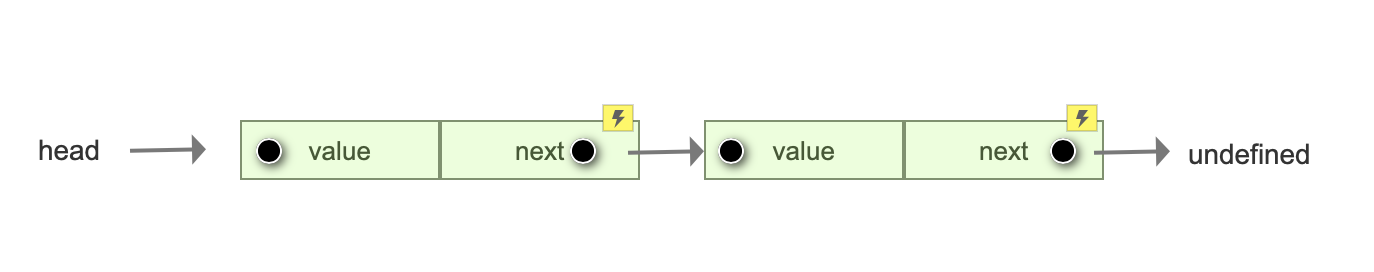
链表
子项:由于子项需要 value, next两个属性,所以采用 Node 类来实现一个子类,之后维护也可以对这个 Node 类做扩展。
LinkedList: 用 head来记录当前第一项后续的值都可以通过遍历不断去获取 next 的值拿到链表中所有的值。
// 用于描述一个子项
class Node {
constructor(element){
this.value = element
this.next = undefined
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor(){
this.head = undefined
this.count = 0
}
push(element){
let node = new Node(element)
if(this.isEmpty()){
this.head = node
}else{
// 取出最后一位
let current = this.getElementAt(this.count-1)
current.next = node
}
this.count++
}
removeAt(index){
if(index>=0&&index<this.count){
let current
// 当前项大于0说明有上一项
if(index>0){
// 获取到前一位的子项
let pre = this.getElementAt(index-1)
current = pre.next
// 将上一项的 next 指针指向下一项完成删除当前项
pre.next = current.next
}else{
// 说明当前项是第一项
current = this.head
this.head = current.next
}
this.count--
// 返回删除项的值
return current.value
}
return -1
}
isEmpty(){
return this.count === 0
}
getElementAt(index){
if(index>=0&&index<this.count){
let current = this.head
while (index>0) {
current = current.next
index--
}
return current
}
return -1
}
// 找出和当前值的序号
indexOf(element){
let current = this.head
for(let i=0;i<this.count;i++){
if(element === current.value){
return i
}
current = current.next
}
return -1
}
insert(element,index){
let node = new Node(element)
if(index>=0&&index<=this.count){
if(index===0){
let current = this.head
node.next = current
this.head = node
}else{
let pre = this.getElementAt(index-1)
let current = pre.next
pre.next = node
node.next = current
}
this.count++
}
}
toString(){
let arr = []
let current = this.head
for(let i=0;i<this.count;i++){
arr.push(current.value)
current = current.next
}
return arr.join()
}
}
最后
对栈-队列-链表有了初步对认识,尝试用这些数据结构去做一些有趣的算法,接下来会继续了解二叉树,算法。