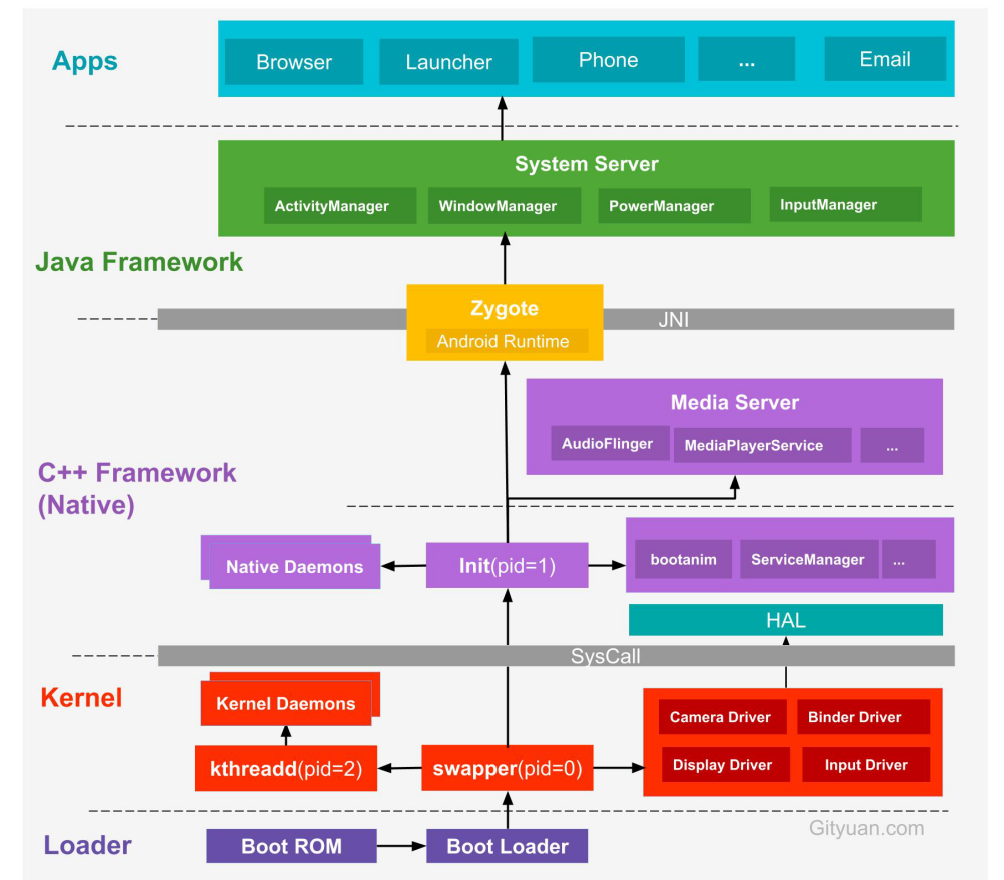
引入 init 进程
-
启动电源以及系统启动
当电源按下时,引导芯片代码从预定义的地方(固化在ROM)开始执行。加载引导程序Boot Loader到RAM中,然后执行。
-
Boot Loader
Boot Loader 是在Android操作系统运行前的一段小程序。目的就是把OS拉起来运行
-
Linux内核启动
当内核启动时,设置缓存、被保护储存器、计划列表、加载驱动。在内核完成系统设置后,首先找到
init.rc文件,并启动init进程。 -
init进程启动
init进程主要用来初始化和启动属性服务,也是用来启动
Zygote进程
init.rc文件,是用于初始化手机,启动init进程的文件,里面存放的叫Android Init Language,Android 通过特定的解析来读取rc文件, Android Init Language
init 进程入口
以main函数为入口(文章代码均为Android 9.0代码)
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
...
property_init(); // 对属性服务初始化
...
sigchld_handler_init(); // 设置子进程信号处理函数,防止init进程的子进程变为僵尸进程
...
start_property_service(); //启动属性服务
...
LoadBootScripts(am, sm);//解析init.rc文件
...
auto next_process_restart_time = RestartProcesses(); //重启进程
}
属性服务: 类似于Windows平台的注册表,通过键值对的方式记录一些信息,恢复出厂设置的开关。
僵尸进程: 子进程终止后,并没有被父进程回收。此时系统进程表里面还是保留的子进程的信息。 系统进程表被占满后,无法再创建新进程。
我们进入到LoadBootScripts方法
static void LoadBootScripts(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) {
Parser parser = CreateParser(action_manager, service_list); //创建解析器
...
parser.ParseConfig("/init.rc"); // 解析init.rc文件
...
}
Parser CreateParser(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) {
Parser parser;
parser.AddSectionParser("service", std::make_unique<ServiceParser>(&service_list, subcontexts)); //创建ServiceParser对象
parser.AddSectionParser("on", std::make_unique<ActionParser>(&action_manager, subcontexts));
parser.AddSectionParser("import", std::make_unique<ImportParser>(&parser));
return parser;
}
bool Parser::ParseConfigFile(const std::string& path, size_t* parse_errors) {
...
ParseData(path, *config_contents, parse_errors);
...
}
void Parser::ParseData(const std::string& filename, const std::string& data, size_t* parse_errors) {
...
if (auto result = section_parser->EndSection(); !result) { //把service 添加到 serviceList中
...
section_parser->ParseSection(std::move(args), filename, state.line);
...
}
Result<Success> ServiceParser::ParseSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args, const std::string& filename, int line) {
...
service_ = std::make_unique<Service>(name, restart_action_subcontext, str_args);// 创建service对象
return Success();
}
从上述代码可以看出,首先创建解析器,以 service 为例,如果读到的是 service 便相应的创建解析器 ServiceParser, 然后开始解析 init.rc,到最后创建出service对象。
//init.rc
on nonencrypted
class_start main // 对应 init.zygoteXX.rc
class_start late_start
//init.zygote32.rc
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
static Result<Success> do_class_start(const BuiltinArguments& args) {
for (const auto& service : ServiceList::GetInstance()) {
if (service->classnames().count(args[1])) {
if (auto result = service->StartIfNotDisabled(); !result) {
...
}
Result<Success> Service::StartIfNotDisabled() {
...
return Start(); //服务启动
...
}
Result<Success> Service::Start() {
...
pid = fork(); //fork进程
if (pid == 0) {
if (!ExpandArgsAndExecv(args_)) { //进程启动
...
可以看到在解析 init.rc 文件的时候,会去调用 class_start main,而这个 main 则定义在 init.zygoteXX.rc 中,根据之前的解析,此时便会启动zygote进程
zygote进程
通过 Android.mk 可以知道,/system/bin/app_process 所对应的 cpp 文件就是 app_main.cpp
Android.mk
app_process_src_files := app_main.cpp
进入 app_main 的 main 函数
app_main.CPP
int main(int argc, char* const argv[]) {
...
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote); //使用JNI 建立与java关系,调用 ZygoteInit.main()方法
...
}
AndroidRuntime.CPP
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote) {
...
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) { //启动java虚拟机
return;
}
if (startReg(env) < 0) { //为java虚拟机注册JNI
return;
}
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className != NULL ? className : ""); // 格式化一下类名
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName); //找到 ZygoteInit类
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main","([Ljava/lang/String;)V"); //找到main方法
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray); //启动方法
...
}
可以看到,当zygote进程创建后,首先会启动jvm,然后注册jni方法,调用java层的 ZygoteInit 的main方法,我们现在进入到java层
ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(); //创建
ZygoteServerzygoteServer.registerServerSocketFromEnv(socketName); // 创建LocalServerSocket 服务端
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog); //预加载类、资源
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer); //创建SystemService 进程
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList); //等待AMS 请求创建新的应用程序进程
...
}
void registerServerSocketFromEnv(String socketName) {
...
mServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(fd); //创建 LocalServerSocket
...
}
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,
ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
String args[] = {
...
"com.android.server.SystemServer", //保存启动SystemServer的参数
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args); //将数组封装成对象 为创建systemServer而使用
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer( parsedArgs.uid , ...)
};
public static int forkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
int pid = nativeForkSystemServer(
uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits, permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities);
//fork SystemServer 进程
...
}
ZygoteInit java层代码是创建了 LockServiceSocket 和 SystemServer 进程,为framework层提供了初始化操作
ZygoteServer.java
Runnable runSelectLoop(String abiList) {
fds.add(mServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) { //通过判断revents是否改变,来确定当前是否有AMS穿来的信息
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList); //创建sokcet连接
final Runnable command = connection.processOneCommand(this); //fork新进程
}
runSelectLoop 是Zygote进程用来接受AMS消息的地方,当收到AMS所发送的请求,就会fork出新的进程
SystemServer 进程
我们继续通过 forkSystemServer 往下走
ZygoteInit.java
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket(); //关闭zygote 进程创建的socket
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs); //启动SystemServer进程
}
...
}
private static Runnable handleSystemServerProcess(ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs) {
cl = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion); // 创建PathClassLoader
return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
}
因为 frok 实质上是复制进程,而新的进程并不需要ServerSocket,所以会关闭新进程的ServerSocket。
创建 PathClassLoader ,PathClassLoader为Android系统默认的类加载器,只能加载系统中已经安装过的apk /data/dalvik-cache ,而DexClassLoader 为动态加载提供了可能。
ZygoteInit.java
public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit(); // native 方法 启动Binder线程
return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader); // 进入 SystemServer main 方法
}
static void com_android_internal_os_ZygoteInit_nativeZygoteInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz){
gCurRuntime->onZygoteInit();
}
virtual void onZygoteInit(){
sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self();
ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\n");
proc->startThreadPool(); //启动 Binder线程池
}
zygote 启动了Binder线程池,具体分析会在后续章节中写。
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader); //反射 main
}
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,ClassLoader classLoader) {
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class }); // 反射 获取SystemServer main方法,最后在ZygoteInit处进行调用
}
SystemServer
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
private void run() {
System.loadLibrary("android_servers"); //加载动态库 libandroid_servers.so
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext); //创建SystemServiceManager
startBootstrapServices(); // 启动引导服务
startCoreServices(); //启动核心服务
startOtherServices(); //启动其他服务
}
private void startBootstrapServices() {
...
traceBeginAndSlog("StartActivityManager");
ActivityTaskManagerService atm = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityTaskManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService = ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.startService(
mSystemServiceManager, atm);
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
mWindowManagerGlobalLock = atm.getGlobalLock();
traceEnd();
...
}
反射调用 SystemServer 的 main 方法,可以看到在 new SystemServer().run() 中启动了很多必须的服务 例如AMS,PMS
public SystemService startService(String className) {
serviceClass = (Class<SystemService>)Class.forName(className);
return startService(serviceClass);
}
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext); //反射服务对象
startService(service);
}
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
service.onStart(); //调用服务的onStart方法
}
最后调用的都是各个服务的 onStart 方法
Launcher启动
SystemServer
private void startOtherServices() {
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> {
...
}
}
ActivityManagerService
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback, TimingsTraceLog traceLog) {
startHomeActivityLocked(currentUserId, "systemReady");
}
boolean startHomeActivityLocked(int userId, String reason) {
Intent intent = getHomeIntent(); //获取launcher intent
mActivityStartController.startHomeActivity(intent, aInfo, myReason); //启动launcher
}
Intent getHomeIntent() {
Intent intent = new Intent(mTopAction, mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null); //mTopAction = Intent.ACTION_MAIN;
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
return intent;
}
当AMS启动完毕,会获取HomeIntent,而HomeIntent其实对应的就是我们的Laucher
ActivityStartController
void startHomeActivity(Intent intent, ActivityInfo aInfo, String reason) {
mSupervisor.moveHomeStackTaskToTop(reason); //移动到HomeStack
mLastHomeActivityStartResult = obtainStarter(intent, "startHomeActivity: " + reason)
.setOutActivity(tmpOutRecord)
.setCallingUid(0)
.setActivityInfo(aInfo)
.execute();
}
ActivityStarter
int execute() {
try {
if (mRequest.mayWait) {
return startActivityMayWait(...);
} else {
return startActivity(...); //到了 startActivity 流程了
}
} finally {
onExecutionComplete();
}
最后还是通过startActivity启动起了我们的Launcher
总结
init 进程启动总结
- 创建和挂载所需的文件目录
- 初始化和启动属性服务
- 防止僵尸进程的出现
- 解析 init.rc配置文件,并启动Zygote进程
Zygote 进程启动总结
- 创建java虚拟机,并且注册JNI方法
- 通过JNI调用ZygoteInit 的main方法,进入framework层
- 创建LockServiceSocket,通过runSelectLoop方法,等待AMS的请求,来创建新的进程
- 启动SystemServer进程
SystemServer 进程启动总结
- 启动 Binder 线程池 ,提供跨进程通信
- 创建 SystemSericeManager
- 启动各种系统服务 AMS PMS等
Launcher 启动总结
- SystemServer 启动完毕后,通知AMS
- AMS 启动laucher