这篇文章记录一下本人刷题的思路和解法,刷题的顺序是按照覃超老师的《算法面试通关40讲》课程,边学习边记录,还没有学完,持续更新。
链表部分
206. Reverse Linked List
反转链表
循环
三个指针,注意处理head为空的情况
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null, curr = head, next;
while(curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
}
递归
翻转next之后的链表,再翻转头结点,注意保存并返回新的头结点
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
}
24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
成对反转
循环
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode p1 = dummy, p2;
while(p1.next != null && p1.next.next != null) {
p2 = p1.next.next;
p1.next.next = p2.next;
p2.next = p1.next;
p1.next = p2;
p1 = p2.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
递归
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode n = head.next;
head.next = swapPairs(n.next);
n.next = head;
return n;
}
}
141. Linked List Cycle
判断链表有环 快慢指针
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode walker = head, runner = head;
while(runner != null && runner.next != null) {
walker = walker.next;
runner = runner.next.next;
if(walker == runner) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
142. Linked List Cycle II
找到环中第一个节点
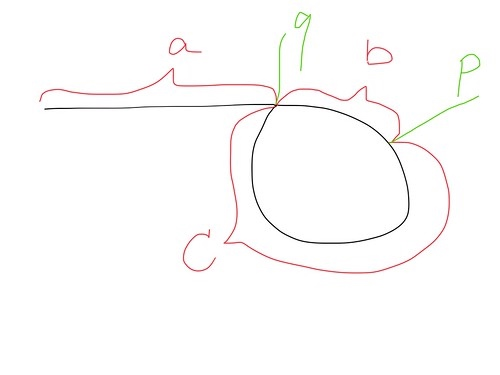
a + b + mr
fast 走了
a + b + nr
fast 的速度是 slow 的两倍,所以有
2(a + b + mr) = a + b + nr
a + b = (n - 2m)r = or
又因为
b + c = r
所以有
a = c + pr
上面 m、n、o、p 都是未知整数,不影响结果。所以一个指针从 p 点出发,一个指针从head出发,每次前进一步,肯定会在 q 点相遇。
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow) {
slow = head;
while(slow != fast) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}
25. Reverse Nodes in k-Group
每K个元素一组,反转链表
循环
- 实现辅助方法 reverse,用于反转 head 到 tail;
- 定义dummy和tail,用于记录当前已经反转完成的部分;
- 每次数k个节点出来,反转完成后加到结尾;
- 如果节点不足k个,就把剩下的加到结尾然后返回。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0), tail = dummy;
ListNode currHead = head, curr = head, nextHead;
while(true) {
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if(curr == null) {
tail.next = currHead;
return dummy.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
nextHead = curr;
tail.next = reverse(currHead, nextHead);
tail = currHead;
currHead = nextHead;
}
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head, ListNode tail) {
ListNode prev = null, curr = head, next;
while(curr != null && curr != tail) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
}
递归
- 数出k个节点,如果不够就返回head;
- 递归反转后面的部分;
- 反转k个节点,尾部加上后面反转完成的节点。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode p = head;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if(p == null) {
return head;
}
p = p.next;
}
ListNode prev = reverseKGroup(p, k), curr = head, next;
for(int i = 0; i< k; i++) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
}
栈和队列
队列和栈应该使用 LinkedList 或者 ArrayDeque,队列对应的方法应该使用 offer / poll / peek,这三个方法不会抛出异常;双端队列使用 的方法为 offerFirst / offerLast / pollFirst / pollLast / peekFirst / peekLast 栈对应的方法应该使用 push / pop / peek。
20. Valid Parentheses
括号匹配问题,注意空的 stack 调用 pop 方法会抛出异常,Stack 和 Deque 都是这样,所以要做判断。
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
LinkedList<Character> stack = new LinkedList<>();
for(char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if(c == '('){
stack.push(')');
} else if(c == '[') {
stack.push(']');
} else if(c == '{') {
stack.push('}');
} else if(stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop() != c) {
return false;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
232. Implement Queue using Stacks
用栈实现队列,没什么难度,满了再倒过来
class MyQueue {
private final Deque<Integer> s1;
private final Deque<Integer> s2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
s1 = new LinkedList<>();
s2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
s2.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
peek();
return s1.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
if(s1.isEmpty()) {
while(!s2.isEmpty()) {
s1.push(s2.pop());
}
}
return s1.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty();
}
}
225. Implement Stack using Queues
用队列实现栈,在push的时候反转一遍,这样pop和peek就不会出问题了
class MyStack {
private final Queue<Integer> q;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
q = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
q.offer(x);
for(int i = 0; i < q.size() - 1; i++) {
q.offer(q.poll());
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return q.poll();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return q.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return q.isEmpty();
}
}
703. Kth Largest Element in a Stream
最大K个值,使用优先级队列。注意默认排序方式是升序,即最小堆。
class KthLargest {
private final Queue<Integer> q;
private final int k;
public KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) {
this.q = new PriorityQueue<>(k);
this.k = k;
for(int i : nums) {
add(i);
}
}
public int add(int val) {
if(q.size() < k) {
q.offer(val);
} else if(val > q.peek()) {
q.poll();
q.offer(val);
}
return q.peek();
}
}
优先级队列
239. Sliding Window Maximum
滑动窗口求最大值
使用最大堆
有两点需要注意:
- Queue 继承了 Collection 接口,也有 remove 指定元素的方法;
- 默认是最小堆,要传入最大堆,注意反转 Comparator 的写法;
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums.length == 0) {
return nums;
}
Queue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer i1, Integer i2) {
return Integer.compare(i2, i1);
}
});
for(int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
q.offer(nums[i]);
}
int[] res = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
for(int i = k - 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
q.offer(nums[i]);
res[i - k + 1] = q.peek();
q.remove(nums[i - k + 1]);
}
return res;
}
}
双端队列
看起来比较优雅,但是时间复杂度其实是 O(kn),最坏情况下每个元素都需要和 k 个元素做比较。
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums.length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>(k);
int[] res = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(!q.isEmpty() && i >= k && nums[i - k] == q.peekFirst()) {
q.pollFirst();
}
while(!q.isEmpty() && q.peekLast() < nums[i]) {
q.pollLast();
}
q.offer(nums[i]);
if(i >= k - 1) {
res[i - k + 1] = q.peekFirst();
}
}
return res;
}
}
哈希表
242. Valid Anagram
判断是不是同构字符串,即每个字母使用的数量都一样,三种解法,排序、哈希表以及数组代替哈希表。
使用 HashMap
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if(s.length() != t.length()) {
return false;
}
Map<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap();
for(char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if(!map.containsKey(c)) {
map.put(c, 1);
} else {
map.put(c, map.get(c) + 1);
}
}
for(char c : t.toCharArray()) {
Integer count = map.get(c);
if(count == null || count == 0){
return false;
} else {
map.put(c, count - 1);
}
}
return true;
}
}
使用数组
题目中有说明,所有的字符都是小写字母,因此可以使用一个长度为26的数组记录每个字符出现的次数,每个字符和字符'a'相减得到其index。
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if(s.length() != t.length()) {
return false;
}
int[] table = new int[26];
for(char c : s.toCharArray()) {
table[c - 'a']++;
}
for(char c : t.toCharArray()) {
table[c - 'a']--;
}
for(int i : table) {
if(i != 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
1. Two Sum
三种解法:
- 暴力循环,两层嵌套;
- HashMap 遍历两遍,第一遍把所有元素和对应的index放进去,第二遍根据当前元素nums[i]查找target-nums[i],找到就返回下标;
- HashMap 遍历一遍,根据当前元素nums[i]查找target-nums[i],找到就返回下标,找不到把nums[i]和i放进去。
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[]{map.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
return null;
}
}
15. 3Sum
给定一个数组,找到其中所有和为0的三个元素的组合,不能有重复组合。
使用Set
内层类似 two sum 的解法,复杂度是O(N2),注意需要先排序,否则解决不了重复值的问题
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
Set<List<Integer>> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>();
for(int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
int search = - nums[i] - nums[j];
if(s.contains(search)) {
set.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], search));
} else {
s.add(nums[j]);
}
}
}
return new ArrayList(set);
}
}
双指针1
外层依次遍历,内层双指针,难点是重复值问题,注意如果 nums[i] == nums[i + 1],应该跳过的是 i + 1,不能跳过 i,否则会漏掉结果。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i< nums.length - 2 && nums[i] <= 0; i++) {
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1])
continue;
int j = i + 1, k = nums.length - 1;
while(j < k) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k];
if(sum > 0) {
k--;
} else if(sum < 0) {
j++;
} else {
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]));
while(j < k && nums[j + 1] == nums[i])
j++;
while(j < k && nums[k - 1] == nums[k])
k--;
j++;
k--;
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
双指针2
和上面类似,使用 set 来避免重复值问题。由于已经排序,所以 nums[i] <= nums[j] <= nums[k],因此 set 中的每个 list 都是有序的,因此重复值可以排除掉。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
Set<List<Integer>> set = new HashSet<>();
final int n = nums.length;
for(int i = 0; i< n; i++) {
int j = i + 1, k = n - 1;
while(k > j) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k];
if(sum > 0) {
k--;
} else if(sum < 0) {
j++;
} else {
set.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]));
j++;
k--;
}
}
}
return new ArrayList(set);
}
}
二叉树
98. Validate Binary Search Tree
验证二叉搜索树。注意二叉搜索树的定义,是左子树中所有的元素都小于当前元素,右子树中所有的元素都大于当前元素,并不是每个节点 left < val < right 就可以了,例如 [4,3,7,1,5,6,8] 这棵树,每个节点都满足 left < val < right,但却不是二次搜索树。
问题的难点在于,每个节点验证子树是否合法时,要和左子树的最大节点比较,又要和右子树的最小节点比较,同时需要向上级返回当前子树的最小值和最大值,所以一个返回值是做不到的。解决方法有两个,一种是返回一个int数组,分别放入最小值和最大值,即解法一;另一种是自上而下,通过传入最大最小值完成判断,不必将这两个值传回,即解法二。
还有另外一种思路,搜索二叉树中序遍历的结果是有序的,所以直接中序遍历就可以了,即解法三。
递归解法一
checkNode 方法返回 null 表示子树不合法,否则是个长度为2的数组,第一位是子树中的最小值,第二位是子树中的最大值。
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return root == null || checkNode(root) != null;
}
private int[] checkNode(TreeNode root) {
int[] left = null, right = null;
if(root.left != null) {
left = checkNode(root.left);
if(left == null || left[1] >= root.val) {
return null;
}
}
if(root.right != null) {
right = checkNode(root.right);
if(right == null || right[0] <= root.val) {
return null;
}
}
return new int[] {
left != null ? left[0]: root.val,
right != null ? right[1]: root.val
};
}
}
递归解法二
自上而下,传入最大值和最小值限定。注意这里 min 和 max 要使用Integer,传入 null 表示没有限制。如果使用 int 并且传入 Integer.MIN_VALUE 和 Integer.MAX_VALUE 的话,树中将不能保存 Integer.MIN_VALUE 和 Integer.MAX_VALUE,导致有的 TestCase 无法通过。
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return isValidBST(root, null, null);
}
private boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, Integer min, Integer max) {
if(root == null) return true;
if(min != null && root.val <= min || max != null && root.val >= max) return false;
return isValidBST(root.left, min, root.val) && isValidBST(root.right, root.val, max);
}
}
中序遍历法
递归遍历,需要使用成员变量保存前一个值,不需要用队列保存所有值。
class Solution {
private Integer prev;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return true;
if(!isValidBST(root.left))
return false;
if(prev != null && prev >= root.val) {
return false;
} else {
prev = root.val;
}
return isValidBST(root.right);
}
}
236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
最小公共祖先。
递归
很牛逼的一种解法,公共节点有两种情况,一种情况 p 或者 q 为另一个的祖先节点,另一种情况就是 p 和 q 分别分布在祖先节点的两侧。
对于每个节点,有以下几种情况:
- 左侧右侧都没有 p 或者 q,那么这个节点没用,返回 null;
- 某一侧有 p 或者 q,返回这一侧;
- 两侧都有,这个节点就是最小公共节点,返回它,它的所有节点都会符合上一点,最终会返回当前节点。
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left == null)
return right;
else if(right == null)
return left;
else
return root;
}
}
查找公共路径
从 root 开始分别查找 p 和 q,记录下来路径,找到路径中最后一个重合的节点即可。
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Deque<TreeNode> sp = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> sq = new LinkedList<>();
if(!search(root, p, sp) || !search(root, q, sq)) {
return null;
}
TreeNode res = null;
while(sp.peekFirst() == sq.peekFirst()) {
res = sp.pollFirst();
sq.pollFirst();
}
return res;
}
private boolean search(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, Deque<TreeNode> q) {
if(root == null)
return false;
q.offerLast(root);
if(root == target || search(root.left, target, q) || search(root.right, target, q))
return true;
q.pollLast();
return false;
}
}
235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
二叉搜索树的最小公共祖先,比较简单,根据二叉搜索树的特点,可以直接根据值来判断。
递归
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null) return root;
if(p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
} else if(p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
} else {
return root;
}
}
}
循环
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
while(true) {
if(p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) {
root = root.left;
} else if(p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val) {
root = root.right;
} else {
return root;
}
}
}
}
144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
先序遍历二叉树
递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
preorderTraversal(root,list);
return list;
}
private void preorderTraversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if(root == null) return;
list.add(root.val);
preorderTraversal(root.left, list);
preorderTraversal(root.right, list);
}
}
循环
使用一个栈,右侧先入栈
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return Collections.emptyList();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root);
TreeNode curr;
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
curr = stack.pop();
list.add(curr.val);
if(curr.right != null) {
stack.push(curr.right);
}
if(curr.left != null) {
stack.push(curr.left);
}
}
return list;
}
}
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
中序遍历二叉树
递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
inorderTraversal(root, list);
return list;
}
private void inorderTraversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if(root == null) return;
inorderTraversal(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val);
inorderTraversal(root.right, list);
}
}
循环
遍历的步骤如下:
- root 入栈,并另 root = root.left,直到 root 为 null;
- 出栈并赋值给 root,添加 root 的值,并另 root = root.right,回到步骤1;
- 直到 root 为空,且栈为空。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return Collections.emptyList();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
while(!stack.isEmpty() || root != null) {
if(root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
} else {
root = stack.pop();
list.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
return list;
}
}
145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
后序遍历二叉树
递归
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
postorderTraversal(root, list);
return list;
}
private void postorderTraversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if(root == null) return;
postorderTraversal(root.left, list);
postorderTraversal(root.right, list);
list.add(root.val);
}
}
循环
使用一个栈,每个元素都入栈出栈一次,出栈的时候加入列表中并子节点入栈。注意这样对应的其实是【根右左】的顺序,结果是反的,所以加入到列表的时候要加到表头,相当于完成了一次反转。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return Collections.emptyList();
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
root = stack.pop();
list.push(root.val);
if(root.left != null) {
stack.push(root.left);
}
if(root.right != null) {
stack.push(root.right);
}
}
return list;
}
}
102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
层序遍历,并且每一行输出一个list
循环
使用双端队列保存每个节点的子节点,指针 last 记住每一行的最后一个节点,当到达每一行的末尾时,将 last 赋值为队列末尾的节点即可。
也可以使用一个普通队列,但是要加一个指针,一直记录队尾的节点。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return Collections.emptyList();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode curr, last = root;
q.offer(root);
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<>();
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
curr = q.poll();
level.add(curr.val);
if(curr.left != null) {
q.offer(curr.left);
}
if(curr.right != null) {
q.offer(curr.right);
}
if(curr == last) {
list.add(level);
level = new ArrayList<>();
last = q.peekLast();
}
}
return list;
}
}
递归解法
将要返回的大 list 传给递归函数,以及要处理的节点,节点所在层级,这样就能把每个节点加到对应行中。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
levelOrder(list, root, 0);
return list;
}
private void levelOrder(List<List<Integer>> list, TreeNode root, int level) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
List<Integer> l;
if(list.size() == level) {
l = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(l);
} else {
l = list.get(level);
}
l.add(root.val);
levelOrder(list, root.left, level + 1);
levelOrder(list, root.right, level + 1);
}
}
103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal
循环解法
使用双端队列,从左往右时加到队尾,从右往左是加到队头,用指针 last 记录每一行的最后一个节点。注意如果是要求直接打印的话,只有这种方法可以搞定。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return Collections.emptyList();
boolean lr = true;
Deque<TreeNode> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> ll = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode curr, last = root;
dq.push(root);
while(!dq.isEmpty()) {
curr = lr ? dq.pollFirst() : dq.pollLast();
ll.add(curr.val);
if(lr) {
if(curr.left != null) {
dq.offerLast(curr.left);
}
if(curr.right != null) {
dq.offerLast(curr.right);
}
} else {
if(curr.right != null) {
dq.offerFirst(curr.right);
}
if(curr.left != null) {
dq.offerFirst(curr.left);
}
}
if(curr == last) {
last = lr ? dq.peekFirst() : dq.peekLast();
lr = !lr;
list.add(ll);
ll = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
return list;
}
}
循环解法二
这种更简单一些,和普通层序遍历差不多,只不过从右往左时元素是加到列表头部的,相当于做了反转。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return Collections.emptyList();
boolean lr = true;
Deque<TreeNode> dq = new ArrayDeque<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> ll = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode curr, last = root;
dq.push(root);
while(!dq.isEmpty()) {
curr = dq.pollFirst();
if(lr) {
ll.add(curr.val);
} else {
ll.add(0, curr.val);
}
if(curr.left != null) {
dq.offerLast(curr.left);
}
if(curr.right != null) {
dq.offerLast(curr.right);
}
if(curr == last) {
last = dq.peekLast();
lr = !lr;
list.add(ll);
ll = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
return list;
}
}
递归解法
和上面的题类似,不过要根据当前行数奇偶,判断从前端还是后端插入。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
zigzagLevelOrder(list, root, 0);
return list;
}
private void zigzagLevelOrder(List<List<Integer>> list, TreeNode root, int level) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
List<Integer> l;
if(list.size() == level) {
l = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(l);
} else {
l = list.get(level);
}
if(level % 2 == 0) {
l.add(root.val);
} else {
l.add(0, root.val);
}
zigzagLevelOrder(list, root.left, level + 1);
zigzagLevelOrder(list, root.right, level + 1);
}
}
分治
50. Pow(x, n)
求 x 的 n 次方,注意 n 可能是负数,也可能是 Integer.MIN_VALUE,Integer.MIN_VALUE 取负还是它本身,这是个坑。
注意一点,余数的绝对值等于被除数绝对值和除数绝对值取余的结果,符号和被除数一致。
分治法一
这种解法用了分治思想,每次减少一半,除不尽的再乘以一次 x。有一点就是 n 为负数的情况,其实不需要做特殊处理,只是真正相乘的时候判断一下,乘上它的倒数就可以了,这样也不需要处理 Integer.MIN_VALUE 了。
class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
if(n == 0) return 1;
double half = myPow(x, n / 2);
double remainder = n % 2 == 0 ? 1 : n > 0 ? x : 1 / x;
return half * half * remainder;
}
}
分治法二
和上面类似,核心问题是将 pow(x, n) 转化为 pow(x * x, n / 2),同时不要忘记处理 n 为负数的情况。
class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
if(n == 0) return 1;
return myPow(x * x, n / 2) * (n % 2 == 0 ? 1 : n > 0 ? x : 1 / x);
}
}
位移法
位移法比较巧妙,例如 x10 = x8 + 2,即把 n 拆解成 2 的幂和的形式,然后 x 每次自称,也就是 x 的1,2,4,16...次幂,如果 n 的当前位为1,就乘上去。这个解法没法处理负数,所以 Integer.MIN_VALUE 和负数需要转换一下。
class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
if(n == Integer.MIN_VALUE)
return myPow(x * x, n / 2);
if(n < 0)
return myPow(1 / x, -n);
double r = 1;
while(n > 0) {
if((n & 1) != 0)
r *= x;
x *= x;
n >>= 1;
}
return r;
}
}
169. Majority Element
找到数组中数量超过总数一半的那个数。
Map 解法
使用 HashMap,时间复杂度 O(N),空间复杂度 O(N)。
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i : nums) {
int count = map.containsKey(i) ? map.get(i) + 1 : 1;
if(count > nums.length / 2)
return i;
map.put(i, count);
}
return 0;
}
}
排序解法
时间复杂度 O(NlogN)。
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length / 2];
}
}
摩尔投票法
时间复杂度 O(N)。
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int m = nums[0];
int count = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] == m) {
count++;
} else if(count == 0) {
m = nums[i];
count = 1;
} else {
count--;
}
}
return m;
}
}
分治解法
分治也可以解决,时间复杂度是 O(NlogN),注意两边 majority 不一致的时候要比较 lm 和 rm 哪个出现比较多,是在 lo 到 hi 中数的。
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
return majority(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private int majority(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
if(lo == hi)
return nums[lo];
int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
int lm = majority(nums, lo, mid);
int rm = majority(nums, mid + 1, hi);
if(lm == rm)
return lm;
int lc = count(nums, lo, hi, lm);
int rc = count(nums, lo, hi, rm);
return lc >= rc ? lm : rm;
}
private int count(int[] nums, int lo, int hi, int target) {
int count = 0;
for(int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
if(nums[i] == target)
count++;
return count;
}
}
贪心
122. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
买卖股票最佳时机,允许多次买卖。
只要涨就买,跌就卖。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < prices.length - 1; i++)
if(prices[i + 1] > prices[i])
p += prices[i + 1] - prices[i];
return p;
}
}
BFS 和 DFS
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
return root == null ? 0 : Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
if(root.left == null)
return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
if(root.right == null)
return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
22. Generate Parentheses
生成所有匹配括号。
这个问题的重点在于,什么样的括号组合是合法的。和括号匹配那道题不同,这里只会出现一种括号,所以不需要用栈去验证,规则其实很简单,从左往右扫描,任何时刻左括号的数量多于右括号的数量,直到结束,这样的字符串就是合法的。
所以生成的方法就是递归,生成的过程中及时去掉不符合条件的分支,生成完成后加入列表中即可。
class Solution {
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
generate(n, n, "", list);
return list;
}
private void generate(int left, int right, String str, List<String> list) {
if (left == 0 && right == 0) {
list.add(str);
return;
}
if (left > 0)
generate(left - 1, right, str + '(', list);
if (right > left)
generate(left, right - 1, str + ')', list);
}
}
剪枝
51. N-Queens
N 皇后问题,需要注意下面几点:
- 使用三个 Set 分别记录已经被占用的列(col)、左斜(sum)和右斜(diff),这样的好处是简化计算并且便于回退。另一种方法是使用二位数组涂色,缺点是无法回退,所以每次都需要复制数组,麻烦且空间开销较大;
- 使用 int 数组 curr 记录每一行中 Q 所在的列,因为确定每行有且只有一个 Q,所以使用以为数组即可;
- 注意终止条件。
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Integer> sum = new HashSet();
Set<Integer> diff = new HashSet();
Set<Integer> col = new HashSet();
int[] curr = new int[n];
solve(n, 0, sum, diff, col, list, curr);
return list;
}
private void solve(int n, int row, Set<Integer> sum, Set<Integer> diff, Set<Integer> col, List<List<String>> list, int[] curr) {
if(row == n) {
list.add(toList(curr));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (col.contains(i) || sum.contains(row + i) || diff.contains(row - i))
continue;
col.add(i);
sum.add(row + i);
diff.add(row - i);
curr[row] = i;
solve(n, row + 1, sum, diff, col, list, curr);
col.remove(i);
sum.remove(row + i);
diff.remove(row - i);
}
}
private List<String> toList(int[] arr) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
StringBuilder row = new StringBuilder();
for(int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
row.append(j == arr[i] ? 'Q' : '.');
}
list.add(row.toString());
}
return list;
}
}
52. N-Queens II
这题的区别是不需要输出答案,只需要计算结果数量
思路和上题相同,只是不再需要记录 Q 所在的位置,也不需要返回 Q 的具体摆放方式,只要返回数量即可。
class Solution {
public int totalNQueens(int n) {
Set<Integer> sum = new HashSet(), diff = new HashSet(), col = new HashSet();
return solve(n, 0, col, sum, diff);
}
private int solve(int n, int row, Set<Integer> col, Set<Integer> sum, Set<Integer> diff) {
if(row == n)
return 1;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (col.contains(i) || sum.contains(row + i) || diff.contains(row - i))
continue;
col.add(i);
sum.add(row + i);
diff.add(row - i);
count += solve(n, row + 1, col, sum, diff);
col.remove(i);
sum.remove(row + i);
diff.remove(row - i);
}
return count;
}
}
37. Sudoku Solver
数独求解,注意数独的规则,每一行是1-9,每一列是1-9,并且整体被划分为 9 个 3 x 3 的区间,每个区间也要包含 1-9。
总体思路就是从头到尾遍历每个格子,如果是空的就根据规则填上数字,再继续下一个位置。搜索完每个值之后要还原空位,再尝试下一个值,直到成功。
注意位置计算的技巧,以及还原现场。
class Solution {
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
solve(board, 0);
}
private boolean solve(char[][] board, int count) {
for(int i = count; i < 81; i++) {
int row = i / 9;
int col = i % 9;
if(board[row][col] == '.') {
for(char c = '1'; c <= '9'; c++) {
boolean repeated = false;
for(int k = 0; k < 9; k++) {
if(board[row][k] == c || board[k][col] == c
|| board[row / 3 * 3 + k / 3][col / 3 * 3 + k % 3] == c) {
repeated = true;
break;
}
}
if(!repeated) {
board[row][col] = c;
if(solve(board, i + 1))
return true;
board[row][col] = '.';
}
}
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
36. Valid Sudoku
判断数独是否合法,不需要解出来,只需要验证已经填上的数字是不是合法。
暴力求解
分别遍历行、列、块,使用一个 int 作为 Set,记录每个值是否出现过,这个解法看起来不优雅,但是效率是最高的,也没有空间开销。
class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
int set, flag;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
set = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] != '.') {
int k = board[i][j] - '1';
flag = 1 << k;
if ((set & flag) > 0)
return false;
set |= flag;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
set = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[j][i] != '.') {
int k = board[j][i] - '1';
flag = 1 << k;
if ((set & flag) != 0)
return false;
set |= flag;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
set = 0;
int row = i / 3 * 3;
int col = i % 3 * 3;
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[row + j / 3][col + j % 3] != '.') {
int k = board[row + j / 3][col + j % 3] - '1';
flag = 1 << k;
if ((set & flag) != 0)
return false;
set |= flag;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
使用 Set
这个写法很讨巧,使用一个 Set,记录区分了行、列、块三种情况,并且记录了对应的 index 信息。注意 Set.add 方法返回值是 boolean 类型,如果元素已经存在,返回值是 false。
这种写法看起来会比较简短,但是效率并不高,还需要分配一个 Set。
class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
char c = board[i][j];
if (c != '.'
&& (!set.add("r" + i + c) || !set.add("c" + j + c)
|| !set.add("b" + i / 3 + j / 3 + c)))
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
二分查找
69. Sqrt(x)
开平方。
二分查找
难点在于处理好边界。
- 如果使用乘法,必定会出现溢出的情况,所以要使用除法;
- 0 和 1 要处理好;
- 由于结果要求整数,会存在取整的问题,要处理好。
class Solution {
public int mySqrt(int x) {
int lo = 1, hi = x, mid;
while(hi >= lo) {
mid = (hi + lo) >>> 1;
if(x / mid < mid)
hi = mid - 1;
else if(x / (mid + 1) > mid)
lo = mid + 1;
else
return mid;
}
return 0;
}
}
牛顿迭代法
牛顿迭代法公式:xn+1 = xn - f(xn) / f'(xn)
f(x) = x2 - a,f'(x) = 2x,所以有 xn+1 = 1 / 2 * ( xn + a / xn )
这里溢出问题不好处理,可以使用 long 防止溢出。
class Solution {
public int mySqrt(int x) {
long r = x;
while(r * r > x) {
r = (r + x / r) / 2;
}
return (int)r;
}
}
Trie 树
208. Implement Trie (Prefix Tree)
实现 Trie 树。
class Trie {
private final TrieNode root;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int index = c - 'a';
if (curr.children[index] == null) {
curr.children[index] = new TrieNode();
}
curr = curr.children[index];
}
curr.isWord = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int index = c - 'a';
if (curr.children[index] == null) {
return false;
}
curr = curr.children[index];
}
return curr.isWord;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char c : prefix.toCharArray()) {
int index = c - 'a';
if (curr.children[index] == null) {
return false;
}
curr = curr.children[index];
}
return true;
}
private static class TrieNode {
private TrieNode[] children;
private boolean isWord;
public TrieNode() {
children = new TrieNode[26];
}
}
}
212. Word Search II
给定一个二维数组和单词表,在数组中查找出现的单词。注意单词只要是相邻的字母构成的就可以,方向上下左右都可以,也允许弯折。
我的解法
- 首先需要解决单词表的问题,这里不能使用 Set,必须使用 TrieTree,因为搜索的时候要逐个增加字母再去匹配,使用 TrieTree 更合适;
- 使用 Set path 记录已经使用的位置;
- 记录当前已经拼成的单词为 curr。
class Solution {
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
if (board.length == 0 || board[0].length == 0)
return Collections.emptyList();
Trie trie = new Trie();
for (String word : words)
trie.add(word);
Set<String> result = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> path = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
path.clear();
search(board, trie, result, path, "", i, j);
}
}
return new ArrayList(result);
}
private void search(char[][] board, Trie trie, Set<String> result, Set<String> path, String curr, int row, int col) {
if(path.contains(row + "," + col))
return;
curr += board[row][col];
if(trie.search(curr))
result.add(curr);
if(trie.startsWith(curr)) {
String location = row + "," + col;
path.add(location);
if(row > 0)
search(board, trie, result, path, curr, row - 1, col);
if(row + 1 < board.length)
search(board, trie, result, path, curr, row + 1, col);
if(col > 0)
search(board, trie, result, path, curr, row, col - 1);
if(col + 1 < board[0].length)
search(board, trie, result, path, curr, row, col + 1);
path.remove(location);
}
}
static class Trie {
Node root = new Node();
void add(String word) {
Node curr = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int i = c - 'a';
if (curr.children[i] == null)
curr.children[i] = new Node();
curr = curr.children[i];
}
curr.isWord = true;
}
boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
Node curr = root;
for (char c : prefix.toCharArray()) {
int i = c - 'a';
if (curr.children[i] == null)
return false;
curr = curr.children[i];
}
return true;
}
boolean search(String word) {
Node curr = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int i = c - 'a';
if (curr.children[i] == null)
return false;
curr = curr.children[i];
}
return curr.isWord;
}
private static class Node {
boolean isWord;
Node[] children = new Node[26];
}
}
}
大神的解法
解法非常牛逼,总体思路上和上面是一致的,但是细节处理的很好,虽然我写的一次性AC兴奋了半天,但是有几点还是比大神差了很多。
- TrieTree 其实不需要完整的实现,融合到搜索的过程中即可,否则会增加很多重复计算;
- 如何记录已经使用过的位置?可以用一个 Set,位置保存为类似 row + "," + col 的样式,用来判重,但是大神给出了更简单的方式,直接将对应的位置字母替换为 # 即可,记得用完之后要设置回来,回溯嘛;
- 每个 Node 可以保存它对应的单词,如果没有就是 null,这样就避免了计算过程中需要传递当前搜索到的单词的麻烦;
- 题目要求结果不能重复,可以使用 Set 存储最后再转换为 List,但大神的解法是添加完单词后,将 node 中保存的 word 去掉,这样就避免了重复。
综上,膜拜大神!
class Solution {
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
if (board.length == 0 || board[0].length == 0)
return Collections.emptyList();
TrieNode root = new TrieNode();
for (String word : words) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int i = c - 'a';
if (curr.children[i] == null)
curr.children[i] = new TrieNode();
curr = curr.children[i];
}
curr.word = word;
}
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
search(board, root, result, i, j);
}
}
return result;
}
private void search(char[][] board, TrieNode node, List<String> result, int row, int col) {
char c = board[row][col];
if(c == '#' || node.children[c - 'a'] == null) return;
node = node.children[c - 'a'];
if(node.word != null) {
result.add(node.word);
node.word = null;
}
board[row][col] = '#';
if(row > 0)
search(board, node, result, row - 1, col);
if(row + 1 < board.length)
search(board, node, result, row + 1, col);
if(col > 0)
search(board, node, result, row, col - 1);
if(col + 1 < board[0].length)
search(board, node, result, row, col + 1);
board[row][col] = c;
}
private static class TrieNode {
String word;
TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26];
}
}
位运算
整数的原码、反码、补码都一样,负数的表示:
原码:第一位表示符号位,后面的位表示数值;
反码:第一位表示符号位,后面各位为原码取反;
补码:反码加1
| 原码 | 反码 | 补码 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0110 0100 | 0110 0100 | 0110 0100 |
| -100 | 1110 0100 | 1001 1011 | 1001 1100 |
常用技巧:
x ^ 0 = x
x ^ 1s = ~x //1s表示所有位都是1
x ^ (~x) = 1s
x ^ x = 0
交换两个变量:a = a ^ b; b = a ^ b; a = a ^ b;
a ^ b ^ c = a ^ (b ^ c)
x & 1 == 0 或 1 => 判断奇偶,也适用负数
x = x & (x - 1) => 清空最低位的1,也适用负数
x & -x => 得到最低位的 1,也适用负数
191. Number of 1 Bits
数1的个数
位移法
注意是无符号右移,否则如果 n 为负数结果就是错的。
public class Solution {
// you need to treat n as an unsigned value
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
int count = 0;
while(n != 0) {
count += n & 1;
n >>>= 1;
}
return count;
}
}
消减法
利用 n & (n - 1) 可以消除最低位 1 的特性。
public class Solution {
// you need to treat n as an unsigned value
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
int count = 0;
while(n != 0) {
n &= n - 1;
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
231. Power of Two
338. Counting Bits
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int num) {
int[] res = new int[num + 1];
int pow = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
if ((i & (i - 1)) == 0) {
res[i] = 1;
pow = i;
} else {
res[i] = res[i - pow] + 1;
}
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int num) {
int[] res = new int[num + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
res[i] = res[i >> 1] + (i & 1);
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int num) {
int[] res = new int[num + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
res[i] = res[i & (i - 1)] + 1;
}
return res;
}
}
动态规划
70. Climbing Stairs
爬楼梯,一次只能一阶或者两阶。
第 n 阶肯定是从第 n - 1 阶或者第 n - 2 阶然后登了一下上来的,这样考虑就是斐波那契问题了。
注意 DP 中有个很重要的思维方式,把从顶向下改为从底向上,能减少缓存的使用。
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int f0 = 1, f1 = 1, tmp;
while(n-- > 1) {
tmp = f1;
f1 += f0;
f0 = tmp;
}
return f1;
}
}
120. Triangle
给定一个数字组成的三角形,求从顶部到底部所有路径中最小的和。
这是个 DP 的问题,有两个点要注意:
- 从上到下计算的话,最终会生成 n 个值,再取最小值,不如从下到上计算,结果只有一个;
- 不需要用二维数组记录,因为每一次只会用到前一行的值,使用一位数组就够了。 DP 保存中间状态时,考虑两个问题,一个是中间状态足够计算下一步,一个是中间状态能得出最终结果,只要满足这两个条件,中间状态的数据结构越简单越好。有时候二维的问题可以用一维存储中间状态,一维的问题用一两个变量保存中间状态。这种做法叫做状态压缩。
class Solution {
public int minimumTotal(List<List<Integer>> triangle) {
int[] dp = new int[triangle.size() + 1];
for (int i = triangle.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j + 1]) + triangle.get(i).get(j);
return dp[0];
}
}
152. Maximum Product Subarray
求乘积最大的子串。注意给定数组 nums 是 int 类型,但有可能会是负数。
朴素的 DP 解法
计算所有从 j 到 i 的数的乘积,统计其最大值,使用一维数组保存来减少重复计算。时间复杂度为 O(N2),空间复杂度为 O(N)。
class Solution {
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int max = nums[0];
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
dp[j] *= nums[i];
max = Math.max(max, dp[j]);
}
dp[i] = nums[i];
max = Math.max(max, dp[i]);
}
return max;
}
}
更简单的 DP
首先是递推公式,记以第 i 个元素结尾的子串最大乘积为 max(i),最小乘积为 min(i)。那么 max(i) 应该取 nums[i]、nums[i) * max[i - 1]、nums[i] * min(i - ) 之中的最小值,所以保存状态需要包含最大值和最小值。另外最后一种情况仅当 nums[i] 为负数时发生,所以可以通过判断 nums[i] 是否为负数进行特殊处理,交换最小最大值。
class Solution {
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int res = nums[0];
for (int i = 1, max = res, min = res; i < nums.length; i++) {
int tmp = Math.max(Math.max(nums[i], nums[i] * max), nums[i] * min);
min = Math.min(Math.min(nums[i], nums[i] * max), nums[i] * min);
max = tmp; //不要直接修改 max 值,否则 min 就没法计算了
res = Math.max(max, res);
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int res = nums[0];
for (int i = 1, max = res, min = res; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] < 0) {
int tmp = max;
max = min;
min = tmp;
}
max = Math.max(nums[i], nums[i] * max);
min = Math.min(nums[i], nums[i] * min);
res = Math.max(max, res);
}
return res;
}
}
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
买卖股票I,只能买入卖出一次,min 记录 i 之前的最低价格,在 i 时卖出的最大价格应该是 i - min。
买卖股票II是贪心问题,前面已经有了。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int max = 0, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i : prices) {
min = Math.min(min, i);
max = Math.max(max, i - min);
}
return max;
}
}
123. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
买卖股票III,只能买卖两次
简单粗暴的解法
分为前半部分和后半部分,每一部分的求解方法和只能购买一次相同
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int min, m1, m2, max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
m1 = 0;
m2 = 0;
min = prices[0];
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
min = Math.min(min, prices[j]);
m1 = Math.max(m1, prices[j] - min);
}
min = prices[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j < prices.length; j++) {
min = Math.min(min, prices[j]);
m2 = Math.max(m2, prices[j] - min);
}
max = Math.max(m1 + m2, max);
}
return max;
}
}
DP 解法
这个算法参考大神的答案,非常不好理解,解释一下这几个变量: b1 表示买入一次的最低价格,s1 表示卖出一次的最高获利,b2 表示第二次买入的最低价格,可以理解为卖出第一次后再买入第二次后的获利总和,s2 表示第二次卖出后最大获利。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if (prices.length < 2)
return 0;
int b1 = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int s1 = 0;
int b2 = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int s2 = 0;
for (int p : prices) {
b1 = Math.min(b1, p);
s1 = Math.max(s1, p - b1);
b2 = Math.min(b2, p - s1);
s2 = Math.max(s2, p - b2);
}
return s2;
}
}
188. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock IV
允许进行至多 K 次交易。 这个题目和上面的题目思路是一样的。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
if (prices.length <= 1)
return 0;
if (k >= prices.length) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
res += Math.max(0, prices[i] - prices[i - 1]);
}
return res;
}
int[] buy = new int[k + 1];
int[] sell = new int[k + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
buy[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int p : prices) {
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
buy[i] = Math.min(buy[i], p - sell[i - 1]);
sell[i] = Math.max(sell[i], p - buy[i]);
}
}
return sell[k];
}
}