第一篇容错架构篇:主要讲几个过程:
1.从directory获取所有的invokers
2.使用route进一步过滤删选出可执行的invokers
3.最终使用负载策略获取最终执行方法的那个invoker
第二篇:directory:主要讲directory的invokers是何时写入?
有个回调notify方法,注册中心变更时候调用,会实时同步更新
第三篇:route:将具体的实现路由策略:
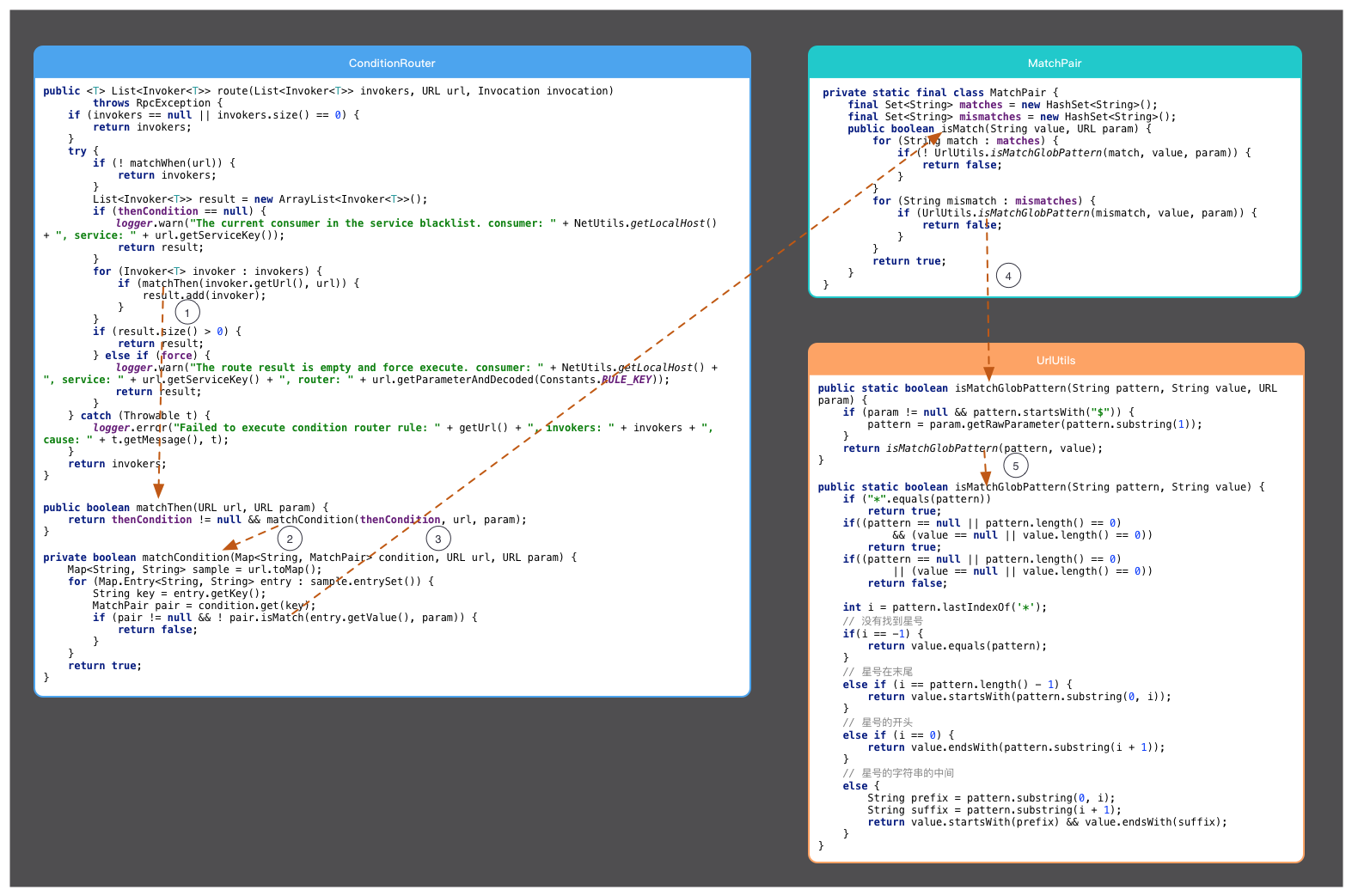
如何实现?怎么写嵌套列表?换行后先空三个,再写+ - *等
invokers = routerChain.route(getConsumerUrl(), invocation);
public List<Invoker<T>> route(URL url, Invocation invocation) {
List<Invoker<T>> finalInvokers = invokers;
for (Router router : routers) {
finalInvokers = router.route(finalInvokers, url, invocation);
}
return finalInvokers;
}
具体route规则看图
第四篇:cluster讲解
cluster对用户来讲是个黑盒的概念,里面相当于封装了一堆的invokers,在使用dubbo的时后用户只需要知道有个cluster就可以
这一节主要讲了cluster在dubbo中的九种实现,最需要关注的是缺省的failover实现,失败后快速重试,包含这九种底层实现应该掌握几种主要的
第五篇:loadbalance篇
1.loadbalance顶层接口:select方法和getWeight方法(预热前逐渐降权)
protected int getWeight(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
//获取权重值,默认为100
int weight = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), "weight" ,100);
if (weight > 0) {
//服务提供者启动时间戳
long timestamp = invoker.getUrl().getParameter("remote.timestamp" , 0L);
if (timestamp > 0L) {
//当前时间-启动时间=运行时长
int uptime = (int) (System.currentTimeMillis() - timestamp);
//获取服务预热时间 默认10分钟
int warmup = invoker.getUrl().getParameter("warmup" , 600000 );
//如果服务运行时间小于预热时间,即服务启动未到达10分钟
if (uptime > 0 && uptime < warmup) {
//重新计算服务权重
weight = calculateWarmupWeight(uptime, warmup, weight);
}
}
}
return weight;
}
当满足程序执行时间小于预热时间的话就重新计算权重,这也就是个降权的过程;
运行时长
公式
权重
1分钟
1/10*100
10
2分钟
2/10*100
20
3分钟
3/10*100
30
5分钟
5/10*100
50
10分钟
10/10*100
100
为什么要这样做?
是为了在服务启动之初不至于承受高负载的压力,进行一段的服务预热,类似的还jvm预热
2.关注算法实现:
a.randomloadbalance(权重随机)
(1).判断是否随机
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
// save for later use
weights[i] = weight;
// Sum
totalWeight += weight;
if (sameWeight && weight != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false ;
}
}
(2).执行选择算法,方法比较巧妙
// If (not every invoker has the same weight & at least one invoker's weight>0), select randomly based on totalWeight.
int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
// Return a invoker based on the random value.
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
offset -= weights[i];
if (offset < 0) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
重点: 虽然这个随机算法理解起来是比较容易的,面试一般不会问这个,但是假如我们要实现类似的功能,他这个代码实现的思路还是很优雅的,非常具有借鉴意义.他这个实现思路从纯数学角度是很好理解的,我们还是按照上面数学分析中的前提条件.我们知道总权重为10(1+2+3+4),那么怎么做到按权重随机呢?根据10随机出一个整数,假如为随机出来的是2.然后依次和权重相减,比如2(随机数)-1(A的权重) = 1,然后1(上一步计算的结果)-2(B的权重) = -1,此时-1 < 0,那么则调用B,其他的以此类推
b.RoundRobinLoadBalance(轮询)
基础轮询:就是让invokers的每一个依次去执行方法,然后一轮过后执行下一轮,普通轮询适合各个机器性能完全一样,大家随便挨着一个个来
www.baidu.com
关注加权轮询:机器性能不一样,比较差的挨不住那么狠,就得根据性能划分,牛逼的机器多跑,差机器少执行,所以来加权:
protected <T> Invoker<T> do Select(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
//全限定类型+方法名
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
//服务提供者数量
int length = invokers.size();
//最大权重
int maxWeight = 0;
//最小权重
int minWeight = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
final LinkedHashMap<Invoker<T>, IntegerWrapper> invokerToWeightMap =
new LinkedHashMap<Invoker<T>, IntegerWrapper>();
int weightSum = 0;
//循环主要用于查找最大和最小权重,计算权重总和等
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
maxWeight = Math.max(maxWeight, weight); // Choose the maximum weight
minWeight = Math.min(minWeight, weight); // Choose the minimum weight
if (weight > 0) {
//将Invoker对象和对应的权重大小IntegerWrapper放入Map中
invokerToWeightMap.put(invokers.get(i), new IntegerWrapper(weight));
weightSum += weight;
}
}
}
此处参考:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903806841405448
核心就是靠取模执行,代码执行看起来晦涩,参考这位老哥的说法:
blog.csdn.net/weixin_3376… 自己跑几下类似代码就能大体看懂了,主要还是借助--让权重小的早早退出后续批次操作,实现权重效果
c.LeastActiveLoadBalance 最少活跃数算法:
算法步骤:
1.初始化最小活跃数-1,最小活跃数下标数组,相同最小活跃数的长度
2.执行循环,找出最小活跃数,下标数组和权重是否相同
3.长度只有一个那么直接调用即可
4.长度不为1看是否所有权重都相同,那么随机一个
5.按照权重系数进行选择,同最初的随机算法一样,用减法来确定分配
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i);
int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive(); // 活跃数
int weight = invoker.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.WEIGHT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_WEIGHT); // 权重
if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) { // 发现更小的活跃数,重新开始
leastActive = active; // 记录最小活跃数
leastCount = 1; // 重新统计相同最小活跃数的个数
leastIndexs[0] = i; // 重新记录最小活跃数下标
totalWeight = weight; // 重新累计总权重
firstWeight = weight; // 记录第一个权重
sameWeight = true ; // 还原权重相同标识
} else if (active == leastActive) { // 累计相同最小的活跃数
leastIndexs[leastCount++] = i; // 累计相同最小活跃数下标
totalWeight += weight; // 累计总权重
// 判断所有权重是否一样
if (sameWeight && i > 0
&& weight != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false ;
}
}
}
// assert(leastCount > 0)
if (leastCount == 1) {
// 如果只有一个最小则直接返回
return invokers.get(leastIndexs[0]);
}
if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {
// 如果权重不相同且权重大于0则按总权重数随机
int offsetWeight = random.nextInt(totalWeight);
// 并确定随机值落在哪个片断上
for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) {
int leastIndex = leastIndexs[i];
offsetWeight -= getWeight(invokers.get(leastIndex), invocation);
if (offsetWeight <= 0)
return invokers.get(leastIndex);
}
}
// 如果权重相同或权重为0则均等随机
return invokers.get(leastIndexs[random.nextInt(leastCount)]);
关于最小活跃数算法:核心就是找到活跃值最小的invokers,给放到数组中,在找寻最小活跃数数组的过程中,也找到了总权重和是否权重都相同及权重数组,根据找到的最小活跃数的数量来执行对应 选择方法,一个就一个,多个再根据是否权重都相同来执行随机方法还是加权随机
敲黑板划重点
活跃数的变化是在com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.filter.ActiveLimitFilter中,如果没有配置dubbo:reference的actives属性,默认是调用前活跃数+1,调用结束-1,鉴于很多人可能没用过这个属性,所以我把文档截图贴出来
d.一致性hash算法
具体一致性算法参考对应文章
dubbo默认只对第一个参数进行hash
<dubbo:parameter key="hash.arguments" value="0,1" />
<dubbo:parameter key="hash.nodes" value="320" />
关于一致性hash算法三个关键点:原理,down机后影响,虚拟节点