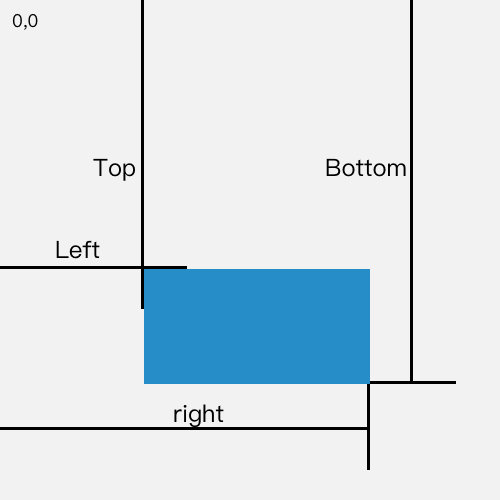
起因
前几天公司要求写一个锚点自动高亮功能,页面滚动到哪里锚点高亮到哪里。
所以这里简单记录一下,因为遇到了自动高亮判定的问题,所以发在这里,如果有更好的方法,希望能教教我~~
效果图

点击这里看运行效果
分析一下实现步骤
这是大概的dom结构
<html>
<body>
<ul>
<li><a href="#a1">a1</a></li>
<li><a href="#a2">a2</a></li>
<li><a href="#a3">a3</a></li>
<li><a href="#a4">a4</a></li>
<li><a href="#a5">a5</a></li>
</ul>
<div id="container">
<div id="a1"></div>
<div id="a2"></div>
<div id="a3"></div>
<div id="a4"></div>
<div id="a5"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
需要处理的元素
- 页面中需要处理的有
a标签 即图中anchor - 锚点的位置即各种带
id的元素,如图中a1 element和a2 element - 包裹这些锚点位置的
容器,如果是整个页面那就是document,或者就是自定义的滚动容器,这里统一叫container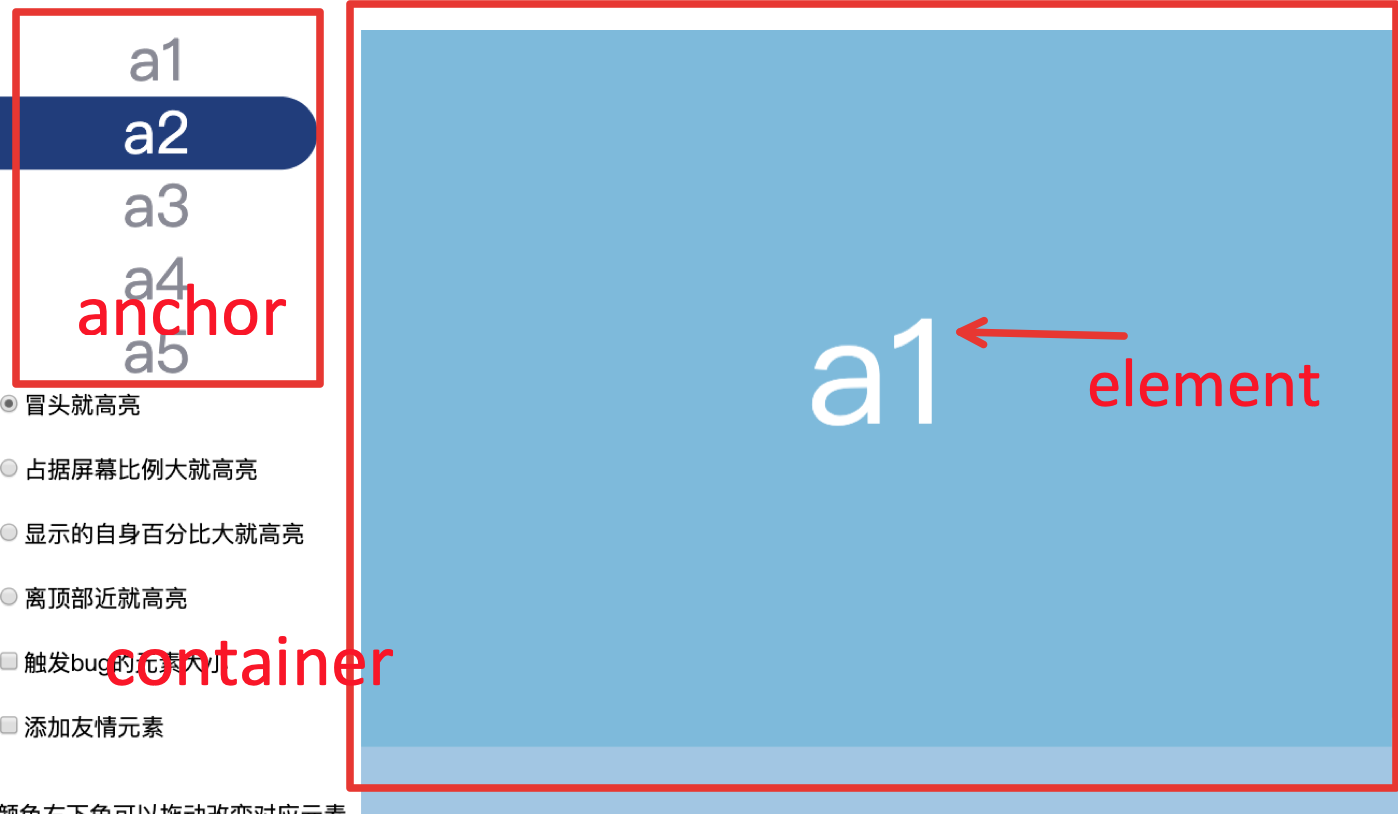
如何手动高亮 a 标签
高亮效果,这里就是简单的给对应的 a 标签添加一个class即可
// 获取a所有元素
function getAllAnchorElement(container) {
const target = container ? container : document
return target.querySelectorAll('a')
}
// 对应id的添加高亮类名,非对应id移除之前添加的高亮类名
function highLightAnchor(id){
getAllAnchorElement().forEach(element => {
element.classList.remove('highLight')
if (element.hash.slice(1) == id) {
element.classList.add('highLight')
}
});
}
如何自动高亮 a 标签
原理很简单,就是监听容器元素的滚动,在对应条件下去自动高亮a标签
// 这里注意需要用 thorttle 处理一下handleScroll 函数,不然触发次数太多可能卡页面哦 🤪🤪
const throttleFn = throttle(handleScroll, 100)
// 如果你没有阻止滚动事件,可以加上 passive: true 可以提高滚动性能
ScrollContrainer.addEventListener('scroll', throttleFn, {passive: true})
但是这个对应条件有点麻烦,我一共想了3种方法,各有缺点和优点,如果大家有完美的方法,望不吝赐教
我这里方案都是通过 getBoundingClientRect 来判断元素的位置。
这里贴一点MDN上的解释
返回值是一个 DOMRect 对象,这个对象是由该元素的 getClientRects() 方法返回的一组矩形的集合, 即:是与该元素相关的CSS 边框集合 。
DOMRect 对象包含了一组用于描述边框的只读属性——left、top、right和bottom,单位为像素。除了 width 和 height 外的属性都是相对于视口的左上角位置而言的。
有掘友提出用 IntersectionObserver API 这个更好!这个方案是我一开始就用的,但是有一个情况他处理不了,在下图中,当 a3 和 a4 都完整出现后,它们的intersectionRatio 就一直为1 后,entries 数组就不包含 a3 和 a4,会导致某些方案的比例比较不准,所以没有采用,如果我的用法有错,请告诉我谢谢谢谢

我这里4种方案,先说第一种
方案1:谁冒头就高亮谁
let highligthId;//需要高亮的id
const windowHeight = this.ScrollContrainer.offsetHeight //容器高度
this.anchors.forEach(element => {
const id = element.hash.slice(1)
const target = document.getElementById(id)
if (target) {
const {
top
} = target.getBoundingClientRect()
// 当元素头部可见时
if (top < windowHeight) {
highligthId = id
}
}
})
if (highligthId) {
// 调用高亮方法
this.highLightAnchor(highligthId)
}
优点
- 简单
缺点
- 初始状态如果
第一个元素没有满屏比如a1,屏幕下方漏出一点a2元素,那a1元素的高亮会里面跳走,这个时候a1再也高亮不到了
方案2:谁占据屏幕比例大就高亮谁
let highligthId;
let maxRatio = 0 // 占据屏幕的比例
const windowHeight = this.ScrollContrainer.offsetHeight
this.anchors.forEach(element => {
const id = element.hash.slice(1)
const target = document.getElementById(id)
if (target) {
let visibleRatio = 0;
let {
top,
height,
bottom
} = target.getBoundingClientRect();
// 当元素全部可见时
if (top >= 0 && bottom <= windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = height / windowHeight
}
// 当元素就头部可见时
if (top >= 0 && top < windowHeight && bottom > windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = (windowHeight - top) / windowHeight
}
// 当元素占满屏幕时
if (top < 0 && bottom > windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = 1
}
// 当元素尾部可见时
if (top < 0 && bottom > 0 && bottom < windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = bottom / windowHeight
}
if (visibleRatio >= maxRatio) {
maxRatio = visibleRatio;
highligthId = id;
}
}
});
if (highligthId) {
this.highLightAnchor(highligthId)
}
优点
- 当每一个元素都大于半屏时,效果好
缺点
- 在页面最顶部 如果
a2的比例比a1大,那a1就无法高亮了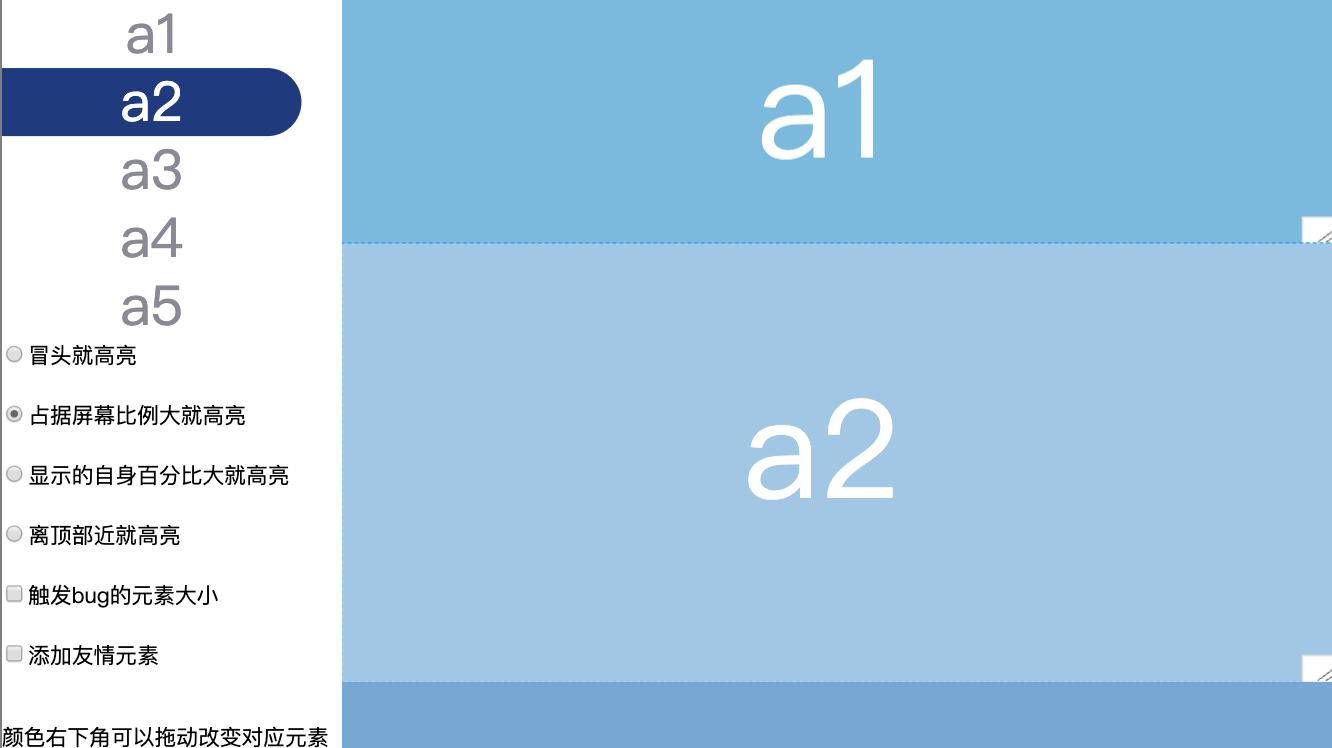
- 在页面最底部,如图中
a5比a4小,那么a5就无法高亮,因为a5占据屏幕的比例是大不过a4的
方案3:谁显示的自身百分比大就高亮谁
代码判断条件和 谁占据屏幕比例大就高亮谁 的方案一样,就是分母不一样
let highligthId;
let maxRatio = 0
const windowHeight = this.ScrollContrainer.offsetHeight
this.anchors.forEach(element => {
const id = element.hash.slice(1)
const target = document.getElementById(id)
if (target) {
let visibleRatio = 0;
let {
top,
height,
bottom
} = target.getBoundingClientRect();
// 当元素全部可见时
if (top >= 0 && bottom <= windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = 1
}
// 当元素就头部可见时
if (top >= 0 && top < windowHeight && bottom > windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = (windowHeight - top) / height
}
// 当元素占满屏幕时
if (top < 0 && bottom > windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = windowHeight / height
}
// 当元素尾部可见时
if (top < 0 && bottom > 0 && bottom < windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = bottom / height
}
if (visibleRatio >= maxRatio) {
maxRatio = visibleRatio;
highligthId = id;
}
}
});
if (highligthId) {
this.highLightAnchor(highligthId)
}
优点
- 当每一个元素都大于半屏时,效果好
- 在有连续出现小元素的时候效果会比
谁占据屏幕比例大就高亮谁的方案好一点
缺点
-
在页面顶部
a1和a2都全部显示,那a1的优先级就没有a2高,无法高亮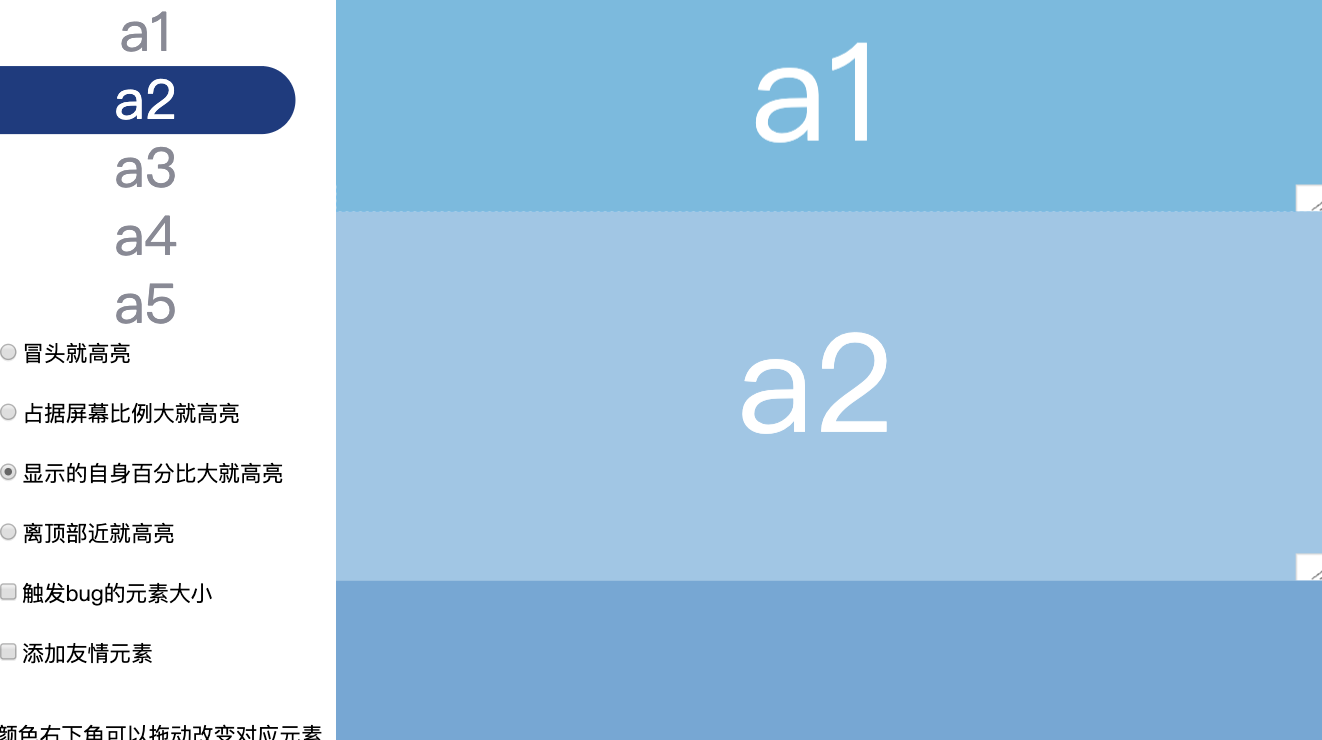
-
在页面中间
a3很小,那么a3出现后就每次计算比例都是1,a4 就必须等a3开始消失,才有可能高亮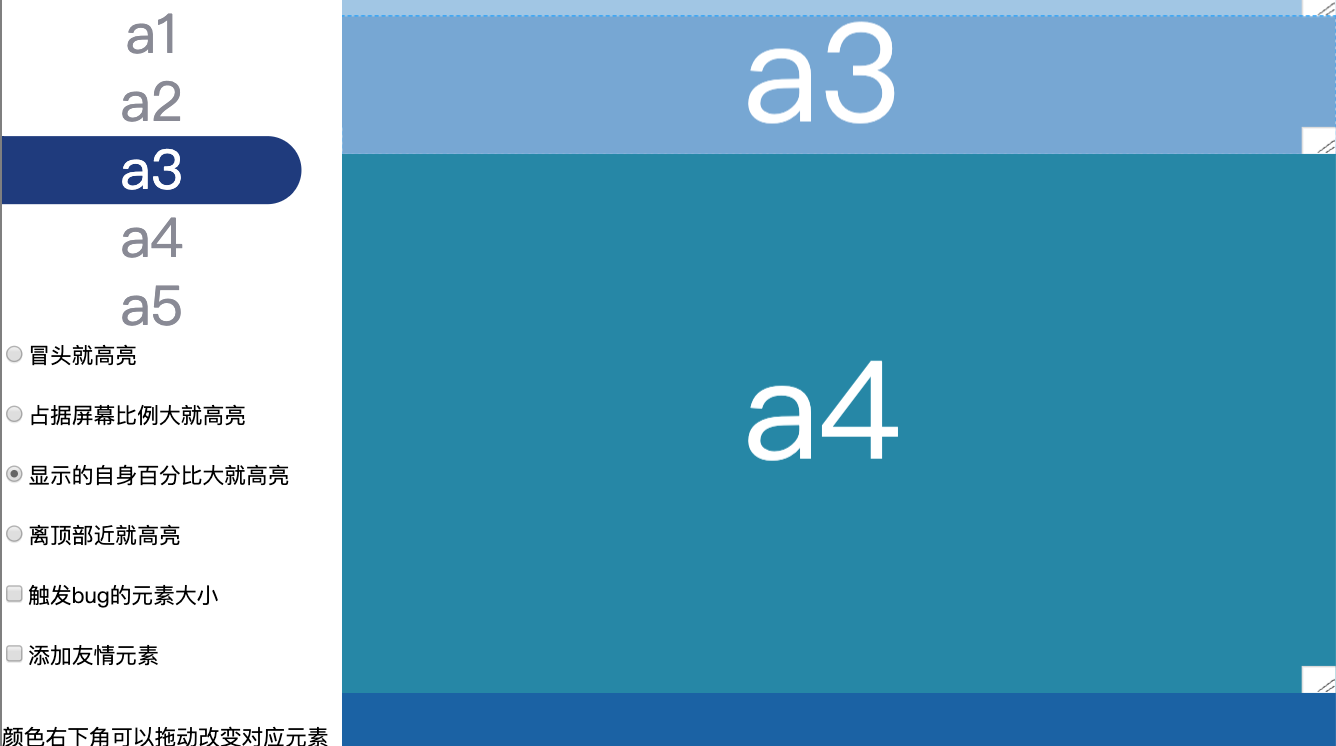
(新增)方案4:谁离顶部近就高亮谁
type4(e, offsetTop = 0) {
let highligthId = Array.prototype.reduce.call(this.anchors, (prev, curr) => {
const id = curr.hash.slice(1)
const target = document.getElementById(id)
if (target) {
const {
top
} = target.getBoundingClientRect()
// 当元素头部距离顶部小于规定范围时 即 top <= offsetTop
return top <= offsetTop && top > prev.top ? {
id,
top
} : prev
} else {
return prev
}
}, {
id: null,
top: -Infinity
}).id;
if (highligthId) {
this.highLightAnchor(highligthId)
}
}
优点
- 简单,在页面尾部有
额外元素撑场面的时候效果好,或者最后一个元素本身就有一屏幕高的时候效果好
缺点
- 在
没有额外元素撑场面时,底部元素a5无法高亮
最后
通过以上可以看到我能想到的方案在某些情况下都有问题。
在我的工作中因为每一个元素都至少有半屏都大小,所以谁占据屏幕比例大就高亮谁这个方案效果是综合起来效果最好的。
其实一开始用的是谁显示的自身百分比大就高亮谁这个方案,但是这个方案在某一个元素特别特别长的时候效果就差点。
如果以上内容对你有帮助,请问可以骗个赞吗 👍👍👍👍
最后的最后附上全部代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="#a1">a1</a></li>
<li><a href="#a2">a2</a></li>
<li><a href="#a3">a3</a></li>
<li><a href="#a4">a4</a></li>
<li><a href="#a5">a5</a></li>
</ul>
<input type="radio"
name="strategy"
checked
value="type1">冒头就高亮<br><br>
<input type="radio"
name="strategy"
value="type2">占据屏幕比例大就高亮<br><br>
<input type="radio"
name="strategy"
value="type3">显示的自身百分比大就高亮<br><br>
<input type="radio"
name="strategy"
value="type4">离顶部近就高亮<br><br>
<input type="checkbox"
name="bug"
value="abnormality">触发bug的元素大小<br><br>
<input type="checkbox"
name="friendly_link"
value="friendly_link">添加友情元素<br><br>
<p>颜色右下角可以拖动改变对应元素的大小</p>
</nav>
<div id="container">
<div id="a1"></div>
<div id="a2"></div>
<div id="a3"></div>
<div id="a4"></div>
<div id="a5"></div>
<div id="friendly_link"></div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
function throttle(fn, interval = 1000) {
let timer = null;
return function(...args) {
if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null
fn.call(this, ...args)
}, interval);
}
}
}
class AutoHighLightAnchor {
// anchors;
// ScrollContrainer;
// throttleFn;
// strategy;
constructor(anchorsContainer, ScrollContrainer, strategy = AutoHighLightAnchor.Strategys.type1) {
this.anchors = anchorsContainer.querySelectorAll('a')
this.ScrollContrainer = ScrollContrainer;
this.strategy = strategy;
this.init()
}
init(strategy = this.strategy) {
if (this.throttleFn) {
this.remove()
}
this.throttleFn = throttle(this[strategy].bind(this), 100)
this.throttleFn() // 初始执行一次更新位置
this.ScrollContrainer.addEventListener('scroll', this.throttleFn, {
passive: true
})
}
remove() {
this.ScrollContrainer.removeEventListener('scroll', this.throttleFn, {
passive: true
})
}
highLightAnchor(id) {
this.anchors.forEach(element => {
element.classList.remove('highLight')
if (element.hash.slice(1) == id) {
element.classList.add('highLight')
}
});
}
type1(e) {
let highligthId;
const windowHeight = this.ScrollContrainer.offsetHeight
this.anchors.forEach(element => {
const id = element.hash.slice(1)
const target = document.getElementById(id)
if (target) {
const {
top
} = target.getBoundingClientRect()
// 当元素头部可见时
if (top < windowHeight) {
highligthId = id
}
}
})
if (highligthId) {
this.highLightAnchor(highligthId)
}
}
type2(e) {
let highligthId;
let maxRatio = 0
const windowHeight = this.ScrollContrainer.offsetHeight
this.anchors.forEach(element => {
const id = element.hash.slice(1)
const target = document.getElementById(id)
if (target) {
let visibleRatio = 0;
let {
top,
height,
bottom
} = target.getBoundingClientRect();
// 当元素全部可见时
if (top >= 0 && bottom <= windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = height / windowHeight
}
// 当元素就头部可见时
if (top >= 0 && top < windowHeight && bottom > windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = (windowHeight - top) / windowHeight
}
// 当元素占满屏幕时
if (top < 0 && bottom > windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = 1
}
// 当元素尾部可见时
if (top < 0 && bottom > 0 && bottom < windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = bottom / windowHeight
}
if (visibleRatio >= maxRatio) {
maxRatio = visibleRatio;
highligthId = id;
}
}
});
if (highligthId) {
this.highLightAnchor(highligthId)
}
}
type3(e) {
let highligthId;
let maxRatio = 0
const windowHeight = this.ScrollContrainer.offsetHeight
this.anchors.forEach(element => {
const id = element.hash.slice(1)
const target = document.getElementById(id)
if (target) {
let visibleRatio = 0;
let {
top,
height,
bottom
} = target.getBoundingClientRect();
// 当元素全部可见时
if (top >= 0 && bottom <= windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = 1
}
// 当元素就头部可见时
if (top >= 0 && top < windowHeight && bottom > windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = (windowHeight - top) / height
}
// 当元素占满屏幕时
if (top < 0 && bottom > windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = windowHeight / height
}
// 当元素尾部可见时
if (top < 0 && bottom > 0 && bottom < windowHeight) {
visibleRatio = bottom / height
}
if (visibleRatio >= maxRatio) {
maxRatio = visibleRatio;
highligthId = id;
}
}
});
if (highligthId) {
this.highLightAnchor(highligthId)
}
}
type4(e, offsetTop = 0) {
let highligthId = Array.prototype.reduce.call(this.anchors, (prev, curr) => {
const id = curr.hash.slice(1)
const target = document.getElementById(id)
if (target) {
const {
top
} = target.getBoundingClientRect()
// 当元素头部距离顶部小于规定范围时 即 top <= offsetTop
return top <= offsetTop && top > prev.top ? {
id,
top
} : prev
} else {
return prev
}
}, {
id: null,
top: -Infinity
}).id;
if (highligthId) {
this.highLightAnchor(highligthId)
}
}
}
AutoHighLightAnchor.Strategys = {
type1: 'type1',
type2: 'type2',
type3: 'type3',
type4: 'type4'
}
const high = new AutoHighLightAnchor(document.querySelector('ul'), document.querySelector('#container'),
AutoHighLightAnchor.Strategys.type1)
document.querySelectorAll('input[type=radio]').forEach(element => {
element.onchange = e => high.init(e.target.value)
})
document.querySelector('input[name=bug]').onchange = e => {
const value = e.target.checked
const elements = document.querySelectorAll('#container>div')
if (value) {
const abnormality = [30, 120, 20, 30, 50]
elements.forEach((element, index) => {
element.style.height = abnormality[index] + 'vh'
})
} else {
elements.forEach((element, index) => {
element.style.height = (100 - 10 * index) + 'vh'
})
}
}
document.querySelector('input[name=friendly_link]').onchange = e => {
const value = e.target.checked
const element = document.querySelector('#friendly_link')
if (value) {
element.style.display = 'block'
} else {
element.style.display = 'none'
}
}
</script>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
a {
display: block;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
color: #898A95;
line-height: 50px;
font-size: 40px;
border-radius: 0 50px 50px 0;
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
}
.highLight {
color: #ffffff;
background: #1b3781;
}
nav {
width: 250px;
float: left;
height: 100vh;
overflow: scroll;
}
ul {
width: 220px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
}
#container {
height: 100vh;
overflow: scroll;
}
#container>div {
position: relative;
resize: vertical;
overflow: scroll;
/* color: #ffffff;
font-size: 30px; */
}
#container>div::after {
content: attr(id);
display: block;
font-size: 100px;
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
width: 100%;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
}
#container>div:hover {
outline: 1px dashed #09f;
}
#container>div::-webkit-scrollbar {
width: 25px;
height: 20px;
}
#a1 {
height: 90vh;
background-color: #77b9e1;
}
#a2 {
height: 90vh;
background-color: #9fc6e6;
}
#a3 {
height: 90vh;
background-color: #73a5d7;
}
#a4 {
height: 90vh;
background-color: #1387aa;
}
#a5 {
height: 90vh;
background-color: #0c5ea8;
}
#friendly_link {
display: none;
height: 90vh;
background-color: #7e92d3;
}
</style>
</html>