首先来看一段简单的线程池代码
package com.tedu.data;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
/**
* @author ldjun
*/
public class Test {
private static class Worker implements Runnable {
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue;
public Worker(BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this.workQueue = workQueue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " start!");
while (true) {
try {
Runnable runnable = workQueue.take();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " execute task");
runnable.run();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static class ThreadPool {
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>();
private Worker[] workers;
public ThreadPool(int threadCount) {
workers = new Worker[threadCount];
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
workers[i] = new Worker(workQueue);
new Thread(workers[i], "worker" + i).start();
}
}
public void execute(Runnable runnable) {
try {
workQueue.put(runnable);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool pool = new ThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
pool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println("this is a task");
});
}
}
}
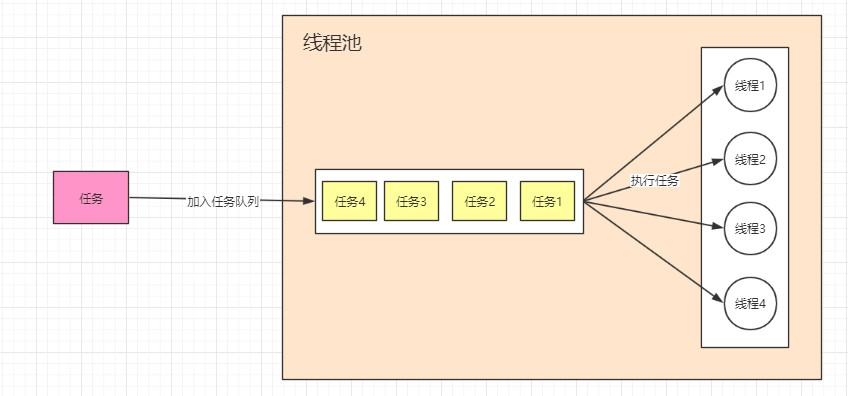
简要分析
1、线程池有两个重要属性:workQueue(需要执行的任务队列)
workers(维护的线程数组),且每个线程都有一个线程池队列(workQueue)的引用。用于在队列中取任务并进行执行一个方法:execute,用于接收任务并把任务放入队列中
任务本质:实现了runnable接口的类
思考:
如果队列满了怎么办?
队列类型有哪些?
一般开发中任务怎么来?是一次网络请求一个任务吗?
线程池的线程数量怎么设置比较合理?
让我们带着这些疑问去揭露JAVA实现线程池的神秘面纱吧!
阅读源码就是要带着目的去,阅读源码就是要带着目的去。包含即引用,包含即引用