Given an array nums and a value val, remove all instances of that value in-place and return the new length.
Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
The order of elements can be changed. It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the new length.
Example 1:
Given nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3,
Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length. Example 2:
Given nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2,
Your function should return length = 5, with the first five elements of nums containing 0, 1, 3, 0, and 4.
Note that the order of those five elements can be arbitrary.
It doesn't matter what values are set beyond the returned length.
这道题对内存有限制,所以首先想到的是用两个指针,一个指向返回数组的末尾,一个用来循环遍历给定的数组,代码很简单。
但还是有需要注意的点:
1、end的起始位置
2、如果给定nums在下标为0的值=val时应该怎么处理
3、给定nums为空或者元素值均与val相等时应该怎么处理
写完之后,看了官方给的解答,给出了两种解答。
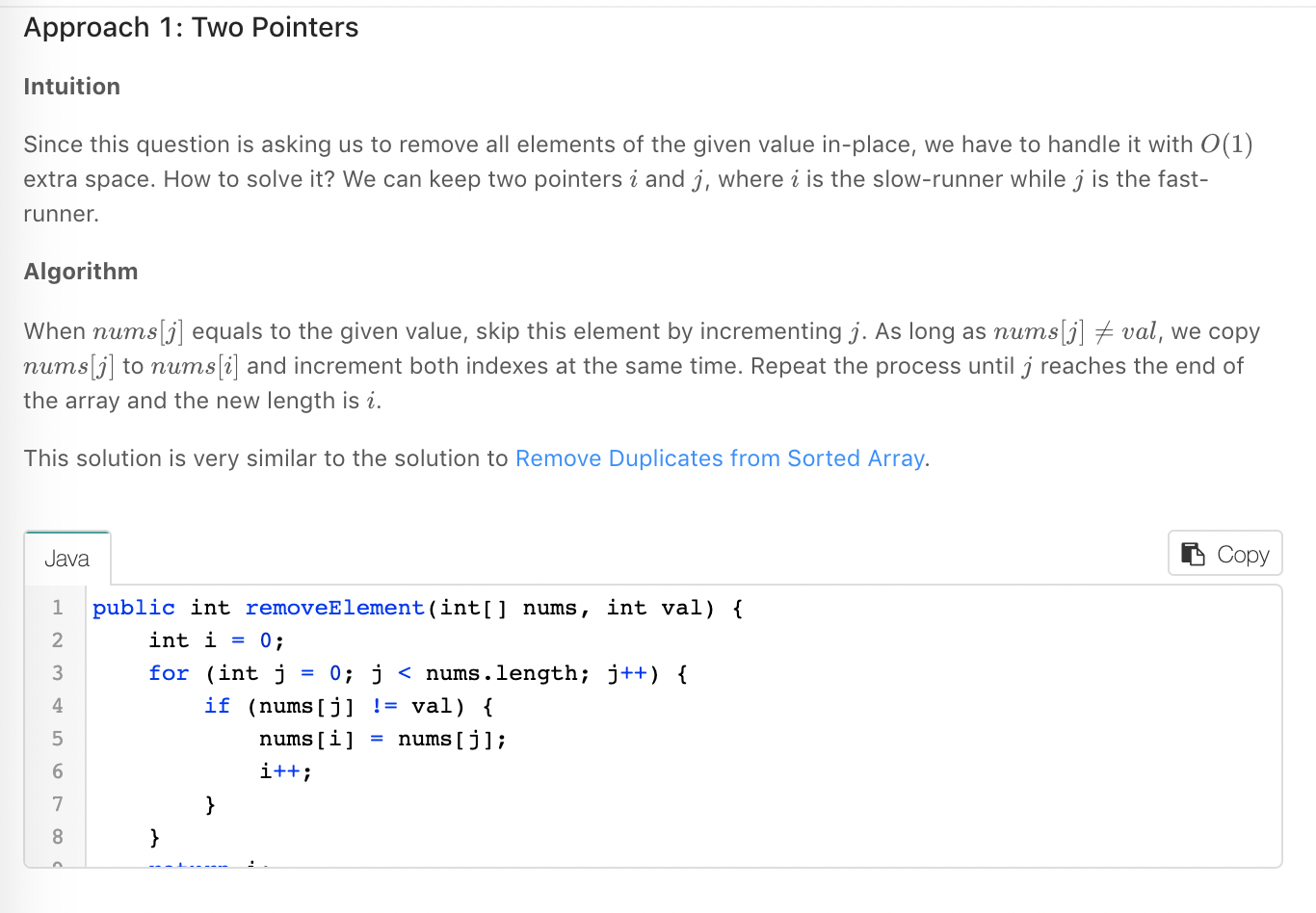
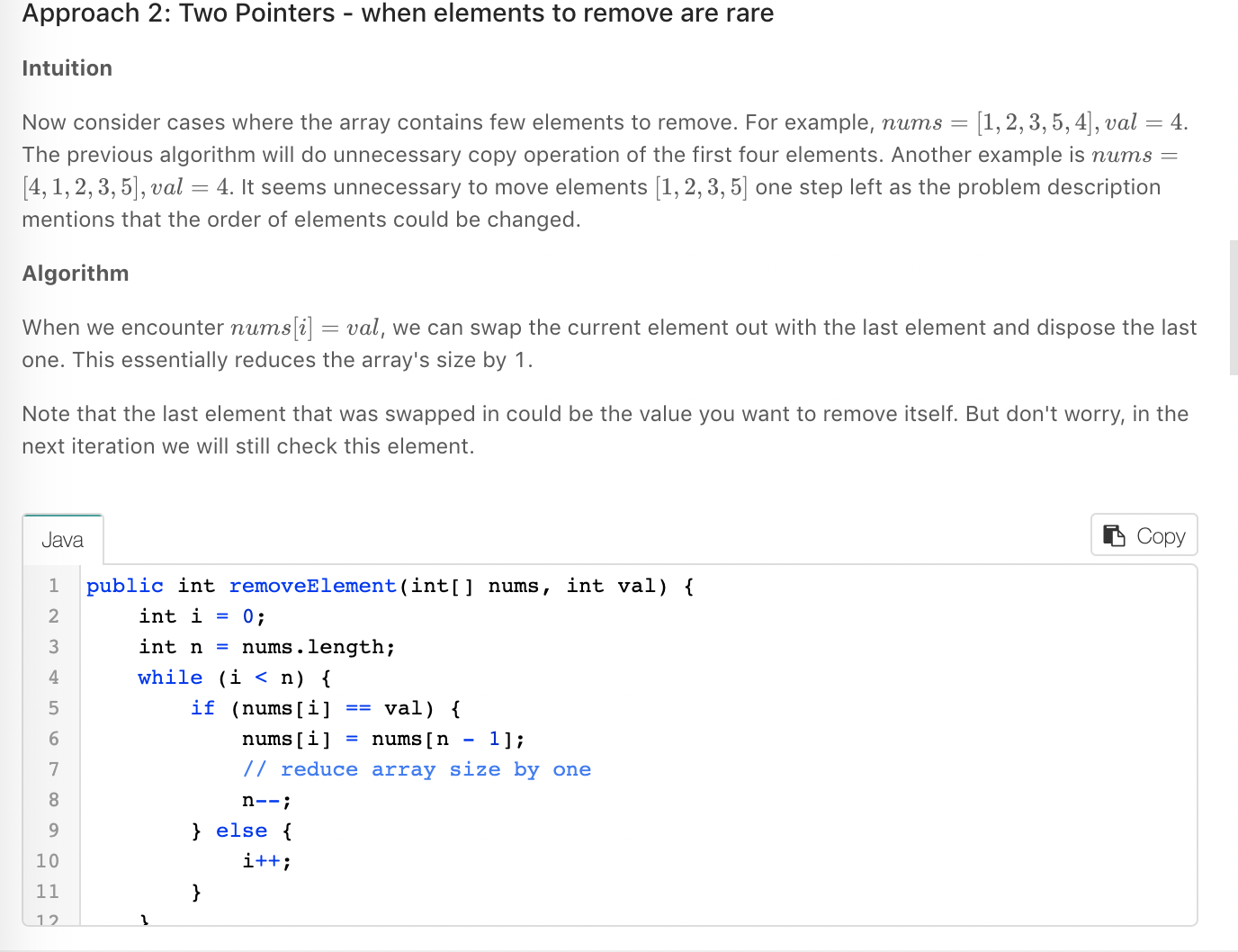
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
if (nums.size() == 0) return 0;
int begin = 0;
for (int end = 0; end < nums.size(); end ++) {
if (val != nums[end]) {
nums[begin] = nums[end];
begin ++;
}
}
return begin ;
}
};
下面这种方式是别人写的
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
return std::distance(nums.begin(), std::remove(nums.begin(), nums.end(), val));
}