History
History基本概念
History对象包含用户(在浏览器窗口中)访问过的 URL。History对象是window对象的一部分,可通过window.history属性对其进行访问。
早期的history只有三个方法: go(),back(),forward()。由此带来的问题是ajax请求不能添加状态到history,以致无法使用浏览器的后退和前进回到上一个状态。
为了解决这个问题(同时也是由于hash url的方式太过于hack),H5引入新的history API:
pushState(), replaceState()以及新的属性state。新的History结构如下:
interface History {
readonly attribute long length;
readonly attribute any state;
void go(optional long delta);
void back();
void forward();
void pushState(any data, DOMString title, optional DOMString? url = null);
void replaceState(any data, DOMString title, optional DOMString? url = null);
};
pushState()将状态推入历史记录栈,同时改变浏览器url,浏览器并不会刷新,也不会触发onhashchange方法。replaceState()则会替换最新的历史记录window.onpopstate是popstate事件在window对象上的事件处理程序.每当处于激活状态的历史记录条目发生变化时,popstate事件就会在对应window对象上触发。
如果当前处于激活状态的历史记录条目是由pushState创建或者由replaceState方法修改过的, 则popstate事件对象的state属性包含了这个历史记录条目的state对象的一个拷贝。调用history.pushState()或者history.replaceState()不会触发popstate事件. popstate事件只会在浏览器某些行为下触发, 比如点击后退、前进按钮(或者在JavaScript中调用history.back()、history.forward()、history.go()方法)。
History具体实现
目前react项目的history均由history库实现,该库提供了三种history供router使用。
HashHistory
hashHistory的原理是利用html的锚点(#),通过改变location.hash去修改浏览器history。这种实现方式优势是实现和使用都比较简单,缺点是不够美观,服务器无法记录用户浏览路径。
BrowserHistory
browserHistory利用了H5 新增的history API去修改浏览器记录,其提供的push方法本质上等于history.pushState+notifiy(listeners)(通知Router重新渲染)。优点是美观,可以存储状态,服务器可以记录用户浏览路径。缺点是需要服务器配置支持,因为pathname的每一次改变都需要发请求,服务器如不做相应配置会报404错误
MemoryHistory
memoryHistory在内存中保存着自己的location数组。在创建memory history的时候你可以传入一些信息用于设置初始状态。这个状态包括:保存在数组中的位置信息以及当前位置在这个数组中的索引。通常用于非浏览器环境(node或native app)。
createHashHistory和createBrowserHistory都会返回一个封装后的history对象,这里的histroy不同于window.history,props.location也不同于window.location,例如网址www.abc.com/#/test, window.location.pathname为 ’ / ’ , props.location.pathname为 ’ /test’,这是由于createHashHistory为了统一使用方法内部做了处理。所以在代码中不要使用window.location来做路由判断,也不要使用window.history进行路由操作。
React router推荐使用browserHistory,如采用nginx服务器,则服务器需做如下针对性配置:
location / {
try_files $uri /index.html;
}
React Router
React router V4 分为react-router和react-router-dom包,react-router-dom依赖react-router,并提供了hashRouter,broserRouter,Link等组件,所以通常只需引入react-router-dom包即可。
React router实现原理
React router的核心是Router和Route两个React组件,工作原理是比较props.history.location.pathname和Route组件的path来选择渲染不同的组件。如果没有定制history的需求,直接使用hashRouter或browserRouter即可。实现原理如下图:
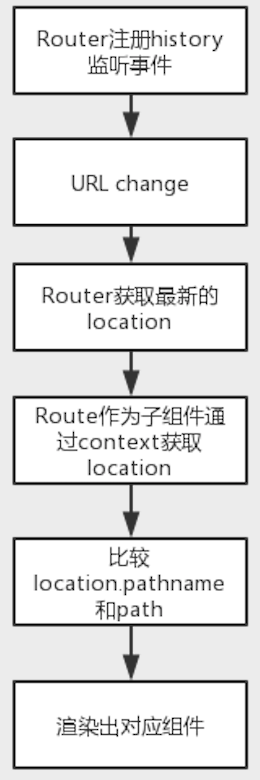
下面就Router和Route的代码具体分析:
Router源码
注册监听事件
this.unlisten = props.history.listen(location => {
if (this._isMounted) {
this.setState({ location });
} else {
this._pendingLocation = location;
}
});
由于路由组件可能在较深的层级,故将location通过context传递给Route组件
render() {
return (
<RouterContext.Provider
children={this.props.children || null}
value={{
history: this.props.history,
location: this.state.location,
match: Router.computeRootMatch(this.state.location.pathname),
staticContext: this.props.staticContext
}}
/>
);
}
Route
将从context中拿到的location与props中的path比较决定是否渲染该组件
render() {
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{context => {
invariant(context, "You should not use <Route> outside a <Router>");
const location = this.props.location || context.location;
const match = this.props.computedMatch
? this.props.computedMatch // <Switch> already computed the match for us
: this.props.path
? matchPath(location.pathname, this.props)
: context.match;
const props = { ...context, location, match };
let { children, component, render } = this.props;
// Preact uses an empty array as children by
// default, so use null if that's the case.
if (Array.isArray(children) && children.length === 0) {
children = null;
}
return (
<RouterContext.Provider value={props}>
{props.match
? children
? typeof children === "function"
? __DEV__
? evalChildrenDev(children, props, this.props.path)
: children(props)
: children
: component
? React.createElement(component, props)
: render
? render(props)
: null
: typeof children === "function"
? __DEV__
? evalChildrenDev(children, props, this.props.path)
: children(props)
: null}
</RouterContext.Provider>
);
}}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
);
}