原文链接heartbeat.fritz.ai/image-class…
最近,针对React Native和Expo应用程序的TensorFlow.js的alpha版本发布了。目前支持加载预先训练的模型并训练新模型,以下是公告推文:
TensorFlow.js提供了许多预训练的模型,这些模型简化了从头开始训练新机器学习模型的耗时任务。在本教程中,我们将探索TensorFlow.js和MobileNet预训练的模型架构,以对React Native移动应用程序中的输入图像进行分类。
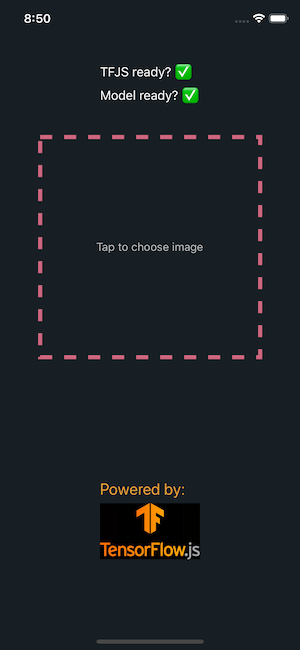
在本教程结束时,该应用程序将如下所示:
注:以前,我确实接触过Google的Vision API来构建图像分类应用程序,该应用程序可判定给定图像是否为热狗。如果您有兴趣阅读该示例,请点击以下链接:heartbeat.fritz.ai/build-a-not…
本文目录
- 环境准备
- 将TF.js集成到Expo应用程序中
- 测试TF.js集成
- 加载MobileNet模型
- 询问用户权限
- 将原始图像转换为张量
- 加载和分类图像
- 允许用户选择图像
- 运行应用
- 结论
完整代码链接:github.com/amandeepmit…
环境准备
- 本地环境
Nodejs >= 10.x.x expo-cli- 适用于
Android或iOS的Expo Client应用程序,用于测试该APP
将TF.js集成到Expo应用程序中
在React Native中使用TensorFlow库,第一步是集成平台适配器-- tfjs-react-native模块,支持从Web加载所有主要的tfjs模型。它还使用expo-gl提供了GPU支持。
打开终端窗口,并通过执行以下命令来创建新的Expo应用程序。
expo init mobilenet-tfjs-expo
接下来,请确保生成一个由Expo管理的应用程序。然后在app所在目录中安装以下依赖项:
yarn add @react-native-community/async-storage @tensorflow/tfjs @tensorflow/tfjs-react-native expo-gl @tensorflow-models/mobilenet jpeg-js
注:如果您想使用react-native-cli生成应用程序,则可以按照明确的说明来修改metro.config.js文件和其他必要步骤,如此处所述。
即便您使用了Expo,也仍然需要安装tfjs模块依赖的async-storage。
测试TF.js集成
我们需要确保在呈现应用程序之前将tfjs成功加载到应用程序中。这里有一个异步函数称为tf.ready()。打开App.js文件,导入必要的依赖项,并定义isTfReady初始状态为false。
import React from 'react'
import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native'
import * as tf from '@tensorflow/tfjs'
import { fetch } from '@tensorflow/tfjs-react-native'
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
isTfReady: false
}
async componentDidMount() {
await tf.ready()
this.setState({
isTfReady: true
})
//Output in Expo console
console.log(this.state.isTfReady)
}
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text>TFJS ready? {this.state.isTfReady ? <Text>Yes</Text> : ''}</Text>
</View>
)
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
alignItems: 'center',
justifyContent: 'center'
}
})
export default App
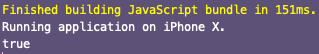
由于生命周期方法是异步的,因此仅在实际加载tfjs时才会将isTfReady的值更新为true。
您可以在模拟器设备中看到输出,如下所示。

加载MobileNet模块
与上一步骤类似,在提供输入图像之前,您还必须加载MobileNet模型。从Web上加载经过预先训练的TensorFlow.js模型是一个昂贵的网络调用,将花费大量时间。修改App.js文件以加载MobileNet模型。首先导入它:
import * as mobilenet from '@tensorflow-models/mobilenet'
添加初始状态其他的属性:
state = {
isTfReady: false,
isModelReady: false
}
修改生命周期方法:
async componentDidMount() {
await tf.ready()
this.setState({
isTfReady: true
})
this.model = await mobilenet.load()
this.setState({ isModelReady: true })
}
最后,当模型加载完成后,让我们在屏幕上显示一个指示器。
<Text>
Model ready?{' '}
{this.state.isModelReady ? <Text>Yes</Text> : <Text>Loading Model...</Text>}
</Text>
当模块加载时,会展示以下的信息:


询问用户权限
现在,平台适配器和模型都已集成在React Native应用程序中,我们需要添加一个异步功能,以请求用户的许可以访问相机。使用Expo的图像选择器组件构建iOS应用程序时,这是必不可少的步骤。
在继续之前,请运行以下命令以安装Expo SDK提供的所有软件包。
expo install expo-permissions expo-constants expo-image-picker
在APP.js中添加import声明
import Constants from 'expo-constants'
import * as Permissions from 'expo-permissions'
在APP类中添加方法:
getPermissionAsync = async () => {
if (Constants.platform.ios) {
const { status } = await Permissions.askAsync(Permissions.CAMERA_ROLL)
if (status !== 'granted') {
alert('Sorry, we need camera roll permissions to make this work!')
}
}
}
在componentDidMount()内部调用此异步方法:
async componentDidMount() {
await tf.ready()
this.setState({
isTfReady: true
})
this.model = await mobilenet.load()
this.setState({ isModelReady: true })
// add this
this.getPermissionAsync()
}
将原始图像转换为张量
该应用将要求用户从手机的相机或图库中上传图像。您必须添加一个方法来加载图像,并允许TensorFlow解码图像中的数据。 TensorFlow支持JPEG和PNG格式。
在App.js文件中,首先导入jpeg-js程序包,该程序包将用于解码图像中的数据。
import * as jpeg from 'jpeg-js'
方法imageToTensor解码图片的宽度,高度和二进制数据,该方法接受原始图像数据的参数。
imageToTensor(rawImageData) {
const TO_UINT8ARRAY = true
const { width, height, data } = jpeg.decode(rawImageData, TO_UINT8ARRAY)
// Drop the alpha channel info for mobilenet
const buffer = new Uint8Array(width * height * 3)
let offset = 0 // offset into original data
for (let i = 0; i < buffer.length; i += 3) {
buffer[i] = data[offset]
buffer[i + 1] = data[offset + 1]
buffer[i + 2] = data[offset + 2]
offset += 4
}
return tf.tensor3d(buffer, [height, width, 3])
}
TO_UINT8ARRAY数组表示8位无符号整数的数组。构造方法Uint8Array()是新的ES2017语法。对于不同的类型化数组,每种类型的数组在内存中都有其自己的字节范围。
加载和分类图像
接下来,我们添加另一个称为classifyImage的方法,该方法将从图像中读取原始数据,并在分类后以预测形式产生结果。
必须在应用程序组件的state中保存该图像源的路径,以便从源中读取图像。同样,也必须包括上述异步方法产生的结果。 这是最后一次修改App.js文件中的现有状态。
state = {
isTfReady: false,
isModelReady: false,
predictions: null,
image: null
}
添加异步方法:
classifyImage = async () => {
try {
const imageAssetPath = Image.resolveAssetSource(this.state.image)
const response = await fetch(imageAssetPath.uri, {}, { isBinary: true })
const rawImageData = await response.arrayBuffer()
const imageTensor = this.imageToTensor(rawImageData)
const predictions = await this.model.classify(imageTensor)
this.setState({ predictions })
console.log(predictions)
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
}
}
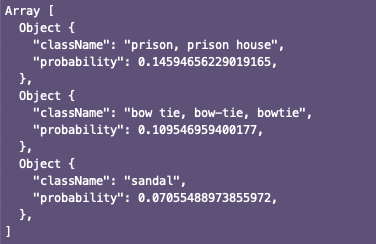
预训练模型的结果以数组形式产生。举例如下:
允许用户选择图像
从系统设备的相机中选择图像,需要使用expo-image-picker包提供的异步方法ImagePicker.launchImageLibraryAsync。导入包:
import * as Permissions from 'expo-permissions'
添加selectImage方法用于:
- 让用户选择图片
- 选择图像,在
state.image中填充源URI对象 - 最后,调用
classifyImage()方法根据给定的输入进行预测
selectImage = async () => {
try {
let response = await ImagePicker.launchImageLibraryAsync({
mediaTypes: ImagePicker.MediaTypeOptions.All,
allowsEditing: true,
aspect: [4, 3]
})
if (!response.cancelled) {
const source = { uri: response.uri }
this.setState({ image: source })
this.classifyImage()
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
}
}
包expo-image-picker返回一个对象。如果用户取消了选择图像的过程,则图像选择器模块将返回单个属性:canceled:true。如果成功,则图像选择器模块将返回属性,例如图像本身的uri。因此,上述片段中的if语句具有重要的意义。
运行应用
要完成此程序,需要在用户单击添加图像的位置添加不透明度。
这是App.js文件中render方法的完整代码段:
render() {
const { isTfReady, isModelReady, predictions, image } = this.state
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<StatusBar barStyle='light-content' />
<View style={styles.loadingContainer}>
<Text style={styles.commonTextStyles}>
TFJS ready? {isTfReady ? <Text>✅</Text> : ''}
</Text>
<View style={styles.loadingModelContainer}>
<Text style={styles.text}>Model ready? </Text>
{isModelReady ? (
<Text style={styles.text}>✅</Text>
) : (
<ActivityIndicator size='small' />
)}
</View>
</View>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.imageWrapper}
onPress={isModelReady ? this.selectImage : undefined}>
{image && <Image source={image} style={styles.imageContainer} />}
{isModelReady && !image && (
<Text style={styles.transparentText}>Tap to choose image</Text>
)}
</TouchableOpacity>
<View style={styles.predictionWrapper}>
{isModelReady && image && (
<Text style={styles.text}>
Predictions: {predictions ? '' : 'Predicting...'}
</Text>
)}
{isModelReady &&
predictions &&
predictions.map(p => this.renderPrediction(p))}
</View>
<View style={styles.footer}>
<Text style={styles.poweredBy}>Powered by:</Text>
<Image source={require('./assets/tfjs.jpg')} style={styles.tfLogo} />
</View>
</View>
)
}
}
完整的styles对象:
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#171f24',
alignItems: 'center'
},
loadingContainer: {
marginTop: 80,
justifyContent: 'center'
},
text: {
color: '#ffffff',
fontSize: 16
},
loadingModelContainer: {
flexDirection: 'row',
marginTop: 10
},
imageWrapper: {
width: 280,
height: 280,
padding: 10,
borderColor: '#cf667f',
borderWidth: 5,
borderStyle: 'dashed',
marginTop: 40,
marginBottom: 10,
position: 'relative',
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center'
},
imageContainer: {
width: 250,
height: 250,
position: 'absolute',
top: 10,
left: 10,
bottom: 10,
right: 10
},
predictionWrapper: {
height: 100,
width: '100%',
flexDirection: 'column',
alignItems: 'center'
},
transparentText: {
color: '#ffffff',
opacity: 0.7
},
footer: {
marginTop: 40
},
poweredBy: {
fontSize: 20,
color: '#e69e34',
marginBottom: 6
},
tfLogo: {
width: 125,
height: 70
}
})
从终端窗口执行expo start命令来运行此程序。您会注意到的第一件事是,在Expo客户端中引导应用程序后,它将要求权限。
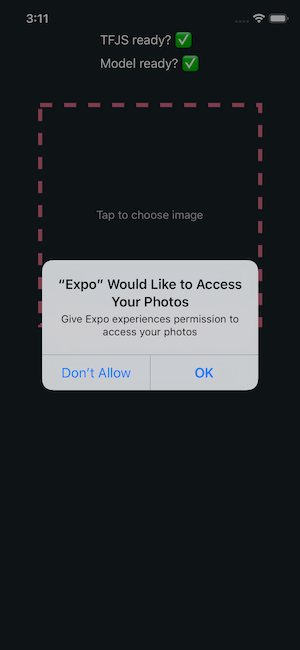
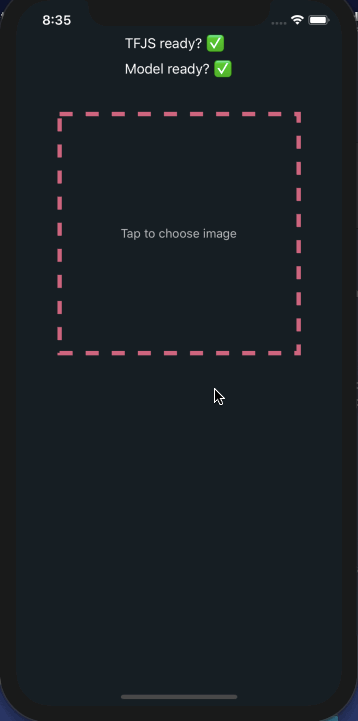

结论
这篇文章的目的是让您抢先了解如何在React Native应用中实现TesnorFlow.js模型,以及更好地理解图像分类,这是基于计算机视觉的机器学习的核心用例。
由于在撰写本文时,用于React Native的TF.js处于alpha版本,因此我们希望将来能看到更多更高级的示例来构建实时应用程序。
这里有一些我觉得非常有用的资源。
tfjs-react-native GitHub存储库,其中包含更多使用不同预训练模型的示例
Infinite Red的NSFW JS和React Native示例清晰明了,非常有帮助
Tensorflow.js简介