一.水平居中
将一个元素水平居中很简单,可以考虑以下几种情况
1. 当元素是inline或者inline-*元素(例如文本元素或者a元素)
当行内元素其父元素为块级元素时,可以在父元素上使用text-align属性使得元素水平居中。
css样式
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
background-color: #f06d06;
}
header{
text-align: center;
background-color: white;
margin-top: 20px;
}
nav{
background-color: white;
margin-top: 50px;
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
nav a{
text-decoration: none;
background-color: black;
}

text-align属性对于inline,inline-block,inline-table等元素都将起作用
2. 当元素为块级元素时
当你想要居中的元素为块级元素时,可以在该元素上将margin-left和margin-right设置为auto,元素通常设有一个宽度。当没有设置宽度时,元素默认是充满的,也就不需要设置水平居中了
css样式
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
background-color: #f06d06;
}
header{
background-color: white;
margin-top: 20px;
padding: 10px;
}
header p {
width: 100px;
padding: 20px;
background-color: skyblue;
margin: 0 auto;
}

二.垂直居中
1.当元素是inline或者inline-*元素(例如文本元素或者a元素),有且只有一行时。
1.1 可以将行内元素/文本元素的上下padding设置成相等即可。
css样式
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
background: #f06d06;
}
main {
background: white;
margin: 20px 0;
padding: 50px;
}
main a {
background: black;
color: white;
padding: 40px 0;
text-decoration: none;
}

1.2 当你的文本不需要换行(nowrap)时,可以将文本元素的父元素的height与line-hieght设置成一样,即可垂直居中文本。
css样式
main{
background-color: black;
}
main div{
background-color: skyblue;
height: 100px;
line-height: 100px;
white-space: nowrap;
}

2.当元素是inline或者inline-*元素(例如文本元素或者a元素),有多行时。
在这种情况你也可以设置上内边距和下内边距相等,但有时候包含文本的元素是table cell时将不会起作用。在这种情况下需要用到vertical-align属性,该属性用于行内元素在其父容器内的垂直对齐方式。
以下两种情况中第二种情况所设置的padding将不会起作用,需要用到vertical-align属性
body {
background: #f06d06;
}
table {
background: white;
width: 240px;
border-collapse: separate;
margin: 20px;
height: 250px;
}
table td {
background: black;
color: white;
padding: 20px;
border: 10px solid white;
/* 默认vertical-align为middle; */
}
.center-table {
display: table;
height: 250px;
background: white;
width: 240px;
margin: 20px;
}
.center-table p {
display: table-cell;
margin: 0;
background: black;
color: white;
padding: 20px;
border: 10px solid white;
vertical-align: middle;
}

3. 当元素为块级元素时
3.1 当元素为块级元素时,并且它的高度已知,那么只要在父元素上将上下padding都设置成父元素的高度减去子元素的高度的一半即可,并将父元素的盒模型设置成border-box即可。
css样式
.parent{
height: 250px;
box-sizing: border-box;
background-color: aqua;
/*padding的上下边距都设置成(250-100)/2即75px*/
padding: 75px 0;
}
.child{
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
}
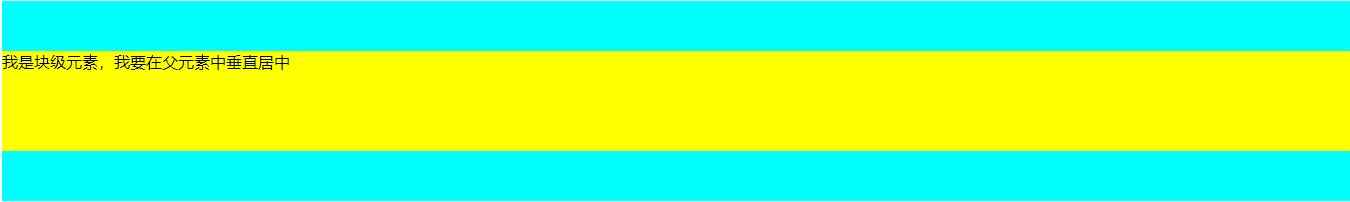
3.2 当元素为块级元素时,并且它的高度知道,也可以使用以下方法。
css样式
.parent{
height: 300px;
background-color: aqua;
position: relative;
}
.parent .child{
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -50px;
/* 或者使用transform: translateY(-50%); */
}

3.3 当元素为块级元素时,并且它的高度不知道,在元素上使用translate来代替margin。下列结果与上述例子一样。
css样式
.parent{
height: 300px;
background-color: aqua;
position: relative;
}
.parent .child{
background-color: yellow;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
或者使用transform: translateY(-50%);
}
3.4 可以在父元素上使用flexbox
css样式
.parent{
background-color: aqua;
height: 200px;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.child{
background-color: yellow;
}

三.垂直水平居中
1.当元素的宽高确定时
.parent{
height: 200px;
background-color: brown;
position: relative;
}
.child{
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: aqua;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
/* margin设置为宽高的一半 */
margin-left: -100px;
margin-top: -50px;
}

2.当元素的宽高不确定时,元素身上使用translate的百分比形式,百分比形式是基于元素自身的宽高的,以此来代替上述例子中的margin。
.parent{
height: 200px;
background-color: brown;
position: relative;
}
.child{
background-color: aqua;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
}

3.在元素的父元素使用flexbox
.parent{
height: 200px;
background-color: brown;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.child{
background-color: aqua;
}
