Javassist基础
Javassist是一个操作Java字节码的类库,它可以在一个已经编译好的类中添加新的方法,或者是修改已有的方法,并且不需要对字节码有深入的了解。它可以绕过编译,直接操作字节码,实现代码注入。使用它的最佳时机就是在构建工具gradle将源文件编译成.class之后,再将.class打包成.dex之前。
- 读写字节码:一个Javassist.CtClass表示一个.class文件,所以他就是处理.class的关键。
- 对象的获取:通过ClassPool.getClass(className)或者是ClassPool.get(class全路径)。这里的classPool它是CtClass的容器,内部是一个hash表,类名作为hash表的key,classPool对象一般通过ClassPool.getDefault()来获取,这里使用的是JVM的类搜索路径。如果想要添加额外的类搜索路径可以通过pool.insert方法添加,比如pool.insertClassPath("user/local/lib"),则将“user/local/lib”添加到搜索路径中
- 冻结类:一个类只能被JVM加载一次,所以如果要修改类的话要对其进行解冻,利用ctClass.defrost(),这样就可以对类进行修改了,解冻之前一般都会判断是否被冻住了(ctClass.isFrozen())
- 保存和释放:如果对一个类修改了,那么就要对其进行保存,使用的是ctClass.writeFIle(path)。一般为了避免内存溢出(CtClass对象过多导致),一般在修改保存后,手动对该对象进行删除(ctClass.detach())
- ctClass中的重要方法:getName(),getAnnotations(),getDeclaredMethod(),getField(),getInterfaces(),getDeclaredConstruct()
- 在方法体中插入代码:也就通过ctClass.getDeclaredMethod()方法中返回的方法ctMethod,调用insertBefore(),insertAfter()和addCatch()方法,把代码片段插入到方法体中。上面的三个方法都能接收一个表示语句或者语句块的String对象。所以这里的$是有特殊含义的。$0表示this,$1,$2等表示第一个,第二个参数等
无痕埋点的实现细节
同样它也需要定义plugin,它与aspectJ一样需要引入操作的框架
apply plugin: 'groovy'
apply plugin: 'maven'
dependencies {
compile gradleApi()
compile localGroovy()
compile 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.1.4'
compile 'org.javassist:javassist:3.20.0-GA'
}
repositories {
jcenter()
}
uploadArchives {
repositories.mavenDeployer {
//本地仓库路径,以放到项目根目录下的 repo 的文件夹为例
repository(url: uri('../repo'))
//groupId ,自行定义
pom.groupId = 'com.sensorsdata'
//artifactId
pom.artifactId = 'autotrack.android'
//插件版本号
pom.version = '1.0.0'
}
}
这里的transform具体代码为
class SensorsAnalyticsTransform extends Transform {
private static Project project
SensorsAnalyticsTransform(Project project) {
this.project = project
}
@Override
String getName() {
return "SensorsAnalyticsAutoTrack"
}
/**
* 需要处理的数据类型,有两种枚举类型
* CLASSES 代表处理的 java 的 class 文件,RESOURCES 代表要处理 java 的资源
* @return
*/
@Override
Set<QualifiedContent.ContentType> getInputTypes() {
return TransformManager.CONTENT_CLASS
}
/**
* 指 Transform 要操作内容的范围,官方文档 Scope 有 7 种类型:
* 1. EXTERNAL_LIBRARIES 只有外部库
* 2. PROJECT 只有项目内容
* 3. PROJECT_LOCAL_DEPS 只有项目的本地依赖(本地jar)
* 4. PROVIDED_ONLY 只提供本地或远程依赖项
* 5. SUB_PROJECTS 只有子项目。
* 6. SUB_PROJECTS_LOCAL_DEPS 只有子项目的本地依赖项(本地jar)。
* 7. TESTED_CODE 由当前变量(包括依赖项)测试的代码
* @return
*/
@Override
Set<QualifiedContent.Scope> getScopes() {
return TransformManager.SCOPE_FULL_PROJECT
}
@Override
boolean isIncremental() {
return false
}
@Override
void transform(Context context, Collection<TransformInput> inputs, Collection<TransformInput> referencedInputs, TransformOutputProvider outputProvider, boolean isIncremental) throws IOException, TransformException, InterruptedException {
if (!incremental) {
outputProvider.deleteAll()
}
/**Transform 的 inputs 有两种类型,一种是目录,一种是 jar 包,要分开遍历 */
inputs.each { TransformInput input ->
/**遍历 jar*/
input.jarInputs.each { JarInput jarInput ->
/**重命名输出文件(同目录copyFile会冲突)*/
String destName = jarInput.file.name
/**截取文件路径的 md5 值重命名输出文件,因为可能同名,会覆盖*/
def hexName = DigestUtils.md5Hex(jarInput.file.absolutePath).substring(0, 8)
/** 获取 jar 名字*/
if (destName.endsWith(".jar")) {
destName = destName.substring(0, destName.length() - 4)
}
File copyJarFile = SensorsAnalyticsInject.injectJar(jarInput.file.absolutePath, project)
def dest = outputProvider.getContentLocation(destName + hexName, jarInput.contentTypes, jarInput.scopes, Format.JAR)
FileUtils.copyFile(copyJarFile, dest)
context.getTemporaryDir().deleteDir()
}
/**遍历目录*/
input.directoryInputs.each { DirectoryInput directoryInput ->
SensorsAnalyticsInject.injectDir(directoryInput.file.absolutePath, project)
def dest = outputProvider.getContentLocation(directoryInput.name,
directoryInput.contentTypes, directoryInput.scopes, Format.DIRECTORY)
/**将input的目录复制到output指定目录*/
FileUtils.copyDirectory(directoryInput.file, dest)
}
}
}
}
这里重点就是SensorsAnalyticsInject.injectJar()和SensorsAnalyticsInject.injectDir,也就是对dir和jar的处理。injectDir其实就是遍历,执行injectClass
private static void injectClass(File classFile, String path) {
String filePath = classFile.absolutePath
if (!filePath.endsWith(".class")) {
return
}
if (!filePath.contains('R$')
&& !filePath.contains('R2$')
&& !filePath.contains('R.class')
&& !filePath.contains('R2.class')
&& !filePath.contains("BuildConfig.class")) {
int index = filePath.indexOf(path)
String className = filePath.substring(index + path.length() + 1, filePath.length() - 6).replaceAll("/", ".")
if (!className.startsWith("android")) {
try {
CtClass ctClass = pool.getCtClass(className)
//解冻
if (ctClass.isFrozen()) {
ctClass.defrost()
}
boolean modified = false
CtClass[] interfaces = ctClass.getInterfaces()
if (interfaces != null) {
Set<String> interfaceList = new HashSet<>()
for (CtClass c1 : interfaces) {
interfaceList.add(c1.getName())
}
for (CtMethod currentMethod : ctClass.getDeclaredMethods()) {
MethodInfo methodInfo = currentMethod.getMethodInfo()
AnnotationsAttribute attribute = (AnnotationsAttribute) methodInfo
.getAttribute(AnnotationsAttribute.visibleTag)
if (attribute != null) {
for (Annotation annotation : attribute.annotations) {
if ("@com.sensorsdata.analytics.android.sdk.SensorsDataTrackViewOnClick" == annotation.toString()) {
if ('(Landroid/view/View;)V' == currentMethod.getSignature()) {
currentMethod.insertAfter(SDK_HELPER + ".trackViewOnClick(\$1);")
modified = true
break
}
}
}
}
String methodSignature = currentMethod.name + currentMethod.getSignature()
if ('onContextItemSelected(Landroid/view/MenuItem;)Z' == methodSignature) {
currentMethod.insertAfter(SDK_HELPER + ".trackViewOnClick(\$0,\$1);")
modified = true
} else if ('onOptionsItemSelected(Landroid/view/MenuItem;)Z' == methodSignature) {
currentMethod.insertAfter(SDK_HELPER + ".trackViewOnClick(\$0,\$1);")
modified = true
} else {
SensorsAnalyticsMethodCell methodCell = SensorsAnalyticsConfig.isMatched(interfaceList, methodSignature)
if (methodCell != null) {
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer()
stringBuffer.append(SDK_HELPER)
stringBuffer.append(".trackViewOnClick(")
for (int i = methodCell.getParamStart(); i < methodCell.getParamStart() + methodCell.getParamCount(); i++) {
stringBuffer.append("\$")
stringBuffer.append(i)
if (i != (methodCell.getParamStart() + methodCell.getParamCount() - 1)) {
stringBuffer.append(",")
}
}
stringBuffer.append(");")
currentMethod.insertAfter(stringBuffer.toString())
modified = true
}
}
}
}
if (modified) {
ctClass.writeFile(path)
ctClass.detach()//释放
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
}
}
}
其实上面做的事无非就是以下几件: 1:排除一些不需要处理的类比如R.class 2:获取类所实现的所有接口 3:如果实现了某些接口,遍历类中的所有方法 4:如果方法的signature与当前的一致(如onContextItemSelected(Landroid/view/MenuItem;)Z)或者添加了某个注解,那么就执行insertAfter(XXX)代码,当然XXX是定义好的 5:如果修改了文件就保存和释放
剩下的则是定义plugin和生成resource文件,此处省略。
属性值的传递,注解值的获取
首先依然是定义plugin和transform,其代码与上面是一样的,这两步就忽略了,主要看操作字节码的过程 这里首先是像某个特定方法中插入代码,比如有个方法为public void test(),那么在获取到ctClass后,遍历它的所有方法,然后通过方法名字和signature来确定是否是这个方法
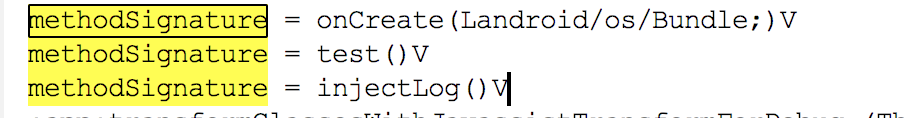
String methodSignature = currentMethod.name + currentMethod.getSignature()
System.out.println("methodSignature = " + methodSignature)
if ('test()V' == methodSignature) {
currentMethod.insertAfter(SDK_HELPER + ".injectLog();")
modified = true
}
其中MainActivity中的代码为
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
test();
}
public void test() {
Log.e("tag", "这是一个测试方法");
}
}
打点的helper代码为
public class InjectMethodHelper {
public static void injectLog() {
Log.e("tag", "这是插入的一段打点代码");
}
public static void injectAnnotationLog(String id, String value) {
Log.e("Tag", "这是插入的一段注解打点代码===>>id====>>" + id + "=====>>value====>>" + value);
}
}
在build的时候就可以看到log
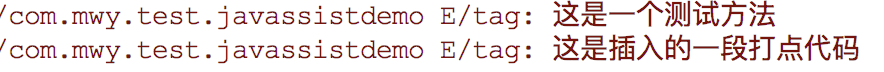
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AnnotationTest {
String id();
String value();
}
在mainActivity中声明一个方法,并且在onCreate中调用
@AnnotationTest(id = "idNo.1", value = "valueNo.1")
public void testAnnotation() {
Log.e("tag", "这是一个有注解的方法");
}
那么在处理字节码时就需要处理注解,其处理过程如下
for (CtMethod currentMethod : ctClass.getDeclaredMethods()) {
//拿到所有注解
Object[] annotations = currentMethod.getAnnotations()
if (annotations != null && annotations.length > 0) {
MethodInfo methodInfo = currentMethod.getMethodInfo()
AnnotationsAttribute attribute = (AnnotationsAttribute) methodInfo.getAttribute(AnnotationsAttribute.visibleTag)
//拿到所需要的注解
Annotation annotation = attribute.getAnnotation(ANNOTATION_HELPER)
if (annotation != null) {
//注解中定义的值的名字
def names = annotation.getMemberNames()
//拿到注解的值
String id = annotation.getMemberValue("id")
String values = annotation.getMemberValue("value")
//打印log,这个会在build的时候就能打印
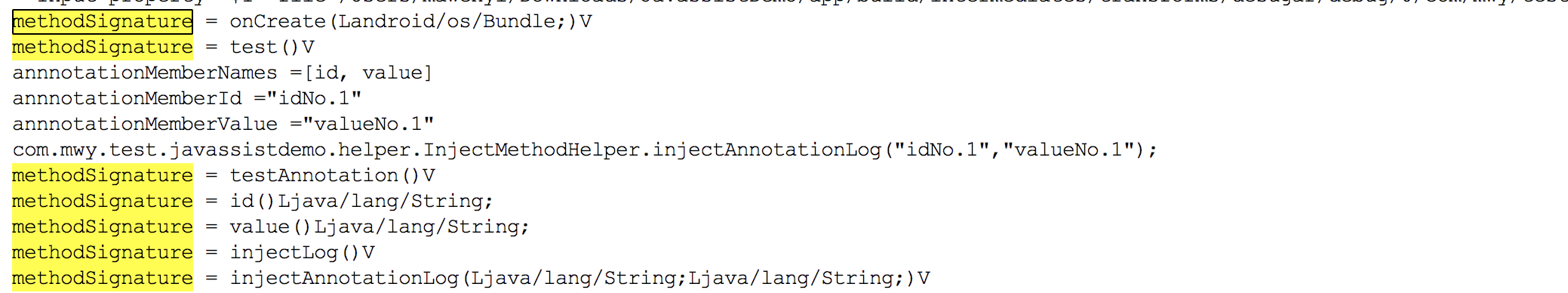
System.out.println("annnotationMemberNames =" + names.toString())
System.out.println("annnotationMemberId =" + id)
System.out.println("annnotationMemberValue =" + values)
//将得到的值传给某个方法时要采用${value}这种形式,而且像insertXXX方法中传递的时候也要用StringBuilder
//如果用String+string的方式会报编译错误
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer()
stringBuffer.append(SDK_HELPER)
stringBuffer.append(".injectAnnotationLog(")
stringBuffer.append("${id}")
stringBuffer.append(",")
stringBuffer.append("${values}")
stringBuffer.append(");")
System.out.println(stringBuffer.toString())
currentMethod.insertAfter(stringBuffer.toString())
modified = true
}
}
String methodSignature = currentMethod.name + currentMethod.getSignature()
System.out.println("methodSignature = " + methodSignature)
if ('test()V' == methodSignature) {
currentMethod.insertAfter(SDK_HELPER + ".injectLog();")
modified = true
}
}
上面的注释已经很明白了,即通过MethodInfo拿到所有运行时注解Attribute,然后利用这个attribute拿到指定的Annotation,通过getMemberValue就可以获取到指定注解的值,这里直接写死了,如果不写死,那么就通过getMemberNames来获取直接的名字,然后利用这里的名字取出注解的值。值得注意的是这里的insertAfter方法,传入的是利用StringBuilder创建的一个String,原因在于这里需要将刚才获取到的属性值传递给固定的方法,如果采用String+String的方式的话,编译器会报错。 这时候我们可以看一下build的过程中打印log

private static void injectClass(File classFile, String path) {
String filePath = classFile.absolutePath
if (!filePath.endsWith(".class")) {
return
}
if (!filePath.contains('R$')
&& !filePath.contains('R2$')
&& !filePath.contains('R.class')
&& !filePath.contains('R2.class')
&& !filePath.contains("BuildConfig.class")) {
int index = filePath.indexOf(path)
String className = filePath.substring(index + path.length() + 1, filePath.length() - 6).replaceAll("/", ".")
if (!className.startsWith("android")) {
try {
CtClass ctClass = pool.getCtClass(className)
//解冻
if (ctClass.isFrozen()) {
ctClass.defrost()
}
boolean modified = false
for (CtMethod currentMethod : ctClass.getDeclaredMethods()) {
//拿到所有注解
Object[] annotations = currentMethod.getAnnotations()
if (annotations != null && annotations.length > 0) {
MethodInfo methodInfo = currentMethod.getMethodInfo()
AnnotationsAttribute attribute = (AnnotationsAttribute) methodInfo.getAttribute(AnnotationsAttribute.visibleTag)
//拿到所需要的注解
Annotation annotation = attribute.getAnnotation(ANNOTATION_HELPER)
if (annotation != null) {
//注解中定义的值的名字
def names = annotation.getMemberNames()
//拿到注解的值
String id = annotation.getMemberValue("id")
String values = annotation.getMemberValue("value")
//打印log,这个会在build的时候就能打印
System.out.println("annnotationMemberNames =" + names.toString())
System.out.println("annnotationMemberId =" + id)
System.out.println("annnotationMemberValue =" + values)
//将得到的值传给某个方法时要采用${value}这种形式,而且像insertXXX方法中传递的时候也要用StringBuilder
//如果用String+string的方式会报编译错误
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer()
stringBuffer.append(SDK_HELPER)
stringBuffer.append(".injectAnnotationLog(")
stringBuffer.append("${id}")
stringBuffer.append(",")
stringBuffer.append("${values}")
stringBuffer.append(");")
System.out.println(stringBuffer.toString())
currentMethod.insertAfter(stringBuffer.toString())
modified = true
}
}
String methodSignature = currentMethod.name + currentMethod.getSignature()
System.out.println("methodSignature = " + methodSignature)
if ('test()V' == methodSignature) {
currentMethod.insertAfter(SDK_HELPER + ".injectLog();")
modified = true
}
}
if (modified) {
ctClass.writeFile(path)
ctClass.detach()//释放
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace()
}
}
}
}