定时任务schedule
什么是定时任务
- 某个时间定时处理某个任务
- 发邮件、短信等
- 消息提醒
- 订单通知
- 统计报表系统
常见的定时任务
- Java⾃带的java.util.Timer类配置⽐较麻烦,有时间延后问题
- Quartz框架: 配置更简单,xml或者注解适合分布式或者⼤型调度作业
- SpringBoot框架⾃带
springboot使用注解方式开启定时任务的例子
- 启动类⾥⾯ @EnableScheduling开启定时任务,⾃动扫描
- 定时任务业务类 加注解 @Component被容器扫描
- 定时执⾏的⽅法加上注解 @Scheduled(fixedRate=2000) 定期执⾏⼀次
简单实现
@Component
class TimeTask {
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 2500)
public void sum(){
System.out.println("当前时间"+new Date());
}
}
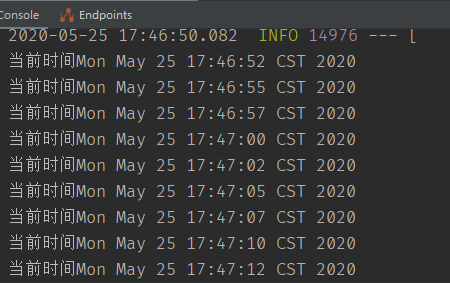
启动项目,看到每2秒打印一次信息
cron 定时任务表达式 @Scheduled(cron="*/1 * * * * *") 表示每秒,crontab ⼯具 tool.lu/crontab/ fixedRate: 定时多久执⾏⼀次(上⼀次开始执⾏时间点后xx秒再次执⾏;) fixedDelay: 上⼀次执⾏结束时间点后xx秒再次执⾏
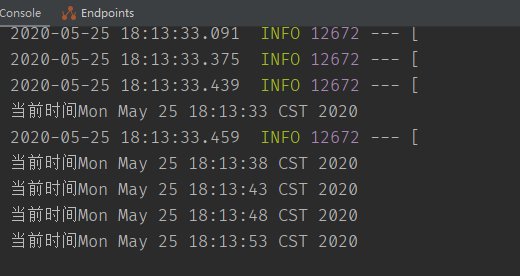
使用fixedDelay
@Component
class TimeTask {
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 2500)
public void sum(){
try {
System.out.println("当前时间"+new Date());
Thread.sleep(2500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
可以看到变成5秒执行一次
异步任务
什么是异步任务
想吃泡面了,在烧水的时候,同时能把泡面包装拆掉。即多个任务同时进行 适⽤于处理log、发送邮件、短信……等
- 下单接⼝->查库存 1000
- 余额校验 1500
- ⻛控⽤户1000
启动类⾥⾯使⽤@EnableAsync注解开启功能,⾃动扫描
定义异步任务类并使⽤@Component标记组件被容器扫描,异步⽅法加上@Async
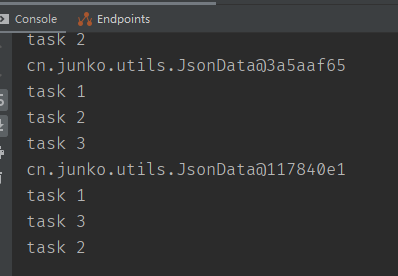
简单演示
编写异步方法,启动类⾥⾯使⽤@EnableAsync注解开启功能
@Component
@Async
public class AsyncTask {
public void task1(){
try {
Thread.sleep(4000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("task 1");
}
public void task2(){
try {
Thread.sleep(4000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("task 2");
}
public void task3(){
try {
Thread.sleep(4000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("task 3");
}
}
在controller调用
@RequestMapping("async")
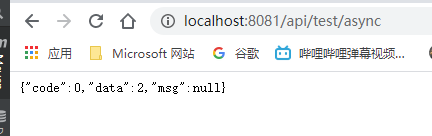
public JsonData testAsync(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
asyncTask.task1();
asyncTask.task2();
asyncTask.task3();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
return JsonData.buildSuccess(end-start);
}
可以看到方法的打印是随机的并且同时完成,而非等待4s轮流调用
异步任务Future获取结果
定义异步任务类获取结果
要把异步任务封装到类⾥⾯,不能直接写到Controller 增加Future 返回结果 AsyncResult("task执⾏完成"); 如果需要拿到结果 需要判断全部的 task.isDone()
在之前的异步代码中添加
public Future<String> task4(){
try {
Thread.sleep(4000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new AsyncResult<String>("task4");
}
public Future<String> task5(){
try {
Thread.sleep(4000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new AsyncResult<String>("task5");
}
然后进行判断调用
@RequestMapping("future")
public JsonData testAsyncFuture(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Future<String> task4 = asyncTask.task4();
Future<String> task5 = asyncTask.task5();
System.out.println(task4+">>>and<<<"+task5);
while (true){
if (task4.isDone() && task5.isDone()){
try {
String s = task4.get()+"<<<>>>"+task5.get();
System.out.println(s);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
break;
}
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
return JsonData.buildSuccess(end-start);
}