spring ioc 源码分析
1.起步
XmlBeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("test.xml"));
2.ClassPathResource 源码
ClassPathResource 类的关系

核心构造方法
// String cleanPath(String path):
// 清理文件路径,这个方法配合applyRelativePath就可以计算一些简单的相对路径了
//d:/java/wolfcode/../other/Some.java
// 打印:d:/java/other/Some.java
public ClassPathResource(String path, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
String pathToUse = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
if (pathToUse.startsWith("/")) {
pathToUse = pathToUse.substring(1);
}
this.path = pathToUse;
this.classLoader = (classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
3.XmlBeanFactory分析
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {
//看 XmlBeanDefinitionReader的构造 需要传入一个AliasRegistry类型的
//DefaultListableBeanFactory 实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口 而它继承了
//AliasRegistry接口 传入this 设置XmlBeanDefinitionReader 内属性 BeanDefinitionRegistry
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
}
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
}
看类图一目了然
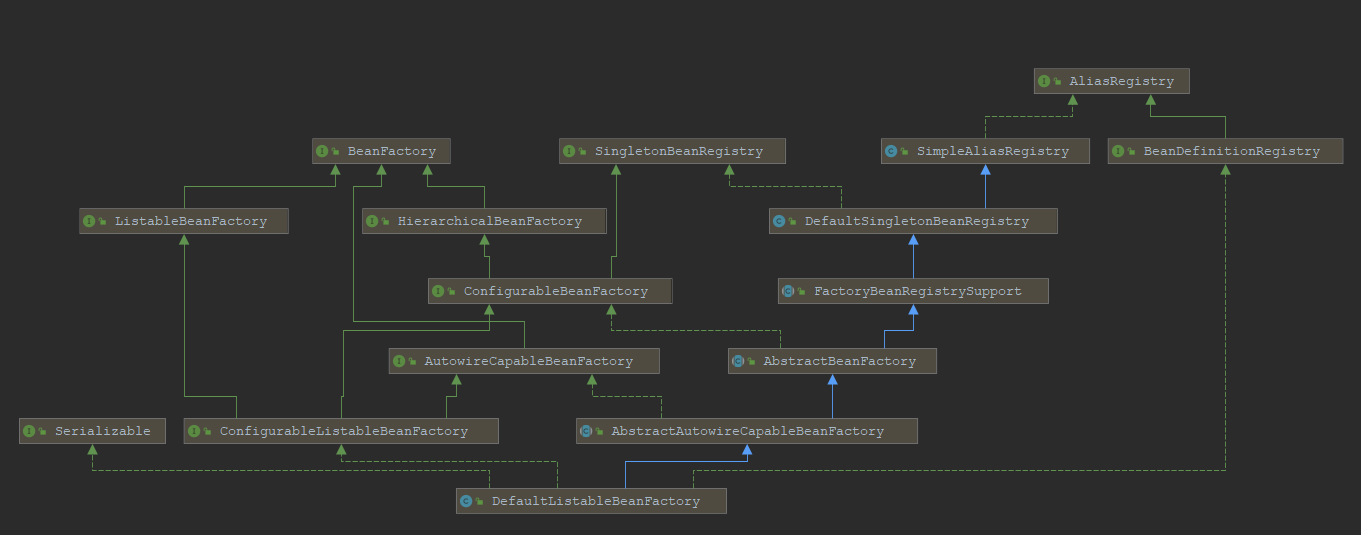
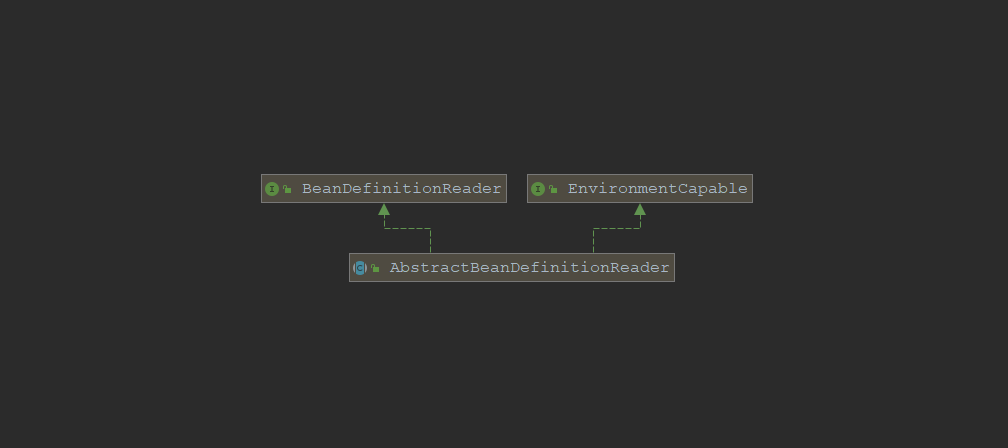
进入loadBeanDefinitions方法
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
发现调用的另一个重载的方法
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
//首先从本地的local取 encodedResource如果存在直接取出 不需要重新设置
//为了线程能使用同一个 currentResources
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
//这里就是防止文件的重复加载 这里要知道set集合的特性
//如果Set集合中不包含要添加的对象,则添加对象并返回true;否则返回false
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
进入关键方法 doLoadBeanDefinitions
//这里面就是SAX解析 转换成document对象
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
//注册BeanDefinition
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
来看看registerBeanDefinition方法
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//创建一个解析器
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
//起始的beanDefinitionMap BeanDefinition数量
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
//交给BeanDefinitionDocumentReader去注册BeanDefinition
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
接着点进去看方法 这里面光注册就使用了两个方法第一个方法将Document 转成Element 并设置属性readerContext doRegisterBeanDefinitions就是做注册BeanDefinition的事情 spring中许多方法都是这样 核心逻辑都是用一个方法去写,看着比较清楚
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
//获取delegate,看看有没有委托的reader(默认一般是没有的)
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
//创建BeanDefinitionParserDelegate,赋值给delegate
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
//判断根节点是不是默认命名空间,如果是,获取应用环境
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
//判断这个节点的应用环境是不是符合要求,比如是不是生产环境,如果不是,则不解析这个root节点下的内容
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
//模板模式 使用者可以自己扩展
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
进入parseBeanDefinitions方法
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//判断根节点是不是默认命名空间
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
//默认标签解析
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
//自定义标签解析
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//import标签
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
//alias标签
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
//bean标签
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
4.import标签
进入importBeanDefinitionResource 方法
protected void importBeanDefinitionResource(Element ele) {
// 获取 resource 的属性值
String location = ele.getAttribute(RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTE);
// 为空,直接退出
if (!StringUtils.hasText(location)) {
getReaderContext().error("Resource location must not be empty", ele);
return;
}
//解析系统属性,格式如 :"${user.dir}"
location = getReaderContext().getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(location);
Set<Resource> actualResources = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
// 判断 location 是相对路径还是绝对路径
boolean absoluteLocation = false;
try {
absoluteLocation = ResourcePatternUtils.isUrl(location) || ResourceUtils.toURI(location).isAbsolute();
}
catch (URISyntaxException ex) {
// cannot convert to an URI, considering the location relative
// unless it is the well-known Spring prefix "classpath*:"
}
// 绝对路径
if (absoluteLocation) {
try {
// 直接根据地址加载相应的配置文件
int importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(location, actualResources);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]");
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error(
"Failed to import bean definitions from URL location [" + location + "]", ele, ex);
}
}
else {
//相对路径则根据相应的地质计算出绝对路径地址
try {
int importCount;
Resource relativeResource = getReaderContext().getResource().createRelative(location);
if (relativeResource.exists()) {
//解析引入的配置文件
importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(relativeResource);
actualResources.add(relativeResource);
}
else {
String baseLocation = getReaderContext().getResource().getURL().toString();
importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(
StringUtils.applyRelativePath(baseLocation, location), actualResources);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Imported " + importCount + " bean definitions from relative location [" + location + "]");
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to resolve current resource location", ele, ex);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to import bean definitions from relative location [" + location + "]",
ele, ex);
}
}
// 解析成功后,进行监听器激活处理
Resource[] actResArray = actualResources.toArray(new Resource[0]);
getReaderContext().fireImportProcessed(location, actResArray, extractSource(ele));
}
5.alias标签
protected void processAliasRegistration(Element ele) {
//获取beanName
String name = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
//获取alias
String alias = ele.getAttribute(ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean valid = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
getReaderContext().error("Name must not be empty", ele);
valid = false;
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(alias)) {
getReaderContext().error("Alias must not be empty", ele);
valid = false;
}
if (valid) {
try {
// 注册alias
getReaderContext().getRegistry().registerAlias(name, alias);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register alias '" + alias +
"' for bean with name '" + name + "'", ele, ex);
}
//注册别之后通知监所器 相应的处理
getReaderContext().fireAliasRegistered(name, alias, extractSource(ele));
}
}
//aliasMap 从别名映射到规范名称
public void registerAlias(String name, String alias) {
Assert.hasText(name, "'name' must not be empty");
Assert.hasText(alias, "'alias' must not be empty");
synchronized (this.aliasMap) {
//如果beanName与alias相同的话不记录alias,并删除对应的alias
if (alias.equals(name)) {
this.aliasMap.remove(alias);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Alias definition '" + alias + "' ignored since it points to same name");
}
}
else {
String registeredName = this.aliasMap.get(alias);
if (registeredName != null) {
if (registeredName.equals(name)) {
// An existing alias - no need to re-register
return;
}
//如果alias不允许被覆盖则抛出异常
if (!allowAliasOverriding()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot define alias '" + alias + "' for name '" +
name + "': It is already registered for name '" + registeredName + "'.");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding alias '" + alias + "' definition for registered name '" +
registeredName + "' with new target name '" + name + "'");
}
}
//当A->B存在时,若再次出现A->B->C时候则会抛出异常
checkForAliasCircle(name, alias);
this.aliasMap.put(alias, name);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Alias definition '" + alias + "' registered for name '" + name + "'");
}
}
}
}