第三章 自定义MyBatis框架
3.1.自定义MyBatis
3.1.1.自定义的目的
自定义MyBatis是为了深入了解MyBatis的原理
3.1.2.主要调用
public class MyBatisTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.读取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2.创建SqlSessionFactory工厂
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(in);
//3.使用工厂生产SqlSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//4.使用SQLSession创建Dao接口的代理对象
UserDao userDao = session.getMapper(UserDao.class);
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
List<User> users = userDao.findAll();
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
//6.释放资源
session.close();
in.close();
}
}
3.1.3.第一步:将配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml转为流文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration>
<configuration>
<!--配置环境-->
<environments default="mysql">
<!--配置mysql的环境-->
<environment id="mysql">
<!--配置事务类型-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!--配置数据源(连接池)-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--配置连接数据库的基本信息-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="1234"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!--指定映射配置文件的位置,映射配置文件指的是每个dao独立的配置文件-->
<!--<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/wzm/dao/UserDao.xml"/>
</mappers>-->
<!--如果是用注解来配置-->
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.wzm.dao.UserDao"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
3.1.4.第二步:使用类加载器读取配置文件的类
public class Resources {
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String filePath) {
return Resources.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(filePath);
}
}
3.1.5.第三步:解析配置文件
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream config) {
Configuration cfg = XMLConfigBuilder.loadConfiguration(config);
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(cfg);
}
}
//主要是通过反射将属性值保存到map中
public class XMLConfigBuilder {
public static Configuration loadConfiguration(InputStream config) {
Configuration cfg = new Configuration();
try {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(config);
Element root = document.getRootElement();
List<Element> propertyElements = root.selectNodes("//property");
for (Element propertyElement : propertyElements) {
String name = propertyElement.attributeValue("name");
if ("driver".equals(name)) {
String driver = propertyElement.attributeValue("value");
cfg.setDriver(driver);
}
if ("url".equals(name)) {
String url = propertyElement.attributeValue("value");
cfg.setUrl(url);
}
if ("username".equals(name)) {
String username = propertyElement.attributeValue("value");
cfg.setUsername(username);
}
if ("password".equals(name)) {
String password = propertyElement.attributeValue("value");
cfg.setPassword(password);
}
}
List<Element> mapperElements = root.selectNodes("//mappers/mapper");
for (Element mapperElement : mapperElements) {
Attribute attribute = mapperElement.attribute("resource");
if (attribute != null) {
System.out.println("使用的是XML");
String mapperPath = attribute.getValue();
Map<String, Mapper> mappers = loadMapperConfiguration(mapperPath);
cfg.setMappers(mappers);
} else {
System.out.println("使用的是注解");
String daoClassPath = mapperElement.attributeValue("class");
Map<String, Mapper> mappers = loadMapperAnnotation(daoClassPath);
cfg.setMappers(mappers);
}
}
return cfg;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
config.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return cfg;
}
private static Map<String, Mapper> loadMapperConfiguration(String mapperPath) throws IOException {
InputStream in = null;
Map<String, Mapper> mappers = new HashMap<String, Mapper>();
try {
in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(mapperPath);
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(in);
Element root = document.getRootElement();
String namespace = root.attributeValue("namespace");
List<Element> selectElements = root.selectNodes("//select");
for (Element selectElement : selectElements) {
String id = selectElement.attributeValue("id");
String resultType = selectElement.attributeValue("resultType");
String queryString = selectElement.getText();
String key = namespace + "." + id;
Mapper mapper = new Mapper();
mapper.setQueryString(queryString);
mapper.setResultType(resultType);
mappers.put(key, mapper);
}
return mappers;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return mappers;
}
private static Map<String, Mapper> loadMapperAnnotation(String daoClassPath) throws Exception {
Map<String, Mapper> mappers = new HashMap<String, Mapper>();
Class daoClass = Class.forName(daoClassPath);
Method[] methods = daoClass.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
boolean isAnnotated = method.isAnnotationPresent(Select.class);
if (isAnnotated) {
Mapper mapper = new Mapper();
Select selectAnno = method.getAnnotation(Select.class);
String queryString = selectAnno.value();
mapper.setQueryString(queryString);
Type type = method.getGenericReturnType();
if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {
ParameterizedType ptype = (ParameterizedType) type;
Type[] types = ptype.getActualTypeArguments();
Class domainClass = (Class) types[0];
String resultType = domainClass.getName();
mapper.setResultType(resultType);
}
String methodName = method.getName();
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
String key = className + "." + methodName;
mappers.put(key, mapper);
}
}
return mappers;
}
}
3.1.6.第四步:DefaultSqlSessionFactory工厂生产出DefaultSqlSession对象
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private Configuration cfg;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration cfg) {
this.cfg = cfg;
}
public SqlSession openSession() {
return new DefaultSqlSession(cfg);
}
}
3.1.7.第五步:DefaultSqlSession执行动态代理
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Configuration cfg;
private Connection connection;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration cfg) {
this.cfg = cfg;
this.connection = DataSourceUtil.getConnection(cfg);
}
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> daoInterfaceClass) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(daoInterfaceClass.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{daoInterfaceClass}, new MapperProxy(cfg.getMappers(), connection));
}
public void close() {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.1.8.第六步:执行sql语句
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler {
private Map<String, Mapper> mappers;
private Connection connection;
public MapperProxy(Map<String, Mapper> mappers, Connection connection) {
this.mappers = mappers;
this.connection = connection;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
String key = className + "." + methodName;
Mapper mapper = mappers.get(key);
if (mapper == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("传入的参数有误");
}
return new Executor().selectList(mapper, connection);
}
}
public class Executor {
public <E> List<E> selectList(Mapper mapper, Connection conn) {
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
String queryString = mapper.getQueryString();
String resultType = mapper.getResultType();
Class domainClass = Class.forName(resultType);
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(queryString);
rs = pstm.executeQuery();
List<E> list = new ArrayList<E>();
while (rs.next()) {
E obj = (E) domainClass.newInstance();
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 1; i < columnCount; i++) {
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i);
Object columnValue = rs.getObject(columnName);
PropertyDescriptor pd = new PropertyDescriptor(columnName, domainClass);
Method writeMethod = pd.getWriteMethod();
writeMethod.invoke(obj, columnValue);
}
list.add(obj);
}
return list;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
release(pstm, rs);
}
return null;
}
private void release(PreparedStatement pstm, ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (pstm != null) {
try {
pstm.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.2.自定义 Mybatis 的设计模式简单了解
3.2.1.工厂模式SqlSessionFactory
工厂模式是常用的实例化对象模式,是用工厂方法替代new操作的一种模式。可以给系统带来更大的可扩展性和尽量少的修改量。
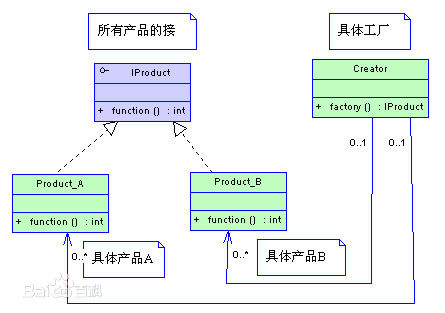
假设我们建立一个专门生成Phone的简单工厂
public class Factory() {
public static Phone creator(int which) {
if(which==1) {
renturn new PhoneA();
}
else if(which==2) {
return new PhoneB();
}
}
}
那么我们在程序中如果要创建Phone则可以使用
Phone PhoneA = Factor.creator(1);
这样就涉及不到Phone的具体的实现类,达到封装效果,也就减少错误修改的机会,这个原理可以用很通俗的话来比喻:就是具体事情做得越多,越容易犯错误。对于每个做过具体工作的人都深有体会,相反,官做得越高,说出的话越抽象越笼统,犯错误可能性就越少。
3.2.2.代理模式MapperProxyFactory
定义:
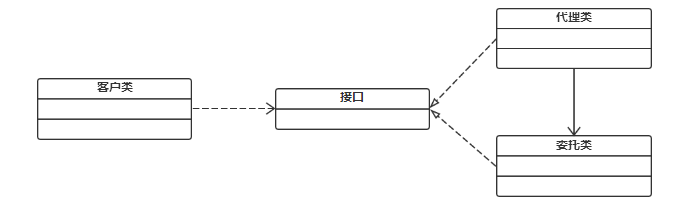
代理模式给某一个对象提供一个代理对象,并由代理对象控制对原对象的引用。通俗的来讲代理模式就是我们生活中常见的中介。
组成:
抽象角色:通过接口或抽象类声明真实角色实现的业务方法。
代理角色:实现抽象角色,是真实角色的代理,通过真实角色的业务逻辑方法来实现抽象方法,并可以附加自己的操作。
真实角色:实现抽象角色,定义真实角色所要实现的业务逻辑,供代理角色调用。
代理模式分为静态代理、动态代理:
静态代理:是由程序员创建或工具生成代理类的源码,再编译代理类。所谓静态也就是在程序运行前就已经存在代理类的字节码文件,代理类和委托类的关系在运行前就确定了。
动态代理:是在实现阶段不用关心代理类,而在运行阶段才指定哪一个对象。
举个例子来说明:
假如说我现在想买一辆二手车,虽然我可以自己去找车源,做一系列的车辆过户流程,但是这确实太浪费我的时间和精力了。我只是想买一辆车而已,为什么我还要额外做这么多事呢?于是我就通过中介公司来买车,他们来给我找车源,帮我办理车辆过户流程,我只是负责选择自己喜欢的车,然后付钱就可以了。如图所示:
3.2.3.构建者模式SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
定义:
构建者模式又称建造者模式,其主要功能是将一个复杂的对象的构建和表示进行分离,使得同样的构建过程可以创建不同的标示形式。构建者模式隐藏了复杂对象的创建过程并加以才抽象,通过子类的继承或者重载的方式,动态的创建具有复合属性的对象。
模型图:
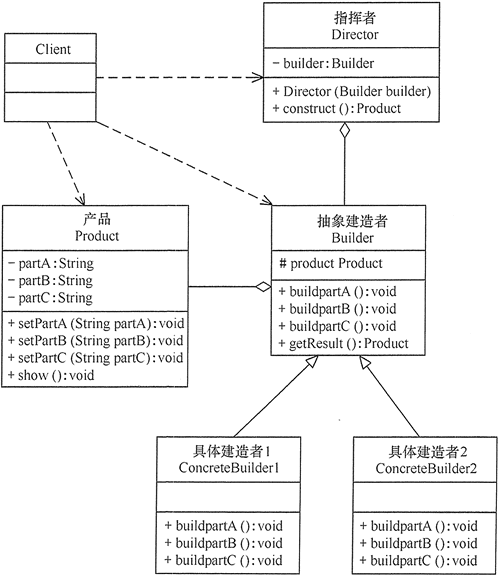
创建者模式的四个部分组成:
抽象创建者角色:给出一个抽象接口,以规范产品对象的各个组成成分的建造。一般而言,此接口独立于应用 程序的商业逻辑。模式中直接创建产品对象的是具体创建者角色。具体创建者必须实现这个接口的N种方法:一是 建造方法,比如图中的 buildPartA 和 buildPartB 和buildPartC方法;另一种是结果返回方法,即图中的 setProduct 方 法。一般来说,产品所包含的零件数目与建造方法的数目相符。换言之,有多少零件,就有多少相应的建造方法。
具体创建者角色:他们在应用程序中负责创建产品的实例。这个角色要完成的任务包括: 1、实现抽象创建者所声明的抽象方法,给出一步一步的完成产品创建实例的操作。 2、在创建完成后,提供产品的实例。
导演者角色:这个类调用具体创建者角色以创建产品对象。但是导演者并没有产品类的具体知识,真正拥有产 品类的具体知识的是具体创建者角色。
产品角色:产品便是建造中的复杂对象。一般说来,一个系统中会有多于一个的产品类,而且这些产品类并不 一定有共同的接口,而完全可以使不相关联的。
待续ing...