
在开始学习深克隆和浅克隆之前,我们先来看下面代码,有什么问题?
程序执行效果:
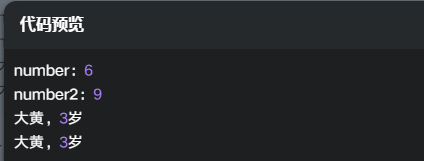
可以看出,如果使用等号复制时,对于值类型来说,彼此之间的修改操作是相对独立的,而对于引用类型来说,因为复制的是引用对象的内存地址,所以修改其中一个值,另一个值也会跟着变化,原理如下图所示:
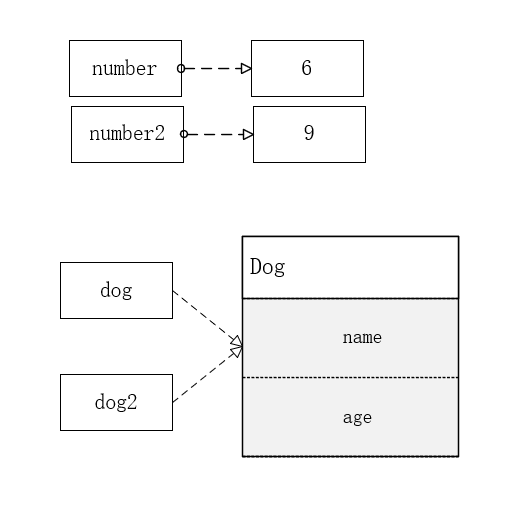
因此为了防止这种问题的发生,就要使用对象克隆来解决引用类型复制的问题。
一、浅克隆
浅克隆的默认实现方法是 clone(),实现代码如下:

程序执行结果:

可以看出使用克隆就可以解决引用类型复制的问题了,原理如下图所示:
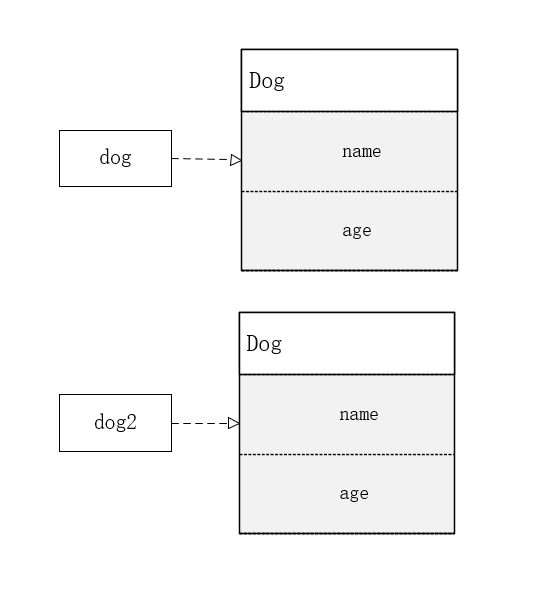
以上这种复制方式叫做浅克隆。
浅克隆的实现条件:需要克隆的对象必须实现 Cloneable 接口,并重写 clone() 方法,即可实现对此对象的克隆。
然而使用浅克隆也会存在一个问题,请参考以下代码。
class CloneTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
DogChild dogChild = new DogChild();
dogChild.name = 二狗;
Dog dog4 = new Dog();
dog4.name = 大黄;
dog4.dogChild = dogChild;
Dog dog5 = (Dog) dog4.clone();
dog5.name = 旺财;
dog5.dogChild.name = 狗二;
System.out.println(dog name 4:+dog4.name);
System.out.println(dog name 5:+dog5.name);
System.out.println(dog child name 4:+dog4.dogChild.name);
System.out.println(dog child name 5:+dog5.dogChild.name);
}
}
class Dog implements Cloneable {
public String name;
public DogChild dogChild;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
class DogChild {
public String name;
}
程序执行结果:
dog name 4:大黄
dog name 5:旺财
dog child name 4:狗二
dog child name 5:狗二
也就是说浅克隆,只会复制对象的值类型,而不会复制对象的引用类型。原因如下图所示:
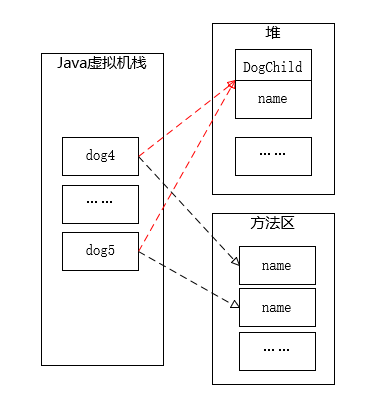
要处理引用类型不被复制的问题,就要使用到深克隆。
二、深克隆
定义:深克隆就是复制整个对象信息,包含值类型和引用类型。
深克隆的实现方式通常包含以下两种。
序列化实现深克隆:先将原对象序列化到内存的字节流中,再从字节流中反序列化出刚刚存储的对象,这个新对象和原对象就不存在任何地址上的共享,这样就实现了深克隆。
所有引用类型都实现克隆:要复制对象的所有引用类型都要实现克隆,所有对象都是复制的新对象,从而实现了深克隆。
深克隆实现方式一:序列化
实现思路:先将要拷贝对象写入到内存中的字节流中,然后再从这个字节流中读出刚刚存储的信息,作为一个新对象返回,那么这个新对象和原对象就不存在任何地址上的共享,自然实现了深拷贝。请参考以下代码:
class CloneTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
BirdChild birdChild = new BirdChild();
birdChild.name = 小小鸟;
Bird bird = new Bird();
bird.name = 小鸟;
bird.birdChild = birdChild;
// 使用序列化克隆对象
Bird bird2 = CloneUtils.clone(bird);
bird2.name = 黄雀;
bird2.birdChild.name = 小黄雀;
System.out.println(bird name: + bird.name);
System.out.println(bird child name: + bird.birdChild.name);
System.out.println(bird name 2: + bird2.name);
System.out.println(bird child name 2: + bird2.birdChild.name);
}
}
class CloneUtils {
public staticT clone(T obj) {
T cloneObj = null;
try {
//写入字节流
ByteArrayOutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
//分配内存,写入原始对象,生成新对象
ByteArrayInputStream bi = new ByteArrayInputStream(bo.toByteArray());//获取上面的输出字节流
ObjectInputStream oi = new ObjectInputStream(bi);
//返回生成的新对象
cloneObj = (T) oi.readObject();
oi.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return cloneObj;
}
}
程序执行结果:
bird name:小鸟
bird child name:小小鸟
bird name 2:黄雀
bird child name 2:小黄雀
深克隆实现方式二:所有引用类型都实现克隆
class SerializableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ParrotChild parrotChild = new ParrotChild();
parrotChild.name = 小鹦鹉;
Parrot parrot = new Parrot();
parrot.name = 大鹦鹉;
parrot.parrotChild = parrotChild;
// 克隆
Parrot parrot2 = (Parrot) parrot.clone();
parrot2.name = 老鹦鹉;
parrot2.parrotChild.name = 少鹦鹉;
System.out.println(parrot name: + parrot.name);
System.out.println(parrot child name: + parrot.parrotChild.name);
System.out.println(parrot name 2: + parrot2.name);
System.out.println(parrot child name 2: + parrot2.parrotChild.name);
}
}
class Parrot implements Cloneable {
public String name;
public ParrotChild parrotChild;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Parrot bird = (Parrot) super.clone();
bird.parrotChild = (ParrotChild) parrotChild.clone();
return bird;
}
}
class ParrotChild implements Cloneable {
public String name;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
程序执行结果:
parrot name:大鹦鹉
parrot child name:小鹦鹉
parrot name 2:老鹦鹉
parrot child name 2:少鹦鹉
三、克隆相关面试题
1.使用克隆有什么好处?
答:好处包含以下几点:
使用方便:假如要复制一个对象,但这个对象中的部分属性已经被修改过了,如果不使用克隆的话,需要给属性手动赋值,相比克隆而已麻烦很多;
性能高:查看 clone 方法可以知道,它是 native 方法,native 方法是原生函数,使用操作系统底层的语言实现的,因此执行效率更高;
隔离性:克隆可以确保对象操作时相互隔离。
clone() 源代码,如下图:

2.浅克隆和深克隆有什么区别?
答:区别主要在对引用类型的复制上,具体信息如下:
浅克隆:只会复制对象的值类型,而不会复制对象的引用类型;
深克隆:复制整个对象,包含值类型和引用类型。
3.如何实现浅克隆?
答:克隆的对象实现 Cloneable 接口,并重写 clone() 方法就可以实现浅克隆了。
4.以下代码执行的结果是?
import java.util.Arrays;
class CloneTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
CloneObj cloneObj = new CloneObj();
cloneObj.name = 老王;
cloneObj.age = 30;
cloneObj.sistersAge = new int[]{18, 19};
CloneObj cloneObj2 = (CloneObj) cloneObj.clone();
cloneObj2.name = 磊哥;
cloneObj2.age = 33;
cloneObj2.sistersAge[0] = 20;
System.out.println(cloneObj.name + | + cloneObj2.name);
System.out.println(cloneObj.age + | + cloneObj2.age);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(cloneObj.sistersAge) + | + Arrays.toString(cloneObj2.sistersAge));
}
}
class CloneObj implements Cloneable {
public String name;
public int age;
public int[] sistersAge;
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
答:执行结果如下。
老王|磊哥
30|33
[20, 19]|[20, 19]
5.深克隆如何实现?有几种实现方式?
答:一般实现方式有以下两种:
通过序列化实现深克隆(序列化实现方式:Java 原生序列化、JSON 序列化、Hessian 序列化);
所有引用类型都实现克隆,从而实现深克隆。
6.为什么不能直接使用 Object 的 Clone 方法,还要重写 clone() 方法之后才能实现克隆?
答:虽然所有类都是 Object 的子类,但因为 Object 中的 clone() 方法被声明为 protected 访问级别,所以非 java.lang 包下的其他类是不能直接使用的。因此要想实现克隆功能,就必须实现 Cloneable,并重写 clone() 方法才行。
7.序列化可不可以实现深克隆?实现的原理是什么?
答:先将原对象序列化到内存的字节流中,再从字节流中反序列化出刚刚存储的对象,这个新对象和原对象就不存在任何地址上的共享,这样就实现了深克隆。
四、总结
调用 Object 类中的 clone() 方法默认是浅克隆,浅克隆只能复制值类型,不能复制引用类型,因此更多的场景下我们需要深克隆,深克隆通常的实现方式有两种:序列化方式或把所有的引用类型都实现克隆。