接下来阅读触发时间相关源码
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager
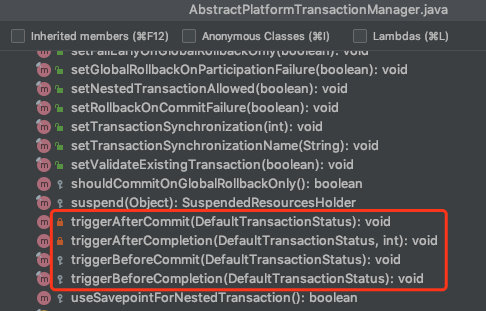
可以看到触发事件有四个. commit前后,completion前后, 我们看下方代码比较直观
private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
try {
boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;
try {
prepareForCommit(status);
triggerBeforeCommit(status);
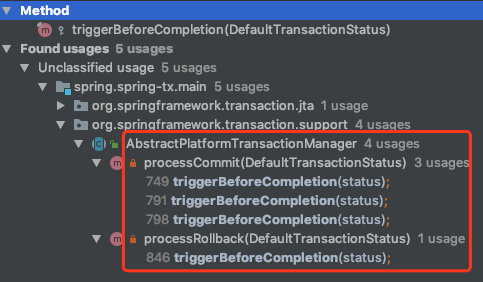
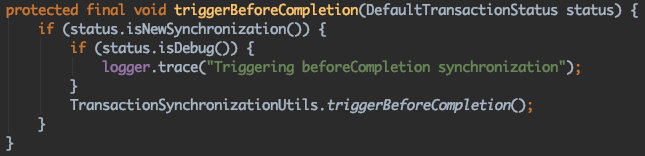
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
beforeCompletionInvoked = true;
boolean globalRollbackOnly = false;
if (status.isNewTransaction() || isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
globalRollbackOnly = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
}
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");
}
status.releaseHeldSavepoint();
}
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");
}
doCommit(status);
}
// Throw UnexpectedRollbackException if we have a global rollback-only
// marker but still didn't get a corresponding exception from commit.
if (globalRollbackOnly) {
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
"Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
}
}
catch (UnexpectedRollbackException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
throw ex;
}
catch (TransactionException ex) {
// can only be caused by doCommit
if (isRollbackOnCommitFailure()) {
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
}
else {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
}
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
}
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
}
doRollbackOnCommitException(status, err);
throw err;
}
// Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there
// propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.
try {
triggerAfterCommit(status);
}
finally {
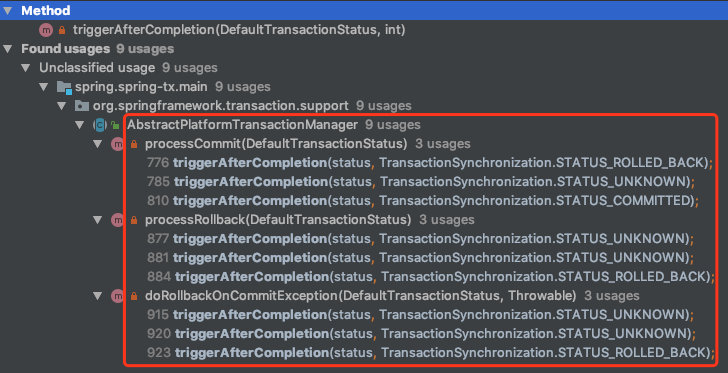
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);
}
}
finally {
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
commit流程:
- 预提交(扩展)
- 触发triggerBeforeCommit
- 触发triggerBeforeCompletion
- 提交
- 发生TransactionException异常说明已经被标记rollback或者需要rollback,则执行triggerAfterCompletion处理,最终执行cleanupAfterCompletion
- 发生RuntimeException或者Error则会判断是否执行triggerBeforeCompletion,如果执行则执行triggerAfterCompletion,如果未执行则先triggerBeforeCompletion,最终执行cleanupAfterCompletion
- triggerAfterCommit
- triggerAfterCompletion
- cleanupAfterCompletion
private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
try {
try {
triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Rolling back transaction to savepoint");
}
status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
}
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback");
}
doRollback(status);
}
else if (status.hasTransaction()) {
if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - marking existing transaction as rollback-only");
}
doSetRollbackOnly(status);
}
else {
if (status.isDebug()) {
logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - letting transaction originator decide on rollback");
}
}
}
else {
logger.debug("Should roll back transaction but cannot - no transaction available");
}
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
throw err;
}
triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
}
finally {
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
}
}
Rollback流程:
- 触发triggerBeforeCompletion
- rollback(并不一定触发回滚,可能是设置回滚标识)
- 发生异常触发triggerAfterCompletion,并往上抛
- 触发triggerAfterCompletion
- cleanupAfterCompletion
triggerBeforeCommit
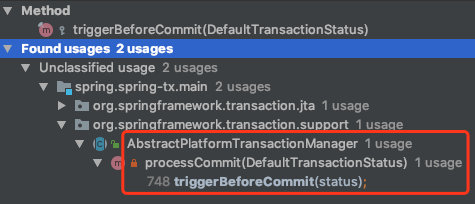
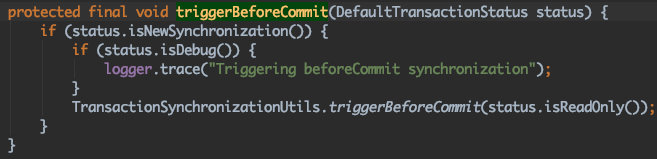
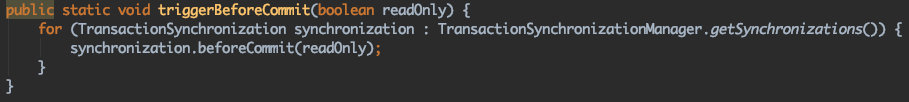
triggerAfterCommit
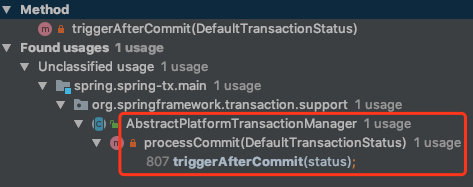
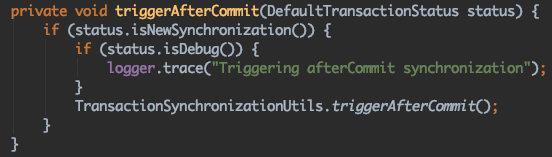
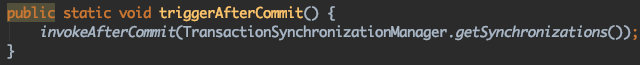
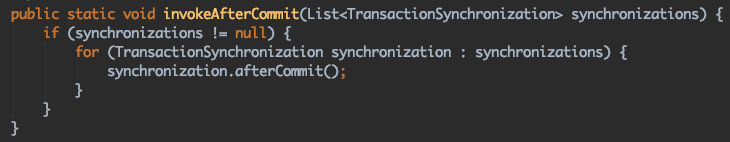
triggerBeforeCompletion

triggerAfterCompletion
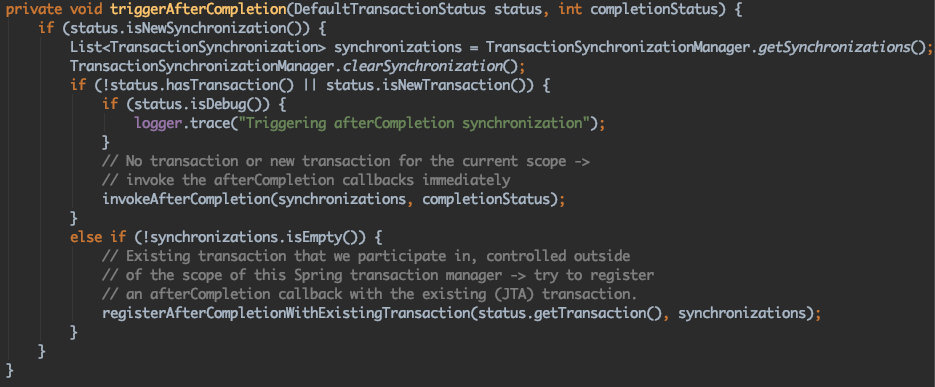
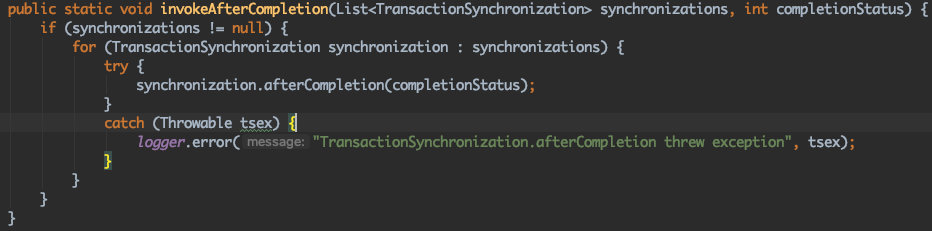
到这里,我们的关注点就应该是TransactionSynchronization.至于TransactionSynchronizationUtils,只是通过TransactionSynchronizationManager..getSynchronizations()获取TransactionSynchronization,然后遍历调用而已
TransactionSynchronization
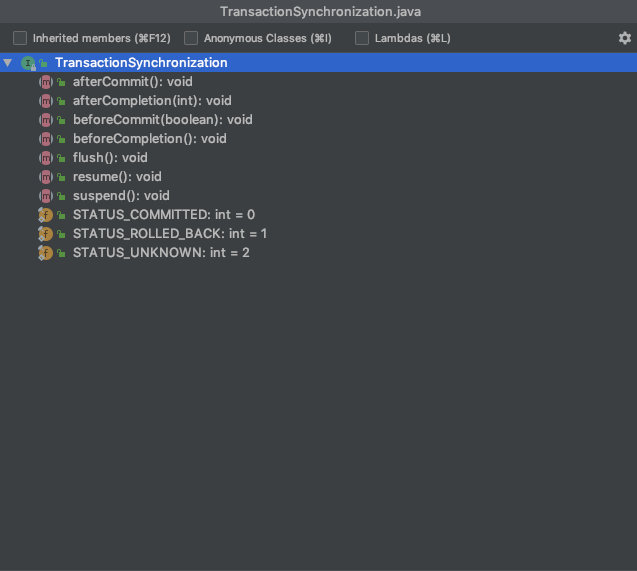
子类
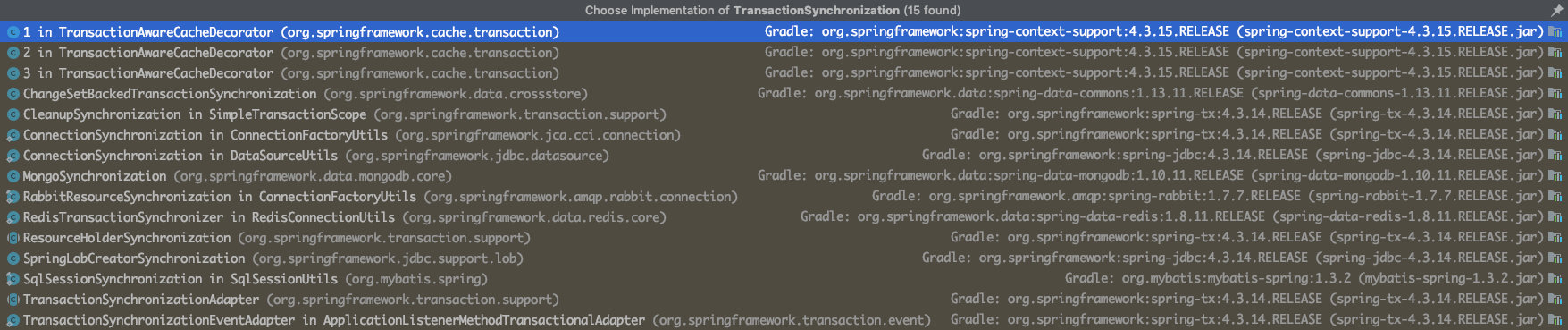
SqlSessionSynchronization(Mybatis)
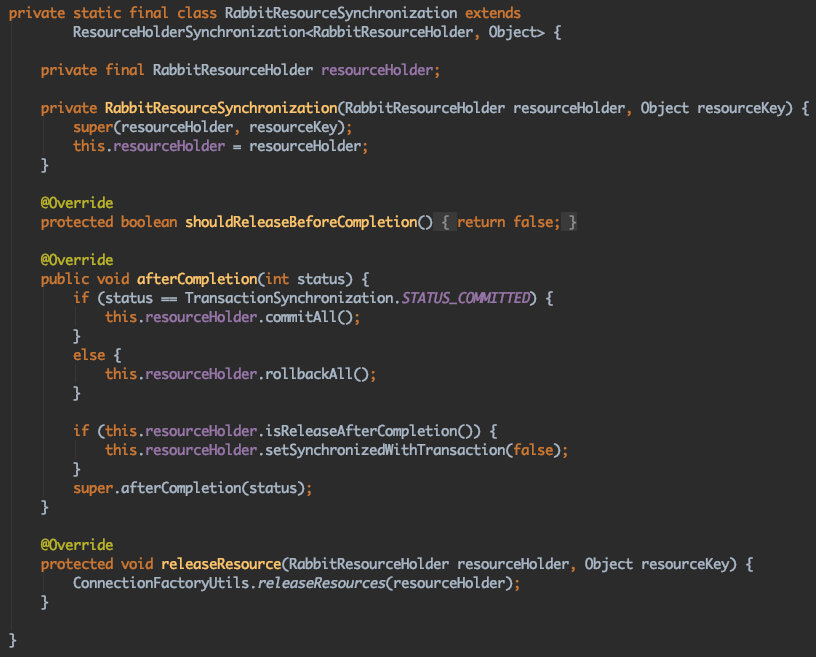
RabbitResourceSynchronization
RedisTransactionSynchronizer
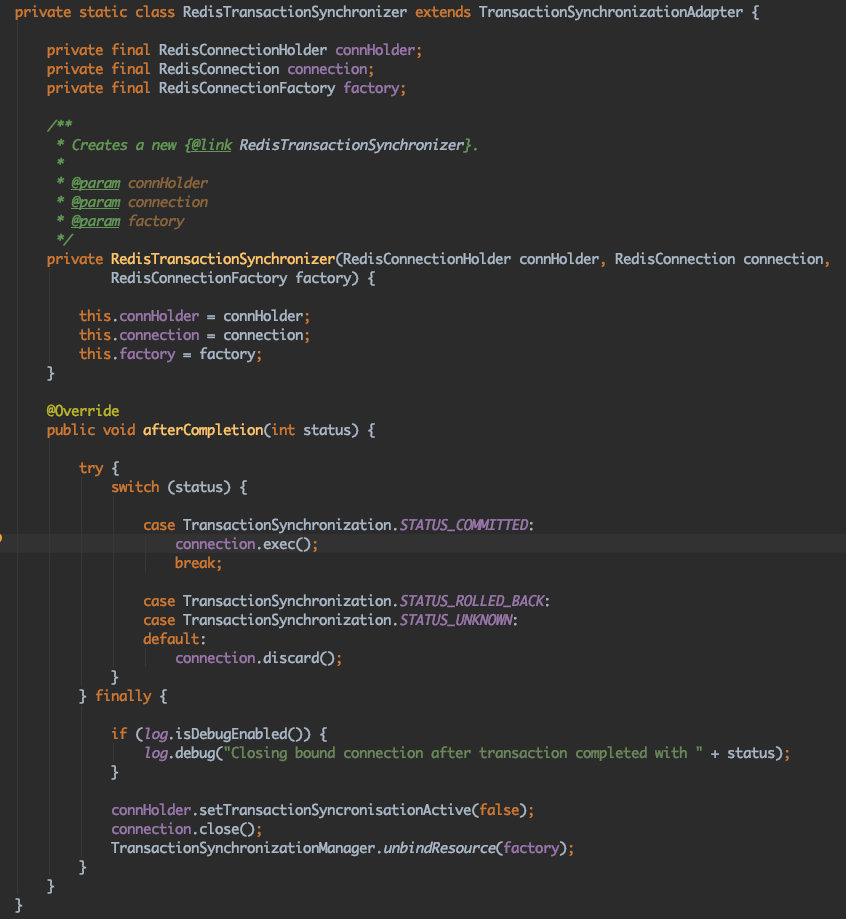
仅举例表示对接实现
目前项目中使用RabbitMQ, 当RabbitTemplate.channelTransacted = true时,会绑定TransactionSynchronization在使用@Transactional的方法之后会走到此处,执行RabbitMQ的发送和回滚
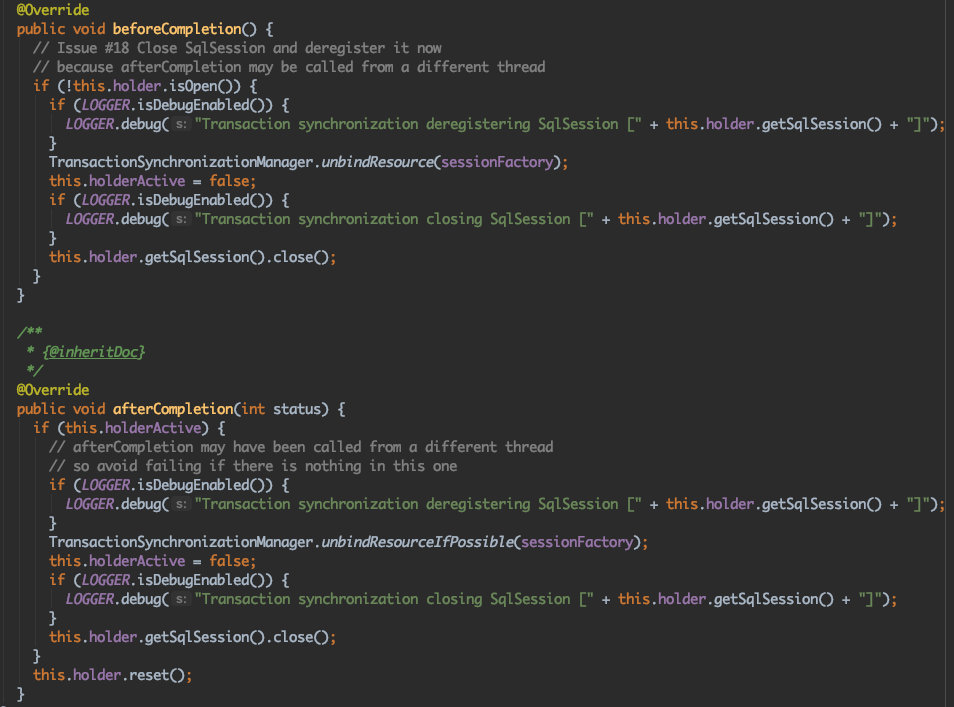
我们发现两个类是继承了ResourceHolderSynchronization
ResourceHolderSynchronization
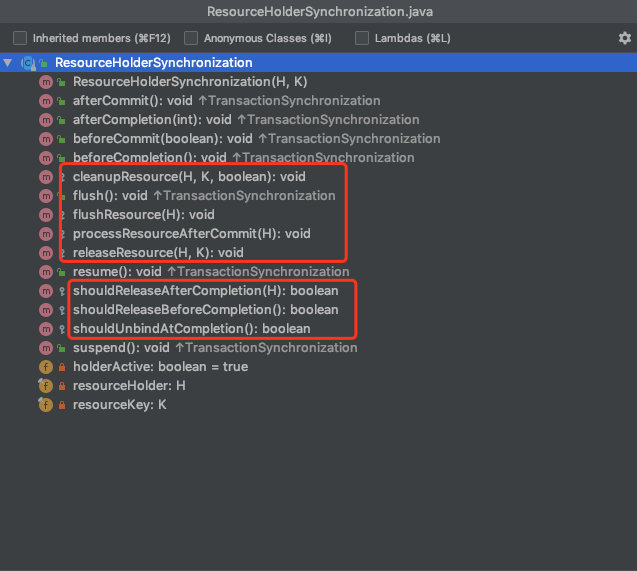
相比TransactionSynchronization 增加了红框的几个方法
核心的commit和completion已经做出抽象实现.具体又子类具体实现
看一下代码
@Override
public void suspend() {
if (this.holderActive) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(this.resourceKey);
}
}
@Override
public void resume() {
if (this.holderActive) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(this.resourceKey, this.resourceHolder);
}
}
@Override
public void flush() {
flushResource(this.resourceHolder);
}
@Override
public void beforeCommit(boolean readOnly) {
}
@Override
public void beforeCompletion() {
if (shouldUnbindAtCompletion()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(this.resourceKey);
this.holderActive = false;
if (shouldReleaseBeforeCompletion()) {
releaseResource(this.resourceHolder, this.resourceKey);
}
}
}
@Override
public void afterCommit() {
if (!shouldReleaseBeforeCompletion()) {
processResourceAfterCommit(this.resourceHolder);
}
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(int status) {
if (shouldUnbindAtCompletion()) {
boolean releaseNecessary = false;
if (this.holderActive) {
// The thread-bound resource holder might not be available anymore,
// since afterCompletion might get called from a different thread.
this.holderActive = false;
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResourceIfPossible(this.resourceKey);
this.resourceHolder.unbound();
releaseNecessary = true;
}
else {
releaseNecessary = shouldReleaseAfterCompletion(this.resourceHolder);
}
if (releaseNecessary) {
releaseResource(this.resourceHolder, this.resourceKey);
}
}
else {
// Probably a pre-bound resource...
cleanupResource(this.resourceHolder, this.resourceKey, (status == STATUS_COMMITTED));
}
this.resourceHolder.reset();
}
/**
* Return whether this holder should be unbound at completion
* (or should rather be left bound to the thread after the transaction).
* <p>The default implementation returns {@code true}.
*/
protected boolean shouldUnbindAtCompletion() {
return true;
}
/**
* Return whether this holder's resource should be released before
* transaction completion ({@code true}) or rather after
* transaction completion ({@code false}).
* <p>Note that resources will only be released when they are
* unbound from the thread ({@link #shouldUnbindAtCompletion()}).
* <p>The default implementation returns {@code true}.
* @see #releaseResource
*/
protected boolean shouldReleaseBeforeCompletion() {
return true;
}
/**
* Return whether this holder's resource should be released after
* transaction completion ({@code true}).
* <p>The default implementation returns {@code !shouldReleaseBeforeCompletion()},
* releasing after completion if no attempt was made before completion.
* @see #releaseResource
*/
protected boolean shouldReleaseAfterCompletion(H resourceHolder) {
return !shouldReleaseBeforeCompletion();
}
/**
* Flush callback for the given resource holder.
* @param resourceHolder the resource holder to flush
*/
protected void flushResource(H resourceHolder) {
}
/**
* After-commit callback for the given resource holder.
* Only called when the resource hasn't been released yet
* ({@link #shouldReleaseBeforeCompletion()}).
* @param resourceHolder the resource holder to process
*/
protected void processResourceAfterCommit(H resourceHolder) {
}
/**
* Release the given resource (after it has been unbound from the thread).
* @param resourceHolder the resource holder to process
* @param resourceKey the key that the ResourceHolder was bound for
*/
protected void releaseResource(H resourceHolder, K resourceKey) {
}
/**
* Perform a cleanup on the given resource (which is left bound to the thread).
* @param resourceHolder the resource holder to process
* @param resourceKey the key that the ResourceHolder was bound for
* @param committed whether the transaction has committed ({@code true})
* or rolled back ({@code false})
*/
protected void cleanupResource(H resourceHolder, K resourceKey, boolean committed) {
}
可能这里讲的比较乱.大概说一下这些用途吧 TransactionSynchronization这个类更多扩展的用途是在于afterCompletion,对于像jdbc,rabbit,redis这些可以在执行结束后释放Transactional resources
我们再回头想一下,我们是从TransactionSynchronizationManager才找到TransactionSynchronization.为什么TransactionSynchronization会放在TransactionSynchronizationManager.TransactionSynchronizationManager的意义在于什么?我们看一下
TransactionSynchronizationManager
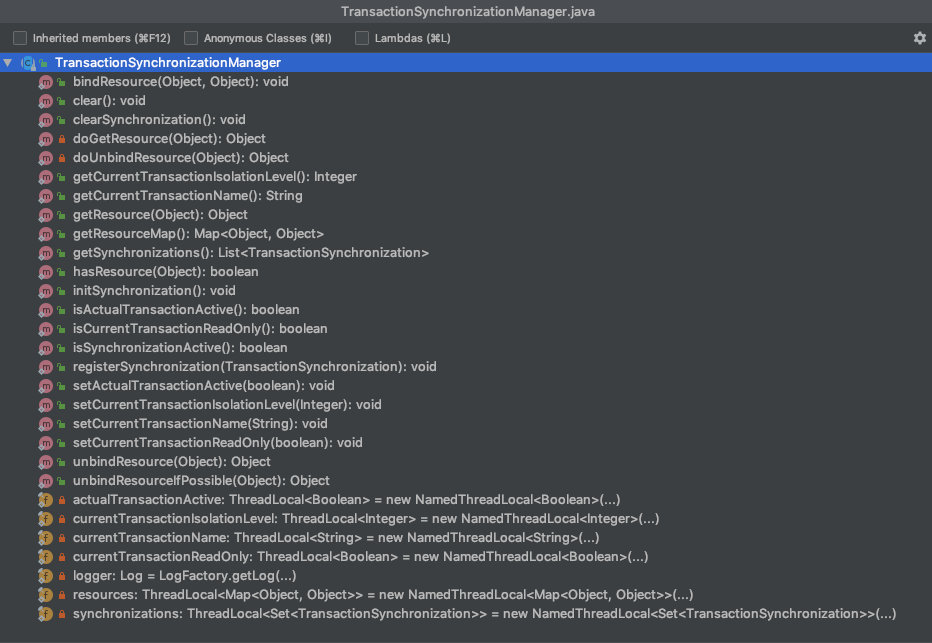
方法大致如下 注册,解绑,绑定,获取,清空 我们看一下属性
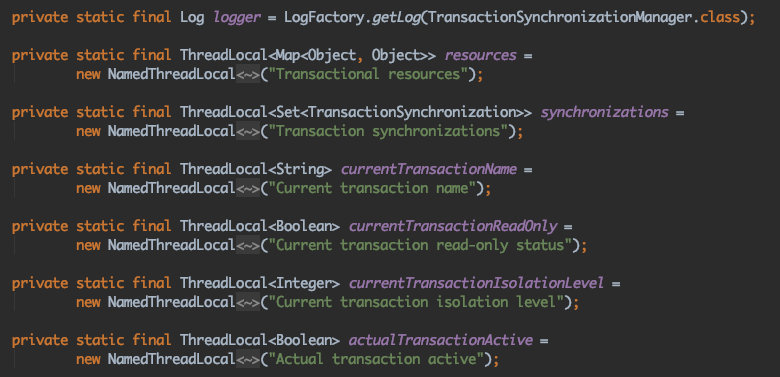
看到ThreadLocal,似乎知道了些什么 多个线程,每个线程又需要对应多个厂商的事务连接,并且每个事务连接朝生夕死,虽然spring容器支持多例,但是多例如何传递?需要怎么处理? 通过TransactionSynchronizationManager的ThreadLocal来在线程上下文传递.也许才是最解耦最优雅的方式
总结
AbstractPlatformTransactionManager提供抽象方法,子类具体实现(RabbitTransactionManager, DataSourceTransactionManager) TransactionSynchronization提供接口供第三方扩展注册,用于一个事务的多方处理(db, mq等, 实现如RabbitResourceSynchronization, RedisTransactionSynchronizer, SqlSessionSynchronization) 那么问题又来了AbstractPlatformTransactionManager的实现类在什么时候注册,是么时候获取? TransactionSynchronization的实现类在什么时候注册?什么时候绑定?什么时候获取? 写一篇讲解Spring定义抽象的实现类何时加载处理