概念
Redux 是JavaScript状态容器,提供可预测化的状态管理。
跟React没有关系。
适用场景
你可能不需要使用Redux,但是在以下情况,建议使用Redux。
- 用户的使用方式复杂
- 不同身份的用户有不同的使用方式
- 多个用户之间可以协作
- 与服务器大量交互
- View要从多个来源获取数据
工作流程
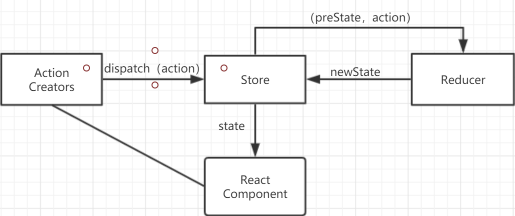
Redux组成部分(基本概念和API)
Action
Action是一个对象,里面包含了View想要改变state的信息。
Action中必须有type字段,表示Action的名称。
const action ={
type:'add_todo_item',
value
}
Action描述当前发生的事情,改变state的唯一方法,就是派发Action
Action Creator
View要发送给多少种消息,就会有多少种Action,如果都手写,会很麻烦,可以定义一个函数来生成Action,这个函数就叫做Action Creator。
export addTodoItemAction(value){
return {
type:ADD_TODO_ITEM,
value
}
}
// 必须返回一个Action对象,包含type字段
store
概念
store就是数据保存的地方,可以理解为一个容器,整个应用只有一个store。
创建
import { createStore } from 'redux'
import reducer from './reducer'
// 使用createStore方法创建store,接收reducer作为参数
const store = createStore(reducer)
获取store中的数据
使用store.getState()
store.getState()
store.dispatch
dispatch方法是派发action的唯一方法。
接收一个Action对象作为参数,将它发送给store。
Reducer
store将Action派发出去之后,根据不同Action的type,必须返回一个State,这样View才会发生变化。这种State的计算过程就在Reducer中完成。
Reducer是一个纯函数,接收Action和当前的State作为参数,返回一个新的State。
const defaultState ={
inputValue:'',
list:[]
}
// 可以为state定义默认的state,作为整个应用的初始状态
export default (state=defaultState,action)=>{
if( action.type === 'change_input_value') {
const newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state))
console.log(action.value)
newState.inputValue = action.value
console.log(newState.inputValue)
return newState
}
return state
}
纯函数
纯函数最重要的特征是 同样的输入,必定得到同样的输出。
纯函数必须遵守以下约束:
- 不能修改参数
- 不能调用系统的I/O的API
- 不能调用Date或者Math.random()方法,因为每次都会得到不一样的结果
store.subscribe
Store允许使用store.subscribe() 订阅监听函数,一旦State发生变化,就自动执行这个函数。
在React中,只需要将组件重新setState()就可以了。
store.subscribe(
()=>{
this.setState( store.getState() )
}
)
// 当store中的数据发生变化时,就重新 调用store.getState()方法 ,获取最新的state,
// 并且将得到的结果作为setState()方法的参数。触发组件更新。
Redux三大原则
Redux使用
安装
yarn add redux
使用
创建store
import { createStore } from 'redux'
import reducer from './reducer'
const store = createStore(
reducer
)
export default store
创建reducer文件
const defaultState ={
inputValue:'',
list:[]
}
export default (state=defaultState,action)=>{
if( action.type === 'change_input_value') {
const newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state))
console.log(action.value)
newState.inputValue = action.value
console.log(newState.inputValue)
return newState
}
return state
}
视图组件订阅store
import React,{ Component } from 'react'
import store from './store'
export default class TodoList extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props)
// 初始化 store
this.state = store.getState()
console.log(this.state)
// 订阅store
store.subscribe(()=>{
this.setState(store.getState())
})
}
handleInputChange = (e) =>{
// 需求: 当input改变时,修改state
// 修改state只能通过 dispatch action
// ChangeInputValueAction() 是Action Creator导出的一个函数 ,用于生成对应的Action
const action =ChangeInputValueAction(e.target.value)
// 派发Action
store.dispatch(action)
}
....
}
中间件
概念
中间件指的是 action和store之间。
中间件就是一个函数,对store.dispatch进行了改造,在发出action和执行Reducer这两步之间,添加了其他功能。
使用
import { applyMiddleware,createStore} from 'redux'
import createLogger from 'redux-logger'
const logger = createLogger()
const store = createStore(
reducer,
applyMiddleware(logger)
)
要想使用中间件,就必须通过applyMiddleware方法。
案例: TodoList Redux版本
index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import TodoList from './TodoList'
ReactDOM.render(<TodoList />, document.getElementById('root'));
TodoList.js
import React,{ Component } from 'react'
import 'antd/dist/antd.css'
import store from './store'
import { Input,Button,List } from 'antd'
import {
ChangeInputValueAction,
AddListItemAction,
DeleteListItemAction
} from './store/actionCreator'
export default class TodoList extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props)
this.state = store.getState()
console.log(this.state)
store.subscribe(()=>{
this.setState(store.getState())
})
}
// handleStoreChange =() =>{
// }
handleInputChange = (e) =>{
// 需求: 当input改变时,修改state
// 修改state只能通过 dispatch action
const action =ChangeInputValueAction(e.target.value)
store.dispatch(action)
}
handleItemDelete = (index) => {
// 点击item删除
console.log(index)
const action = DeleteListItemAction(index)
store.dispatch(action)
}
handleBtnClick = () =>{
const action = AddListItemAction()
store.dispatch(action)
}
render(){
return(
/**
* redux
* 组成部分:
* 1. store
* 2. reducer
* 3. actionTypes
* 4. actionCreator
* 三大原则:
* 1. store是唯一的
* 2. store中的数据是只读的
* 3. 修改数据 只能通过dispach方法
* 数据流程
* aactionCreatore => 创建action
* 通过dispach派发acion store.dispatch
* store接受到action之后,会自动转发给reducer
* reducer是一个纯函数,接收action,以及preState,返回一个新的state给store
* store接收新的state 更新 数据
* 组件订阅store,当store中的数据更新时,执行对应的回调方法,获取getState()
*
*
*/
/**
* 需求描述
* 一个input 一个 button 一个list
*/
<div>
<Input
style= {{ width:'300px',marginLeft:'50px',marginTop:'50px'}}
value={ this.state.inputValue}
onChange ={ this.handleInputChange}
/>
<Button
style= {{ marginLeft:'15px'}}
onClick = { this.handleBtnClick }
>提交</Button>
<List
style= {{
width:'300px',
marginLeft:'50px',
marginTop:'20px',
backgroundColor:'#ccc'
}}
bordered
dataSource ={ this.state.list }
renderItem ={ (item,index) => (<List.Item onClick ={ ()=>this.handleItemDelete(index)}>{item}</List.Item>)}
/>
</div>
)
}
}
store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'redux'
import reducer from './reducer'
const store = createStore(
reducer
)
export default store
store/reducer.js
const defaultState ={
inputValue:'',
list:[]
}
export default (state=defaultState,action)=>{
if( action.type === 'change_input_value') {
const newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state))
console.log(action.value)
newState.inputValue = action.value
console.log(newState.inputValue)
return newState
}
if( action.type === 'add_list_item') {
const newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state))
newState.list.push(newState.inputValue)
newState.inputValue = ''
return newState
}
if(action.type ==="delete_list_item") {
console.log(action.type)
console.log(action.index)
// console.log(value)
const newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state))
newState.list.splice(action.index,1)
return newState
}
return state
}
store/actionCreator.js
import {
CHANGE_INPUT_VALUE,
DELETE_LIST_ITEM,
ADD_LIST_ITEM
} from './actionTypes'
export const ChangeInputValueAction = (value) =>(
{
type:CHANGE_INPUT_VALUE,
value
}
)
export const AddListItemAction = () =>(
{
type:ADD_LIST_ITEM,
}
)
export const DeleteListItemAction = (index) =>(
{
type:DELETE_LIST_ITEM,
index
}
)
store/actionType.js
export const CHANGE_INPUT_VALUE ='change_input_value'
export const DELETE_LIST_ITEM ='delete_list_item'
export const ADD_LIST_ITEM ='add_list_item'