技巧一,理解指针或引用的含义
将某个变量赋值给指针,实际上就是将这个变量的地址赋值给指针,或者反过来说,指针存储了这个变量的内存地址,指向了这个变量将,通过指针就能找到这个变量。
警惕指针丢失和内存泄漏
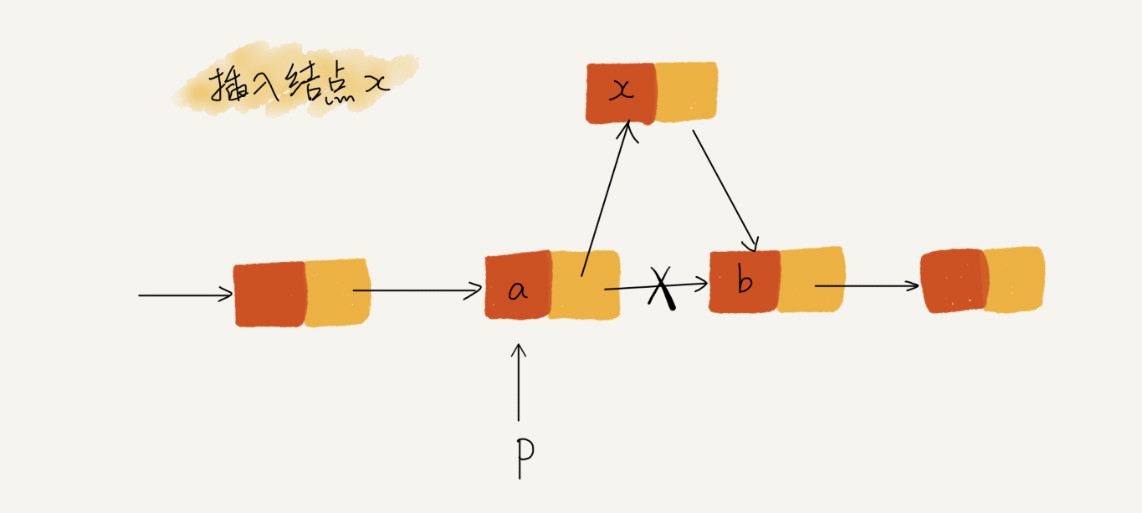
在插入结点时,一定要注意操作的顺序,要先将结点 x 的 next 指针指向结点 b,再把结点 a 的 next 指针指向结点 x,也可以认为是要将 a 的 next 指针保存下来。这样才不会丢失指针,导致内存泄漏。
在删除结点时,也一定要记得手动释放内存空间,否则会有内存泄漏的问题。
如果使用的是 Java 这种虚拟机自动管理内存的语言来说,内存泄漏不需要我们操心。
技巧二,利用哨兵简化实现难度
具体的例子看 链表(下):如何轻松写出正确的链表代码? 的「技巧三:利用哨兵简化实现难度」
技巧三,重点留意边界条件处理
几个经常用来检查链表代码是否正确的边界条件有这样几个:
- 如果链表为空时,代码是否能正常工作?
- 如果链表只包含一个结点时,代码能否正常工作?
- 如果链表只包含两个结点时,代码能否正常工作?
- 代码逻辑在处理头结点和尾结点的时候,是否能正常工作?
技巧四,举例画图,辅助思考
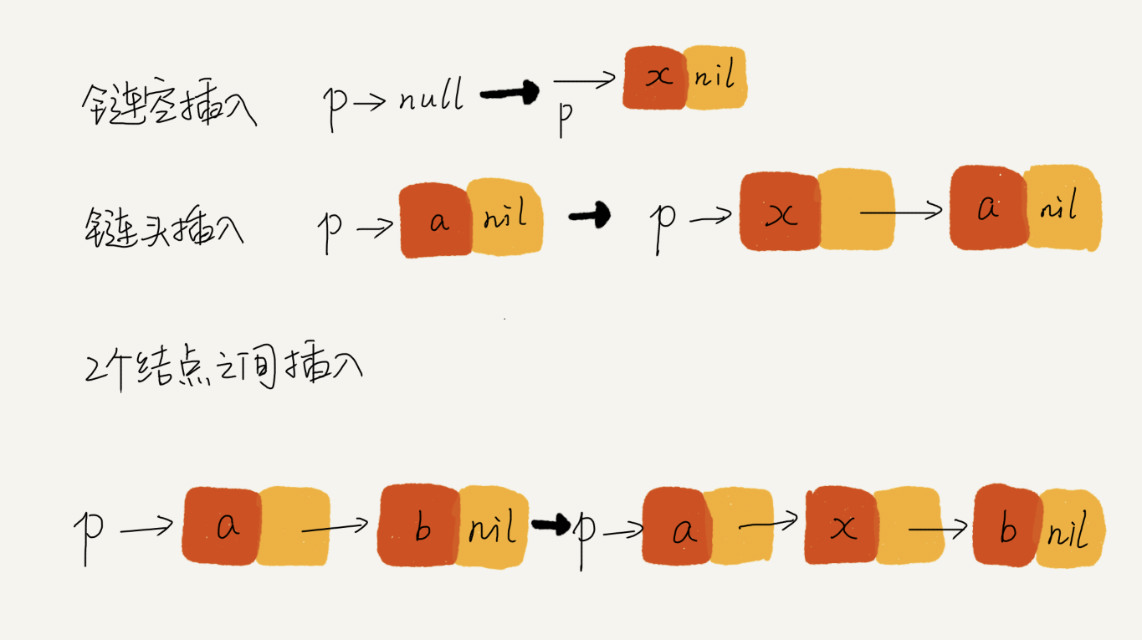
找一个具体的例子,把它画在纸上,释放一些脑容量。把各种情况都举一个例子,画出插入前和插入后的链表变化。
技巧五,多写多练,没有捷径
熟能生巧,将下面 5 个常见的链表操作都写熟练。
单链表翻转
/**
* 单链表翻转
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
*
* @param list 目标链表
* @return 返回翻转后的链表
*/
public static Node reverse(Node list) {
Node prev = null;
Node curr = list;
while (curr != null) {
Node next = curr.next; // 先保存下面的数据
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
链表中环的检测
/**
* 检测环
* 时间复杂度 O(n) 取决于环的大小
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
*
* @param list 目标链表
* @return 是否存在环
*/
public static boolean checkCircle(Node list) {
if (list == null) return false;
Node slow = list;
Node fast = list;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (fast == slow) return true;
}
return false;
}
两个有序的链表合并
/**
* 有序链表合并
*
* @param la
* @param lb
* @return
*/
public static Node mergeSortedList(Node la, Node lb) {
if (la == null) return lb;
if (lb == null) return la;
Node head = null;
if (la.data < lb.data) {
head = la;
la = la.next;
} else {
head = lb;
lb = lb.next;
}
Node tmp = head; // 用一个指针来进行合并操作
while (la != null && lb != null) {
if (la.data < lb.data) {
tmp.next = la;
la = la.next;
} else {
tmp.next = lb;
lb = lb.next;
}
tmp = tmp.next; // 指针始终指向尾结点
}
if (la != null) {
tmp.next = la;
} else {
tmp.next = lb;
}
return head;
}
删除链表倒数第 n 个结点
/**
* 删除倒数第 k 个元素
*
* @param list
* @param k
* @return
*/
public static Node deleteLastKth(Node list, int k) {
if (list == null) return null;
Node fast = list;
int i = 1;
while (fast != null && i < k) { // 找到顺数第 k 个元素
fast = fast.next;
i++;
}
if (fast == null) return list; // 不够 k 个元素
Node slow = list;
Node slowPre = null;
while (fast.next != null) { // fast 指针遍历完剩下的链表
fast = fast.next;
slowPre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
}
// slowPre == null 说明 k == list 的 length
if (slowPre == null) {
list = list.next; // 所以就是删除头结点
} else {
slowPre.next = slowPre.next.next;
}
return list;
}
求链表的中间结点
/**
* 找到中间元素
*
* @param list
* @return
*/
public static Node findMiddleNode(Node list) {
if (list == null) return null;
Node fast = list;
Node slow = list;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}