个人博客: shimeng.info
背景概论
在计算机结构中我们知道CPU和内存的速度是严重不匹配的, 如果每一次取数据都是直接向内存中取,那么会造成CPU的大量空转,因此会有一块Cache,叫做高速缓存,而之所以会增加高速缓存,是因为在计算机领域中有一个原理:访问局部性,也叫做局部性原理。
访问局部性(英语:Locality of reference)指的是应用程序在访问内存的时候,倾向于访问内存中较为靠近的值。一种是时间局部性,另一种是空间局部性。时间局部性指的是,程序在运行时,最近刚刚被引用过的一个内存位置容易再次被引用,比如在调取一个函数的时候,前不久才调取过的本地参数容易再度被调取使用。空间局部性指的是,最近引用过的内存位置以及其周边的内存位置容易再次被使用。 --- wikipedia维基百科
同样在操作系统内,32位的操作系统最大的内存为4G(2^32),当一个几十G,几百G的数据启动的时候,加载到内存中的往往是一部分的数据,其他的数据都是放到了辅存里面,也就是磁盘中。这个时候内存也是充当了缓存的功能。
当然这两个的原因是不同的,一个是速度的问题,一个是容量的问题。但是解决方法的原理都是一样的,通过中间增加了缓存,解决了资源不够的问题。
因此这也就衍生了缓存的高效利用的算法,叫做缓存置换算法。具体的实现方式有三种,分别为FIFO(先进先出)、LRU(最近最少使用算法)、LFU(最不经常使用算法)。
三种算法的数据结构也有多种,本次主要使用双向链表的实现来完成三种算法。首先来看下如何实现一个双向链表
双向链表实现
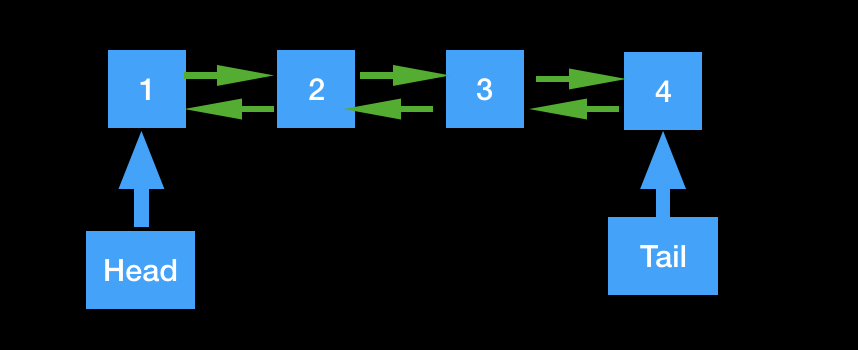
双向链表的每个节点有两个指针,分别指向前驱和后继,也有两个指针,分别指向头节点和尾节点,头节点的前驱为空,尾节点的后继也为空。
链表节点的实现
class Node {
// 构造函数 节点的表示形式为 k-v
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
// 辅助展示的打印方法
toString() {
return `${this.key} : ${JSON.stringify(this.value)}`;
}
}
Node节点传入key和value,作为键值,next和prev默认为空
双向链表构造函数
class DoubleLinkedList {
constructor(capacity = 100) {
// 头尾节点
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
// 容量
this.capacity = capacity;
// 节点数
this.count = 0;
}
}
双向链表添加元素
- 头部添加
只需要记住一点的是头部元素的prev为null就行
// 头部添加元素
unshift(key, value) {
const newNode = new Node(key, value);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
this.head.prev = null;
this.head.next = null;
} else {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
this.head.prev = null;
}
this.count++;
return newNode;
}
- 尾部添加
同样的需要知道尾部的next指针为null
// 尾部添加节点
push(key, value) {
const newNode = new Node(key, value);
if (!this.tail) {
this.tail = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
this.tail.next = null;
this.tail.prev = null;
} else {
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
this.tail.next = null;
}
this.count++;
return newNode;
}
- 通过key获取key所在节点的value值
// 获得任意key所在的节点
get(key) {
let currNode = this.head;
let returnNode = null;
while (currNode) {
if (currNode.key === key) {
returnNode = currNode;
break;
}
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return returnNode;
}
- 删除头节点
// 删除头节点
shift() {
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
const deleteNode = this.head;
if (deleteNode.next) {
deleteNode.next.prev = null;
this.head = deleteNode.next;
} else {
this.head = this.tail = null;
}
this.count--;
return deleteNode;
}
- 删除尾节点
// 删除尾节点
pop() {
// 尾部为空 返回null
if (!this.tail) {
return null;
}
const deleteNode = this.tail;
// 有上一个节点
if (deleteNode.prev) {
deleteNode.prev.next = null;
this.tail = deleteNode.prev;
} else {
// 没有上一个节点
this.tail = this.head = null;
}
this.count--;
return deleteNode;
}
- 删除key所在的节点
// 删除任意node节点
delete(node) {
// node不存在 则删除尾节点
if (!node) {
return this.deleteTail();
}
// 删除的节点为头节点
if (node === this.head) return this.shift();
// 删除的节点为尾节点
if (node === this.tail) return this.pop();
node.next.prev = node.prev;
node.prev.next = node.next;
this.count--;
return node;
}
为双向链表添加toString方法,方便打印查看链表内容
// 打印
toString() {
let currNode = this.head;
let result = '';
while (currNode) {
result += currNode.toString();
currNode = currNode.next;
if (currNode) {
result += ' => ';
}
}
console.log(result || 'Null');
return result;
}
使用
const list = new DoubleLinkedList(10);
// 头部添加节点
list.unshift(1, { a: '1' });
// 打印
list.toString();
// 尾部添加节点
list.push(2, { a: '2' });
// 打印
list.toString();
// 尾部添加节点
list.push(3, { a: '3' });
// 打印
list.toString();
// 打印key为2的节点
console.log(list.get(2).toString());
// 删除key为2的节点
list.delete(list.get(2));
// 打印
list.toString();
// 弹出尾部节点
list.pop();
// 打印
list.toString();
// 弹出头部节点
list.shift();
// 打印
list.toString();

缓存置换算法
接下来就可以根据双向链表实现缓存置换算法。
先进先出算法 FIFO first input first output
将缓存看作一个先进先出的队列,然后当缓存满的时候,将队列头部的节点替换
const DoubleLinkedList = require('./doubleLinkList');
class FIFOCache {
constructor(capacity = 0) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.count = 0;
this.map = {};
this.list = new DoubleLinkedList(capacity);
}
}
capacity作为缓存的容量,当等于该容量时替换旧的数据节点。this.map作为节点的映射,节点的key作为键值,节点作为value。this.list是链表的实例。
get(key) {
if (!this.map[key]) {
return null;
}
return this.map[key].value;
}
先判断map中是否包含该节点,包含返回map中的值,否则返回null。
put(key, value) {
if (!this.capacity) {
return null;
}
if (this.map[key]) {
// 删除旧数据
const oldNode = this.map[key];
this.list.delete(oldNode);
this.count--;
} else {
if (this.capacity === this.count) {
// 容量已满 删除头节点
const oldNode = this.list.shift();
delete this.map[oldNode].key;
this.count--;
}
}
// 将新数据插入链表尾部
const newNode = this.list.push(key, value);
this.map[newNode.key] = newNode;
this.count++;
}
put方法首先判断map中是否包含该键,包含则删除旧的节点,否则再判断是否容量已满,容量已满则删除头节点。 最终将新的数据插入到链表的尾部,并更新map中的数据
最近最少使用算法 LRU least recently used
当我们把之前插入的数据放到链表当头部,新插入的节点放到链表当尾部,每次获取数据时,我们都将该节点放到链表的尾部,最终删除节点的时候只需要从头部删除就可以了。这样就保证了头部的节点是当前最近最少使用的数据。看代码,和FIFO的类似
class LRUCache {
constructor(capacity = 0) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.count = 0;
this.map = {};
this.list = new DoubleLinkedList(capacity);
}
get(key) {
const node = this.map[key];
if (!node) {
return null;
}
// 删除链表中的节点
// 将其放到链表的尾部
this.list.delete(node);
this.list.push(key, node.value);
return node.value;
}
put(key, value) {
if (!this.capacity) return null;
const currNode = this.map[key];
if (currNode) {
// 删除当前节点
this.list.delete(currNode);
this.count--;
} else {
// 删除老的节点
if (this.capacity === this.count) {
const oldNode = this.list.shift();
delete this.map[oldNode.key];
}
}
// 被使用的节点放到链表的尾部
const newNode = this.list.push(key, value);
this.map[key] = newNode;
this.count++;
}
toString() {
this.list.toString();
}
}
最不经常使用算法 LFU least frequently used
LFU需要淘汰的是使用频率最低的节点,这个时候就需要针对每个节点增加表示其频率的字段。同样在映射中也需要增加不同频率的映射。先看代码吧
class LFUCache {
constructor(capacity = 0) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.count = 0;
this.map = {};
this.freqMap = {};
}
}
在这里多了一个freqMap,因为要在freqMap中保存不同频率的链表,其键为频率值,其值为包含该频率节点的链表。这里还需要实现一个更新其频率的方法
updateFreq(node) {
let freq = node.freq;
// 删除node之前所在频率的链表
node = this.freqMap[freq].delete(node);
// 链表不包含数据了,删除该链表
if (!this.freqMap[freq].count) {
delete this.freqMap[freq];
}
// 频率自增
freq++;
// 是否存在新频率的链表,不存在则创建
if (!this.freqMap[freq]) {
this.freqMap[freq] = new DoubleLinkedList(this.capacity);
}
// 节点插入新的频率列表
const newNode = this.freqMap[freq].push(node.key, node.value);
newNode.freq = freq;
// 返回新的节点
return newNode;
}
当访问一个节点的时候,动态的更新该节点的频率值,并且更新其所在的链表,接下来看下get操作
get(key) {
const node = this.map[key];
if (!node) {
return null;
}
this.updateFreq(node);
return node.value;
}
查看本地map中是否存在该节点,然后更新频率值,返回节点的值。麻烦一些的是put操作
put(key, value) {
if (!this.capacity) return null;
const currNode = this.map[key];
let newNode;
// 命中缓存
if (currNode) {
currNode.value = value;
newNode = this.updateFreq(currNode);
this.map[key] = newNode;
} else {
// 缓存已满
if (this.capacity === this.count) {
const minFreq = Math.min.apply(null, Object.keys(this.freqMap));
const oldNode = this.freqMap[minFreq].pop();
// 链表不包含数据了,删除该链表
if (!this.freqMap[freq].count) {
delete this.freqMap[freq];
}
delete this.map[oldNode.key];
this.count--;
}
const initFreq = 1;
if (!this.freqMap[initFreq]) {
this.freqMap[initFreq] = new DoubleLinkedList(this.capacity);
}
newNode = this.freqMap[initFreq].push(key, value);
newNode.freq = initFreq;
this.map[newNode.key] = newNode;
this.count++;
}
return newNode;
}
需要先判断是否命中缓存,如果this.map中存在,则更新频率,更新this.map中的值, 否则没有命中缓存,查看缓存是否已满,满的话,找到最小频率,删除其尾部的节点
由于为了和FIFO和LRU链表中的Node节点保持一直,所以说在代码中硬编码了freq属性,不过主要的思路都是一致的。