Vue的渲染机制指的是Vue怎么将单文件组件中的template转换为AST(语法树),再将AST转换成render函数,最后生成虚拟dom节点(包含创建元素节点的一切信息的JavaScript对象),并创建元素节点挂载到页面上,基本过程如下图:
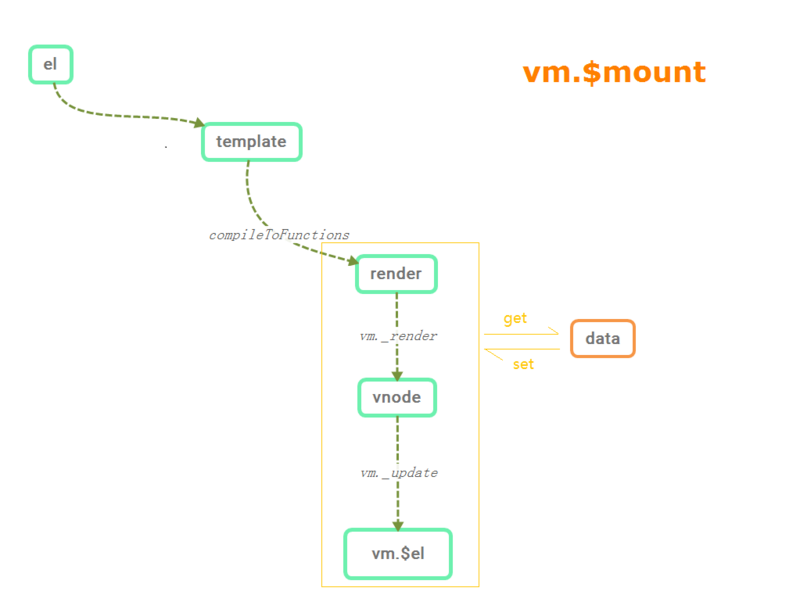 本节先介绍模板编译生成render函数的过程。
本节先介绍模板编译生成render函数的过程。
模板编译过程
模板编译成渲染函数经历了三个阶段: 将模板解析成AST、遍历AST标记静态节点以及静态根节点和使用AST生成render函数。 以下面模板为例:
<div id="app">{{ message }}</div>
首先获取组件的模板内容
var template = options.template;
if (template) {
// 针对字符串模板和选择符匹配模板
if (typeof template === 'string') {
// 选择符匹配模板,以'#'为前缀的选择符
if (template.charAt(0) === '#') {
// 获取匹配元素的innerHTML
template = idToTemplate(template);
}
} else if (template.nodeType) {
// 针对DOM元素匹配,获取匹配元素的innerHTML
template = template.innerHTML;
} else {
{
warn('invalid template option:' + template, this);
}
return this
}
} else if (el) {
// 如果没有传入template模板,则默认以el元素所属的根节点作为基础模板
template = getOuterHTML(el);
}
获取模板后处理的核心过程如下:
compileToFunctions(template, {
outputSourceRange: "development" !== 'production',
shouldDecodeNewlines: shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref: shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments
}, this)
...
var compiled = compile(template, options);
...
var compiled = baseCompile(template.trim(), finalOptions);
上面的代码是在创建编译器,真正的编译过程: 解析、优化以及生成render函数,代码如下:
var ast = parse(template.trim(), options);
if (options.optimize !== false) {
optimize(ast, options);
}
var code = generate(ast, options);
template解析
真正的解析函数是parseHTML,它的参数是template,和一个options对象,这个对象包含了start、end、chars以及comment对标签处理的函数:
parseHTML(template, {
warn: warn$2,
expectHTML: options.expectHTML,
isUnaryTag: options.isUnaryTag,
canBeLeftOpenTag: options.canBeLeftOpenTag,
shouldDecodeNewlines: options.shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref: options.shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
shouldKeepComment: options.comments,
outputSourceRange: options.outputSourceRange,
// 处理起始标签
start: function start (tag, attrs, unary, start$1, end) {
...
var element = createASTElement(tag, attrs, currentParent);
...
},
// 用来处理结束标签
end: function end (tag, start, end$1) {
var element = stack[stack.length - 1];
// pop stack
stack.length -= 1;
currentParent = stack[stack.length - 1];
if (options.outputSourceRange) {
element.end = end$1;
}
closeElement(element);
},
// 用来处理文本
chars: function chars (text, start, end) {
...
},
// 处理评论内容
comment: function comment (text, start, end) {
// adding anyting as a sibling to the root node is forbidden
// comments should still be allowed, but ignored
if (currentParent) {
var child = {
type: 3,
text: text,
isComment: true
};
if (options.outputSourceRange) {
child.start = start;
child.end = end;
}
currentParent.children.push(child);
}
}
});
return root
}
parseHTML函数核心内容为:
while (html) {
last = html;
// Make sure we're not in a plaintext content element like script/style
// 父元素为正常元素
if (!lastTag || !isPlainTextElement(lastTag)) {
var textEnd = html.indexOf('<');
// html以标签开头
if (textEnd === 0) {
// Comment:
if (comment.test(html)) {
var commentEnd = html.indexOf('-->');
if (commentEnd >= 0) {
if (options.shouldKeepComment) {
options.comment(html.substring(4, commentEnd), index, index + commentEnd + 3);
}
advance(commentEnd + 3);
continue
}
}
// Doctype:
var doctypeMatch = html.match(doctype);
if (doctypeMatch) {
advance(doctypeMatch[0].length);
continue
}
// End tag: 处理结束标签
...
// Start tag:
// 解析起始标签
...
}
...
} else {
// 父元素为script、style、textarea的处理逻辑
...
}
if (html === last) {
options.chars && options.chars(html);
if (!stack.length && options.warn) {
options.warn(("Mal-formatted tag at end of template: \"" + html + "\""), { start: index + html.length });
}
break
}
}
基本过程如下:
html=<div id="app">{{ message }}</div>首先获取textEnd === 0,接下来可判断html是以div标签起始的,进行parseStartTag处理
var startTagMatch = parseStartTag();
if (startTagMatch) {
// 对获取起始标签的属性,生成键值对
handleStartTag(startTagMatch);
if (shouldIgnoreFirstNewline(startTagMatch.tagName, html)) {
advance(1);
}
continue
}
返回对象为
{
attrs: [" id="app"", "id", "=", "app", undefined, undefined, index: 0, input: " id="app">{{ message }}<button @click="update">更新</button></div>", groups: undefined, start: 4, end: 13],
end: 14,
start: 0,
tagName: "div",
unarySlash: ""
}
其中unarySlash表示是否是闭合标签。在经过handleStartTag函数处理后调用start函数
if (!unary) {
stack.push({ tag: tagName, lowerCasedTag: tagName.toLowerCase(), attrs: attrs,start: match.start, end: match.end });
lastTag = tagName;
}
// 上面根据parseStartTag返回的对象生成attrs
if (options.start) {
options.start(tagName, attrs, unary, match.start, match.end);
}
options.start函数处理后生成
{attrsList: [{
end: 13
name: "id"
start: 5
value: "app"
}],
attrsMap: {id: "app"},
children: [],
end: 14,
parent: undefined,
rawAttrsMap: {id: {name: "id", value: "app", start: 5, end: 13}},
start: 0,
tag: "div",
type: 1}
先判断标签是否是闭合标签,如果是的话直接closeElement,不是的话,更新currentParent并且将当前元素推入stack栈。
if (!unary) {
currentParent = element;
stack.push(element);
} else {
closeElement(element);
}
需要注意的是: stack栈的作用是维护DOM的层级,防止HTML标签的不匹配。
2. 这个while的第一次循环结束,html被截取为{{ message }}</div>,此时计算textEnd为13,此时处理的是文本元素
// 为文本节点
var text = (void 0), rest = (void 0), next = (void 0);
if (textEnd >= 0) {
rest = html.slice(textEnd);
while (
!endTag.test(rest) &&
!startTagOpen.test(rest) &&
!comment.test(rest) &&
!conditionalComment.test(rest)
) {
// < in plain text, be forgiving and treat it as text
next = rest.indexOf('<', 1);
if (next < 0) { break }
textEnd += next;
rest = html.slice(textEnd);
}
text = html.substring(0, textEnd);
}
if (textEnd < 0) {
text = html;
}
if (text) {
advance(text.length);
}
if (options.chars && text) {
options.chars(text, index - text.length, index);
}
此时rest = </div>, text = {{ message }},由 options.chars函数处理文本,具体代码为
...
var children = currentParent.children;
...
if (text) {
if (!inPre && whitespaceOption === 'condense') {
// condense consecutive whitespaces into single space
text = text.replace(whitespaceRE$1, ' ');
}
var res;
var child;
// 带变量的文本节点, type = 2
if (!inVPre && text !== ' ' && (res = parseText(text, delimiters))) {
child = {
type: 2,
expression: res.expression,
tokens: res.tokens,
text: text
};
} else if (text !== ' ' || !children.length || children[children.length - 1].text !== ' ') {
// 不带变量的文本节点,type = 3
child = {
type: 3,
text: text
};
}
if (child) {
if (options.outputSourceRange) {
child.start = start;
child.end = end;
}
children.push(child);
}
}
经由parseText函数
function parseText (
text,
delimiters
) {
// 匹配 {{ message }}
var tagRE = delimiters ? buildRegex(delimiters) : defaultTagRE;
if (!tagRE.test(text)) {
return
}
var tokens = [];
var rawTokens = [];
var lastIndex = tagRE.lastIndex = 0;
var match, index, tokenValue;
while ((match = tagRE.exec(text))) {
index = match.index;
// push text token
// 把{{左边的文本内容添加到tokens中
if (index > lastIndex) {
rawTokens.push(tokenValue = text.slice(lastIndex, index));
tokens.push(JSON.stringify(tokenValue));
}
// tag token
// 将 {{ message }} 转成 _s(message) 添加到数组
var exp = parseFilters(match[1].trim());
tokens.push(("_s(" + exp + ")"));
rawTokens.push({ '@binding': exp });
lastIndex = index + match[0].length;
}
// 把{{右边的文本内容添加到tokens中
if (lastIndex < text.length) {
rawTokens.push(tokenValue = text.slice(lastIndex));
tokens.push(JSON.stringify(tokenValue));
}
return {
expression: tokens.join('+'),
tokens: rawTokens
}
}
处理后返回
{
expression: "_s(message)",
tokens: [{@binding: "message"}]
}
将该节点push进children,生成
[
{
end: 27,
expression: "_s(message)",
start: 14,
text: "{{ message }}",
tokens: [{@binding: "message"}],
type: 2
}
]
- 第三轮循环时html为
</div>,计算的textEnd = 0,匹配到结束标签
var endTagMatch = html.match(endTag);
if (endTagMatch) {
var curIndex = index;
advance(endTagMatch[0].length);
parseEndTag(endTagMatch[1], curIndex, index);
continue
}
endTagMatch为
[
"</div>", "div", groups: undefined, index: 0, input: "</div>"
]
栈进行遍历,寻找与当前结束标签匹配的起始标签,options.end函数处理
var element = stack[stack.length - 1];
// pop stack
stack.length -= 1;
currentParent = stack[stack.length - 1];
if (options.outputSourceRange) {
element.end = end$1;
}
closeElement(element);
将栈中的元素pop出,currentParent为栈的顶层第一个元素element, 更新元素element的end属性,在进行closeElement主要代码为:
// 对元素的属性进行处理,如ref,slot,is,attrs
if (!inVPre && !element.processed) {
element = processElement(element, options);
}
...
// 将父子关系确认好
if (currentParent && !element.forbidden) {
if (element.elseif || element.else) {
processIfConditions(element, currentParent);
} else {
if (element.slotScope) {
// scoped slot
// keep it in the children list so that v-else(-if) conditions can
// find it as the prev node.
var name = element.slotTarget || '"default"'
;(currentParent.scopedSlots || (currentParent.scopedSlots = {}))[name] = element;
}
// 将当前元素推入到当前父节点的children数组中,更新当前元素的父元素
currentParent.children.push(element);
element.parent = currentParent;
}
}
生成的AST为
{
attrs: [{
dynamic: undefined
end: 13
name: "id"
start: 5
value: ""app""
}]
attrsList: [{name: "id", value: "app", start: 5, end: 13}]
attrsMap: {id: "app"}
children: [{
end: 27,
expression: "_s(message)",
start: 14,
text: "{{ message }}",
tokens: [{@binding: "message"}],
type: 2
}]
end: 33
parent: undefined
plain: false
rawAttrsMap: {id: {name: "id", value: "app", start: 5, end: 13}}
start: 0
tag: "div"
type: 1
}
最后再更新stack和lastTag,stack=[],lastTag='div',循环结束,返回root这个生成的ast。
优化器
接下来进入优化阶段,
optimize(ast, options);
// 生成静态节点以及静态根节点
function optimize (root, options) {
if (!root) { return }
isStaticKey = genStaticKeysCached(options.staticKeys || '');
isPlatformReservedTag = options.isReservedTag || no;
// first pass: mark all non-static nodes.
markStatic$1(root);
// second pass: mark static roots.
markStaticRoots(root, false);
}
首先给ast标记非静态节点
function markStatic$1 (node) {
// 先判断该节点是否是静态节点
node.static = isStatic(node);
if (node.type === 1) {
// do not make component slot content static. this avoids
// 1. components not able to mutate slot nodes
// 2. static slot content fails for hot-reloading
if (
!isPlatformReservedTag(node.tag) &&
node.tag !== 'slot' &&
node.attrsMap['inline-template'] == null
) {
return
}
for (var i = 0, l = node.children.length; i < l; i++) {
var child = node.children[i];
// 递归子节点标记静态节点
markStatic$1(child);
// 如果子节点打完标记后,判断子节点是否是静态节点,如果不是,则父节点node不可能是静态节点,此时需将父节点设置static = false
if (!child.static) {
node.static = false;
}
}
...
}
}
判断是否是静态节点的函数
function isStatic (node) {
if (node.type === 2) { // expression,表达式
return false
}
if (node.type === 3) { // text 文本节点
return true
}
// 如果元素节点没有v-pre,必须同时满足
return !!(node.pre || (
!node.hasBindings && // no dynamic bindings
!node.if && !node.for && // not v-if or v-for or v-else
!isBuiltInTag(node.tag) && // not a built-in 内置标签,如slot、component
isPlatformReservedTag(node.tag) && // not a component,必须是保留标签,<list></list>就不是保留标签
!isDirectChildOfTemplateFor(node) && // 当前节点的父节点不能是带v-for指令的template标签
Object.keys(node).every(isStaticKey) //
))
}
接着找出所有的静态根节点并标记
// second pass: mark static roots.
markStaticRoots(root, false);
具体为
function markStaticRoots (node, isInFor) {
if (node.type === 1) {
if (node.static || node.once) {
node.staticInFor = isInFor;
}
// For a node to qualify as a static root, it should have children that
// are not just static text. Otherwise the cost of hoisting out will
// outweigh the benefits and it's better off to just always render it fresh.
// 对于静态根节点,必须有子节点,且子节点不能只是一个静态文本节点
if (node.static && node.children.length && !(
node.children.length === 1 &&
node.children[0].type === 3
)) {
node.staticRoot = true;
return
} else {
node.staticRoot = false;
}
// 递归子节点
if (node.children) {
for (var i = 0, l = node.children.length; i < l; i++) {
markStaticRoots(node.children[i], isInFor || !!node.for);
}
}
...
}
}
返回的AST为:
{
attrs: [{
dynamic: undefined
end: 13
name: "id"
start: 5
value: ""app""
}]
attrsList: [{name: "id", value: "app", start: 5, end: 13}]
attrsMap: {id: "app"}
children: [{
end: 27,
expression: "_s(message)",
start: 14,
static: false,
text: "{{ message }}",
tokens: [{@binding: "message"}],
type: 2
}]
end: 33
parent: undefined
plain: false,
rawAttrsMap: {id: {name: "id", value: "app", start: 5, end: 13}}
start: 0,
static: false,
staticRoot: false,
tag: "div",
type: 1
}
代码生成器
作用将ast生成render渲染函数,不同的节点生成的方式不一样,具体代码如下:
function generate (
ast,
options
) {
var state = new CodegenState(options);
var code = ast ? genElement(ast, state) : '_c("div")';
return {
render: ("with(this){return " + code + "}"),
staticRenderFns: state.staticRenderFns
}
}
先判断ast是否存在,不存在默认是_c('div'),_c表示
vm._c = function (a, b, c, d) { return createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, false); };
存在则对ast具体处理
function genElement (el, state) {
if (el.parent) {
el.pre = el.pre || el.parent.pre;
}
// 处理静态节点
if (el.staticRoot && !el.staticProcessed) {
return genStatic(el, state)
} else if (el.once && !el.onceProcessed) {
// 处理v-once指令
return genOnce(el, state)
} else if (el.for && !el.forProcessed) {
// 处理v-for指令
return genFor(el, state)
} else if (el.if && !el.ifProcessed) {
// 处理v-if指令
return genIf(el, state)
} else if (el.tag === 'template' && !el.slotTarget && !state.pre) {
// 处理template标签
return genChildren(el, state) || 'void 0'
} else if (el.tag === 'slot') {
// 处理slot内置组件
return genSlot(el, state)
} else {
// component or element
var code;
if (el.component) {
// 处理组件
code = genComponent(el.component, el, state);
} else {
var data;
// 处理元素
if (!el.plain || (el.pre && state.maybeComponent(el))) {
data = genData$2(el, state);
}
// 生成子节点的render函数部分
var children = el.inlineTemplate ? null : genChildren(el, state, true);
code = "_c('" + (el.tag) + "'" + (data ? ("," + data) : '') + (children ? ("," + children) : '') + ")";
}
// module transforms
for (var i = 0; i < state.transforms.length; i++) {
code = state.transforms[i](el, code);
}
return code
}
}
进入genData$2函数为
function genData$2 (el, state) {
var data = '{';
// directives first.
// directives may mutate the el's other properties before they are generated.
var dirs = genDirectives(el, state);
if (dirs) { data += dirs + ','; }
// key
if (el.key) {
data += "key:" + (el.key) + ",";
}
// ref
if (el.ref) {
data += "ref:" + (el.ref) + ",";
}
if (el.refInFor) {
data += "refInFor:true,";
}
// pre
if (el.pre) {
data += "pre:true,";
}
// record original tag name for components using "is" attribute
if (el.component) {
data += "tag:\"" + (el.tag) + "\",";
}
// module data generation functions
for (var i = 0; i < state.dataGenFns.length; i++) {
data += state.dataGenFns[i](el);
}
// attributes,更新attrs的属性形式
if (el.attrs) {
data += "attrs:" + (genProps(el.attrs)) + ",";
}
// DOM props
if (el.props) {
data += "domProps:" + (genProps(el.props)) + ",";
}
// event handlers
if (el.events) {
data += (genHandlers(el.events, false)) + ",";
}
if (el.nativeEvents) {
data += (genHandlers(el.nativeEvents, true)) + ",";
}
// slot target
// only for non-scoped slots
if (el.slotTarget && !el.slotScope) {
data += "slot:" + (el.slotTarget) + ",";
}
// scoped slots
if (el.scopedSlots) {
data += (genScopedSlots(el, el.scopedSlots, state)) + ",";
}
// component v-model
if (el.model) {
data += "model:{value:" + (el.model.value) + ",callback:" + (el.model.callback) + ",expression:" + (el.model.expression) + "},";
}
// inline-template
if (el.inlineTemplate) {
var inlineTemplate = genInlineTemplate(el, state);
if (inlineTemplate) {
data += inlineTemplate + ",";
}
}
data = data.replace(/,$/, '') + '}';
// v-bind dynamic argument wrap
// v-bind with dynamic arguments must be applied using the same v-bind object
// merge helper so that class/style/mustUseProp attrs are handled correctly.
if (el.dynamicAttrs) {
data = "_b(" + data + ",\"" + (el.tag) + "\"," + (genProps(el.dynamicAttrs)) + ")";
}
// v-bind data wrap
if (el.wrapData) {
data = el.wrapData(data);
}
// v-on data wrap
if (el.wrapListeners) {
data = el.wrapListeners(data);
}
return data
}
其功能就是拼接字符串,先给data赋值一个'{', 然后发现节点有哪些属性就将其拼接到data,最后加上一个'}',最后返回一个完整得data:
"{attrs:{"id":"app"}}"
接着对元素节点的子节点进行处理
genChildren(el, state, true);
具体函数为:
function genChildren (
el,
state,
checkSkip,
altGenElement,
altGenNode
) {
var children = el.children;
if (children.length) {
...
var gen = altGenNode || genNode;
return ("[" + (children.map(function (c) { return gen(c, state); }).join(',')) + "]" + (normalizationType$1 ? ("," + normalizationType$1) : ''))
}
}
根据不同子节点类型生成不同的节点字符串将其拼接在一起,genNode函数为:
function genNode (node, state) {
if (node.type === 1) {
return genElement(node, state)
} else if (node.type === 3 && node.isComment) {
return genComment(node)
} else {
return genText(node)
}
}
递归子节点来生成子节点的子节点,最后拼接到一起返回。文本节点的处理
function genText (text) {
return ("_v(" + (text.type === 2
? text.expression // no need for () because already wrapped in _s()
: transformSpecialNewlines(JSON.stringify(text.text))) + ")")
}
动态文本使用express表达式,静态文本用text,把文本放在_v中作为参数,生成的code即render函数为:
"_c('div',{attrs:{"id":"app"}},[_v(_s(message))])"
最后由
updateComponent = function () {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating);
};
中的vm._render()函数调用生成VNode,代码为
vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement);
调用生成的render函数,指向vm._renderProxy,with语句的作用是将代码的作用域设置到一个特定的作用域this中,调用后进入如下:
with(this){return _c('div',{attrs:{"id":"app"}},[_v(_s(message))])}
其中_s表示toString(),生成的VNode为
{
asyncFactory: undefined
asyncMeta: undefined
children: [
{
asyncFactory: undefined,
asyncMeta: undefined,
children: undefined,
componentInstance: undefined,
componentOptions: undefined,
context: undefined,
data: undefined,
elm: undefined,
fnContext: undefined,
fnOptions: undefined,
fnScopeId: undefined,
isAsyncPlaceholder: false,
isCloned: false,
isComment: false,
isOnce: false,
isRootInsert: true,
isStatic: false,
key: undefined
ns: undefined,
parent: undefined,
raw: false,
tag: undefined,
text: "Hello Wolrd",
child: undefined
}],
componentInstance: undefined
componentOptions: undefined
context: Vue {_uid: 0, _isVue: true, $options: {…}, _renderProxy: Proxy, _self: Vue, …}
data: {attrs: {id: 'app'}}
elm: undefined,
fnContext: undefined,
fnOptions: undefined,
fnScopeId: undefined,
isAsyncPlaceholder: false,
isCloned: false,
isComment: false,
isOnce: false,
isRootInsert: true,
isStatic: false,
key: undefined,
ns: undefined,
parent: undefined,
raw: false,
tag: "div",
text: undefined,
child: undefined
}
此时编译过程结束,下篇介绍VNode的渲染过程。