函数和变量的提升
函数提升只是声明式函数会被提升,对于赋值形的不会提升
1.js中var的变量和函数是会被提升的,变量和函数不同的是,变量只是声明提升不会赋值,而函数是整体都提升。但是需要注意一点,赋值式函数是不会被提升的.
比如:
// 1
var func = function(){
alert('ABC');
}
// 2
function func(){
alert('ABC1');
}
func(); // ABC
因为代码2在词法解析的时候会被提升到作用域最前面,而代码段1不会提升。当代码执行的时候,代码段1会覆盖代码段2,才是执行输出应该是代码段1的结果
类的私有属性和原型属性
1.类的私有属性是放在constructor里面的,每个实例独立一份。
function Fn() {
this.x = 10;
this.y = 20;
this.getX = function () {
console.log(this.x);
}
return this;
}
Fn.prototype.sum=function(){
console.log(this.x+this.y);
}
Fn.prototype={
getX:function(){
this.x+=1;
console.log(this.x);
},
getY:function(){
this.y-=1;
console.log(this.y);
}
};
var f1 = new Fn;
var f2 = new Fn;
console.log(f1.getX === f2.getX); // false
因为每个实例上的私有属性和方法都是独立的
2.对于原型属性,每个实例是共享的,拥有同一份prototype的地址。
console.log(f1.__proto__ === f2.__proto__); // true
console.log(f1.__proto__ === Fn.prototype); // true
实例共享prototype,并且实例的__proto__都是指向类的prototype的
3.默认声明一个函数,函数自带一个prototype,并且它的constructor构造器是挂载到prototype上的
function AAA(){alert('AAA')}
console.dir(AAA);
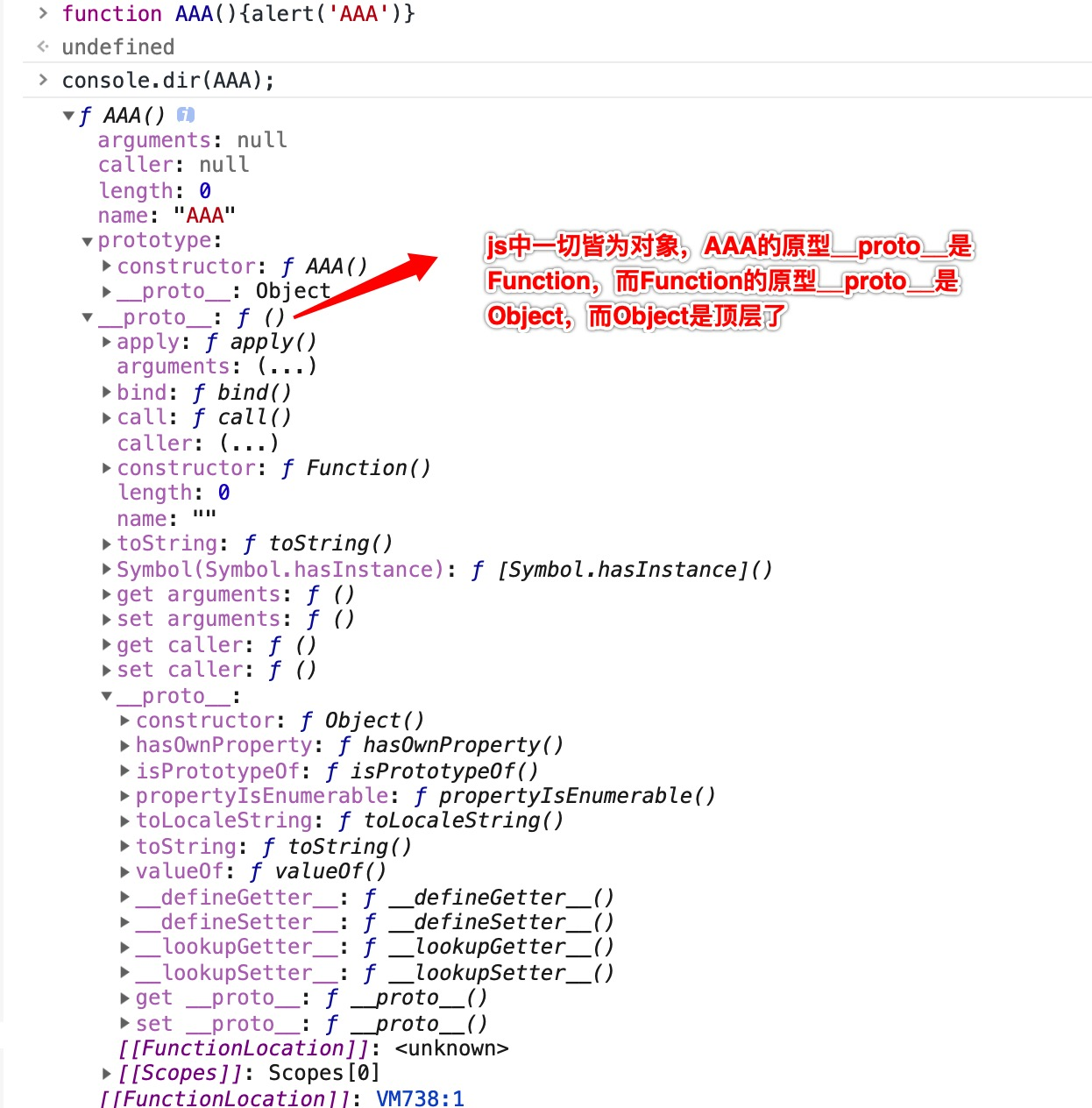
如果声明完不重写prototype,prototype上有constructor指向AAA类,AAA的原型链__proto__指向Function,而Function指向Object
4.new一个实例的时候,实例调用的方法,先找私有方法,如果不存在,再找原型上的方法。
f1.getX(); // 输出10
如果constructor上没有getX,则会调用原型上的getX
5.new操作符执行 参考MDN对new的定义
- 1.创建一个空的简单JavaScript对象(即{});
- 2.链接该对象(即设置该对象的构造函数)到另一个对象 ;
- 3.将步骤1新创建的对象作为this的上下文 ;
- 4.如果该函数没有返回对象,则返回this。
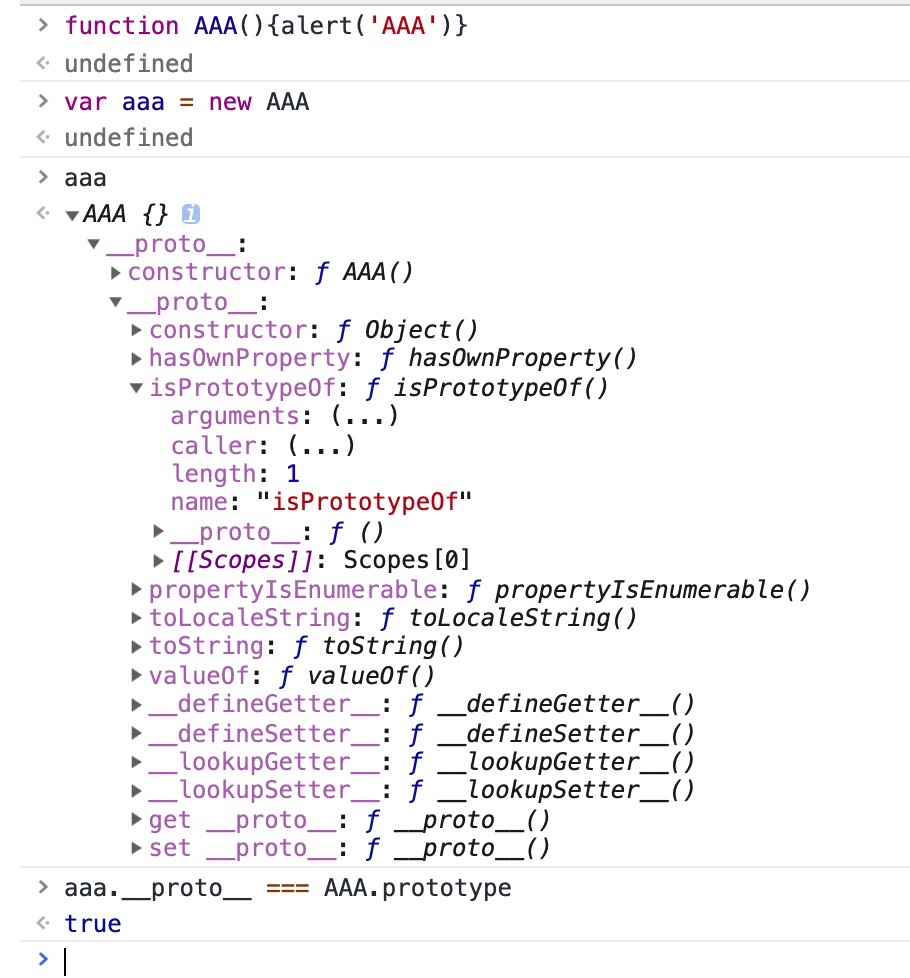
步骤如下:
function AAA(){alert('AAA')}
var aaa = new AAA;
console.dir(aaa);
new AAA步骤解读:
步骤一:声明一个空对象const obj = {};
步骤二:__proto__链接到AAA.prototype;obj.__proto__ = AAA.prototype;
步骤三: AAA.call(obj)
步骤四:return obj
根据上述步骤,手写new源码如下:
// 重写new方法
function createClass(originObj,...args){
// 步骤一
const obj = {};
// 步骤二 此处也可以使用Object.setPrototypeOf
//Object.setPrototypeOf(obj,originObj.prototype)
obj.__proto__ = originObj.prototype;
// 步骤三
originObj.call(obj,...args);
// 步骤四
return obj;
}
function AAA(x,y){
this.x = x || 10;
this.y = y || 20;
this.getY = function(){
return ++this.y;
}
}
AAA.prototype.getX = function(){
return this.x;
}
const aaa = createClass(AAA);
console.log(aaa.getY()); // 21
console.log(aaa.getX()); // 10
const bbb = createClass(AAA,200,300);
console.log(bbb.getY()); // 301
console.log(bbb.getX()); // 200
call实现
call的语法:参考MDN对call定义
fun.call(thisArg, arg1, arg2, ...)
- thisArg 在 fun 函数运行时指定的 this 值。
if(thisArg == undefined|null) this = window,if(thisArg == number|boolean|string) this == new Number()|new Boolean()| new String() - arg1、arg2是函数执行时传入参数。
- 返回值:使用调用者提供的 this 值和参数调用该函数的返回值。若该方法没有返回值,则返回 undefined。
根据描述call的实现步骤如下:
步骤一:判断传入对象是否为undefined或null,如果是则指向window。 obj = obj || window
步骤二:将call里面的this,即call的调用者,存储在传入对象上,这样执行调用者的时候,this自然指向传入对象上。obj.fn = this;
步骤三:执行挂载到传入对象上的fn方法,即call的调用者。obj.fn(...args),传入参数即可。
步骤四:将执行结果return。
源码如下:
Function.prototype.callNew = function(obj,...args){
obj = obj || window
obj.fn = this;
return obj.fn(...args);
}
let x = 1;
let y = 2;
const obj = {
y: 100,
x: 200
}
const obj1 = {
show(){
console.log(this.x+this.y);
}
}
obj1.show.callNew(obj); // 300