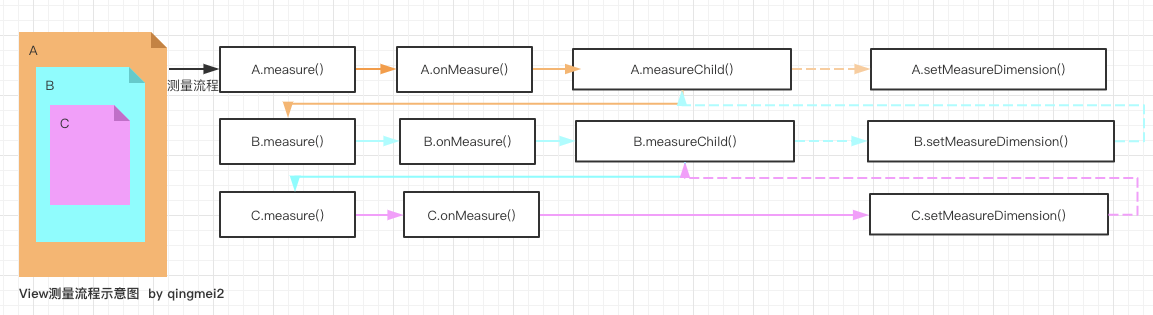
上篇文章分析了View的绘制入口,即ViewRootImpl.requestLayout()方法。 juejin.cn/post/684490…
UI绘制流程,主要包括performMeasure()、performLayout()、performDraw()
测量流程 Measure
入口方法 performMeasure()
/**
* We have one child
*/
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
mView = view;
......
}
}
}
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
// mView即DecorView
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
mView即DecorView,所以会执行View.measure()方法。
public class View {
/**
* <p>
* This is called to find out how big a view should be. The parent
* supplies constraint information in the width and height parameters.
* </p>
*
* <p>
* The actual measurement work of a view is performed in
* {@link #onMeasure(int, int)}, called by this method. Therefore, only
* {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} can and must be overridden by subclasses.
* </p>
*
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec Horizontal space requirements as imposed by the
* parent
* @param heightMeasureSpec Vertical space requirements as imposed by the
* parent
*
* @see #onMeasure(int, int)
*/
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int oWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int oHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(widthMeasureSpec, optical ? -oWidth : oWidth);
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(heightMeasureSpec, optical ? -oHeight : oHeight);
}
// Suppress sign extension for the low bytes
long key = (long) widthMeasureSpec << 32 | (long) heightMeasureSpec & 0xffffffffL;
if (mMeasureCache == null) mMeasureCache = new LongSparseLongArray(2);
final boolean forceLayout = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
// Optimize layout by avoiding an extra EXACTLY pass when the view is
// already measured as the correct size. In API 23 and below, this
// extra pass is required to make LinearLayout re-distribute weight.
final boolean specChanged = widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec
|| heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec;
final boolean isSpecExactly = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY
&& MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
final boolean matchesSpecSize = getMeasuredWidth() == MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
&& getMeasuredHeight() == MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
final boolean needsLayout = specChanged
&& (sAlwaysRemeasureExactly || !isSpecExactly || !matchesSpecSize);
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
// first clears the measured dimension flag
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
int cacheIndex = forceLayout ? -1 : mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
// flag not set, setMeasuredDimension() was not invoked, we raise
// an exception to warn the developer
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
throw new IllegalStateException("View with id " + getId() + ": "
+ getClass().getName() + "#onMeasure() did not set the"
+ " measured dimension by calling"
+ " setMeasuredDimension()");
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
mMeasureCache.put(key, ((long) mMeasuredWidth) << 32 |
(long) mMeasuredHeight & 0xffffffffL); // suppress sign extension
}
/**
* <p>
* Measure the view and its content to determine the measured width and the
* measured height. This method is invoked by {@link #measure(int, int)} and
* should be overridden by subclasses to provide accurate and efficient
* measurement of their contents.
* </p>
*
* <p>
* <strong>CONTRACT:</strong> When overriding this method, you
* <em>must</em> call {@link #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)} to store the
* measured width and height of this view. Failure to do so will trigger an
* <code>IllegalStateException</code>, thrown by
* {@link #measure(int, int)}. Calling the superclass'
* {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} is a valid use.
* </p>
*
* <p>
* The base class implementation of measure defaults to the background size,
* unless a larger size is allowed by the MeasureSpec. Subclasses should
* override {@link #onMeasure(int, int)} to provide better measurements of
* their content.
* </p>
*
* <p>
* If this method is overridden, it is the subclass's responsibility to make
* sure the measured height and width are at least the view's minimum height
* and width ({@link #getSuggestedMinimumHeight()} and
* {@link #getSuggestedMinimumWidth()}).
* </p>
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec horizontal space requirements as imposed by the parent.
* The requirements are encoded with
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec}.
* @param heightMeasureSpec vertical space requirements as imposed by the parent.
* The requirements are encoded with
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec}.
*
* @see #getMeasuredWidth()
* @see #getMeasuredHeight()
* @see #setMeasuredDimension(int, int)
* @see #getSuggestedMinimumHeight()
* @see #getSuggestedMinimumWidth()
* @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getMode(int)
* @see android.view.View.MeasureSpec#getSize(int)
*/
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
}
会再调用View.onMeasure()方法,而DecorView继承FrameLayout,因为measure()方法是final类型,无法重写,而FrameLayout重写了onMeasure()方法,所以会执行FrameLayout.onMeasure()方法。
public class FrameLayout extends ViewGroup {
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
// 遍历child,计算maxWidth和maxHeight
......
// Account for padding too
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground is minimum height and width
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
// 遍历child,调用child.measure()方法
......
}
}
自定义ViewGroup重写ViewGroup的onMeasure()步骤
- 遍历child,计算maxWidth和maxHeight
- 调用setMeasuredDimension()设置宽高
- 遍历child,调用child.measure()
在Android中,View测量的宽高是使用MeasureSpec来描述的。
MeasureSpec
由Mode(模式) + Size(大小)两部分组成,是一个32位int值,前2位表示Mode,后30位表示Size。
/**
* A MeasureSpec encapsulates the layout requirements passed from parent to child.
* Each MeasureSpec represents a requirement for either the width or the height.
* A MeasureSpec is comprised of a size and a mode. There are three possible
* MeasureSpecs are implemented as ints to reduce object allocation. This class
* is provided to pack and unpack the <size, mode> tuple into the int.
*/
public static class MeasureSpec {
// 移位的位数
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has not imposed any constraint
* on the child. It can be whatever size it wants.
*/
// 00左移30位,00 + 00..00
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size
* for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless
* of how big it wants to be.
*/
// 01左移30位,01 + 00..00
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up
* to the specified size.
*/
// 10左移30位,10 + 00..00
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Creates a measure specification based on the supplied size and mode.
*
* @param size the size of the measure specification
* @param mode the mode of the measure specification
* @return the measure specification based on size and mode
*/
public static int makeMeasureSpec(@IntRange(from = 0, to = (1 << MeasureSpec.MODE_SHIFT) - 1) int size,
@MeasureSpecMode int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}
/**
* Extracts the mode from the supplied measure specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the mode from
* @return {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED},
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST} or
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}
*/
@MeasureSpecMode
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
//noinspection ResourceType
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
/**
* Extracts the size from the supplied measure specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the size from
* @return the size in pixels defined in the supplied measure specification
*/
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
}
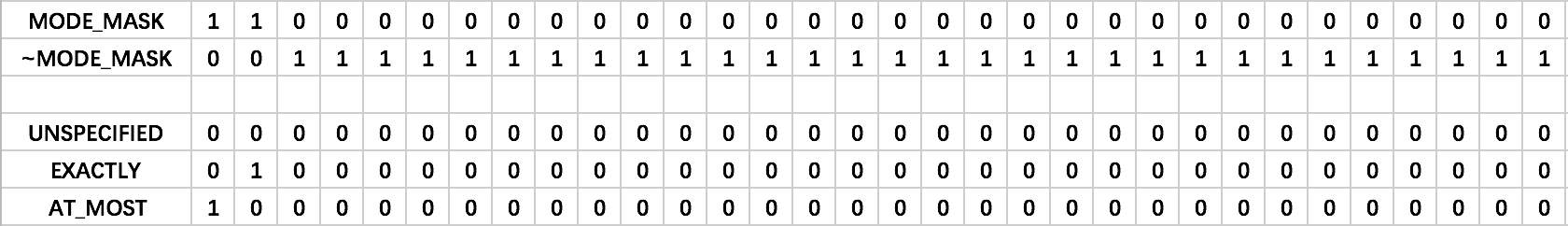
MeasureSpec的创建、Mode和Size的获取,都是通过位运算进行的。
View测量时MeasureSpec如何获取的
从ViewRootImpl.performTraversals()调用performMeasure()地方查找
private void performTraversals() {
......
if (!mStopped || mReportNextDraw) {
boolean focusChangedDueToTouchMode = ensureTouchModeLocally(
(relayoutResult&WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_RES_IN_TOUCH_MODE) != 0);
if (focusChangedDueToTouchMode || mWidth != host.getMeasuredWidth()
|| mHeight != host.getMeasuredHeight() || contentInsetsChanged ||
updatedConfiguration) {
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(mTag, "Ooops, something changed! mWidth="
+ mWidth + " measuredWidth=" + host.getMeasuredWidth()
+ " mHeight=" + mHeight
+ " measuredHeight=" + host.getMeasuredHeight()
+ " coveredInsetsChanged=" + contentInsetsChanged);
// Ask host how big it wants to be
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
// Implementation of weights from WindowManager.LayoutParams
// We just grow the dimensions as needed and re-measure if
// needs be
int width = host.getMeasuredWidth();
int height = host.getMeasuredHeight();
boolean measureAgain = false;
if (lp.horizontalWeight > 0.0f) {
width += (int) ((mWidth - width) * lp.horizontalWeight);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
measureAgain = true;
}
if (lp.verticalWeight > 0.0f) {
height += (int) ((mHeight - height) * lp.verticalWeight);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(height,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
measureAgain = true;
}
if (measureAgain) {
if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(mTag,
"And hey let's measure once more: width=" + width
+ " height=" + height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
layoutRequested = true;
}
}
}
}
}
通过getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width)获取MeasureSpec。
mWidth 即窗口的宽,lp.width即顶层DecorView的LayoutParam属性
/**
* Figures out the measure spec for the root view in a window based on it's
* layout params.
*
* @param windowSize
* The available width or height of the window
*
* @param rootDimension
* The layout params for one dimension (width or height) of the
* window.
*
* @return The measure spec to use to measure the root view.
*/
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
DecorView的MeasureSpec,由窗口大小和自身LayoutParams决定
通过窗口大小和LayoutParams,创建MeasureSpec的规则如下
- LayoutParam.MATCH_PARENT 精确模式,窗口大小
- LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT 最大模式,最大为窗口大小
- 固定大小 精确模式,大小为LayoutParams的大小
测量完DecorView的大小,下面就要测量其Child的大小
前面说过,DecorView继承FrameLayout,在onMeasure()方法中遍历调用Child.measure()方法进行测量,那么是如何获取的Child的MeasureSpec的呢?
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
......
}
调用measureChildWidthMargins(),再调用getChildMeasureSpec()来获取Child的MeasureSpec。
/**
* Does the hard part of measureChildren: figuring out the MeasureSpec to
* pass to a particular child. This method figures out the right MeasureSpec
* for one dimension (height or width) of one child view.
*
* The goal is to combine information from our MeasureSpec with the
* LayoutParams of the child to get the best possible results. For example,
* if the this view knows its size (because its MeasureSpec has a mode of
* EXACTLY), and the child has indicated in its LayoutParams that it wants
* to be the same size as the parent, the parent should ask the child to
* layout given an exact size.
*
* @param spec The requirements for this view
* @param padding The padding of this view for the current dimension and
* margins, if applicable
* @param childDimension How big the child wants to be in the current
* dimension
* @return a MeasureSpec integer for the child
*/
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//noinspection ResourceType
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
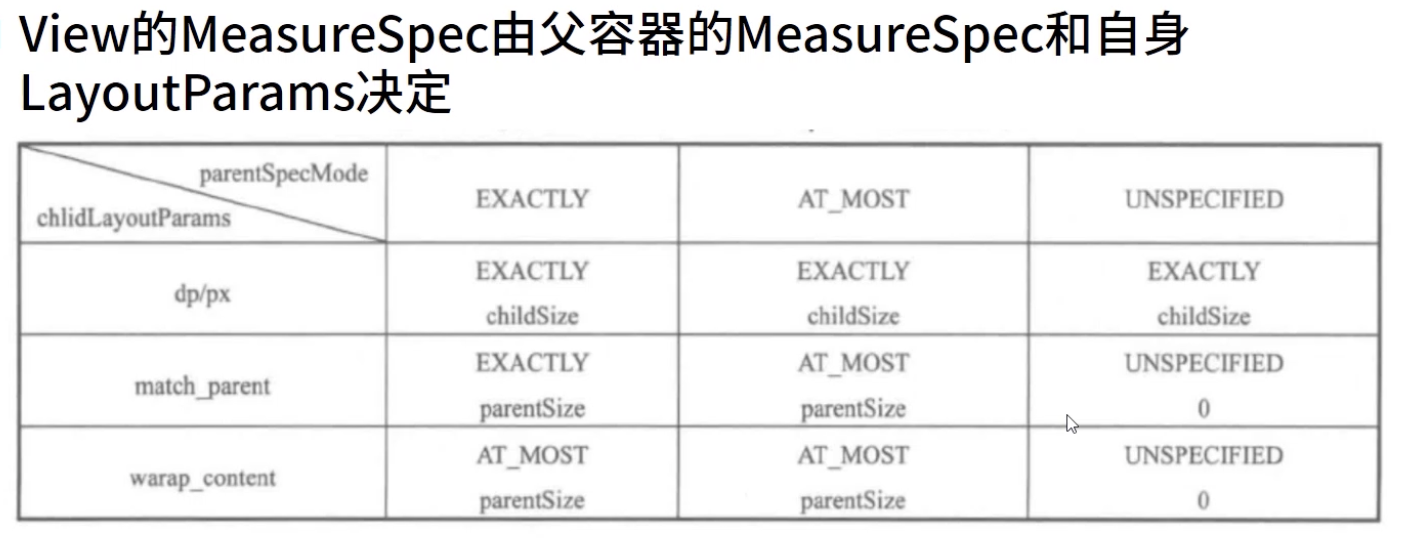
ViewGroup measure --> onMeasure(测量子控件的宽高)--> setMeasuredDimension -->setMeasuredDimensionRaw(保存自己的宽高)
View measure --> onMeasure --> setMeasuredDimension -->setMeasuredDimensionRaw(保存自己的宽高)
自定义View如果不重写onMeasure()方法,会是什么效果
如果不重写,则默认执行View的onMeasure()方法
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
}
会通过getDefaultSize()获取默认的MeasureSpec
/**
* Utility to return a default size. Uses the supplied size if the
* MeasureSpec imposed no constraints. Will get larger if allowed
* by the MeasureSpec.
*
* @param size Default size for this view
* @param measureSpec Constraints imposed by the parent
* @return The size this view should be.
*/
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
可见,AT_MOST和EXACTLY都设置成了父容器的大小。
结论,无论自定义View不重写onMeasure()设置MeasureSpec,那么无论该View的LayoutPrams是MATCH_PARENT或WRAP_CONTENT,都会设置成父容器的剩余大小。
Measure递归流程 图片来源