什么是链表
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。 相比于线性表顺序结构,操作复杂。 百度百科
链表的优缺点
优点
- 链表允许插入和移除表上任意位置上的节点
- 克服数组链表需要预先知道数据大小的缺点
- 充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理
缺点
- 失去了数组随机读取的优点,只能使用顺序查找,效率低
- 由于增加了结点的指针域,空间开销比较大
使用场景
- 不需要知道数据的多少
- 需要频繁的插入
实现功能
- 向链表尾部增加数据(append)
- 向指定位置插入数据(insert)
- 移除指定数据(removeData)
- 移除指定位置数据(removeIndex)
- 向链表头部插入数据(unshift)
- 移除链表头部数据(shift)
- 移除链表尾部数据(pop)
- 查找数据(searchData)
- 转换成字符串输出(toString)
- 是否为空(isEmpty)
- 链表长度(length)
- 获取整个列表(getList)
创建节点
每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
function Node(data) {
this.data = data
this.next = null
}
实现链表
用到的变量
- current(当前节点)
- previous(上一个节点)
- index (当前索引)// 索引从0开始
function List() {
let length = 0
let head = null
this.append = ...
this.insert = ...
this.removeData = ...
this.removeIndex = ...
this.unshift = ...
this.shift = ...
this.pop = ...
this.searchData = ...
this.toString = ...
this.isEmpty = ...
this.length = ...
this.getList = ...
}
向链表尾部增加数据(append)
首先创建一个节点,然后判断链表是否为空,如果为空,那么当前插入节点则为头节点;不为空则遍历链表,找到最后一个节点,将最后一个节点的next指针指向新创建的节点。
this.append = (data) => { // 向链表末尾添加元素
let node = new Node(data)
let current
if (head === null) { // 判断链表是否为空
head = node
}
else {
current = head
while (current.next) {
current = current.next // 找到最后一个节点
}
current.next = node
}
length ++ // 长度+1
return true
}
向指定位置插入数据(insert)
首先判断插入的位置是否越界(0=< position <= length),越界则直接return;没有越界,创建新的节点,先判断是否为首位插入,首位插入,存储当前head为current,改变head为新节点,head的next指向存储的curent;非首位插入,遍历链表判断index 和position 的大小,当index小于position时,把当前的current存储为previous,current赋值为下一个节点,当退出循环时,即是当前节点插入的位置,改变新节点的指向为current,previous的next为新节点
this.insert = (position, data) => { // 向链表指定位置添加元素
if (position >= 0 && position <= length) { //检查是否越界
let node = new Node(data),
current = head,
previous,
index = 0
if (position === 0) { //在第一个位置添加
node.next = current
head = node
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
//通过改变指针,将node链接在previous和current之间
node.next = current
previous.next = node
}
length++
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
移除指定数据(removeData)
首先判断head是否为空,为空直接返回;不为空,遍历链表,判断index小于length并且current的data不等于删除的data,循环退出后,先判断是否存在删除的data,index大于length即不存在,存在即先判断是否为头部,改变head节点的指向。
this.removeData = (data) => { // 通过数据删除链表元素
let previous,
current,
index = 0
if (head === null) {
return false
}
current = head
while (index++ < length && current.data !== data) { // index小于length并且current的data不等于删除的data
previous = current
current = current.next
}
if (index > length) { // data不存在
return false
} else {
if (head.data === data) {
head = current.next
} else {
previous.next = current.next
}
length--
return true
}
}
移除指定位置数据(removeIndex)
首先判断插入的位置是否越界(0=< position <= length),越界则直接return;没有越界,先判断是否为首位删除,首位删除,存储当前head为current,改变head为current的next;非首位删除,遍历链表判断index 和position 的大小,当index小于position时,把当前的current存储为previous,current赋值为下一个节点,当退出循环时,即是当前节点删除的位置,改变previous的next为current的next
this.removeIndex = (position) => { // 通过位置删除链表元素
if (position >= -1 && position < length) {
let previous,
current = head,
index = 0
if (position === 0) { // 首位删除
head = current.next
} else {
while (index++ < position) { // 判断index 和position 的大小
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = current.next
}
length--
return true
} else {
return false
}
}
向链表头部插入数据(unshift)
存储当前head为current,改变head为新节点,head的next指向存储的current
this.unShift = (data) => { //向链表首插入元素
let node = new Node(data),
current = head
node.next = current
head = node
length++
return true
}
移除链表头部数据(shift)
判断链表是否为空,为空直接返回;不为空,存储当前head为current,改变head为current的next
this.shift = () => { //删除链表首元素
let current = head
if (head === null) {
return false
}
else {
head = current.next
length--
return true
}
}
移除链表尾部数据(pop)
判断链表是否为空,为空直接返回,不为空,循环链表,找到next为空的上一个节点,把previous的next置为null
this.pop = () => { // 实现一
let current = head,
previous
if( !current ) return false
else {
while(current && current.next) {
previous = current
current = current.next
}
previous.next = null
length --
return true
}
}
// 实现二
this.pop2 = () => { // 删除链表尾元素
let current
if (head === null) {
return false
}
current = head
while (current && current.next.next) {
current = current.next
}
current.next = null
length--
return true
}
查找数据(searchData)
首先判断head是否为空,为空直接返回;不为空,遍历链表,判断index小于length并且current的data不等于查找的data,循环退出后,先判断是否存在删除的data,index大于length即不存在,存在即返回下标位置和数据。
this.searchData = (data) => { //查找元素
let current,
index = 0
if (head === null) {
return false
}
current = head
while (index++ < length && current.data !== data) {
current = current.next
}
if( index > length) return false
return {
index: --index,
data: current.data
}
}
转换成字符串输出(toString)
循环遍历链表,判断next是否为null,把所有的值链接起来
this.toString = () => { //输出数据组成的字符串
let resultStr = "",
current,
index = length
if (head === null) {
return ""
}
current = head
while (index-- > 0) {
resultStr += "," + current.data
current = current.next
}
return resultStr.slice(1)
}
是否为空(isEmpty)
返回length是否等于0
this.isEmpty = () => {
return length === 0
}
链表长度(length)
返回length
this.length = () => {
return length
}
获取整个列表(getList)
返回head
this.getList = () => {
return head
}
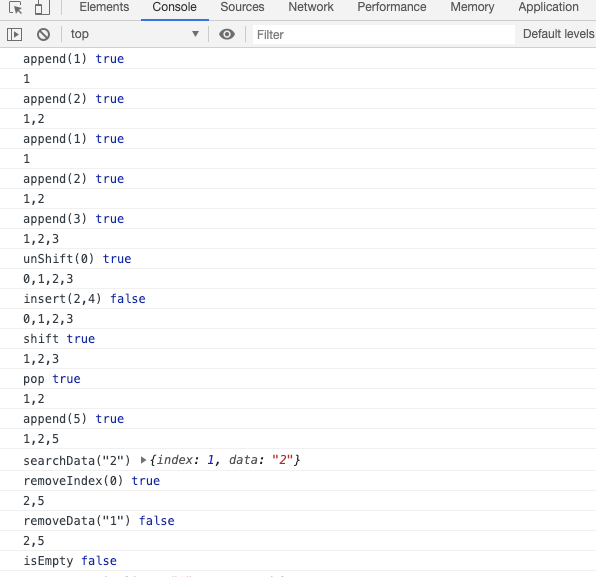
测试
let singleList = new List()
console.log('append(1)', singleList.append("1"))
console.log(singleList.toString())
console.log('append(2)', singleList.append("2"))
console.log(singleList.toString())
console.log('append(3)', singleList.append("3"))
console.log(singleList.toString())
console.log('unShift(0)', singleList.unShift(0))
console.log(singleList.toString())
console.log('insert(2,4)', singleList.insert(5, "4"))
console.log(singleList.toString())
console.log('shift', singleList.shift())
console.log(singleList.toString())
console.log('pop', singleList.pop())
console.log(singleList.toString())
console.log('append(5)', singleList.append("5"))
console.log(singleList.toString())
console.log('searchData("2")', singleList.searchData("2"))
console.log('removeIndex(0)', singleList.removeIndex(0))
console.log(singleList.toString())
console.log('removeData("1")', singleList.removeData("1"))
console.log(singleList.toString())
console.log('isEmpty', singleList.isEmpty())
实现发现
- 移除元素时先判断链表是否为空
- 查找时会用到链表长度
- 临界条件需要多注意