Collection:
- Set
- HashSet(无序)
- LinkedHashSet
- TreeSet
- HashSet(无序)
- List
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
Collection是一组对象的集合,其中的内容称为元素。一些集合允许有重复元素,一些不允许。有些是有序的,有些是无序的。JDK不提供接口的直接实现。它提供了很多子接口的实现,比如Set和List。这些接口通常被用来当作参数传递或者返回,同时对他们进行一些操作。
List
List是一组有序的集合。继承自List接口的最常用的类是ArrayList。
Collection c = new LinkedHashSet();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(c);
// 等价于
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.addAll(c);
Collection常用功能:
- Read
- size()
- isEmpty()
- contains()
- for()
- stream()
- C/U
- add()
- addAll()
- retainAll()
- Delete
- clear()
- remove()
- removeAll()
ArrayList是如何扩容的。
以add方法为例,在添加元素时先保证有足够的空间,ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);,在这个方法中调用ensureExplicitCapacity
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
保证有足够的空间来容纳我们存储的元素。
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 增加1.5倍的容量。
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
Set
- 不允许有重复元素
- Java世界第二重要的东西hashCode
- 同一个对象必须始终返回相同的hashCode
- 两个对象的equals返回true,必须返回相同的hashCode
- 两个对象不相等,也可能返回相同的hashCode
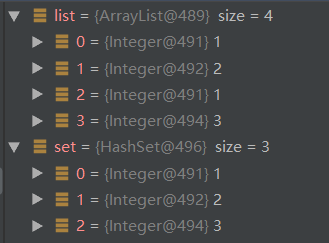
public static void xxx(){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(1);
list.add(3);
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(list);
}
Map
Map存储的是键值对,且键不能重复,每个键只能映射一个值。
- C:
- put("key","value")
- putAll() 将另一个map的数据丢进来
- R
- get("key") 得到key对应的value,若无则返回null
- size() 查看键值对数量
- containsKey()/containsValue() 判断当前map是不是包含某个key或value
- keySet()/values()/entrySet() keySet返回一组key的view,意思是说更改map中的数据,或者keySet返回的数据,会立刻反映到对方身上。entrySet()返回的是每个元素。
- D
- remove()
- clear()
HashMap
HashMap在多线程的情况下进行扩容可能会造成死循环,要在并发的情况下使用的话要用ConcurrentHashmap。
TreeSet/TreeMap
hashSet的顺序是完全随机的,LinkedHashSet保证和插入时的顺序一样,而treeSet则保证是有序的。
public static void main(String[] args){
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1111, 332, 6, 3, 0);
Set set1 = new HashSet(list);
Set set2 = new LinkedHashSet(list);
Set set3 = new TreeSet(list);
set1.forEach(System.out::println); // 随机顺序
set2.forEach(System.out::println); // 存储顺序
set3.forEach(System.out::println); // 从小到大
}
TreeSet最大的用处就是用来排序,可以自己指定排序的方法。其查找效率也比Arrays高,将算法复杂度由线性变为对数复杂度。