
前言
本来一直犹豫要不要写原型相关的东西,思虑再三还是决定水一文 😆😆😆
JavaScript 基于原型实现了继承,所以了解原型及原型链还是很有必要的。
原型
javaScript 的原型是什么?
当提到原型的时候,我们会想到 __proto__ 和 prototype 这两个老生常谈的属性。我们的脑海可能会复现这一样一句话:
每个对象都有 __proto__ 属性,Function 会自带 prototype 属性。查找 obj 有属性的时候,会先从 obj 自身查找,找不到会去 obj 的原型去找,obj 的原型找不到会去 obj 的原型的原型去找(在 obj 的原型链查找)。
那么问题来了,到底从 __proto__ 和 prototype 中那个去寻找呢?
const obj = {};
// 仅演示使用了属性,推荐使用 Object.setPrototypeOf(),设置对象原型
obj.__proto__ = {
name: '__proto__',
};
obj.prototype = {
name: 'prototype',
};
console.log(obj.name);
一个对象的原型指的是 __proto__ 属性。 推荐使用 Object.getPrototypeOf() 获得对象的原型,Object.setPrototypeOf() 设置对象的原型
prototype 是什么,且听下文分解? 😌😌😌
基于原型实现继承
const obj = {};
const objProto = {
name: '__proto__',
obj: { name: 1 },
};
objProto.__proto__ = {
getName() {
console.log(this.name);
},
};
obj.__proto__ = objProto;
console.log(obj.name);// __proto__
obj.getName();// __proto__
继承很简单,只要建立其原型,形成原型链(obj.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__)。
构造函数实现继承
构造函数及 new 操作符
可以大致看下es5 函数定义,加深对 js 的函数理解及理解 new 到底做了什么

const Foo = function _Foo(name = '默认') { this.name = name; };
const foo = new Foo();
console.log(foo.name);
- new Foo() 过程简单说明
// 1. 首先创建一个空对象
const obj = {};
// 2. 对 obj.__proto 赋值
obj.__proto__ = Foo.prototype instanceof Object ? Foo.prototype : Object;
// 3. 更改构造器函数内部this,将其指向新创建的空对象
const result=Foo.apply(obj,arguments);
// 4.返回对象
if(result instanceof Object){
return result;
}
return obj;
- 代码验证 new Foo()
const Foo = function _Foo(name = '默认') {
this.name = name;
// 返回不是对象
return 1;
};
const foo = new Foo();
console.log(foo.name);// 默认
const Foo1 = function _Foo1(name = '默认') {
this.name = name;
return { age: 1 };
};
const foo1 = new Foo1();
console.log(foo1.age);// 1
- 模拟 new 操作过程
function New(func, ...data) {
const obj = {};
obj.__proto__ = func.prototype;
const result = func.apply(obj, data);
if (result instanceof Object) {
return result;
}
return obj;
}
const Foo = function _Foo(name = '默认') {
this.name = name;
return 1;
};
const foo = new Foo();
console.log(foo.name);
const Foo1 = function _Foo1(name = '默认') {
this.name = name;
return { age: 1 };
};
const Foo2 = function _Foo2(name = '默认') {
this.name = name;
};
Foo2.prototype.log = function _log() {
console.log('测试继承 prototype');
};
const ret = New(Foo, '测试');
console.log(ret.name);// 测试
const ret1 = New(Foo1, '测试返回 obj');
console.log(ret1.age);// 1
const ret2 = New(Foo2, '测试正常构造');
console.log(ret2.name);// 测试正常构造
ret2.log();// 测试继承 prototype
基于构造函数和原型实现继承
// 1.通过原型链和构造函数实现继承,A 继承 B ,B 继承 C
const C = function _C(roles = ['徐晓', '吴素', '徐脂虎', '徐渭熊', '徐凤年', '徐龙象']) {
this.roles = roles;
this.c = function _c() {
return '自身 c';
};
};
C.prototype.getRoles = function _getRoles() {
return `${this.roles}-C.getRoles`;
};
const B = function _B(obj, roles) {
// 敲黑板,划重点,B 继承 C ,要在 B 的构造函数调用 C 的构造函数继承 C 中的属性
C.call(this, roles);
this.obj = obj;
this.b = function _b() {
return '自身 b';
};
};
// 将 B 的原型对象指向 C 的实例。
B.prototype = new C();
B.prototype.constructor = B;
B.prototype.study = function _study() {
return `${this.name}-B.study`;
};
// A 重写了 B 中的方法 b
const A = function _A(name, obj, roles) {
B.call(this, obj, roles);
this.name = name;
this.play = function _play() {
return `${this.name}-A.paly`;
};
this.b = function _bb() {
return `${this.name}-A重写b方法`;
};
};
A.prototype = new B();
A.prototype.constructor = A;
A.prototype.getName = function _getName() {
return this.name;
};
const a1 = new A('红薯', { age: 18 }, ['徐凤年']);
const a2 = new A('青鸟', { age: 18 }, ['吴素']);
console.log(a1.play()); // 红薯-A.paly
console.log(a2.play()); // 青鸟-A.paly
console.log(a1.getName()); // 红薯
console.log(a2.getName()); // 青鸟
console.log(a1.study()); // 红薯-B.study
console.log(a2.study()); // 青鸟-B.study
console.log(a1.getRoles()); // 徐凤年-C.getRoles
console.log(a2.getRoles()); // 吴素-C.getRoles
console.log(a2 instanceof B); // true
console.log(a1 instanceof B); // true
console.log(a1 instanceof C); // true
console.log(a1 instanceof C); // true
console.log(a1.b()); // 红薯-A重写b方法
console.log(a1.c()); // 自身 c
console.log(a2.b()); // 青鸟-A重写b方法
console.log(a2.c()); // 自身 c
基于原型链和构造函数实现的继承已经不错了,但是 A 继承 B 的时候 B.call(this, obj, roles);A.prototype = new B();调用了两次造成内存浪费。所以有大神站了出来,搞了一个寄生继承。
寄生继承
- 用中间空对象桥接,实现继承
const MyExtends = function _MyExtends(Son, Parent) {
const F = function _F() {};
const f = new F();
f.__proto__ = Parent.prototype;
Son.prototype = f;
Son.prototype.constructor = Son;
};
- 寄生继承尝试
const MyExtends = function _MyExtends(Son, Parent) {
const F = function _F() { };
const f = new F();
f.__proto__ = Parent.prototype;
Son.prototype = f;
Son.prototype.constructor = Son;
};
const C = function _C(roles = ['徐晓', '吴素', '徐脂虎', '徐渭熊', '徐凤年', '徐龙象']) {
this.roles = roles;
this.c = function _c() {
return '自身 c';
};
};
C.prototype.getRoles = function _getRoles() {
return `${this.roles}-C.getRoles`;
};
const B = function _B(name, roles) {
C.call(this, roles);
this.name = name;
this.b = function _b() {
return '自身 b';
};
};
B.prototype.study = function _study() {
return `${this.name}-B.study`;
};
MyExtends(B, C);
const b2 = new B('陈平安', ['文圣弟子']);
const b1 = new B('宁姚', ['平安的老婆']);
console.log(b2.roles);// ['文圣弟子']
console.log(b1.roles);// ['平安的老婆']
es6 的新特性 class 解决了繁琐的写法
强力推荐看看阮一峰的 ECMAScript 6 入门。买的实体书没看多少,网站上的 doc 看了好几遍,就当支持大神开源了
你有没有好奇 class 是什么呢?
// class 这种写法是语法糖
class Foo {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
getAge () {
return this.age;
}
static age = 1;
static getAge () {
return this.age;
}
}
class Son extends Foo{
constructor (age, name) {
super(name);
this.age;
}
}
console.log(typeof Foo);// function
console.log(Foo instanceof Function);// true
class 和 function 静态方法和静态属性对应
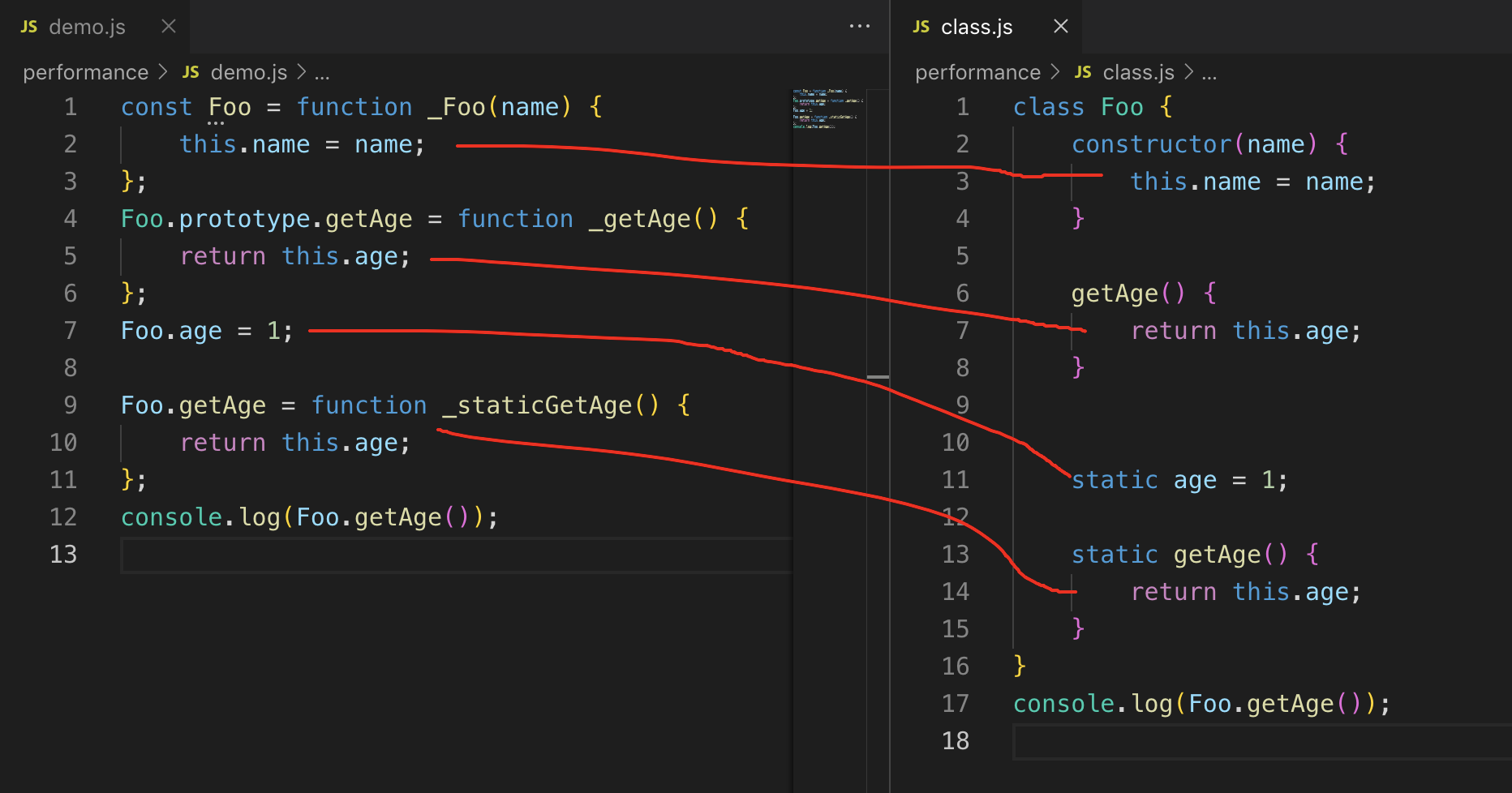
jQuery() 源码解析
下面这个问题困扰好久,一直想不明白为什么写的这么复杂呢?原来是为了安全调用构造函数,new 和 不 new 可以达到同样的效果。
const jQuery = function _jQuery(name = 'jQuery') {
return new jQuery.fn.init(name);
};
jQuery.getAge = function _getAge() {
console.log('getAge');
};
jQuery.prototype.getName = function _getName() {
return this.name;
};
jQuery.fn = jQuery.prototype;
// 这种写法就是为了安全调用构造函数,new 与不 new 达到同样的效果
const init = jQuery.fn.init = function _init(name) {
this.name = name;
};
init.prototype = jQuery.fn;
// 基于 new 创建对象
const jq1 = new jQuery('jq1-创建');
// 直接执行函数,返回对象
const jq2 = jQuery('jq2-创建');
console.log(jq1.getName());
console.log(jq2.getName());
typeof 和 instanceof
// 判断 undefined
const undefinedData = undefined;
console.log(typeof undefinedData);// undefined
// 判断 null,null 是基础数据类型
const nullData = null;
console.log(typeof nullData);// object
// es6 新出来的另一种基础类型,很有用,推荐看看
const symbol = Symbol.for('testSymbol');
console.log(typeof symbol);// symbol
console.log('symbol instanceof Symbol:', symbol instanceof Symbol);// false
// 判断 String 字符串
const str = '1';
console.log(typeof str);// string
console.log('str instanceof String', str instanceof String);// false
const strObj = new String('222');// string
console.log('strObj instanceof String', strObj instanceof String);// true
// 判断 Number 数字
const num = 1;
console.log(typeof num);// number
console.log('num instanceof Number:', num instanceof Number);// false
const numObj = new Number(1);
console.log(typeof numObj);// number
console.log('numObj instanceof Number:', numObj instanceof Number);// true
// 判断 Object
const obj = {};
console.log(typeof obj);// object
console.log('obj instanceof Object:', obj instanceof Object);// true
// 判断 Function
const func = function _func() {
};
console.log(typeof func);// function
console.log('func instanceof Function:', func instanceof Function);
// 判断 Array
const arr = [1, 2];
console.log(typeof arr);// object
console.log('arr instanceof Array:', arr instanceof Array);// ture
// 判断 Date
const date = new Date();
console.log(typeof date);// object
console.log('date instanceof Date:', date instanceof Date);// true
// 判断 Map
const map = new Map();
console.log(typeof map);// object
console.log('map instanceof Map:', map instanceof Map);// true
// 判断 Set
const set = new Set();
console.log(typeof set);// object
console.log('set instanceof Set:', set instanceof Set);// true
typeof 返回类型的小写字符串可以判断 undefined(undefined),String(string),Number(number),Symbol(symbol),Function(function) 类型,其余的都会返回 object
null 为基础类型,但是 typeof null 返回 object
- instanceof
instanceof 是基于原型链判断的
obj1 instanceof obj2 返回 true 的条件:obj2 为 function 并且在 obj1 的原型链中能找到 obj2.prototye 就会返回 true
// 代码验证上面的结论,颠覆了认知 😄😄😄
const obj1 = {};
// obj2 不为 function 会报错
const obj2 = function _obj2() { };
const tempPrototype = { name: 1 };
obj2.prototype = tempPrototype;
obj1.__proto__ = obj2.prototype;
console.log(obj1 instanceof obj2); // true