第二章: 面向对象
概念? 面向对象(类)三要素:继承 封装 多态? js应用举例?面向对象的意义?
1.概念?
写一个类,这类提供很多的方法,通过构造多个实例来,使每个实例都有这个类的方法,和属性。
2.面向对象三要素
① 继承:子类继承父类 (将公共方法抽离出来,提高代码复用率,减少冗余)
// 父类
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
getName() {
return this.name
}
}
// 子类继承父类
class Child extends Person {
constructor(name, number) {
super(name)
this.number = number
}
study() {
console.log('学生号为:' + this.number + '名字:' + this.name)
}
}
// 初始化实例,使用子类方法
let ChilidOne = new Child('marry', 12)
ChilidOne.study()
// 调用继承来的父类方法
let name = ChilidOne.getName()
console.log(name)
② 封装:数据的权限和保密
例子: (ts演示,es6不支持),使用ts定义变量来控制数据权限
public 完全开放
protected 对子类开放
private 对自己开放
ts中定义变量可以体现
http://www.typescriptlang.org/play/index.html (ts转js工具)
封装三要素:
减少耦合,不改外露的不外露
利于数据,接口的权限管理
es6目前不支持,一般以_开头的属性是private
③ 多态:同一接口不同实现
概念: 提出公共部分,继承公共部分后实现不同子类,保持子类的开放性和灵活性。
// 父类
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
getName() {
return this.name
}
}
// 子类继承父类
class A extends Person {
constructor(name, age) {
super(name)
this.age = age
}
getSome() {
console.log(this.name + this.age)
}
}
// 子类继承父类
class B extends Person {
constructor(name, age) {
super(name)
this.age = age
}
getSome() {
console.log(this.name + this.age)
}
}
let a = new A('A', 12)
a.getName()
let b = new B('B', 12)
b.getName()
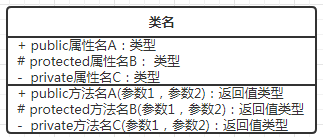
④ UML类图
unified modeling language 统一建模语言
类图,UML 包含很多种图,和本科相关的类图
关系,泛化和关联 (泛化表示继承,关联表示引用关系)
工具: MS OFFICE VISIO
https://www.processon.com/

第三章 设计原则 何为设计? 五大设计原则 从设计到模式 介绍23中设计模式 《UNIX/LINUX设计哲学》
1. 10个设计准则
① 小即是美
② 让每个子程序都做好一个事情
③ 快速创建原型
④ 舍弃高效率而取可移植性 (通用)
⑤ 采用纯文本存储数据
⑥ 充分利用软件的杠杆效应(软件复用)
⑦ 使用shell脚本提高杠杆效应
⑧ 避免强制性的用户界面
⑨ 让每个程序都称为过滤器
小准则
① 允许用户配置环境
② 操作系统小 轻量化
③ 使用小写并简写
④ 沉默是金(要输出标准,否则不输出)
⑤ 各部分只和大于整体
⑥ 寻求90%的解决方案
2. SOLID5个设计原则
S - 单一职责原则
一个程序做好一件事,如果功能过于复杂,拆分保持独立
O - 开放封闭原则
对扩展开放,对修改缝补,增加需求时,扩展新代码,而非修改已有代码,终极目标。
L - 李氏置换原则
子类能覆盖父类,父类能出现的地方子类就能出现,js中使用较少(弱类型&继承使用较少)
I = 接口独立原则
保持接口的单一独立,避免出现“胖接口”.
js终是没有接口的,ts有,使用较少,
类似于单一职责原理,这里更关注接口。
D - 依赖倒置原则
面向接口编程,依赖于抽象而依赖于具体
使用方关注接口不关注具体类的实现
js中使用较少( 没有接口&弱类型 )
3. 23种设计模式
① 创建型
工厂模式 (工厂方法模式,抽象工厂模式,建造者模式)
单例模式
原型模式
② 结构型
适配器模式
装饰器模式
代理模式
外观模式
桥接模式
组合模式
享元模式
③ 行为型 - 1
策略模式
模板方法模式
观察者模式
迭代器模式
职责连模式
命令模式
④ 行为型 - 2
备忘录模式
状态模式
访问者模式
终结者模式
解释器模式
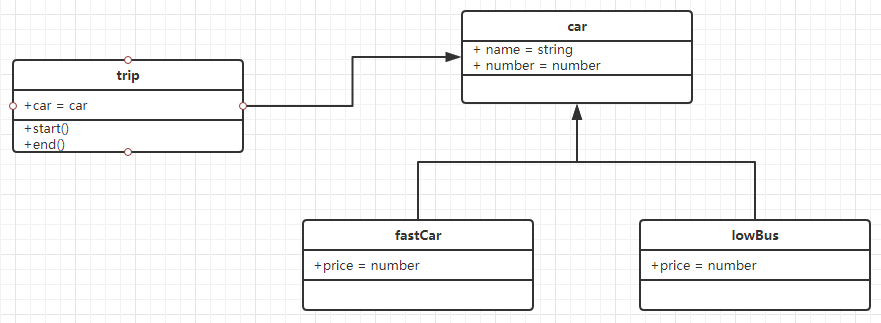
题目1:
打车时,可以打专车或者快车,任何车都有车牌号码和名称。
不同车价格不同,快车没公里1元,专车每公里2元。
行程开始时,显示车辆信息。
行程结束时,显示打车金额(假设行车5公里)
请画出 UML 类图? 用es6 语法写出该示例?
class car {
constructor(number, name) {
this.name = name;
this.number = number;
}
}
class fastCar extends car {
constructor(number, name) {
super(number, name)
this.price = 2;
}
}
class lowCar extends car {
constructor(number, name) {
super(number, name)
this.price = 1;
}
}
class Trip {
constructor(car) {
this.car = car
}
start() {
console.log(`形成开始,名称:${this.car.name},车牌号码:${this.car.number}`)
}
end() {
console.log(`行程结束,价格:${ this.car.price*5}`)
}
}
let kuaiche = new fastCar(100, '快车');
let kcPrice = new Trip(kuaiche)
kcPrice.start();
kcPrice.end();
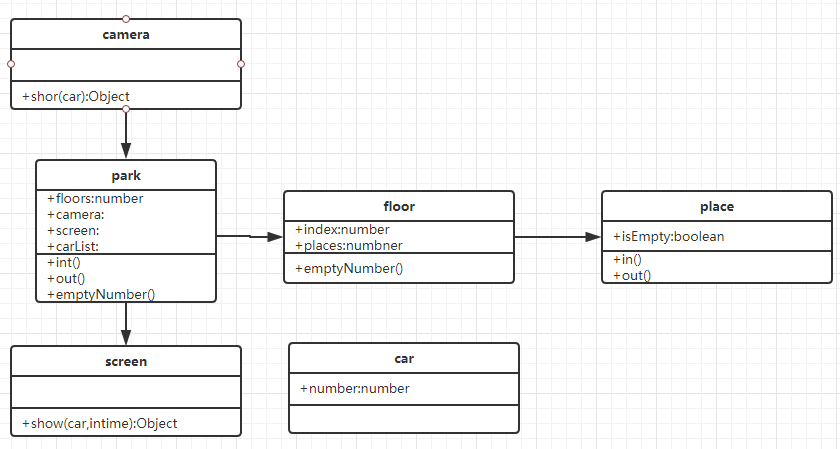
题目2:
某停车场。分3层,每层100个车位
每个车位都能监控到车辆的驶入和离开
车辆进入前,显示每层的空余车位数量
车辆进入时,摄像头科识别车牌号和时间
车辆出来时,出口显示器显示车牌号和停车时长
请画出 UML 类图? es6代码实现?
class park {
constructor(floors, camera) {
this.floors = floors || [];
this.carList = {};
this.Camera = new Camera();
this.Screen = new Screen()
}
int(car) {
let info = this.Camera.shot(car)
const i = Number.parseInt(Math.random() * 100 / 100);
let place = this.floors[0].places[i];
place.int();
info.place = place;
this.carList[car.num] = info;
}
out(car) {
let info = this.carList[car.num];
place = info.place;
place.out();
this.Screen.show(info, info.inTime)
delete this.carList[info.num]
}
emptyNum() {
return this.floors.map(floor => {
return `${floor.index} 层还有${floor.emptyNumber()} 个空余停车位`
}).join('\n')
}
}
class floor {
constructor(index, places) {
this.index = index;
this.places = places;
}
emptyNumber() {
let num = 0;
this.places.forEach(p => {
if (p.empty) {
num = num + 1;
}
});
return num;
}
}
class place {
constructor() {
this.empty = true;
}
int() {
this.empty = false
}
out() {
this.empty = true;
}
}
class car {
constructor(number) {
this.number = number;
}
}
class Camera {
shot(car) {
return {
num: car.number,
inTime: new Date()
}
}
}
class Screen {
show(car, inTime) {
console.log(`车牌号${car.num}`);
console.log(`停车时间${new Date() - inTime}秒`);
}
}
const floors = []
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
const placest = [];
for (let j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
placest[j] = new place();
}
floors[i] = new floor(i + 1, placest)
}
const parkt = new park(floors);
const cart = new car('A100');
parkt.int(cart)
const num = parkt.emptyNum();
console.log(num)
parkt.out(cart)
1 层还有99 个空余停车位
2 层还有100 个空余停车位
3 层还有100 个空余停车位
part.js:132 车牌号A100
part.js:133 停车时间9秒
*/