
为什么要用vuex
官方回答:
Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,并附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要对短期和长期效益进行权衡。如果您不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。确实是如此——如果您的应用够简单,您最好不要使用 Vuex。一个简单的 store 模式就足够您所需了。但是,如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,您很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择
与其他状态管理库对比:
Vuex 背后的基本思想,借鉴了 Flux、Redux 和 The Elm Architecture。与其他模式不同的是,Vuex 是专门为 Vue.js 设计的状态管理库,以利用 Vue.js 的细粒度数据响应机制来进行高效的状态更新。(这也是官方给出的,待会我们源码中也会体现出这一优点)
我们在使用Vue.js开发复杂的应用时,经常会遇到多个组件共享同一个状态,或者多个组件会去更新同一个状态,在项目不复杂的情况下,我们可以组件间通信或者是通过eventBus来维护数据。但是当应用逐渐庞大以后,代码就会变得难以维护,从父组件开始通过prop传递多层嵌套的数据由于层级过深而显得异常脆弱,而事件总线也会因为组件的增多、代码量的增大而显得交互错综复杂,难以捋清其中的传递关系。此时我们就需要用到vuex来为我们集中管理数据了。
Vuex
在说vuex原理之前,大家可以先结合下面的图片想一想你在京东自营店购物是一个怎样的流程,其实这个流程就跟咱们的vuex流程是一样的, 比如你买一件衣服,你得先下单,下完单平台接收到你的下单申请然后通知仓库跟你发货,你收到货后开开心心的穿在了身上,感觉自己美美哒。vuex工作原理也是一样,可以到我的github下载代码。
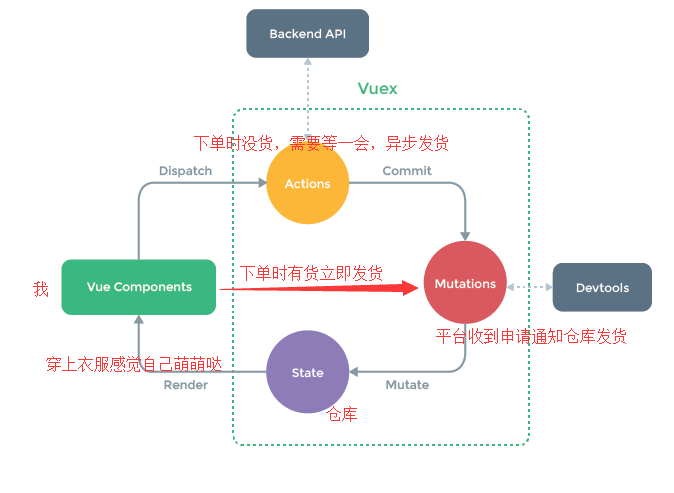
从图中可以看出vuex实现的是一个单向数据流:
组件提交(commit) ->修改(在mutations中)->数据(state修改完成)->渲染到页面(render),
要说的是action是vuex提供处理异步数据的场所,使用action需要在组件内先派发一个dispatch通过action调用commit方法再修改state
vuex轮廓搭建
下面是vuex在项目里使用的基本配置,咱们通过观察下面的图片一步一步的写出我们自己的vuex
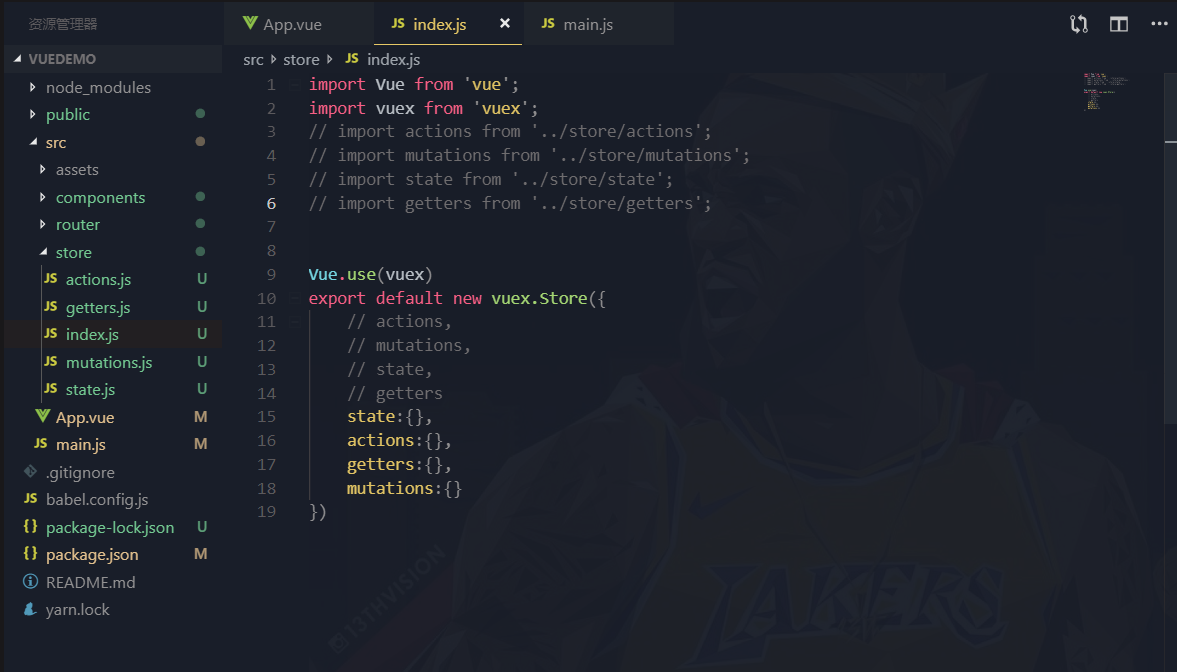
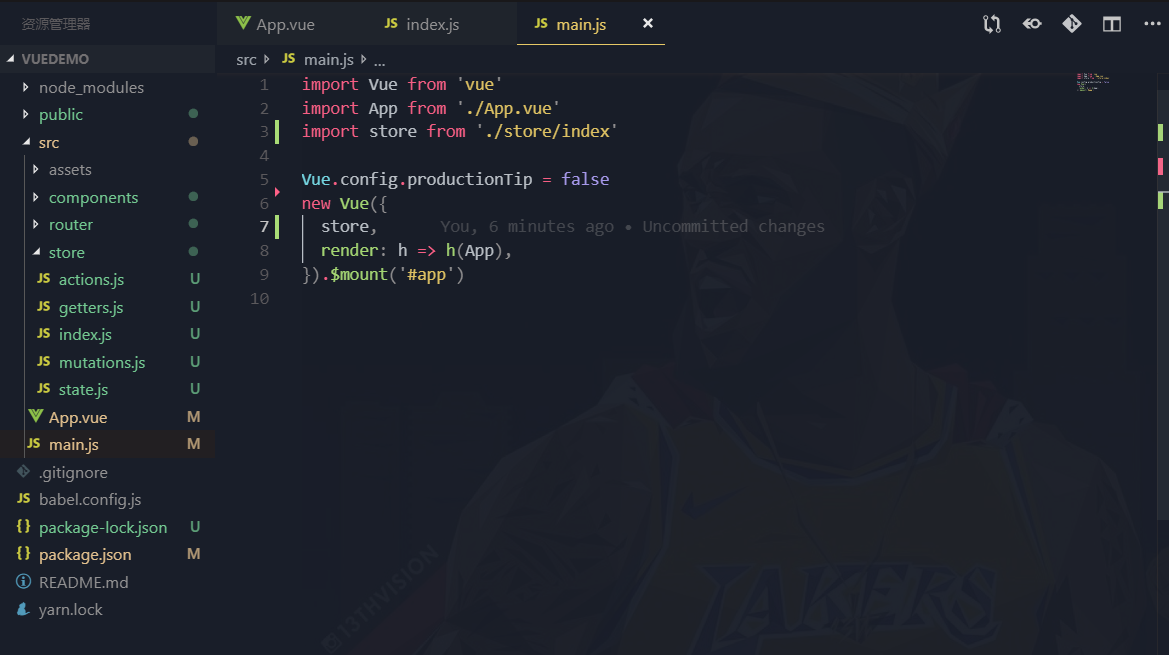
从上面图中可以看到,使用vuex插件要先Vue.use(),然后导出了一个Store的类,类里面传入了,state、actions、getters、mutations对象
所以我们首先要导出一个install方法和一个Store的类
let Vue;
class Store{
constructor(options){ //option中就有 state getters mutations actions
let state = options.state;
this.getters = {};
this.mutations = {};
this.actions = {}
// vuex也具备同样的数据响应,这里也是上面提到过的,vuex巧妙的运用的vue中data的数据响应
// vuex核心就是借用了vue的实例 因为vue的实例数据变化 会刷新视图
this._vm = new Vue({
data:{
state
}
});
// 把模块直接的关系进行整理 自己根据用户传入的参数维护了一个对象
this.modules = new ModuleCollection(options);
// 无论是子模块 还是孙子 所有的mutation 都是根上的
// this是store的实例 [] path this.mdoue.root 当前的根模块
installModule(this,state,[],this.modules.root);
let {commit,dispatch} = this;//拿到原型上面的 commit,dispatch方法 保证this指向的时store
this.commit = (type) =>{
commit.call(this,type);
}
this.dispatch = (type) =>{
dispatch.call(this,type);
}
}
get state(){
// 这个方法可以理解为和Object.definefineProperty get是一个意思
// 在组件中通过this.$Store.state.xxx访问某个属性时返回_vm中的state
return this._vm.state;
}
commit(type){
this.mutations[type].forEach(fn=>fn());
}
dispatch(type){
this.actions[type].forEach(fn=>fn());
}
}
function forEach(obj,callback){
Object.keys(obj).forEach(item=>callback(item,obj[item]));
}
let install = (_Vue) =>{
Vue = _Vue; // 判断Vue是否存在 优化重复use
Vue.mixin({// 把根组件中 store实例 给每个组件都增加一个$store的属性
beforeCreate(){
if(this.$options && this.$options.store){// 判断是否是根组件
this.$store = this.$options.store;
}else{ // 子组件
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.$store
}
}
})
}
export default {
Store,
install
}
实现vuex的分模块机制
class ModuleCollection { // 默认actions mutation 都会定义到store上面
constructor(options){
this.register([],options);
}
register(path,rawModule){
// path 是个空数组 rawModule就是个对象
let newModule = {
_raw:rawModule,// 对象 当前 有state getters 那个对象
_children:{}, // 表示 他包含的模块
state:rawModule.state // 自己模块的状态
}
if(path.length == 0){
this.root = newModule; // 根
}else{
// [a,b]; // reduce方法 {{a.b.c}}
let parent = path.slice(0,-1).reduce((root,current)=>{
return root._children[current];
},this.root);
parent._children[path[path.length-1]] = newModule;
}
if(rawModule.modules){ // 有子模块
forEach(rawModule.modules,(childName,module)=>{
// [a,b];
// [a,d]
this.register(path.concat(childName),module)
});
}
}
}
执行你当前在组件中派发的方法
function installModule(store,rootState,path,rootModule){
// rootState.a = {count:200}
// rootState.a.b = {count:3000}
if(path.length > 0){
let parent = path.slice(0,-1).reduce((root,current)=>{
return root[current];
},rootState)
Vue.set(parent,path[path.length-1],rootModule.state);
}
if(rootModule._raw.getters){
forEach(rootModule._raw.getters,(getterName,getterFn)=>{
Object.defineProperty(store.getters,getterName,{
get:()=>{
return getterFn(rootModule.state);
}
});
});
}
if(rootModule._raw.actions){
forEach(rootModule._raw.actions,(actionName,actionFn)=>{
let entry = store.actions[actionName] || (store.actions[actionName]=[]) ;
entry.push(()=>{
actionFn.call(store,store);
})
});
}
if(rootModule._raw.mutations){
forEach(rootModule._raw.mutations,(mutationName,mutationFn)=>{
let entry = store.mutations[mutationName] || (store.mutations[mutationName]=[]) ;
entry.push(()=>{
mutationFn.call(store,rootModule.state);
})
});
}
forEach(rootModule._children,(childName,module)=>{
installModule(store,rootState,path.concat(childName),module);
})
}
到这里简版的vuex就全部实现了,若文字表述不清的可以到github上的下载在本地调试,感觉写的可以随便点颗星哈哈。有哪里写的不足或者可以优化的地方可以评论交流一起学习。