一、动态引入import
动态引入的两种方法对比:
import FormComponent from './components'
console.log(FormComponent)
方法2:
import('./components').then(itemComponent=>{
console.log(itemComponent)
})
动态 import 提供了 Promise 规范的 API,比如 .then()
二、React.lazy() 和 Suspense
1、reatc.lazy()
动态 import 主要应用场景是延迟加载方法,对于组件来说,并不是很适用,但是 React.lazy 对于组件的加载则是有比较大的帮助。 但是,目前明确指出,React.lazy 和 suspense 并不适用于服务端渲染
查看使用lazy之前和之后的区别: 之前:
import OtherComponent from './components'
function MyComponent() {
return (
<div>
<OtherComponent />
</div>
);
}
之后:
import {lazy} from 'react'
const OtherComponent = lazy(()=>import('./components'))
function MyComponent() {
return (
<div>
<OtherComponent />
</div>
);
}
这个变动会使得在组件渲染的时候,再去加载包含引入路径的组件。
2、Suspense
使用lazy延迟加载是:延迟加载需要一个加载的过程,如果不使用Suspense,则是从上向下一个一个<loading>组件,然后通过变量,如果加载完成,则取消掉<loading>组件,如果直接使用lazy,会报错,需要一个placeholder ui
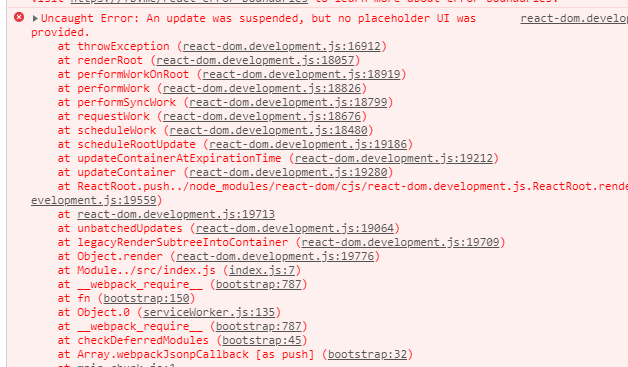
<loading>过程,要使用 Suspense,需要从 react 中 import:
import React, { Component, Suspense } from 'react';

render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
{this.renderList()}
</Suspense>
</header>
</div>
);
}
Suspense 使用的时候,fallback 一定是存在且有内容的, 否则会报错。