最近学习了React context,由于自己刚入门React,此文仅为context的简单记录尝试,不作对context与redux进行比较。
Context的应用场景
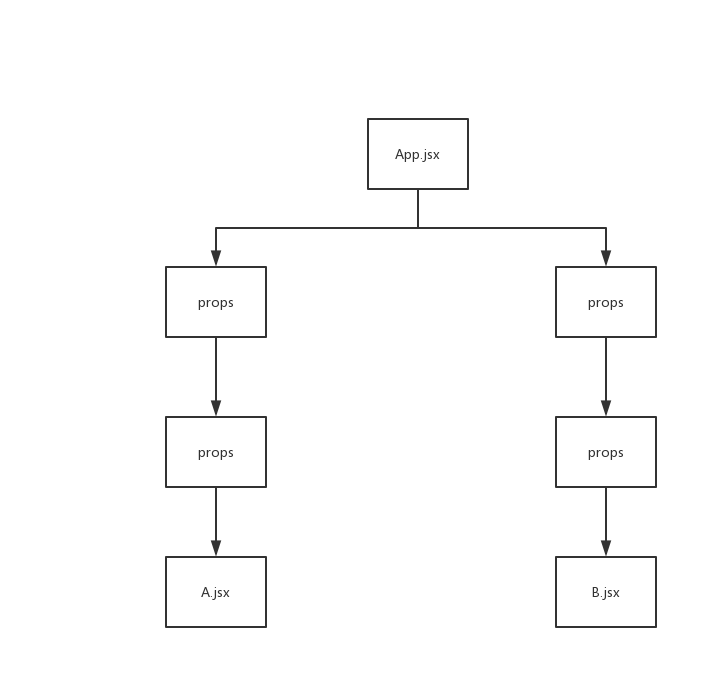
如果App.jsx中有一个共同的值要传给A.jsx组件与B.jsx组件,就得通过中间其他组件,即使中间的组件并不需要他们渲染UI,在更加复杂的应用之中,这使得代码非常的混乱与复杂。
以前有Redux,在React 16.3时推出了新的Context API。
Context用于在React树组件中共享数据,比如用户信息、主题等等,这样子就不用通过props在层层组件中传递信息,使得代码太过混乱。
React Context的API
学习自原官网英文文档,有哪里理解不正确请大佬指出
主要有React.createContext,Context.Provider,Context.Consumer,Class.contextType
React.createContext(defaultValue): 创建
Context对象,并且设置默认值。当有组件订阅(subscrie)Context对象时,会从相距最近的Context.Provider取得值。订阅了Provider的子组件的更新不会受限于shouldComponentUpdate。同时,默认值只有在子组件没有匹配的Provider时才会使用。const MyContext = React.createContext('context默认值');
Context.Provider: 每一个Context对象包含一个
Provider组件,允许消费者组件(consuming component)订阅,同时他们接受value属性,改变传递下去的值<MyContext.Provider value={'Provider修改默认值'}>//Provider是一个组件 </MyContext.Provider>
Context.Consumer: 是一个可以订阅Context值改变的
组件,内部之中让我们以函数组件的方式订阅Context<MyContext.Consumer> //Consumer是一个组件 {value => /* 使用传递过来的value */} </MyContext.Consumer>
Class.contextType: 可在组件Class中赋值Context对象,使得在组件中可以直接使用对应Context的值;但需要订阅多个Context时此方法不可用,此方法只能订阅一个Context。
class Example extends React.Component{ constructor(props) { super(props); const value = this.context//直接访问 } } Example.contextType = MyContext;
实践
这是基础模板,会在基础模板上进行如下实践:使用Context.Consumer订阅单个Context、 使用Context.contextType订阅单个Context、使用Class.Consumer订阅多个组件

使用Context.Consumer订阅单个Context
使用默认值
如果子组件没有匹配到Provider,会直接使用Context中的默认值
const MyContext = React.createContext('context默认值');
class Leaf extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render(){
return(
<MyContext.Consumer>
{
(value) =>{
return (
<h3>
hi!我是叶子组件,MyContext中的值是:'{value}'
</h3>
);
}
}
</MyContext.Consumer>
);
}
}
class App extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<h1>
hi!我是顶层的App组件
</h1>
<Middle />
<Leaf />
</div>
)
}
}
CodePen打开
因为Leaf组件外没有<MyContext.Provider>组件包裹,所以匹配到了Context的默认值
效果如下

使用Context.Provider提供的value
在子组件的父组件上嵌套MyContext.Provider,设置value属性,即可对应修改值
class App extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<MyContext.Provider value={'修改默认值'}>
<h1>
hi!我是顶层的App组件
</h1>
<Middle />
<Leaf />
</MyContext.Provider>
</div>
)
}
}

使用Class.contextType订阅单个Context
通过这种方式订阅可以更方便地在生命周期或者构造函数中使用Context的值
class Leaf extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log(this.context);//直接通过this.context访问
}
render(){
return(<h3>hi!我是叶子组件,MyContext中的值是:'{this.context}' </h3>);
}
}
class App extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<h1>
hi!我是顶层的App组件
</h1>
<Middle />
<Leaf />
</div>
)
}
}
Leaf.contextType = MyContext;//在此订阅
CodePen打开
不然的话可能要这么写:
class App extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<MyContext.Provider value={'修改默认值'}>
<h1>
hi!我是顶层的App组件
</h1>
<Middle />
<MyContext.Consumer>
{(value)=>{
return <Leaf test={value} />;//传给Leaf在生命周期或构造函数中访问
}}
</MyContext.Consumer>
</MyContext.Provider>
</div>
)
}
}
使用Context.Consumer订阅多个组件
本质是通过多个组件嵌套传值,比如下面的例子,MyContext.Consumer传给YourContext.Consumer
const MyContext = React.createContext('MyContext默认值');
const YourContext = React.createContext('YourContext默认值');
class Leaf extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render(){
return(
<MyContext.Consumer>
{mine=>(
<YourContext.Consumer>
{
yours=>(
<div>
<p>MyContext的值:'{mine}'</p>
<p>YourContext的值:'{yours}'</p>
</div>
)}
</YourContext.Consumer>
)}
</MyContext.Consumer>
);
}
}
class App extends React.Component{
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render(){
return (
<div>
<MyContext.Provider value={'MyContext被修改了'}>
<YourContext.Provider value={'YourContext被修改了'}>
<h1>
hi!我是顶层的App组件
</h1>
<Middle />
<Leaf />
</YourContext.Provider>
</MyContext.Provider>
</div>
)
}
}

结语
本文内容基本上是对官网原英文文档的实践,有不正确的大佬们指出。
参考资料
React官网:Context
React's Context API explained: Provider and Consumer