Flask-RESTful是用于快速构建REST API的Flask扩展。
安装
pip install flask
pip install flask-restful1 Hello World
from flask import Flask
from flask_restful import Resource, Api
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
class HelloWorldResource(Resource):
def get(self):
return {'hello': 'world'}
def post(self):
return {'msg': 'post hello world'}
api.add_resource(HelloWorldResource, '/')
# 此处启动对于1.0之后的Flask可有可无
if __name__ == '__main__':
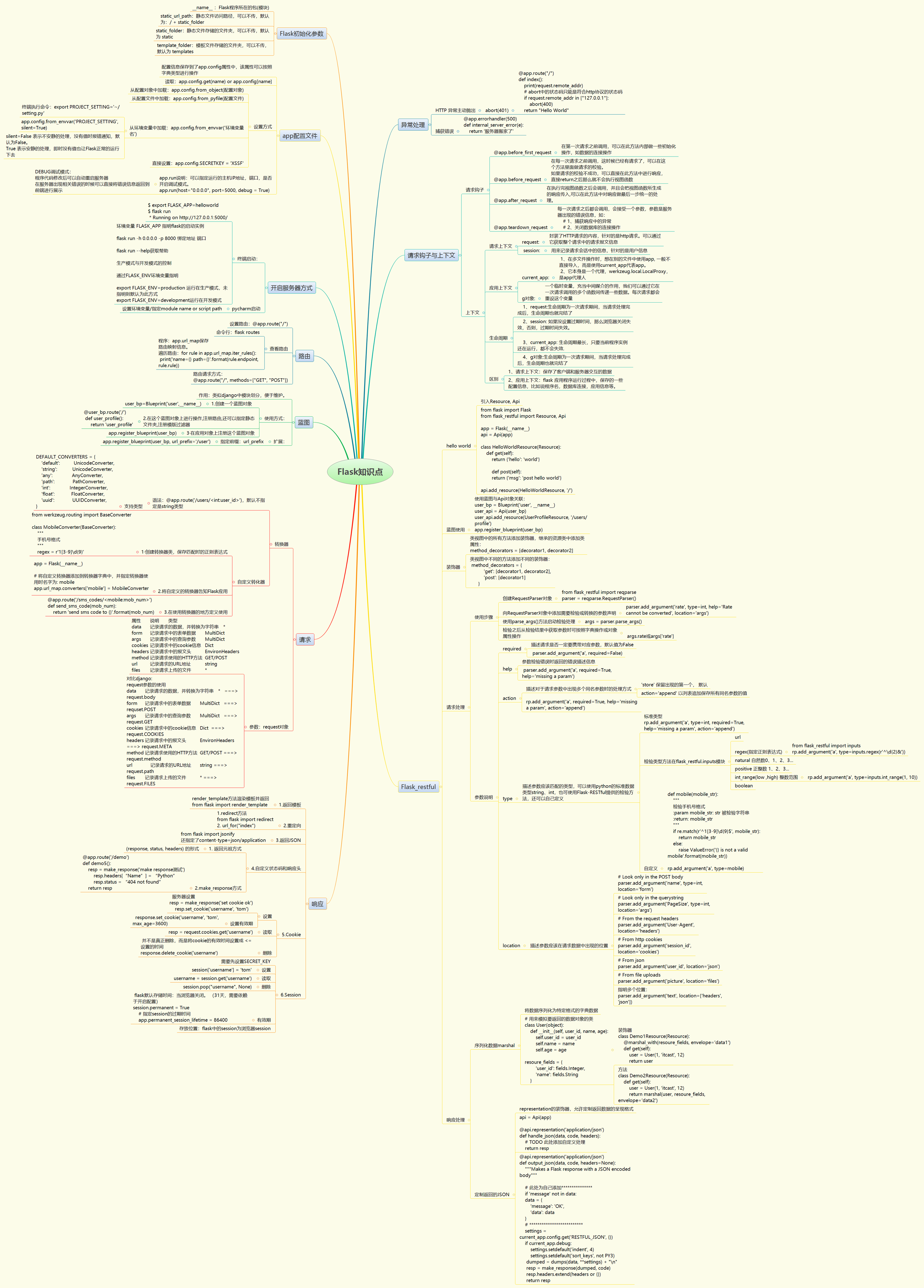
app.run(debug=True)补充:如果是1.0之后,可通过flask程序终端运行:
$ export FLASK_APP=helloworld # 指名要运行的程序文件名
$ flask run
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/也可通过改变pycharm配置运行时的参数来运行。
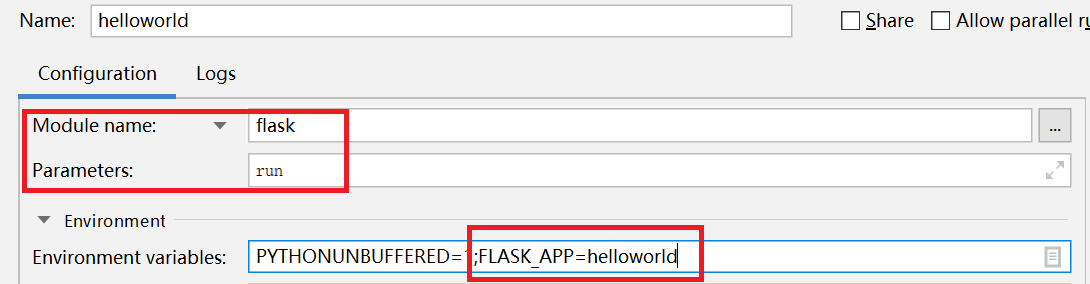
get请求效果如下:
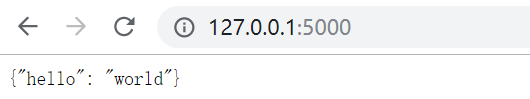
post请求效果如下:
2 视图
2.1 路由
通过endpoint参数为路由起名
api.add_resource(HelloWorldResource, '/', endpoint='HelloWorld')2.2 蓝图
from flask import Flask, Blueprint
from flask_restful import Api, Resource
app = Flask(__name__)
user_bp = Blueprint('user', __name__)
user_api = Api(user_bp)
class UserProfileResource(Resource):
def get(self):
return {'msg': 'get user profile'}
user_api.add_resource(UserProfileResource, '/users/profile')
app.register_blueprint(user_bp)2.3 装饰器
使用method_decorators添加装饰器
类视图中的所有方法添加装饰器
def decorator1(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print('decorator1')
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
def decorator2(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print('decorator2')
return func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
class DemoResource(Resource):
method_decorators = [decorator1, decorator2]
def get(self):
return {'msg': 'get view'}
def post(self):
return {'msg': 'post view'}类视图中不同的方法添加不同的装饰器
class DemoResource(Resource):
method_decorators = {
'get': [decorator1, decorator2],
'post': [decorator1]
}
# 使用了decorator1 decorator2两个装饰器
def get(self):
return {'msg': 'get view'}
# 使用了decorator1 装饰器
def post(self):
return {'msg': 'post view'}
# 未使用装饰器
def put(self):
return {'msg': 'put view'}3 请求
Flask-RESTful 提供了RequestParser类,用来帮助我们检验和转换请求数据。
from flask_restful import reqparse
parser = reqparse.RequestParser()
parser.add_argument('rate', type=int, help='Rate cannot be converted', location='args')
parser.add_argument('name')
args = parser.parse_args()3.1 使用步骤:
创建
RequestParser对象向
RequestParser对象中添加需要检验或转换的参数声明使用
parse_args()方法启动检验处理检验之后从检验结果中获取参数时可按照字典操作或对象属性操作
args.rate或args['rate']
3.2 参数说明
required
描述请求是否一定要携带对应参数,默认值为False
True 强制要求携带
若未携带,则校验失败,向客户端返回错误信息,状态码400
False 不强制要求携带
若不强制携带,在客户端请求未携带参数时,取出值为None
class DemoResource(Resource):
def get(self):
rp = RequestParser()
rp.add_argument('age', required=False)
args = rp.parse_args()
return {'msg': 'data={}'.format(args.age)}help
参数检验错误时返回的错误描述信息
rp.add_argument('a', required=True, help='missing a param')action
描述对于请求参数中出现多个同名参数时的处理方式
action='store'保留出现的第一个, 默认action='append'以列表追加保存所有同名参数的值
rp.add_argument('age', required=True, help='missing age param', action='append')type
描述参数应该匹配的类型,可以使用python的标准数据类型string、int,也可使用Flask-RESTful提供的检验方法,还可以自己定义
标准类型
rp.add_argument('age', type=int, required=True, help='missing age param', action='append')Flask-RESTful提供
检验类型方法在
flask_restful.inputs模块中urlregex(指定正则表达式)from flask_restful import inputs rp.add_argument('age', type=inputs.regex(r'^\d{2}&'))natural自然数0、1、2、3...positive正整数 1、2、3...int_range(low ,high)整数范围rp.add_argument('age', type=inputs.int_range(1, 100))boolean
自定义
def mobile(mobile_str): """ 检验手机号格式 :param mobile_str: str 被检验字符串 :return: mobile_str """ if re.match(r'^1[3-9]\d{9}$', mobile_str): return mobile_str else: raise ValueError('{} is not a valid mobile'.format(mobile_str)) rp.add_argument('mobile', type=mobile)
location
描述参数应该在请求数据中出现的位置
# Look only in the POST body
parser.add_argument('name', type=int, location='form')
# Look only in the querystring
parser.add_argument('PageSize', type=int, location='args')
# From the request headers
parser.add_argument('User-Agent', location='headers')
# From http cookies
parser.add_argument('session_id', location='cookies')
# From json
parser.add_argument('user_id', location='json')
# From file uploads
parser.add_argument('picture', location='files')也可指明多个位置
parser.add_argument('text', location=['headers', 'json'])4 响应
4.1 序列化数据
Flask-RESTful 提供了marshal工具,用来帮助我们将数据序列化为特定格式的字典数据,以便作为视图的返回值。
from flask_restful import Resource, fields, marshal_with
resource_fields = {
'name': fields.String,
'address': fields.String,
'user_id': fields.Integer
}
class Todo(Resource):
@marshal_with(resource_fields, envelope='resource')
def get(self, **kwargs):
return db_get_todo()也可以不使用装饰器的方式
class Todo(Resource):
def get(self, **kwargs):
data = db_get_todo()
return marshal(data, resource_fields)示例:
# 用来模拟要返回的数据对象的类
class User(object):
def __init__(self, user_id, name, age):
self.user_id = user_id
self.name = name
self.age = age
resoure_fields = {
'uer_id': fields.Integer,
'name': fields.String
}
class Demo1Resource(Resource):
@marshal_with(resoure_fields, envelope='data1')
def get(self):
user = User(1, 'itcast', 12)
return user
class Demo2Resource(Resource):
def get(self):
user = User(1, 'itcast', 12)
return marshal(user, resoure_fields, envelope='data2')4.2 自定义返回JSON
需求
想要接口返回的JSON数据具有如下统一的格式
{"message": "描述信息", "data": {要返回的具体数据}}在接口处理正常的情况下, message返回ok即可,但是若想每个接口正确返回时省略message字段
class DemoResource(Resource):
def get(self):
return {'user_id':1, 'name': 'admin'}对于诸如此类的接口,能否在某处统一格式化成上述需求格式?
{"message": "OK", "data": {"user_id":1, "name": "admin"}}解决方案
Flask-RESTful的Api对象提供了一个representation的装饰器,允许定制返回数据的呈现格式
api = Api(app)
@api.representation('application/json')
def handle_json(data, code, headers):
# TODO 此处添加自定义处理
return respFlask-RESTful原始对于json的格式处理方式如下:
代码出处:flask_restful.representations.json
from flask import make_response, current_app
from flask_restful.utils import PY3
from json import dumps
def output_json(data, code, headers=None):
"""Makes a Flask response with a JSON encoded body"""
settings = current_app.config.get('RESTFUL_JSON', {})
# If we're in debug mode, and the indent is not set, we set it to a
# reasonable value here. Note that this won't override any existing value
# that was set. We also set the "sort_keys" value.
if current_app.debug:
settings.setdefault('indent', 4)
settings.setdefault('sort_keys', not PY3)
# always end the json dumps with a new line
# see https://github.com/mitsuhiko/flask/pull/1262
dumped = dumps(data, **settings) + "\n"
resp = make_response(dumped, code)
resp.headers.extend(headers or {})
return resp为满足需求,做如下改动即可:
@api.representation('application/json')
def output_json(data, code, headers=None):
"""Makes a Flask response with a JSON encoded body"""
# 此处为自定义添加***************
if 'message' not in data:
data = {
'message': 'OK',
'data': data
}
# **************************
settings = current_app.config.get('RESTFUL_JSON', {})
# If we're in debug mode, and the indent is not set, we set it to a
# reasonable value here. Note that this won't override any existing value
# that was set. We also set the "sort_keys" value.
if current_app.debug:
settings.setdefault('indent', 4)
settings.setdefault('sort_keys', not PY3)
# always end the json dumps with a new line
# see https://github.com/mitsuhiko/flask/pull/1262
dumped = dumps(data, **settings) + "\n"
resp = make_response(dumped, code)
resp.headers.extend(headers or {})
return resp5.小结
Flask-RESTful的使用介绍到这里,下面整理了一份它的思维导图,其中还包括了Flask的知识点总结。