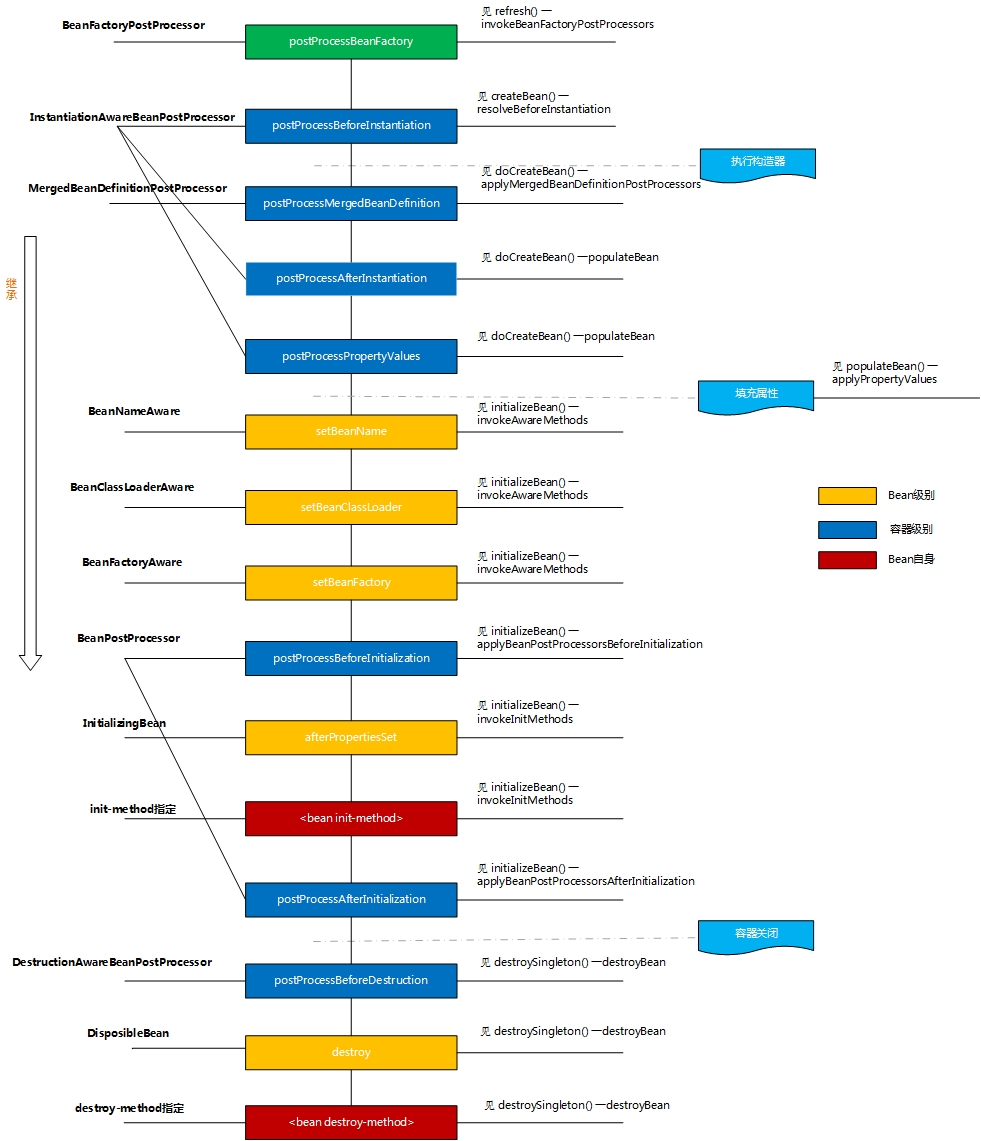
常用扩展接口以及案例(附上源码,注意看原本的英文注释)
1.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
简述:BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor提供的一个补充扩展接口,用来在BeanFactoryPostProcessor之前注册beanDefinition.
example:
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor: processing @Configuration
/**
* Extension to the standard {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} SPI, allowing for
* the registration of further bean definitions <i>before</i> regular
* BeanFactoryPostProcessor detection kicks in. In particular,
* BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor may register further bean definitions
* which in turn define BeanFactoryPostProcessor instances.
*/
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean definition registry after its
* standard initialization. All regular bean definitions will have been loaded,
* but no beans will have been instantiated yet. This allows for adding further
* bean definitions before the next post-processing phase kicks in.
* @param registry the bean definition registry used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
2.BeanFactoryPostProcessor
简述:在注册完beanDefinition信息之后,实例化之前,通过该接口修改beanDefinition。
example:
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor: processing @Configuration
- PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer(resolves ${...} placeholders)
- PropertyOverrideConfigurer(overrides bean property values in an application context definition)
/**
* Allows for custom modification of an application context's bean definitions,
* adapting the bean property values of the context's underlying bean factory.
*
* <p>Application contexts can auto-detect BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans in
* their bean definitions and apply them before any other beans get created.
*
* <p>Useful for custom config files targeted at system administrators that
* override bean properties configured in the application context.
**/
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
3.BeanPostProcessor
简述:Bean处理器,提供初始化前后两个方法(会在bean级别的类Init方法前执行)
example:
- postProcessBeforeInitialization
- BeanValidationPostProcessor
- ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
- postProcessAfterInitialization
- BeanValidationPostProcessor
/**
* Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances,
* e.g. checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies.
*
* <p>ApplicationContexts can autodetect BeanPostProcessor beans in their
* bean definitions and apply them to any beans subsequently created.
* Plain bean factories allow for programmatic registration of post-processors,
* applying to all beans created through this factory.
**/
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
@Nullable
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
4.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
简述:bean实例化处理器
- 提供postProcessBeforeInstantiation - 实例化前方法,例如在实例化前直接返回一个代理类
- postProcessAfterInstantiation - 实例化后方法,返回true/false,决定是否跳过applyPropertyValues、也包括本接口的postProcessAfterInstantiation、postProcessProperties方法;
- postProcessAfterInstantiation、postProcessPropertie-用来处理Bean的property
example:
-
postProcessBeforeInstantiation
- AbstractAutoProxyCreator
-
postProcessAfterInstantiation(基本没用)
-
postProcessProperties
- CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
-
postProcessPropertyValues
- RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
- SpringAutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor(// Inject the BeanFactory before AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor's postProcessPropertyValues method attempts to autowire other configuration beans.)
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor <i>before the target bean gets instantiated</i>.
* The returned bean object may be a proxy to use instead of the target bean,
* effectively suppressing default instantiation of the target bean.
* <p>If a non-null object is returned by this method, the bean creation process
* will be short-circuited. The only further processing applied is the
* {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization} callback from the configured
* {@link BeanPostProcessor BeanPostProcessors}.
* <p>This callback will be applied to bean definitions with their bean class,
* as well as to factory-method definitions in which case the returned bean type
* will be passed in here.
* <p>Post-processors may implement the extended
* {@link SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor} interface in order
* to predict the type of the bean object that they are going to return here.
* <p>The default implementation returns {@code null}.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean to be instantiated
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean object to expose instead of a default instance of the target bean,
* or {@code null} to proceed with default instantiation
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessAfterInstantiation
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#getBeanClass()
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#getFactoryMethodName()
*/
default Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
/**
* Perform operations after the bean has been instantiated, via a constructor or factory method,
* but before Spring property population (from explicit properties or autowiring) occurs.
* <p>This is the ideal callback for performing custom field injection on the given bean
* instance, right before Spring's autowiring kicks in.
* <p>The default implementation returns {@code true}.
* @param bean the bean instance created, with properties not having been set yet
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return {@code true} if properties should be set on the bean; {@code false}
* if property population should be skipped. Normal implementations should return {@code true}.
* Returning {@code false} will also prevent any subsequent InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* instances being invoked on this bean instance.
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessBeforeInstantiation
*/
default boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return true;
}
/**
* Post-process the given property values before the factory applies them
* to the given bean, without any need for property descriptors.
* <p>Implementations should return {@code null} (the default) if they provide a custom
* {@link #postProcessPropertyValues} implementation, and {@code pvs} otherwise.
* In a future version of this interface (with {@link #postProcessPropertyValues} removed),
* the default implementation will return the given {@code pvs} as-is directly.
* @param pvs the property values that the factory is about to apply (never {@code null})
* @param bean the bean instance created, but whose properties have not yet been set
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the actual property values to apply to the given bean (can be the passed-in
* PropertyValues instance), or {@code null} which proceeds with the existing properties
* but specifically continues with a call to {@link #postProcessPropertyValues}
* (requiring initialized {@code PropertyDescriptor}s for the current bean class)
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @since 5.1
* @see #postProcessPropertyValues
*/
default PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return null;
}
/**
* Post-process the given property values before the factory applies them
* to the given bean. Allows for checking whether all dependencies have been
* satisfied, for example based on a "Required" annotation on bean property setters.
* <p>Also allows for replacing the property values to apply, typically through
* creating a new MutablePropertyValues instance based on the original PropertyValues,
* adding or removing specific values.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code pvs} as-is.
* @param pvs the property values that the factory is about to apply (never {@code null})
* @param pds the relevant property descriptors for the target bean (with ignored
* dependency types - which the factory handles specifically - already filtered out)
* @param bean the bean instance created, but whose properties have not yet been set
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the actual property values to apply to the given bean (can be the passed-in
* PropertyValues instance), or {@code null} to skip property population
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessProperties
* @see org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues
* @deprecated as of 5.1, in favor of {@link #postProcessProperties(PropertyValues, Object, String)}
*/
@Deprecated
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return pvs;
}
}
5.SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
简述:
6.MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
简述: 该接口用来合并BeanDefinition。
7.LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor
简述:
8.Aware
- ResourceLoaderAware、ApplicationContextAware、ApplicationEventPublisherAware、MessageSourceAware、BeanFactoryAware、BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、等等
9.init and destory
- InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()、@PostConstruct(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor) or init-methord
- DisposableBean.destroy()、 @PreDestroy(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor) or destroy-methord、DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeDestruction()