一、entry
指定打包入口
1、单入口
module.exports={
entry:'./src/index.js'
};
2、多入口
module.exports={
entry:{
app:'./src/index.js',
adminApp:'./src/adminApp.js'
}
};
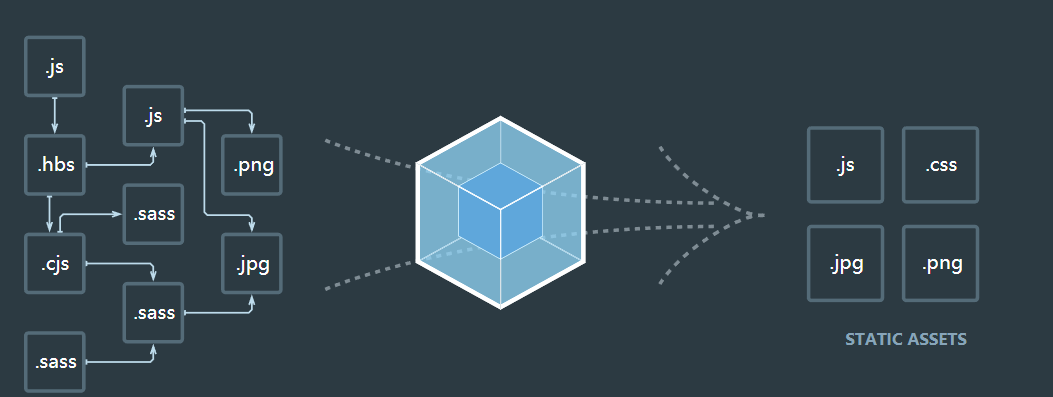
对于非代码比如图片、字体依赖会不断的加入到依赖图中
二、output
指定打包输出
1、单入口配置
module.exports={
entry:'./src/index.js',
output:{
filename:'bundle.js',
path:path.join(__dirname,'dist'),
}
};
2、多入口配置
module.exports={
entry:{
app:'./src/index.js',
adminApp:'./src/adminApp.js'
},
output: {
filename: '[name].js',、//通过占位符确保文件的唯一
path: path.join(__dirname,'dist')
}
};
三、loaders
webpack只支持JS和寄送两种文件类型,通过loaders去支持其他文件类型并把它们转化成有效的模块,添加到依赖图中。 常见的loaders:

module:{
rules:[
{
test: /\.css$/, // 正则匹配所有.css后缀的样式文件
use: ['style-loader', 'css-loader'] // 使用这两个loader来加载样式文件
}
]
},
四、plugins
插件用于bundle文件的优化,资源管理的环境变量注入,作用整个构建过程
常用的plugins:

plugins:[
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: 'index.html',
template: 'index.html',
inject: true
}),
],
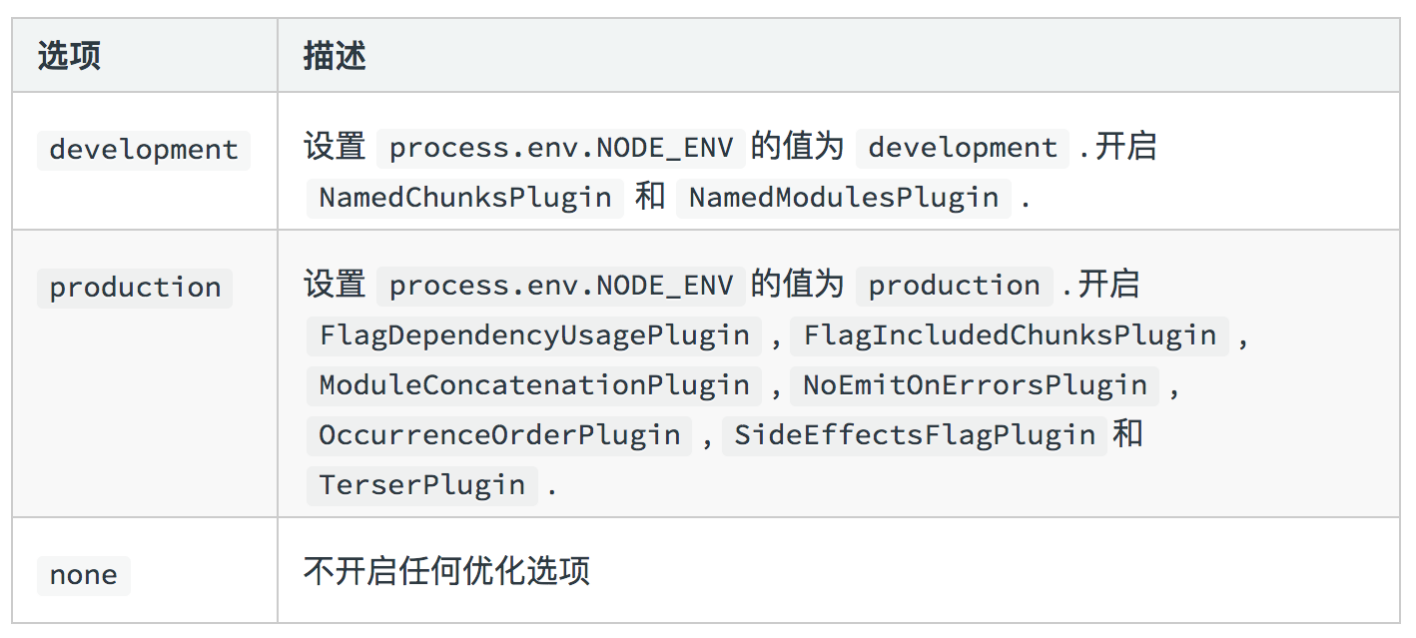
五、mode
mode 用来指定当前的构建环境是production、development还是none。 设置mode可以使用webpack的内置函数,默认值production。
mode:'production'
Mode的内置函数功能