先看一张官网的设计图
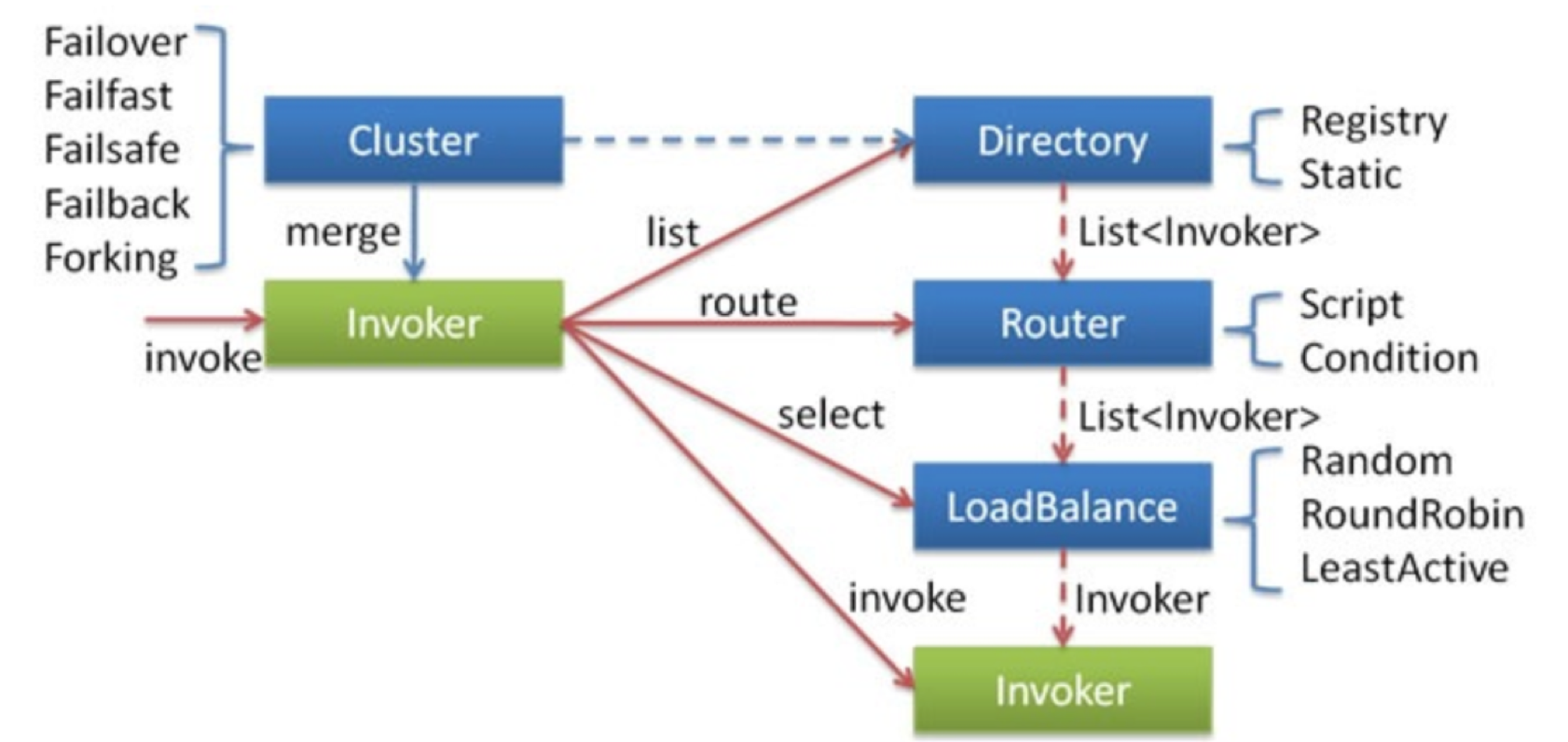
擦。看上去有点懵。。。 先大致搞懂各个关键字的意思吧。
- Invoker: 它代表的是 Provider 的一个可用Service 的抽象,Invoker封装了 Provider 地址及Service 接口信息。
- Directory代表多个 Invoker,可以看成 List ,但与 List 不同的是,它的值可能是动态变化的,比如注册中心的推送变更
- Cluster 将 Directory中的多个 Invoker 伪装成一个 Invoker ,对上层透明。这个过程加入了容错逻辑,调用失败后,重试另一个 (那么 cluser中肯定含有 Directory 属性)//--十逸自己解读
- Router 负责从多个 Invoker 中按照路由规则选出子集,比如读写分离,应用隔离等 (那么 Directory中肯定含有 Router 属性)//十逸自己解读
- LoadBalance 负责从多个 Invoker 中选出具体的一个用于本次调用,选的过程包含了负载均衡算法,调用失败后,需要重选
按照上面图的思路,我们 dubug 下源码
String hello = demoService.sayHello("world");
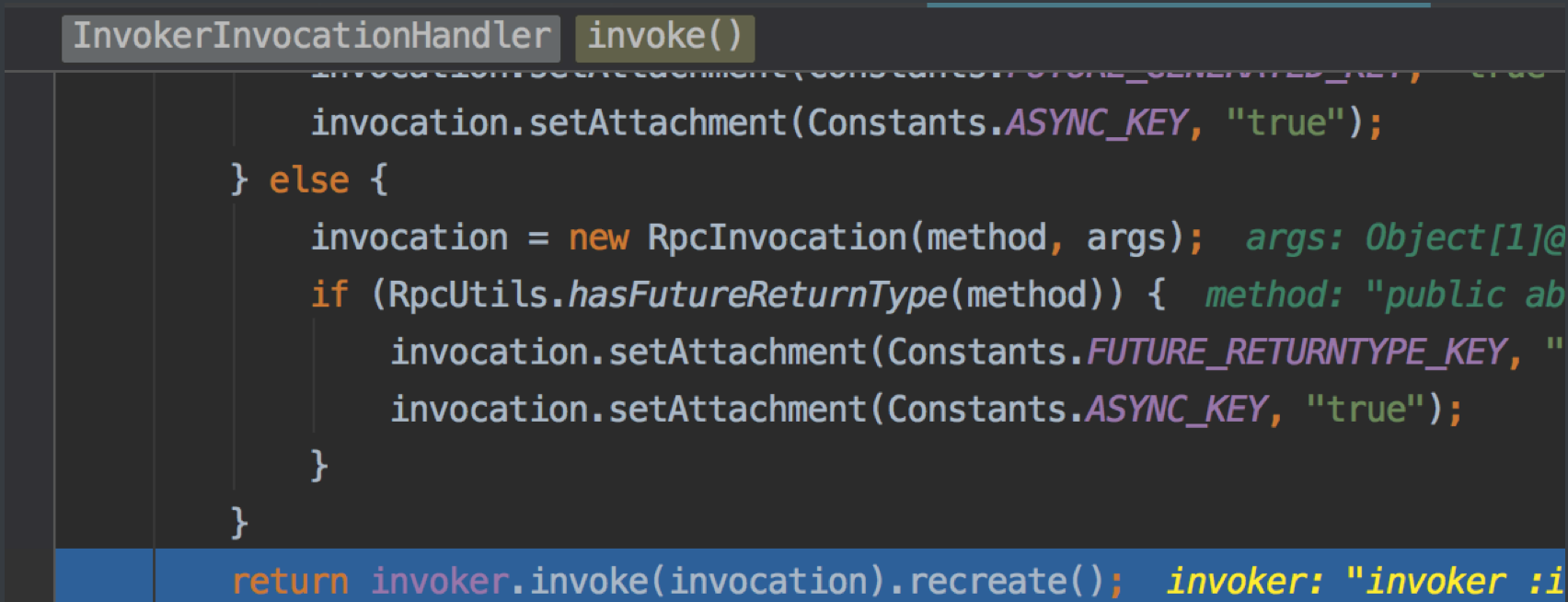
//MockClusterInvoker
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result result = null;
String value = directory.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.MOCK_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString()).trim();
if (value.length() == 0 || value.equalsIgnoreCase("false")) {
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);//进入AbstractClusterInvoker
} else if (value.startsWith("force")) {
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, null);
} else {
try {
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (RpcException e) {
}
return result;
}
//AbstractClusterInvoker
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
// binding attachments into invocation.
Map<String, String> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachments();
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
((RpcInvocation) invocation).addAttachments(contextAttachments);
}
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);//-->进入6 7
LoadBalance loadbalance = initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation);//8
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
}
//AbstractDirectory
public List<Invoker<T>> list(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
if (destroyed) {
throw new RpcException("Directory already destroyed .url: " + getUrl());
}
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = doList(invocation);//5 RegistryDirectory.doList-->6 7
List<Router> localRouters = this.routers; // local reference
if (localRouters != null && !localRouters.isEmpty()) {
for (Router router : localRouters) {
try {
if (router.getUrl() == null || router.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.RUNTIME_KEY, false)) {
invokers = router.route(invokers, getConsumerUrl(), invocation);//6 MockInvokersSelector
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
}
}
}
return invokers;
}
//RegistryDirectory
public List<Invoker<T>> doList(Invocation invocation) {
if (forbidden) {
// 1. No service provider 2. Service providers are disabled
throw new RpcException(RpcException.FORBIDDEN_EXCEPTION);
}
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = null;
Map<String, List<Invoker<T>>> localMethodInvokerMap = this.methodInvokerMap; // local reference
if (localMethodInvokerMap != null && localMethodInvokerMap.size() > 0) {
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
Object[] args = RpcUtils.getArguments(invocation);
if (args != null && args.length > 0 && args[0] != null
&& (args[0] instanceof String || args[0].getClass().isEnum())) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName + "." + args[0]); // The routing can be enumerated according to the first parameter
}
if (invokers == null) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(methodName);
}
if (invokers == null) {
invokers = localMethodInvokerMap.get(Constants.ANY_VALUE);
}
if (invokers == null) {
Iterator<List<Invoker<T>>> iterator = localMethodInvokerMap.values().iterator();
if (iterator.hasNext()) {
invokers = iterator.next();
}
}
}
return invokers == null ? new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(0) : invokers;
}
//MockInvokersSelector
public <T> List<Invoker<T>> route(final List<Invoker<T>> invokers,
URL url, final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
if (invocation.getAttachments() == null) {
return getNormalInvokers(invokers);
} else {
String value = invocation.getAttachments().get(Constants.INVOCATION_NEED_MOCK);
if (value == null)
return getNormalInvokers(invokers);//7
else if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
return getMockedInvokers(invokers);
}
}
return invokers;
}
private <T> List<Invoker<T>> getNormalInvokers(final List<Invoker<T>> invokers) {
if (!hasMockProviders(invokers)) {
return invokers;
} else {
List<Invoker<T>> sInvokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(invokers.size());
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
if (!invoker.getUrl().getProtocol().equals(Constants.MOCK_PROTOCOL)) {
sInvokers.add(invoker);
}
}
return sInvokers;
}
}
//FailoverClusterInvoker
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) {
List<Invoker<T>> copyinvokers = invokers;
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.RETRIES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1;
if (len <= 0) {
len = 1;
}
RpcException le = null; // last exception.
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyinvokers.size()); // invoked invokers.
Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (i > 0) {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
copyinvokers = list(invocation);
// check again
checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation);
}
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyinvokers, invoked);//9
invoked.add(invoker);
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked);
try {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);//-
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.
}
return result;
}