数据结构
数据结构表示数据在计算机中的存储和组织形式,主要描述数据元素之间和位置关系等。选择适当的数据结构可以提高计算机程序的运行效率(时间复杂度)和存储效率(空间复杂度)。
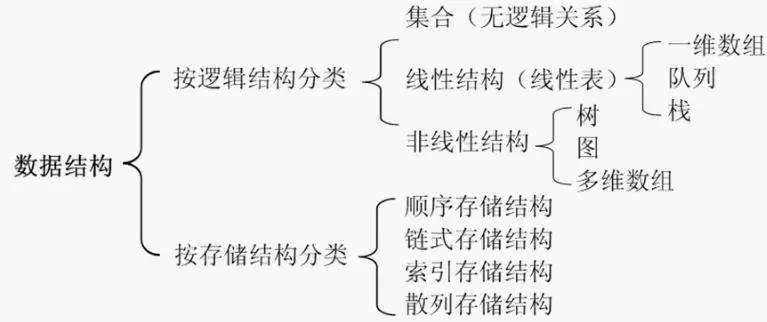
数据结构的三种层次:
- 逻辑结构–抽象层: 主要描述的是数据元素之间的逻辑关系
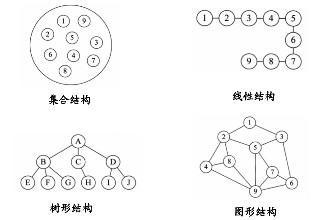
- 集合结构(集): 所有的元素都属于一个总体,除了同属于一个集合外没有其他关系。集合结构不强调元素之间的任何关联性。
- 线性结构(表): 数据元素之间具有一对一的前后关系。结构中必须存在唯一的首元素和唯一的尾元素。
- 树形结构(树): 数据元素之间一对多的关系
- 网状结构(图): 图状结构或网状结构 结构中的数据元素之间存在多对多的关系
-
物理结构–存储层: 主要描述的是数据元素之间的位置关系
-
顺序结构: 顺序结构就是使用一组连续的存储单元依次存储逻辑上相邻的各个元素
优点: 只需要申请存放数据本身的内存空间即可,支持下标访问,也可以实现随机访问。
缺点: 必须静态分配连续空间,内存空间的利用率比较低。插入或删除可能需要移动大量元素,效率比较低
-
链式结构: 链式存储结构不使用连续的存储空间存放结构的元素,而是为每一个元素构造一个节点。节点中除了存放数据本身以外,还需要存放指向下一个节点的指针。
优点: 不采用连续的存储空间导致内存空间利用率比较高,克服顺序存储结构中预知元素个数的缺点 插入或删除元素时,不需要移动大量的元素。
缺点: 需要额外的空间来表达数据之间的逻辑关系, 不支持下标访问和随机访问。
-
索引结构: 除建立存储节点信息外,还建立附加的索引表来标节点的地址。索引表由若干索引项组成。
优点: 是用节点的索引号来确定结点存储地址,检索速度块
缺点: 增加了附加的索引表,会占用较多的存储空间。
-
散列结构: 由节点的关键码值决定节点的存储地址。散列技术除了可以用于查找外,还可以用于存储。
优点: 散列是数组存储方式的一种发展,采用存储数组中内容的部分元素作为映射函数的输入,映射函数的输出就是存储数据的位置, 相比数组,散列的数据访问速度要高于数组
缺点: 不支持排序,一般比用线性表存储需要更多的空间,并且记录的关键字不能重复。
-
-
运算结构–实现层: 主要描述的是如何实现数据结构
- 分配资源,建立结构,释放资源
- 插入和删除
- 获取和遍历
- 修改和排序
每种逻辑结构采用何种物理结构来实现,并没有具体的规定。当一个结构,在逻辑结构中只有一种定义,而在物理结构中却有两种选择,那么这个结构就属于逻辑结构;
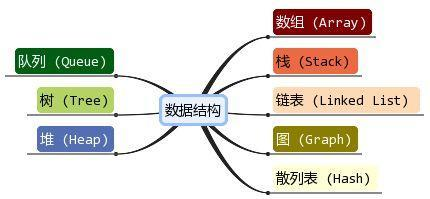
数据结构比较
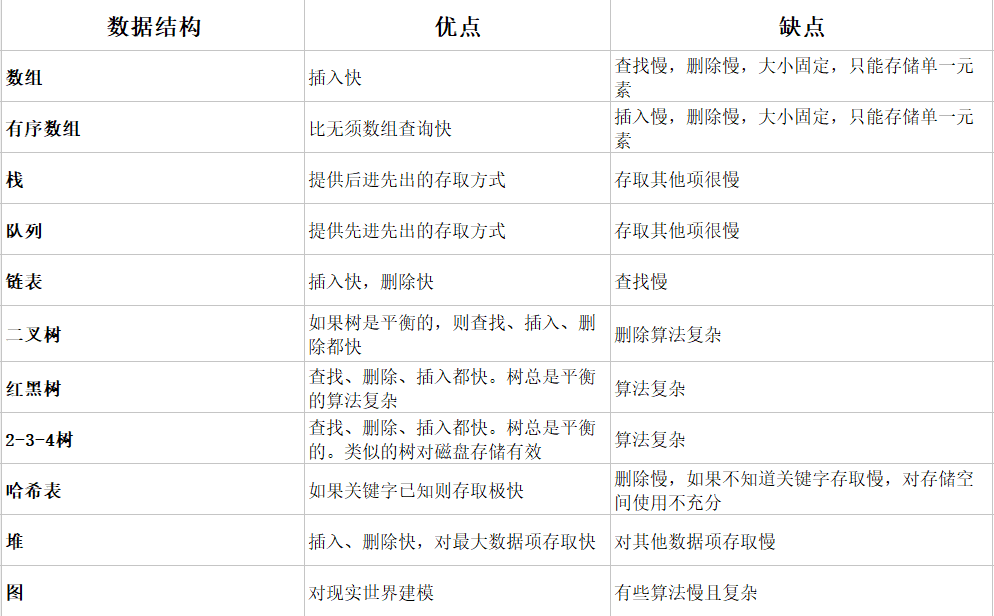
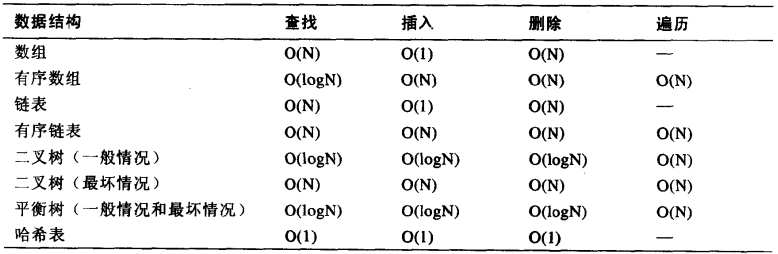
常用的数据结构:
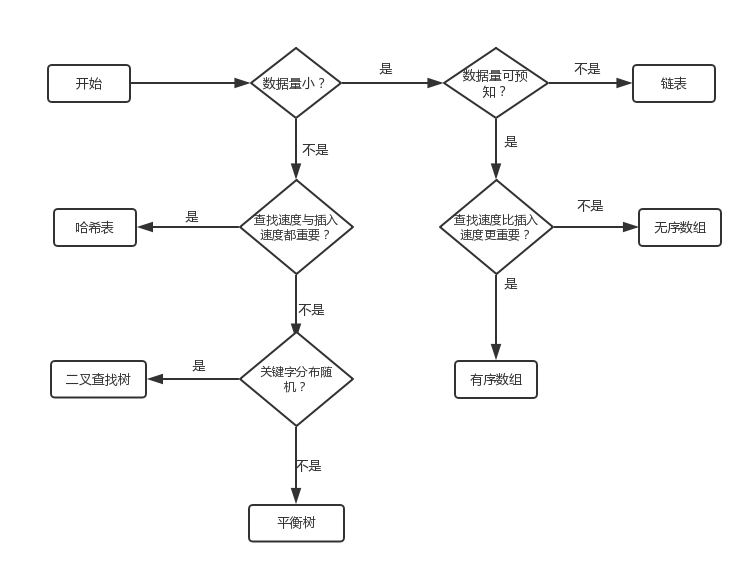
数据结构选择:
O符号
O在算法当中表述的是时间复杂度,它在分析算法复杂性的方面非常有用。常见的有:
- O(1):最低的复杂度,无论数据量大小,耗时都不变,都可以在一次计算后获得。哈希算法就是典型的O(1)
- O(n):线性,n表示数据的量,当量增大,耗时也增大,常见有遍历算法
- O(n²):平方,表示耗时是n的平方倍,当看到循环嵌循环的时候,基本上这个算法就是平方级的,如:冒泡排序等
- O(log n):对数,通常ax=n,那么数x叫做以a为底n的对数,也就是x=logan,这里是a通常是2,如:数量增大8倍,耗时只增加了3倍,二分查找就是对数级的算法,每次剔除一半
- O(n log n):线性对数,就是n乘以log n,按照上面说的数据增大8倍,耗时就是8*3=24倍,归并排序就是线性对数级的算法
Array
在Java中,数组是用来存放同一种数据类型的集合,注意只能存放同一种数据类型。
//只声明了类型和长度
数据类型 [] 数组名称 = new 数据类型[数组长度];
//声明了类型,初始化赋值,大小由元素个数决定
数据类型 [] 数组名称 = {数组元素1,数组元素2,......}
大小固定,不能动态扩展(初始化给大了,浪费;给小了,不够用),插入快,删除和查找慢
模拟实现
public class Array {
private int[] intArray;
private int elems;
private int length;
public Array(int max) {
length = max;
intArray = new int[max];
elems = 0;
}
/** * 添加 * @param value */
public void add(int value){
if(elems == length){
System.out.println("error");
return;
}
intArray[elems] = value;
elems++;
}
/** * 查找 * @param searchKey * @return */
public int find(int searchKey){
int i;
for(i = 0; i < elems; i++){
if(intArray[i] == searchKey)
break;
}
if(i == elems){
return -1;
}
return i;
}
/** * 删除 * @param value * @return */
public boolean delete(int value){
int i = find(value);
if(i == -1){
return false;
}
for (int j = i; j < elems-1; j++) {
//后面的数据往前移
intArray[j] = intArray[j + 1];
}
elems--;
return true;
}
/** * 更新 * @param oldValue * @param newValue * @return */
public boolean update(int oldValue,int newValue){
int i = find(oldValue);
if(i == -1){
return false;
}
intArray[i] = newValue;
return true;
}
/** * 显示所有 */
public void display(){
for(int i = 0 ; i < elems ; i++){
System.out.print(intArray[i]+" ");
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
/** * 冒泡排序 * 每趟冒出一个最大数/最小数 * 每次运行数量:总数量-运行的趟数(已冒出) */
public void bubbleSort(){
for(int i = 0; i < elems-1; i++){//排序趟数 n-1次就行了
System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"趟:");
for(int j = 0; j < elems-i-1; j++){//每趟次数 (n-i) -1是防止下标越界,后面赋值用到了+1
if(intArray[j] > intArray[j+1]){ //控制按大冒泡还是按小冒泡
int temp = intArray[j];
intArray[j] = intArray[j+1];
intArray[j+1] = temp;
}
display();
}
}
}
/*** * 选择排序 * 每趟选择一个最大数/最小数 * 每次运行数量:总数量-运行的趟数(已选出) */
public void selectSort(){
for(int i = 0; i < elems-1; i++) {//排序趟数 n-1次就行了
int min = i;
for(int j = i+1; j < elems; j++){ //排序次数 每趟选择一个数出来,-1次
if(intArray[j] < intArray[min]){
min = j;
}
}
if(i != min ){
int temp = intArray[i];
intArray[i] = intArray[min];
intArray[min] = temp;
}
display();
}
}
/** * 插入排序 * 每趟选择一个待插入的数 * 每次运行把待插入的数放在比它大/小后面 */
public void insertSort(){
int j;
for(int i = 1; i < elems; i++){
int temp = intArray[i];
j = i;
while (j > 0 && temp < intArray[j-1]){
intArray[j] = intArray[j-1];
j--;
}
intArray[j] = temp;
}
display();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array array = new Array(10);
array.add(6);
array.add(3);
array.add(8);
array.add(2);
array.add(11);
array.add(5);
array.add(7);
array.add(4);
array.add(9);
array.add(10);
// array.bubbleSort();
// array.selectSort();
array.insertSort();
// array.display();
// System.out.println(array.find(4));
// System.out.println(array.delete(1));
// array.display();
// System.out.println(array.update(2,6));
// array.display();
}
}
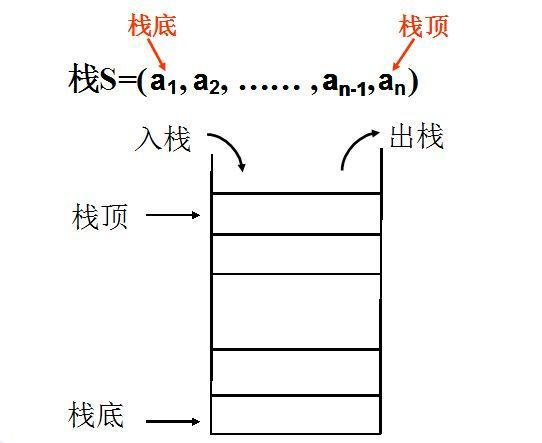
Stack
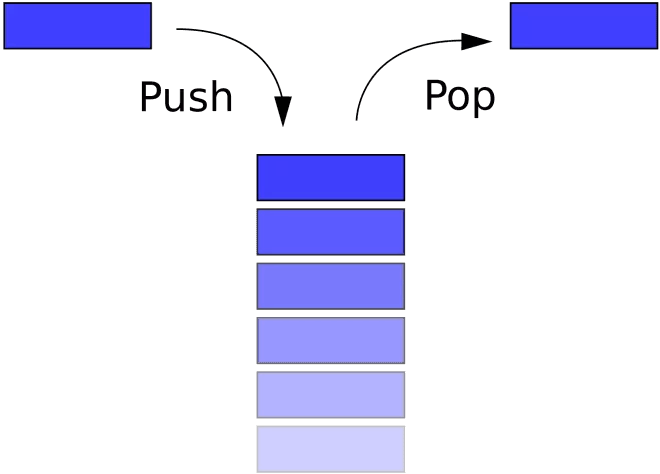
- 栈(stack)又称为堆栈或堆叠,栈作为一种数据结构,它按照先进后出的原则存储数据,先进入的数据被压入栈底,最后的数据在栈顶
- java中Stack是Vector的一个子类,只定义了默认构造函数,用来创建一个空栈。
- 栈是元素的集合,其包含了两个基本操作:push
- 操作可以用于将元素压入栈,pop 操作可以将栈顶元素移除。
- 遵循后入先出(LIFO)原则。
- 时间复杂度:
- 索引: O(n)
- 搜索: O(n)
- 插入: O(1)
- 移除: O(1)
模拟实现
public class Stack {
//小贴士:通常可以利用栈实现字符串逆序,还可以利用栈判断分隔符是否匹配,如<a[b{c}]>,可以正进反出,栈为空则成功。
/**基于数组实现的顺序栈,连续存储的线性实现,需要初始化容量**/
//固定数据类型
//private int[] array;
//动态数据类型
private Object[] objArray;
private int maxSize;
private int top;
public Stack() {
}
public Stack(int maxSize) {
if(maxSize > 0){
objArray = new Object[maxSize];
this.maxSize = maxSize;
top = -1;
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("初始化大小错误:maxSize=" + maxSize);
}
}
/** * 入栈 * @param obj */
public void objPush(Object obj){
//扩容
grow();
//++在前表示先运算再赋值,优先级高,在后表示先赋值再运算,优先级低
objArray[++top] = obj;
}
/** * 出栈 * @return */
public Object objPop(){
Object obj = peekTop();
//声明原顶栈可以回收空间(GC)
objArray[top--] = null;
return obj;
}
/** * 查看栈顶 * @return */
public Object peekTop(){
if(top != -1){
return objArray[top];
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("stack is null");
}
}
/** * 动态扩容 */
public void grow(){
// << 左移运算符,1表示乘以2的1次方
if(top == maxSize-1){
maxSize = maxSize<<1;
objArray = Arrays.copyOf(objArray,maxSize);
}
}
/**基于链式存储,不连续存储的非线性实现**/
private class Node<Object>{
private Object data;
private Node next;
public Node(Object data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
private Node nodeTop;
private int size;
public void nodePush(Object obj){
//栈顶指向新元素,新元素的next指向原栈顶元素
nodeTop = new Node(obj,nodeTop);
size++;
}
public Object nodePop(){
Node old = nodeTop;
//声明原顶栈可以回收空间(GC)
old.next = null;
//栈顶指向下一个元素
nodeTop = nodeTop.next;
size--;
return old.data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[ ");
for(Node<Object> node = nodeTop; node != null; node = node.next){
sb.append(node.data.toString() + " ");
}
return sb.toString()+"]";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Stack stack = new Stack(1);
// stack.objPush("abc");
// stack.objPush(123);
// stack.objPush("de");
// stack.objPush("cd");
// stack.objPush("er");
// stack.objPush("hello");
// stack.objPush(666);
// stack.objPush(545);
// stack.objPush("word");
// while (stack.top != -1){
// System.out.println(stack.objPop());
// }
// System.out.println(stack.peekTop());
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.nodePush("111");
stack.nodePush("222");
stack.nodePush("aaa");
stack.nodePush("bbb");
System.out.println(stack);
while (stack.size > 1)
System.out.println(stack.nodePop());
System.out.println(stack);
}
}
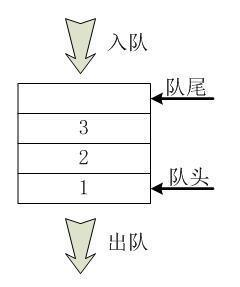
Queue
- 队列是元素的集合,其包含了两个基本操作:enqueue 操作可以用于将元素插入到队列中,而 dequeue 操作则是将元素从队列中移除。
- 遵循先入先出原则 (FIFO)。
- 时间复杂度:
- 索引: O(n)
- 搜索: O(n)
- 插入: O(1)
- 移除: O(1)
public class Queue {
/***
* 1.单向队列(Queue):只能在一端插入数据,另一端删除数据。
* 2.双向队列(Deque):每一端都可以进行插入数据和删除数据操作。
*
* 与栈不同的是,队列中的数据不总是从数组的0下标开始的
* 选择的做法是移动队头和队尾的指针。
* 为了避免队列不满却不能插入新的数据,我们可以让队尾指针绕回到数组开始的位置,这也称为“循环队列”。
* */
// 单向循环队列,顺序存储结构实现
private Object[] objQueue;
//队列大小
private int maxSize;
//顶部
private int top;
//底部
private int bottom;
//实际元素
private int item;
public Queue(int size) {
maxSize = size;
objQueue = new Object[maxSize];
top = 0;
bottom = -1;
item = 0;
}
/**
* 入队
* @param obj
*/
public void add(Object obj){
if(item == maxSize){
throw new RuntimeException(obj+" add error, queue is full");
}
//循环队列,首尾结合,下标控制队首和队尾位置
if(bottom == maxSize-1){
bottom = -1;
}
objQueue[++bottom] = obj;
item++;
}
/**
* 出对
* @return
*/
public Object out(){
if(item == 0){
throw new RuntimeException("queue is null");
}
Object obj = objQueue[top];
//声明原顶栈可以回收空间(GC)
objQueue[top] = null;
top++;
//重置下标
if(top == maxSize){
top = 0;
}
item--;
return obj;
}
//链式存储结构实现
private class NodeQueue<Object>{
private Object data;
private NodeQueue next;
public NodeQueue(Object data, NodeQueue next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
//队列头 出
private NodeQueue queueTop;
//队列尾 进
private NodeQueue queueBottom;
//队列大小
private int size;
public Queue() {
queueTop = null;
queueBottom = null;
size = 0;
}
/**
* 入队
* @param obj
*/
public void addNodeQueue(Object obj){
if(size == 0){
queueTop = new NodeQueue(obj,null);
//指向同一存储地址
queueBottom = queueTop;
}else{
NodeQueue<Object> nodeQueue = new NodeQueue(obj,null);
//让尾节点的next指向新增的节点
queueBottom.next = nodeQueue;
//以新节点作为尾节点
queueBottom = nodeQueue;
}
size ++;
}
/**
* 出队
* @return
*/
public Object removeNodeQueue(){
if(size == 0){
throw new RuntimeException("queue is null");
}
NodeQueue nodeQueue = queueTop;
queueTop = queueTop.next;
//声明原队列头next可以回收空间(GC)
nodeQueue.next = null;
size--;
return nodeQueue.data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("{ ");
for(NodeQueue nodeQueue = queueTop ; nodeQueue != null ; nodeQueue = nodeQueue.next){
sb.append(nodeQueue.data.toString()+" ");
}
return sb.toString()+"}";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue();
queue.addNodeQueue("123");
queue.addNodeQueue("abc");
queue.addNodeQueue("ddd");
System.out.println(queue);
queue.removeNodeQueue();
System.out.println(queue);
queue.removeNodeQueue();
queue.removeNodeQueue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
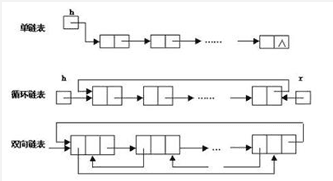
Linked List
- 链表即是由节点(Node)组成的线性集合,每个节点可以利用指针指向其他节点。它是一种包含了多个节点的、能够用于表示序列的数据结构。
- 单向链表: 链表中的节点仅指向下一个节点,并且最后一个节点指向空。
- 双向链表: 其中每个节点具有两个指针 p、n,使得 p 指向先前节点并且 n 指向下一个节点;最后一个节点的 n 指针指向 null。
- 循环链表:每个节点指向下一个节点并且最后一个节点指向第一个节点的链表。
- 时间复杂度:
- 索引: O(n)
- 搜索: O(n)
- 插入: O(1)
- 移除: O(1)
public class LinkedList {
/***
* 链表通常由一连串节点组成,每个节点包含任意的实例数据(data fields)和一或两个用来指向上一个/或下一个节点的位置的链接("links")
*/
private Node head; //链表头
private Node tail; //链表尾
private int size; //节点数
/**
* 双端链表
*/
public class Node{
private Object data;
private Node prev; //上一个
private Node next; //下一个
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public LinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
/**
* 向链表头添加数据
* @param object
*/
public void addHead(Object object){
Node node = new Node(object);
if(size == 0){
head = node;
tail = node;
size++;
}else{
head.prev = node;
node.next = head;
head = node;
size++;
}
}
/**
* 删除头
*/
public void deleteHead(){
//头部指向下一个,prev值为null则说明是链表的头部
if(size != 0){
head.prev = null;
head = head.next;
size--;
}
}
/**
*向链表尾添加数据
* @param object
*/
public void addTail(Object object){
Node node = new Node(object);
if(size == 0){
head = node;
tail = node;
size++;
}else{
node.prev = tail;
tail.next = node;
tail = node;
size++;
}
}
/**
* 删除尾部
*/
public void deleteTail(){
//尾部指向上一个,next值为null则说明是链表的尾部
if(size != 0){
tail.next = null;
tail = tail.prev;
size--;
}
}
/**
* 显示数据
*/
public void display(){
Node node = head;
while (size > 0){
System.out.print("["+node.data+"->");
node = node.next;
size--;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.addHead("123");
// linkedList.addHead("abc");
// linkedList.addHead("%?");
// linkedList.addTail("+_+");
// linkedList.addTail("hello");
linkedList.addTail("word");
linkedList.deleteHead();
linkedList.deleteTail();
linkedList.display();
}
}
单链表反转,链表中环的检测,两个有序的链表合并,删除链表倒数第n个结点,求链表的中间结点
public class LinkedListAlgo {
// 单链表反转
public static Node reverse(Node list) {
Node curr = list, pre = null;
while (curr != null) {
Node next = curr.next;
curr.next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = next;
}
return pre;
}
// 检测环
public static boolean checkCircle(Node list) {
if (list == null) return false;
Node fast = list.next;
Node slow = list;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (slow == fast) return true;
}
return false;
}
// 有序链表合并
public static Node mergeSortedLists(Node la, Node lb) {
if (la == null) return lb;
if (lb == null) return la;
Node p = la;
Node q = lb;
Node head;
if (p.data < q.data) {
head = p;
p = p.next;
} else {
head = q;
q = q.next;
}
Node r = head;
while (p != null && q != null) {
if (p.data < q.data) {
r.next = p;
p = p.next;
} else {
r.next = q;
q = q.next;
}
r = r.next;
}
if (p != null) {
r.next = p;
} else {
r.next = q;
}
return head;
}
// 删除倒数第K个结点
public static Node deleteLastKth(Node list, int k) {
Node fast = list;
int i = 1;
while (fast != null && i < k) {
fast = fast.next;
++i;
}
if (fast == null) return list;
Node slow = list;
Node prev = null;
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
prev = slow;
slow = slow.next;
}
if (prev == null) {
list = list.next;
} else {
prev.next = prev.next.next;
}
return list;
}
// 求中间结点
public static Node findMiddleNode(Node list) {
if (list == null) return null;
Node fast = list;
Node slow = list;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
public static void printAll(Node list) {
Node p = list;
while (p != null) {
System.out.print(p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static Node createNode(int value) {
return new Node(value, null);
}
public static class Node {
private int data;
private Node next;
public Node(int data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
}
}
Binary Tree
二叉树(由一个根结点和两棵互不相交的、分别称为根结点的左子树和右子树组成) 二叉树即是每个节点最多包含左子节点与右子节点这两个节点的树形数据结构。
- 满二叉树: 树中的每个节点仅包含 0 或 2 个节点。
- 完美二叉树(Perfect Binary Tree): 二叉树中的每个叶节点都拥有两个子节点,并且具有相同的高度。
- 完全二叉树: 除最后一层外,每一层上的结点数均达到最大值;在最后一层上只缺少右边的若干结点。
public class BSTree {
private Node tree;
public Node find(int data) {
Node p = tree;
while (p != null) {
if (data < p.data) p = p.left;
else if (data > p.data) p = p.right;
else return p;
}
return null;
}
public void insert(int data) {
if (tree == null) {
tree = new Node(data);
return;
}
Node p = tree;
while (p != null) {
if (data > p.data) {
if (p.right == null) {
p.right = new Node(data);
return;
}
p = p.right;
} else { // data < p.data
if (p.left == null) {
p.left = new Node(data);
return;
}
p = p.left;
}
}
}
public void delete(int data) {
Node p = tree; // p指向要删除的节点,初始化指向根节点
Node pp = null; // pp记录的是p的父节点
while (p != null && p.data != data) {
pp = p;
if (data > p.data) p = p.right;
else p = p.left;
}
if (p == null) return; // 没有找到
// 要删除的节点有两个子节点
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) { // 查找右子树中最小节点
Node minP = p.right;
Node minPP = p; // minPP表示minP的父节点
while (minP.left != null) {
minPP = minP;
minP = minP.left;
}
p.data = minP.data; // 将minP的数据替换到p中
p = minP; // 下面就变成了删除minP了
pp = minPP;
}
// 删除节点是叶子节点或者仅有一个子节点
Node child; // p的子节点
if (p.left != null) child = p.left;
else if (p.right != null) child = p.right;
else child = null;
if (pp == null) tree = child; // 删除的是根节点
else if (pp.left == p) pp.left = child;
else pp.right = child;
}
public Node findMin() {
if (tree == null) return null;
Node p = tree;
while (p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
}
return p;
}
public Node findMax() {
if (tree == null) return null;
Node p = tree;
while (p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
}
return p;
}
public static class Node {
private int data;
private Node left;
private Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
}
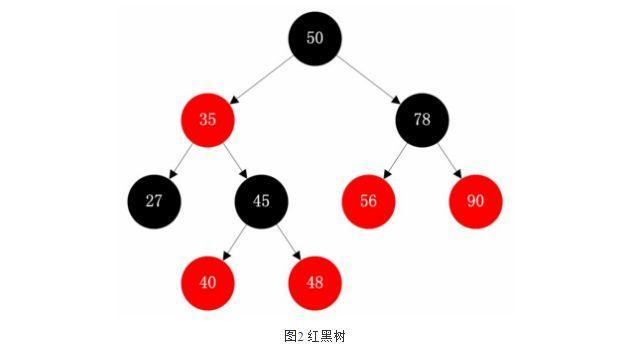
红黑树(每节点五元素,颜色(如果一个节点是红的,则它的两个儿子都是黑的)、键值、左子节点、右字节的、父节点)
public class RBTreeNode<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private T value;//node value
private RBTreeNode<T> left;//left child pointer
private RBTreeNode<T> right;//right child pointer
private RBTreeNode<T> parent;//parent pointer
private boolean red;//color is red or not red
public RBTreeNode(){}
public RBTreeNode(T value){this.value=value;}
public RBTreeNode(T value,boolean isRed){this.value=value;this.red = isRed;}
public T getValue() {
return value;
}
void setValue(T value) {
this.value = value;
}
RBTreeNode<T> getLeft() {
return left;
}
void setLeft(RBTreeNode<T> left) {
this.left = left;
}
RBTreeNode<T> getRight() {
return right;
}
void setRight(RBTreeNode<T> right) {
this.right = right;
}
RBTreeNode<T> getParent() {
return parent;
}
void setParent(RBTreeNode<T> parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
boolean isRed() {
return red;
}
boolean isBlack(){
return !red;
}
/**
* is leaf node
**/
boolean isLeaf(){
return left==null && right==null;
}
void setRed(boolean red) {
this.red = red;
}
void makeRed(){
red=true;
}
void makeBlack(){
red=false;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return value.toString();
}
}
public class RBTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private final RBTreeNode<T> root;
//node number
private java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong size =
new java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong(0);
//in overwrite mode,all node's value can not has same value
//in non-overwrite mode,node can have same value, suggest don't use non-overwrite mode.
private volatile boolean overrideMode=true;
public RBTree(){
this.root = new RBTreeNode<T>();
}
public RBTree(boolean overrideMode){
this();
this.overrideMode=overrideMode;
}
public boolean isOverrideMode() {
return overrideMode;
}
public void setOverrideMode(boolean overrideMode) {
this.overrideMode = overrideMode;
}
/**
* number of tree number
* @return
*/
public long getSize() {
return size.get();
}
/**
* get the root node
* @return
*/
private RBTreeNode<T> getRoot(){
return root.getLeft();
}
/**
* add value to a new node,if this value exist in this tree,
* if value exist,it will return the exist value.otherwise return null
* if override mode is true,if value exist in the tree,
* it will override the old value in the tree
*
* @param value
* @return
*/
public T addNode(T value){
RBTreeNode<T> t = new RBTreeNode<T>(value);
return addNode(t);
}
/**
* find the value by give value(include key,key used for search,
* other field is not used,@see compare method).if this value not exist return null
* @param value
* @return
*/
public T find(T value){
RBTreeNode<T> dataRoot = getRoot();
while(dataRoot!=null){
int cmp = dataRoot.getValue().compareTo(value);
if(cmp<0){
dataRoot = dataRoot.getRight();
}else if(cmp>0){
dataRoot = dataRoot.getLeft();
}else{
return dataRoot.getValue();
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* remove the node by give value,if this value not exists in tree return null
* @param value include search key
* @return the value contain in the removed node
*/
public T remove(T value){
RBTreeNode<T> dataRoot = getRoot();
RBTreeNode<T> parent = root;
while(dataRoot!=null){
int cmp = dataRoot.getValue().compareTo(value);
if(cmp<0){
parent = dataRoot;
dataRoot = dataRoot.getRight();
}else if(cmp>0){
parent = dataRoot;
dataRoot = dataRoot.getLeft();
}else{
if(dataRoot.getRight()!=null){
RBTreeNode<T> min = removeMin(dataRoot.getRight());
//x used for fix color balance
RBTreeNode<T> x = min.getRight()==null ? min.getParent() : min.getRight();
boolean isParent = min.getRight()==null;
min.setLeft(dataRoot.getLeft());
setParent(dataRoot.getLeft(),min);
if(parent.getLeft()==dataRoot){
parent.setLeft(min);
}else{
parent.setRight(min);
}
setParent(min,parent);
boolean curMinIsBlack = min.isBlack();
//inherit dataRoot's color
min.setRed(dataRoot.isRed());
if(min!=dataRoot.getRight()){
min.setRight(dataRoot.getRight());
setParent(dataRoot.getRight(),min);
}
//remove a black node,need fix color
if(curMinIsBlack){
if(min!=dataRoot.getRight()){
fixRemove(x,isParent);
}else if(min.getRight()!=null){
fixRemove(min.getRight(),false);
}else{
fixRemove(min,true);
}
}
}else{
setParent(dataRoot.getLeft(),parent);
if(parent.getLeft()==dataRoot){
parent.setLeft(dataRoot.getLeft());
}else{
parent.setRight(dataRoot.getLeft());
}
//current node is black and tree is not empty
if(dataRoot.isBlack() && !(root.getLeft()==null)){
RBTreeNode<T> x = dataRoot.getLeft()==null
? parent :dataRoot.getLeft();
boolean isParent = dataRoot.getLeft()==null;
fixRemove(x,isParent);
}
}
setParent(dataRoot,null);
dataRoot.setLeft(null);
dataRoot.setRight(null);
if(getRoot()!=null){
getRoot().setRed(false);
getRoot().setParent(null);
}
size.decrementAndGet();
return dataRoot.getValue();
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* fix remove action
* @param node
* @param isParent
*/
private void fixRemove(RBTreeNode<T> node,boolean isParent){
RBTreeNode<T> cur = isParent ? null : node;
boolean isRed = isParent ? false : node.isRed();
RBTreeNode<T> parent = isParent ? node : node.getParent();
while(!isRed && !isRoot(cur)){
RBTreeNode<T> sibling = getSibling(cur,parent);
//sibling is not null,due to before remove tree color is balance
//if cur is a left node
boolean isLeft = parent.getRight()==sibling;
if(sibling.isRed() && !isLeft){//case 1
//cur in right
parent.makeRed();
sibling.makeBlack();
rotateRight(parent);
}else if(sibling.isRed() && isLeft){
//cur in left
parent.makeRed();
sibling.makeBlack();
rotateLeft(parent);
}else if(isBlack(sibling.getLeft()) && isBlack(sibling.getRight())){//case 2
sibling.makeRed();
cur = parent;
isRed = cur.isRed();
parent=parent.getParent();
}else if(isLeft && !isBlack(sibling.getLeft())
&& isBlack(sibling.getRight())){//case 3
sibling.makeRed();
sibling.getLeft().makeBlack();
rotateRight(sibling);
}else if(!isLeft && !isBlack(sibling.getRight())
&& isBlack(sibling.getLeft()) ){
sibling.makeRed();
sibling.getRight().makeBlack();
rotateLeft(sibling);
}else if(isLeft && !isBlack(sibling.getRight())){//case 4
sibling.setRed(parent.isRed());
parent.makeBlack();
sibling.getRight().makeBlack();
rotateLeft(parent);
cur=getRoot();
}else if(!isLeft && !isBlack(sibling.getLeft())){
sibling.setRed(parent.isRed());
parent.makeBlack();
sibling.getLeft().makeBlack();
rotateRight(parent);
cur=getRoot();
}
}
if(isRed){
cur.makeBlack();
}
if(getRoot()!=null){
getRoot().setRed(false);
getRoot().setParent(null);
}
}
//get sibling node
private RBTreeNode<T> getSibling(RBTreeNode<T> node,RBTreeNode<T> parent){
parent = node==null ? parent : node.getParent();
if(node==null){
return parent.getLeft()==null ? parent.getRight() : parent.getLeft();
}
if(node==parent.getLeft()){
return parent.getRight();
}else{
return parent.getLeft();
}
}
private boolean isBlack(RBTreeNode<T> node){
return node==null || node.isBlack();
}
private boolean isRoot(RBTreeNode<T> node){
return root.getLeft() == node && node.getParent()==null;
}
/**
* find the successor node
* @param node current node's right node
* @return
*/
private RBTreeNode<T> removeMin(RBTreeNode<T> node){
//find the min node
RBTreeNode<T> parent = node;
while(node!=null && node.getLeft()!=null){
parent = node;
node = node.getLeft();
}
//remove min node
if(parent==node){
return node;
}
parent.setLeft(node.getRight());
setParent(node.getRight(),parent);
//don't remove right pointer,it is used for fixed color balance
//node.setRight(null);
return node;
}
private T addNode(RBTreeNode<T> node){
node.setLeft(null);
node.setRight(null);
node.setRed(true);
setParent(node,null);
if(root.getLeft()==null){
root.setLeft(node);
//root node is black
node.setRed(false);
size.incrementAndGet();
}else{
RBTreeNode<T> x = findParentNode(node);
int cmp = x.getValue().compareTo(node.getValue());
if(this.overrideMode && cmp==0){
T v = x.getValue();
x.setValue(node.getValue());
return v;
}else if(cmp==0){
//value exists,ignore this node
return x.getValue();
}
setParent(node,x);
if(cmp>0){
x.setLeft(node);
}else{
x.setRight(node);
}
fixInsert(node);
size.incrementAndGet();
}
return null;
}
/**
* find the parent node to hold node x,if parent value equals x.value return parent.
* @param x
* @return
*/
private RBTreeNode<T> findParentNode(RBTreeNode<T> x){
RBTreeNode<T> dataRoot = getRoot();
RBTreeNode<T> child = dataRoot;
while(child!=null){
int cmp = child.getValue().compareTo(x.getValue());
if(cmp==0){
return child;
}
if(cmp>0){
dataRoot = child;
child = child.getLeft();
}else if(cmp<0){
dataRoot = child;
child = child.getRight();
}
}
return dataRoot;
}
/**
* red black tree insert fix.
* @param x
*/
private void fixInsert(RBTreeNode<T> x){
RBTreeNode<T> parent = x.getParent();
while(parent!=null && parent.isRed()){
RBTreeNode<T> uncle = getUncle(x);
if(uncle==null){//need to rotate
RBTreeNode<T> ancestor = parent.getParent();
//ancestor is not null due to before before add,tree color is balance
if(parent == ancestor.getLeft()){
boolean isRight = x == parent.getRight();
if(isRight){
rotateLeft(parent);
}
rotateRight(ancestor);
if(isRight){
x.setRed(false);
parent=null;//end loop
}else{
parent.setRed(false);
}
ancestor.setRed(true);
}else{
boolean isLeft = x == parent.getLeft();
if(isLeft){
rotateRight(parent);
}
rotateLeft(ancestor);
if(isLeft){
x.setRed(false);
parent=null;//end loop
}else{
parent.setRed(false);
}
ancestor.setRed(true);
}
}else{//uncle is red
parent.setRed(false);
uncle.setRed(false);
parent.getParent().setRed(true);
x=parent.getParent();
parent = x.getParent();
}
}
getRoot().makeBlack();
getRoot().setParent(null);
}
/**
* get uncle node
* @param node
* @return
*/
private RBTreeNode<T> getUncle(RBTreeNode<T> node){
RBTreeNode<T> parent = node.getParent();
RBTreeNode<T> ancestor = parent.getParent();
if(ancestor==null){
return null;
}
if(parent == ancestor.getLeft()){
return ancestor.getRight();
}else{
return ancestor.getLeft();
}
}
private void rotateLeft(RBTreeNode<T> node){
RBTreeNode<T> right = node.getRight();
if(right==null){
throw new java.lang.IllegalStateException("right node is null");
}
RBTreeNode<T> parent = node.getParent();
node.setRight(right.getLeft());
setParent(right.getLeft(),node);
right.setLeft(node);
setParent(node,right);
if(parent==null){//node pointer to root
//right raise to root node
root.setLeft(right);
setParent(right,null);
}else{
if(parent.getLeft()==node){
parent.setLeft(right);
}else{
parent.setRight(right);
}
//right.setParent(parent);
setParent(right,parent);
}
}
private void rotateRight(RBTreeNode<T> node){
RBTreeNode<T> left = node.getLeft();
if(left==null){
throw new java.lang.IllegalStateException("left node is null");
}
RBTreeNode<T> parent = node.getParent();
node.setLeft(left.getRight());
setParent(left.getRight(),node);
left.setRight(node);
setParent(node,left);
if(parent==null){
root.setLeft(left);
setParent(left,null);
}else{
if(parent.getLeft()==node){
parent.setLeft(left);
}else{
parent.setRight(left);
}
setParent(left,parent);
}
}
private void setParent(RBTreeNode<T> node,RBTreeNode<T> parent){
if(node!=null){
node.setParent(parent);
if(parent==root){
node.setParent(null);
}
}
}
/**
* debug method,it used print the given node and its children nodes,
* every layer output in one line
* @param root
*/
public void printTree(RBTreeNode<T> root){
java.util.LinkedList<RBTreeNode<T>> queue =new java.util.LinkedList<RBTreeNode<T>>();
java.util.LinkedList<RBTreeNode<T>> queue2 =new java.util.LinkedList<RBTreeNode<T>>();
if(root==null){
return ;
}
queue.add(root);
boolean firstQueue = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty() || !queue2.isEmpty()){
java.util.LinkedList<RBTreeNode<T>> q = firstQueue ? queue : queue2;
RBTreeNode<T> n = q.poll();
if(n!=null){
String pos = n.getParent()==null ? "" : ( n == n.getParent().getLeft()
? " LE" : " RI");
String pstr = n.getParent()==null ? "" : n.getParent().toString();
String cstr = n.isRed()?"R":"B";
cstr = n.getParent()==null ? cstr : cstr+" ";
System.out.print(n+"("+(cstr)+pstr+(pos)+")"+"\t");
if(n.getLeft()!=null){
(firstQueue ? queue2 : queue).add(n.getLeft());
}
if(n.getRight()!=null){
(firstQueue ? queue2 : queue).add(n.getRight());
}
}else{
System.out.println();
firstQueue = !firstQueue;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RBTree<String> bst = new RBTree<String>();
bst.addNode("d");
bst.addNode("d");
bst.addNode("c");
bst.addNode("c");
bst.addNode("b");
bst.addNode("f");
bst.addNode("a");
bst.addNode("e");
bst.addNode("g");
bst.addNode("h");
bst.remove("c");
bst.printTree(bst.getRoot());
}
}
二叉树翻转,深度遍历,广度遍历,求树深度,公共父节点
public class Solution {
private int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
private static List<TreeNode> nodeList = null;
// 初始化树
public void createTree() {
nodeList = new LinkedList();
for(int index = 0; index < array.length; index++) {
nodeList.add(new TreeNode(array[index]));
}
//最后一个父节点在数组中的索引
int lastParentIndex = array.length / 2 - 1;
for(int parentInex = 0; parentInex < lastParentIndex; parentInex++) {
nodeList.get(parentInex).left = nodeList.get(parentInex * 2 + 1);
nodeList.get(parentInex).right = nodeList.get(parentInex * 2 + 2);
}
// 最后一个父节点:因为最后一个父节点可能没有右孩子,所以单独拿出来处理
// 左孩子
nodeList.get(lastParentIndex).left = nodeList.get(lastParentIndex * 2 + 1);
// 右孩子
if(array.length % 2 == 1) {
nodeList.get(lastParentIndex).right = nodeList.get(lastParentIndex * 2 + 2);
}
}
/**
** 二叉树节点
**/
public class TreeNode{
TreeNode left;
TreeNode Right;
int value;
}
//中序
public void printInoderTree(TreeNode root){
//base case
if(root == null){
return;
}
//递归调用printTree
printInoderTree(root.left);
System.out.println(root.val);
printInoderTree(root.right);
}
//中序
public void printPreoderTree(TreeNode root){
//base case
if(root == null){
return;
}
//递归调用printTree
System.out.println(root.val);
printPreoderTree(root.left);
printPreoderTree(root.right);
}
// 铺平二叉树
public TreeNode flatten(TreeNode root){
//base case
if(root == null){
return null;
}
else{
//用递归的思想,把左右先铺平
TreeNode left = flatten(root.left);
TreeNode right = flatten(root.right);
//把左指针和右指针先指向空。
root.left = null;
root.right = null;
//假如左子树生成的链表为空,那么忽略它,把右子树生成的链表指向根节点的右指针
if(left == null){
root.right = right;
return root;
}
//如果左子树生成链表不为空,那么用while循环获取最后一个节点,并且它的右指针要指向右子树生成的链表的头节点
root.right = left;
TreeNode lastLeft = left;
while(lastLeft != null && lastLeft.right != null){
lastLeft = lastLeft.right;
}
lastLeft.right = right;
return root;
}
}
// 链接兄弟节点
public void nextSibiling(TreeNode node){
if(node == null){
return;
}
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(node);
//这个level没有实际用处,但是可以告诉大家怎么判断当前node是第几层。
int level = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
//用这个for循环,可以保证for循环里面对queue不管加多少个子节点,我只处理当前层里面的节点
for(int i = 0;i<size;i++){
//把当前第一个节点拿出来
TreeNode current = queue.poll();
//把子节点加到queue里面
if(current.left != null){
queue.add(current.left);
}
if(current.right != null){
queue.add(current.right);
}
if(i != size -1){
//peek只是获取当前队列中第一个节点,但是并不把它从队列中拿出来
current.next = queue.peek();
}
}
}
level++;
}
}
// 树的深度
public int treeDeep(TreeNode root)
{
if(root == null)
return 0;
TreeNode current = null;
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
int cur,last;
int level = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
cur = 0;//记录本层已经遍历的节点个数
last = queue.size();//当遍历完当前层以后,队列里元素全是下一层的元素,队列的长度是这一层的节点的个数
while(cur < last)//当还没有遍历到本层最后一个节点时循环
{
current = queue.poll();//出队一个元素
cur++;
//把当前节点的左右节点入队(如果存在的话)
if(current.left != null)
{
queue.offer(current.left);
}
if(current.right != null)
{
queue.offer(current.right);
}
}
level++;//每遍历完一层level+1
}
return level;
}
// 公共父节点
public static TreeNode getLastCommonNode(TreeNode pRoot, TreeNode pLeft, TreeNode pRight){
TreeNode treeNode = null;
if(pRoot == null || pLeft.val > pRight.val){
return null;
}
if(pRoot.val >= pRight.val){
treeNode = getLastCommonNode(pRoot.left, pLeft, pRight);
}
if(pRoot.val <= pLeft.val){
treeNode = getLastCommonNode(pRoot.right, pLeft, pRight);
}
if(pRoot.val >= pLeft.val && pRoot.val <= pRight.val){
return pRoot;
}
return treeNode;
}
// 广度遍历
public void levelTraverse(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return;
}
//初始化队列
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
//把根节点加入队列
queue.add(root);
//开始遍历队列
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode current = queue.poll();
System.out.println(current.toString());
//只要当前节点的左右节点不为空,那么我们就可以把其加入到队列的尾部,等待下一次遍历,我们continue这个while循环
if(current.left != null){
queue.add(current.left);
}
if(current.right != null){
queue.add(current.right);
}
}
}
// 深度遍历
public List<List> getPermutation(List<Integer> list){
List result = new ArrayList<>();
permutateHelper(result,new ArrayList<>(), list, new HashSet<Integer>());
return result;
}
private void permutateHelper(List result, List<Integer> temp,List<Integer> list, HashSet<Integer> visited){
//如果temp,temp答案集合满了,我们加入到最终的结果集合内。
if(temp.size() == list.size()){
result.add(new ArrayList(temp));
}
else{
//直接使用for循环进行对原集合的遍历
for(int i = 0; i< list.size();i++){
//如果没有visit过,进行递归
if(!visited.contains(list.get(i))){
int current = list.get(i);
temp.add(current);
visited.add(current);
//进入下一层递归
permutateHelper(result,temp,list,visited);
visited.remove(current);
//这里需要直接remove掉最后一个元素,因为我们的全部的下一层递归已经结束,所以可以把该层的数字删掉,进入for循环的下一个遍历的开始了。这里这个remove的动作就是我们所谓的“回溯”
temp.remove(temp.size()-1);
}
}
}
}
// 反转二叉树
public TreeNode reverseBinaryTree(TreeNode root){
//先处理base case,当root ==null 时,什么都不需要做,返回空指针
if(root == null){
return null;
}
else{
//把左子树翻转
TreeNode left = reverseBinaryTree(root.left);
//把右子树翻转
TreeNode right = reverseBinaryTree(root.right);
//把左右子树分别赋值给root节点,但是是翻转过来的顺序
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
//返回根节点
return root;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
solution.createTree();
solution.levelTraverse(nodeList.get(0));
TreeNode newRoot = solution.invertTree(nodeList.get(0));
solution.levelTraverse(newRoot);
}
}
Heap
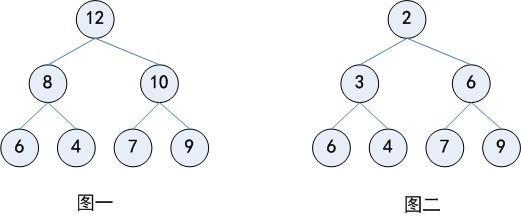
- 堆(也被称为优先队列(队列+排序规则),图一最大堆,图二最小堆)
- 堆是一种特殊的基于树的满足某些特性的数据结构,整个堆中的所有父子节点的键值都会满足相同的排序条件。堆更准确地可以分为最大堆与最小堆,在最大堆中,父节点的键值永远大于或者等于子节点的值,并且整个堆中的最大值存储于根节点;而最小堆中,父节点的键值永远小于或者等于其子节点的键值,并且整个堆中的最小值存储于根节点。
- 时间复杂度:
- 访问最大值 / 最小值: O(1)
- 插入: O(log(n))
- 移除最大值 / 最小值: O(log(n))
public class Heap {
private int[] a; // 数组,从下标 1 开始存储数据
private int n; // 堆可以存储的最大数据个数
private int count; // 堆中已经存储的数据个数
public Heap(int capacity) {
a = new int[capacity + 1];
n = capacity;
count = 0;
}
public void insert(int data) {
if (count >= n) return; // 堆满了
++count;
a[count] = data;
int i = count;
while (i / 2 > 0 && a[i] > a[i / 2]) { // 自下往上堆化
swap(a, i, i / 2); // swap() 函数作用:交换下标为 i 和 i/2 的两个元素
i = i / 2;
}
}
public void removeMax() {
if (count == 0) throw new IllegalStateException("error"); // 堆中没有数据
a[1] = a[count];
--count;
heapify(a, count, 1);
}
private void buildHeap(int[] a, int n) {
for (int i = n/2; i >= 1; --i) {
heapify(a, n, i);
}
}
private void heapify(int[] a, int n, int i) {
while (true) {
int maxPos = i;
if (i*2 <= n && a[i] < a[i*2]) maxPos = i*2;
if (i*2+1 <= n && a[maxPos] < a[i*2+1]) maxPos = i*2+1;
if (maxPos == i) break;
swap(a, i, maxPos);
i = maxPos;
}
}
// n 表示数据的个数,数组 a 中的数据从下标 1 到 n 的位置。
public void sort(int[] a, int n) {
buildHeap(a, n);
int k = n;
while (k > 1) {
swap(a, 1, k);
--k;
heapify(a, k, 1);
}
}
private void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}

Hashing
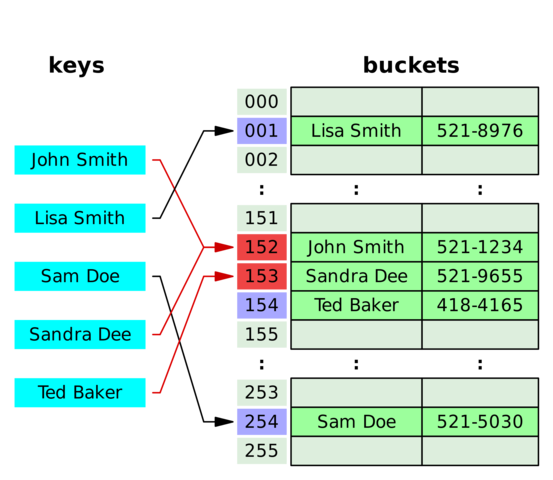
- 哈希能够将任意长度的数据映射到固定长度的数据。哈希函数返回的即是哈希值,如果两个不同的键得到相同的哈希值,即将这种现象称为碰撞。
- Hash Map: Hash Map 是一种能够建立起键与值之间关系的数据结构,Hash Map 能够使用哈希函数将键转化为桶或者槽中的下标,从而优化对于目标值的搜索速度。
- 碰撞解决
- 链地址法(Separate Chaining): 链地址法中,每个桶是相互独立的,包含了一系列索引的列表。搜索操作的时间复杂度即是搜索桶的时间(固定时间)与遍历列表的时间之和。
- 开地址法(Open Addressing): 在开地址法中,当插入新值时,会判断该值对应的哈希桶是否存在,如果存在则根据某种算法依次选择下一个可能的位置,直到找到一个尚未被占用的地址。所谓开地址法也是指某个元素的位置并不永远由其哈希值决定。
Graph
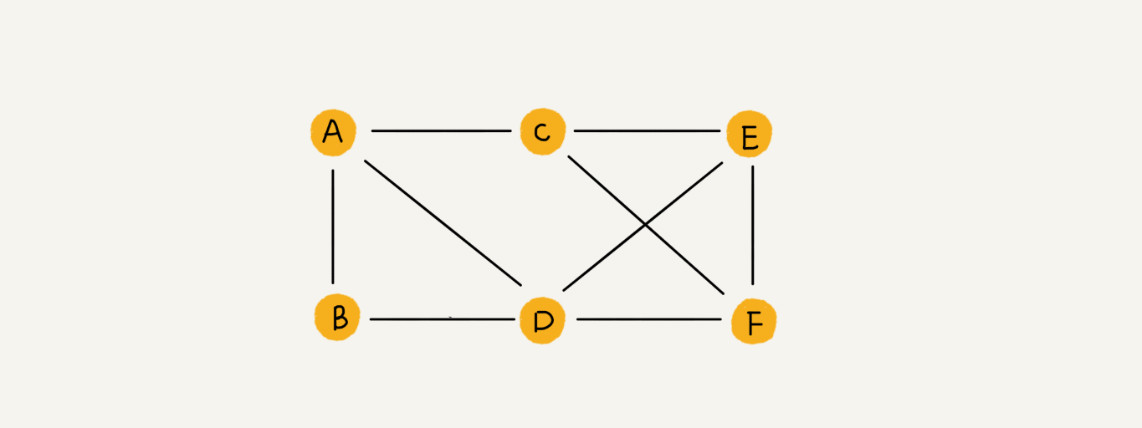
- 图是一种数据元素间为多对多关系的数据结构,加上一组基本操作构成的抽象数据类型。
- 无向图(Undirected Graph): 无向图具有对称的邻接矩阵,因此如果存在某条从节点 u 到节点 v 的边,反之从 v 到 u 的边也存在。
- 有向图(Directed Graph): 有向图的邻接矩阵是非对称的,即如果存在从 u 到 v 的边并不意味着一定存在从 v 到 u 的边。
算法
排序
快速排序
- 稳定: 否
- 时间复杂度:
- 最优时间: O(nlog(n))
- 最坏时间: O(n^2)
- 平均时间: O(nlog(n))
归并排序
- 归并排序是典型的分治算法,它不断地将某个数组分为两个部分,分别对左子数组与右子数组进行排序,然后将两个数组合并为新的有序数组。
- 稳定: 是
- 时间复杂度:
- 最优时间: O(nlog(n))
- 最坏时间: O(nlog(n))
- 平均时间: O(nlog(n))
桶排序
- 桶排序将数组分到有限数量的桶子里。每个桶子再个别排序(有可能再使用别的排序算法或是以递归方式继续使用桶排序进行排序)。
- 时间复杂度:
- 最优时间: Ω(n + k)
- 最坏时间: O(n^2)
- 平均时间:Θ(n + k)
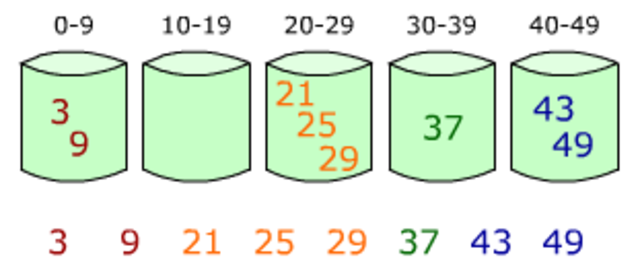
基数排序
- 基数排序类似于桶排序,将数组分割到有限数目的桶中;不过其在分割之后并没有让每个桶单独地进行排序,而是直接进行了合并操作。
- 时间复杂度:
- 最优时间: Ω(nk)
- 最坏时间: O(nk)
- 平均时间: Θ(nk)
堆排序
图算法
深度优先搜索
深度优先算法是一种优先遍历子节点而不是回溯的算法。 时间复杂度: O(|V| + |E|)
广度优先搜索
广度优先搜索是优先遍历邻居节点而不是子节点的图遍历算法。 时间复杂度: O(|V| + |E|)
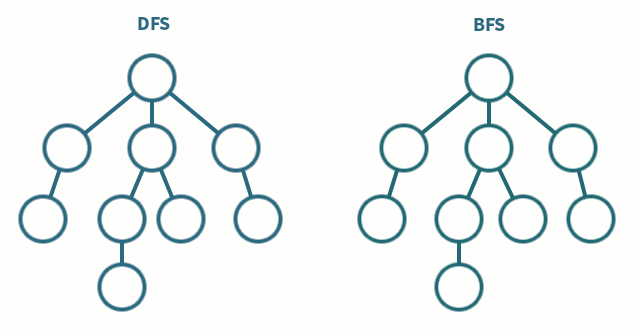
拓扑排序
拓扑排序是对于有向图节点的线性排序,如果存在某条从 u 到 v 的边,则认为 u 的下标先于 v。 时间复杂度: O(|V| + |E|)
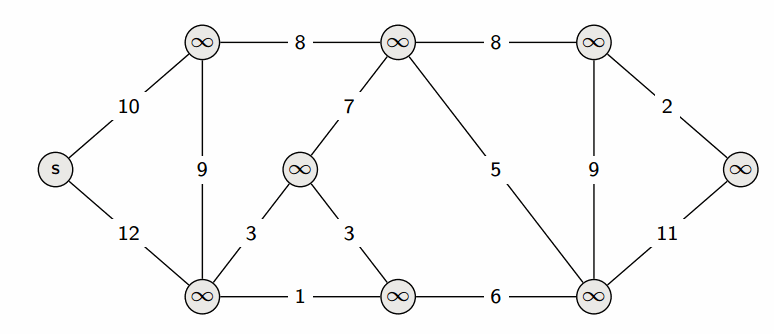
Dijkstra 算法
Dijkstra 算法 用于计算有向图中单源最短路径问题。 时间复杂度: O(|V|^2)
Bellman-Ford 算法
- Bellman-Ford 算法是在带权图中计算从单一源点出发到其他节点的最短路径的算法。
- 尽管算法复杂度大于 Dijkstra 算法,但是它适用于包含了负值边的图。
- 时间复杂度:
- 最优时间: O(|E|)
- 最坏时间: O(|V||E|)
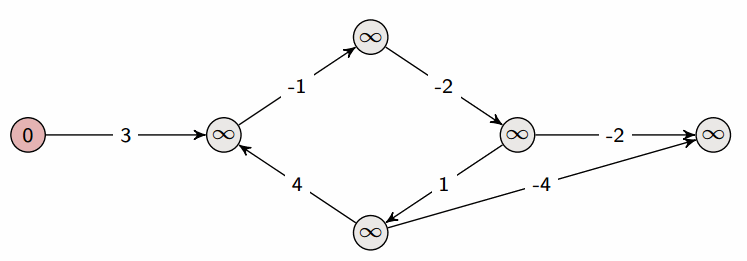
Floyd-Warshall 算法
- Floyd-Warshall 算法 能够用于在无环带权图中寻找任意节点的最短路径。
- 时间复杂度:
- 最优时间: O(|V|^3)
- 最坏时间: O(|V|^3)
- 平均时间: O(|V|^3)
Prim 算法
- Prim 算法是用于在带权无向图中计算最小生成树的贪婪算法。换言之,Prim 算法能够在图中抽取出连接所有节点的边的最小代价子集。
- 时间复杂度: O(|V|^2)
Kruskal 算法
- Kruskal 算法同样是计算图的最小生成树的算法,与 Prim 的区别在于并不需要图是连通的。
- 时间复杂度: O(|E|log|V|)
位运算
- 位运算即是在位级别进行操作的技术,合适的位运算能够帮助我们得到更快地运算速度与更小的内存使用。
- 测试第 k 位: s & (1 << k)
- 设置第 k 位: s |= (1 << k)
- 第 k 位置零: s &= ~(1 << k)
- 切换第 k 位值: s ^= ~(1 << k)
- 乘以 2n: s << n
- 除以 2n: s >> n
- 交集: s & t
- 并集: s | t
- 减法: s & ~t
- 交换 x = x ^ y ^ (y = x)
- 取出最小非 0 位(Extract lowest set bit): s & (-s)
- 取出最小 0 位(Extract lowest unset bit): ~s & (s + 1)
- 交换值: x ^= y; y ^= x; x ^= y;
贪心、动态规划、分治算法
爬楼梯、最大子序。
二叉树的最大路径和:深度搜索和动态规划。
字典树
字典树是一种可以方便人们通过前缀查找单词的一种数据结构,它把具有相同前缀的单词合并到一起,节省了存储空间(和直接用HashMap存相比),同时也可以做前缀查找或者自动补全。
假设我们要收录一下几个单词Tea, Ted, Ten,Inn。那么我们会以以下的方式把这些单词逐一录入树种:
创建初始节点Root, 当前插入节点为根节点
先准备录入Tea,分解Tea的字母T, E, A,先把第一个字母T放入根节点下面。并且把当前插入节点改为T
在T也就是当前插入节点下面放入E,当前插入节点改为E
在E也就是当前插入节点下面放入A,当前插入节点改为A,但是单词所有字母都输入结束了,因此在A上面打个tag,标记该节点是某个单词的结束字母。
自动补全
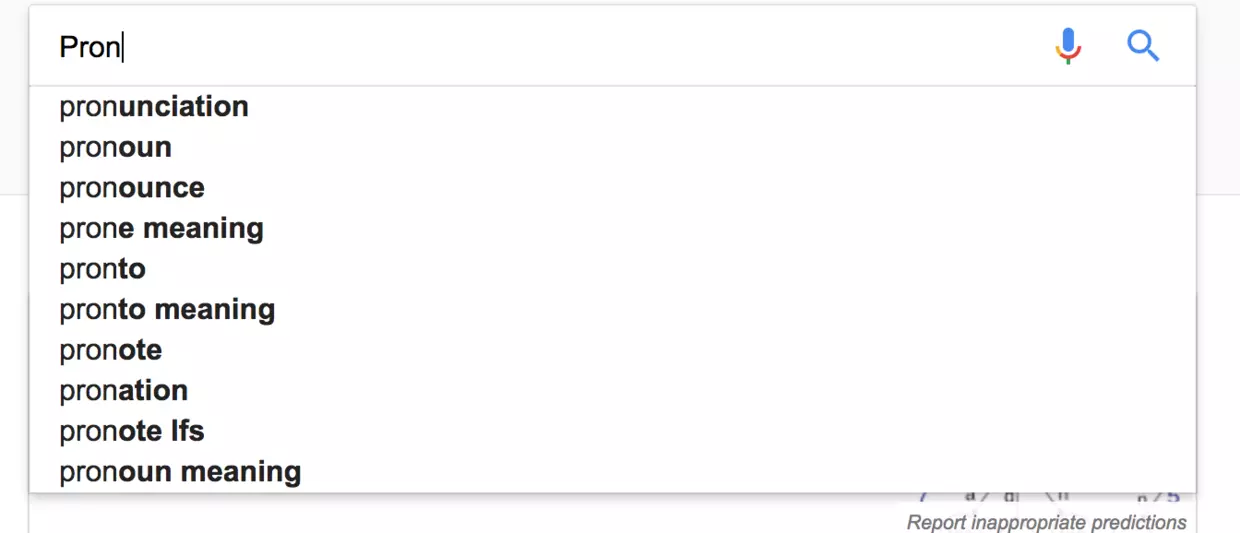
谷歌将很多热门的搜索单词用字典树的方式存储在后端,当Web网页搜索单词的前缀的时候,后端查找到该前缀最后一个节点的位置,将下面的子节点全部排列出来返回给前端。 比如用以上的例子,当用户搜索TE的时候,定位到最后一个节点E,将E节点下面的节点返回并且拼凑出一个完整的字符串,TED和TEA。
实现
public class Tire {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("你好");
trie.insert("你不好");
trie.insert("你不坏");
trie.insert("你不好吗");
// boolean result = trie.search("你不好吗");
// System.out.println(result);
// result = trie.startsWith("你不好吗");
// System.out.println(result);
List<String> results = trie.getAutoCompletionStrings("你不");
for (String s : results) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
/**
* 实现字典树,诀窍就是用什么数据结构保存children,个人偏向用hashmap,因为用数组写起来也麻烦而且会浪费多余的空间。
* 26个字符不一定全都用得到。
*/
class TrieNode {
char c;
Map<Character, TrieNode> children = new HashMap<>();
boolean hasWord;
public TrieNode() {
}
public TrieNode(char c) {
this.c = c;
}
}
class Trie {
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
//curChildren 对应我们讲的当前插入节点,所有要插入的节点都要放在当前插入节点的子节点里面
Map<Character, TrieNode> curChildren = root.children;
char[] wordArray = word.toCharArray();
//循环遍历这次要插入的单词,从第一个字母开始
for (int i = 0; i < wordArray.length; i++) {
char wc = wordArray[i];
//如果当前插入节点有这个字符对应的子节点的话,直接把该子节点变成当前插入节点
if (curChildren.containsKey(wc)) {
cur = curChildren.get(wc);
} else {//如果没有的话,创建一个
TrieNode newNode = new TrieNode(wc);
curChildren.put(wc, newNode);
cur = newNode;
}
curChildren = cur.children;
//如果该节点是插入单词的最后一个字符,打一个tag,表面这是一个单词的结尾
if (i == wordArray.length - 1) {
cur.hasWord = true;
}
}
}
//有时候虽然该单词作为前缀,存在于字典树中,但是却没有这个单词。比如我搜索
//TE。这个前缀存在,但是并没有这个单词,E字母对应的节点没有tag
public boolean search(String word) {
if (searchWordNodePos(word) == null) {
return false;
} else if (searchWordNodePos(word).hasWord)
return true;
else {
return false;
}
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
if (searchWordNodePos(prefix) == null) {
return false;
} else
return true;
}
//搜索制定单词在字典树中的最后一个字符对应的节点。这个方法是搜索的关键
private TrieNode searchWordNodePos(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
char[] sArray = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < sArray.length; i++) {
char c = sArray[i];
if (cur.children.containsKey(c)) {
cur = cur.children.get(c);
} else {
return null;
}
}
return cur;
}
public List<String> getAutoCompletionStrings(String preflix) {
TrieNode lastNode = searchWordNodePos(preflix);
if (lastNode == null) {
return new ArrayList<>();
} else {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
trieHelper(list, "", lastNode);
return list;
}
}
//其实返回字符串就是暴力搜索的一个过程,把最后一个节点一下的所有子节点组合起来。
private void trieHelper(List<String> result, String current, TrieNode node) {
if (node != null && node.hasWord) {
result.add(current);
if (node.children.size() != 0) {
Set<Map.Entry<Character, TrieNode>> set = node.children.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Character, TrieNode> entry : set) {
trieHelper(result, current + entry.getValue().c, entry.getValue());
}
}
} else if (node != null) {
Set<Map.Entry<Character, TrieNode>> set = node.children.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Character, TrieNode> entry : set) {
trieHelper(result, current + entry.getValue().c, entry.getValue());
}
}
return;
}
}
PriorityQueue
会议室问题
会议室问题可以说是排序/优先级队列应用的最具代表性的题目之一了。问题很简单,就是在给定一组会议的数据之后,判断某一个人能否完整的参加完所有会议,或者换个角度,会议安排者最少需要安排多少会议室,才能让所有会议都照常举办(没有会议室冲突)。
public class Interval {
/**
会议开始时间
**/
int start;
/**
会议结束时间
**/
int end;
Interval() {
start = 0;
end = 0;
}
Interval(int s, int e) {
start = s;
end = e;
}
}
在给定一个List of Interval的情况下,判断一个人能不能完整的参于所有list里面的会议。比如:

两个箭头线段代表一个会议的跨越时长,在上图里面,两个会议直接没有重叠,正如图中的红线所示,就算红线一直平行的从左往右移动,也不会横截超过一个会议的箭头线段。所以在上图的情况,一个人是可以参与所有会议的。
但是下图所示:

这些情况下,一个人就不能参与所有的会议了,很明显红线可以同时穿过两个会议的箭头线段。
能不能把每次某个会议开始或者结束当成一个事件Event,每种事件Event可以分两种类型,一种是开始start,一种是结束end,我们只需要对当前所有的全部事件进行排序之后分析,而不需要对时间本身进行循环。
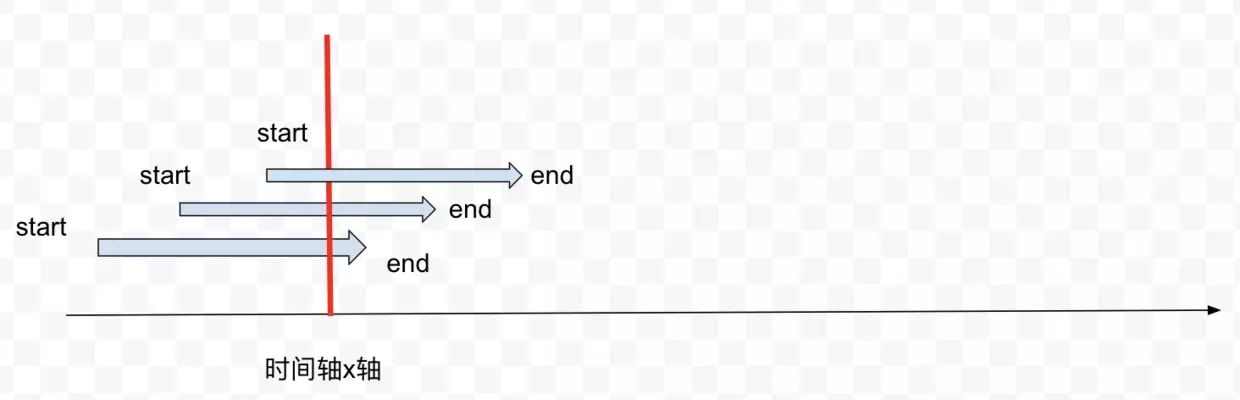
按照时间线来排序的话,我们会先后有三个会议,这三个会议的起始start以此排列,从此图的示例我们可以轻松的看出,同时会有三个会议进行。但是理由呢?理由是因为你看到了线段的重叠么?真正的理由是当三个start事件进入之后,我们的第一个end事件才进入。 所以,再对所有事件排序好之后,每当我们有一个start事件,会议室数量就需要+1,每当我们有一个end事件的时候,会议室数量就-1.因为end代表一个会议结束,因此所需要的会议室数量可以减少。
先定义一个事件:
public class TimeEvent {
/**start类型
**/
public static final int start = 0;
/**end类型
**/
public static final int end = 1;
/**该事件发生的时间
**/
public int time;
/**该事件的类型,是开始还是结束
**/
public int type;
public TimeEvent(int type, int time) {
this.type = type;
this.time = time;
}
}
public boolean canAttendMeetings(Interval[] intervals) {
if (intervals.length == 0) {
return true;
} else {
/**
**定义一个优先级队列,事件按照时间从小到大排列
**/
PriorityQueue<TimeEvent> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<TimeEvent>() {
@Override
public int compare(TimeEvent o1, TimeEvent o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (o1.time == o2.time) {
/**
**这里两个if暂时可能很难理解,我在下面会解释
**/
if (o1.type == TimeEvent.start && o2.type == TimeEvent.end) {
return 1;
}
if (o2.type == TimeEvent.start && o1.type == TimeEvent.end) {
return -1;
}
}
return o1.time - o2.time;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
/**
**把事件的起始和结束事件创建出来并且放入优先级队列
**/
priorityQueue.add(new TimeEvent(TimeEvent.start, intervals[i].start));
priorityQueue.add(new TimeEvent(TimeEvent.end, intervals[i].end));
}
int max = 0;
int current = 0;
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
TimeEvent event = priorityQueue.poll();
if (event.type == TimeEvent.start) {
/**如果是开始事件,会议室数量+1,只要会议室数量大于等于2,返回false**/
current = current + 1;
if (current >= 2) {
return false;
}
} else {
/**如果是开始事件,会议室数量-1.代表到这个时间为止,一个会议结束了。虽然我们
**并不在乎是哪一个会议结束了。
**/
current = current - 1;
}
}
return true;
}
}
if (o1.type == TimeEvent.start && o2.type == TimeEvent.end) {
return 1;
}
if (o2.type == TimeEvent.start && o1.type == TimeEvent.end) {
return -1;
}
其实是处理这样的一种边界情况:

当后一个事件的start和前一个事件的end是同一时间的时候,这种情况算是需要两个会议室还是一个?
假如题目要求这种情况只需要一个会议室,那么,假如两个TimeEvent,分别是start与end,time也相同,我们必须优先处理end,因为先处理end,我们的会议室数量就会先做-1.
按照图中的例子会议室数量会:1,0,1,0这样的变化。
假如题目要求这种情况只需要两个个会议室,那么,假如两个TimeEvent,分别是start与end,time也相同,我们必须优先处理start,因为先处理start,我们的会议室数量就会先做+1.
按照图中的例子会议室数量会:1,2,1,0这样的变化。
合并线段的问题
假设给定一组线段,要求把重叠在一起的线段整合成新的线段返回,比如:
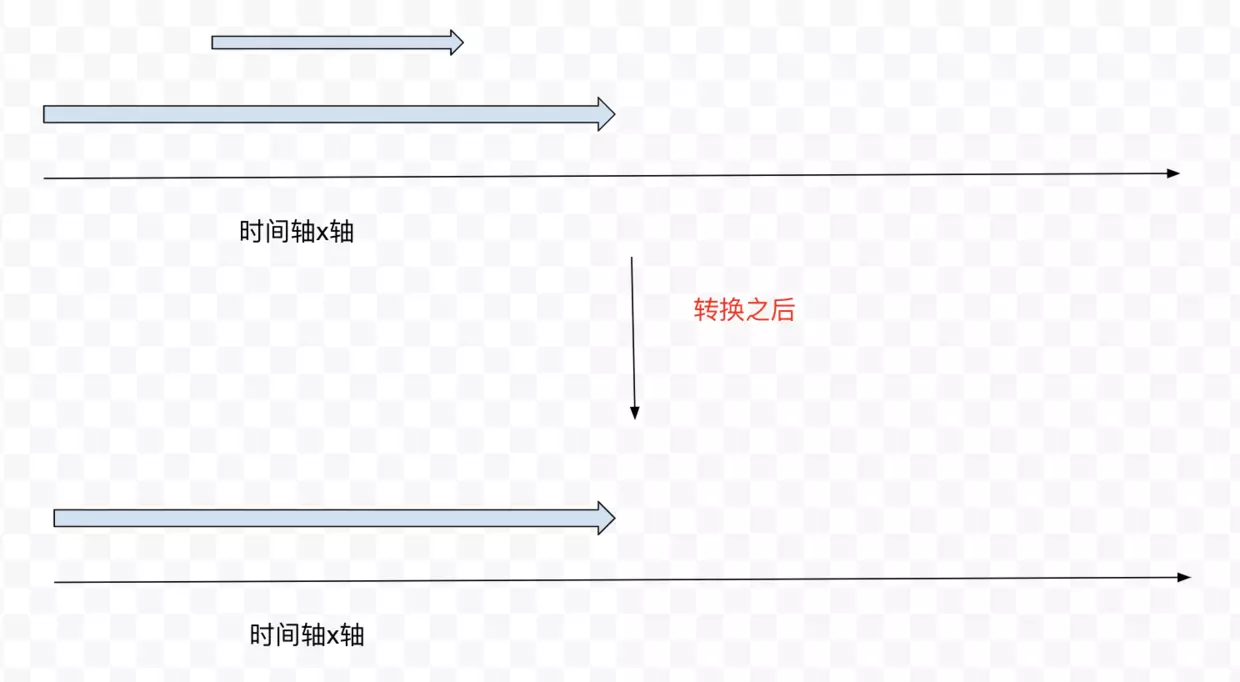


这里的解题思路和上面一样,先把每个线段安装开始时间排序,不同的是,每次在处理当前线段的时候,需要和上一个线段做对比,看看有没有重叠,如果重叠了,则需要删除上一个线段并且生成新的线段。
这里,一个栈Stack可以完美的处理!
步骤如下,
1.线段在优先级队列里面排好序
2.每次提取队列第一个线段
3.与stack中的栈顶线段作对比,
4.如果有重叠,pop栈顶线段,生成新的线段放入栈顶,重复第一步
我们每次只需要处理栈顶线段的原因是,如果栈顶线段和栈顶线段之前的栈内线段有冲突的话,我们在之前的一步已经处理好了,所以当前队列的第一个线段,是绝对不可能和非栈顶线段有重叠的。
public List<Interval> insert(List<Interval> intervals, Interval newInterval) {
/**
**用优先级队列把所有线段排好序,按照起始时间
**/
PriorityQueue<Interval> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<Interval>(new Comparator<Interval>() {
public int compare(Interval o1, Interval o2) {
return o1.start - o2.start;
};
});
for (int i = 0; i < intervals.size(); i++) {
priorityQueue.add(intervals.get(i));
}
priorityQueue.add(newInterval);
/**
**用栈保存处理过的线段
**/
Stack<Interval> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(priorityQueue.remove());
/**
**while循环处理线段
**/
while (!stack.isEmpty() && !priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
Interval inItem = priorityQueue.remove();
Interval originalItem = stack.pop();
/**
**当线段不完全重叠的时候,取两者的最小开始时间和最大结束时间,生成新的线段
**/
if (inItem.start <= originalItem.end && inItem.end > originalItem.end) {
stack.push(new Interval(originalItem.start, inItem.end));
/**
**当线段完全重叠的时候,取两者的中覆盖面最大的那一线段
**/
} else if (inItem.start <= originalItem.end && originalItem.end >= inItem.end) {
stack.push(originalItem);
}
/**
**当线段没有重叠的时候,两者一起入栈
**/
else {
stack.push(originalItem);
stack.push(inItem);
}
}
/**
**因为stack的输出是倒着来的,所以翻转一次。。。
**/
Stack<Interval> stack2 = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack.pop());
}
ArrayList<Interval> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
while (!stack2.isEmpty()) {
arrayList.add(stack2.pop());
}
return arrayList;
}