使用Autolayout的一些Tips,需要的时候可以参考一下。
在xib中对UIScrollView使用autolayout
UIScrollView的contentSize要设置好,否则有警告,可能引发一些异常情况。
注意:UIScrollView在scroll的时候会重新布局界面,会导致代码添加的frame无效,又重新回到autolayout的布局(xib或者代码)。
将UIView的aspect拉出来一个outlet
对这个约束的outlet,改变其contant是无效,而multiplier是只读的。 因此将UIView的aspect拉出来一个outlet其实是没有什么作用的,只能读取其值用做其他用途。
通过UIView的transform来做动画
UIView的transform属性实际上是一个CGAffineTransform类型。
CGPoint * CGAffineTransform = Transformed CGPoint
Markdown格式的公式居然识别不了。
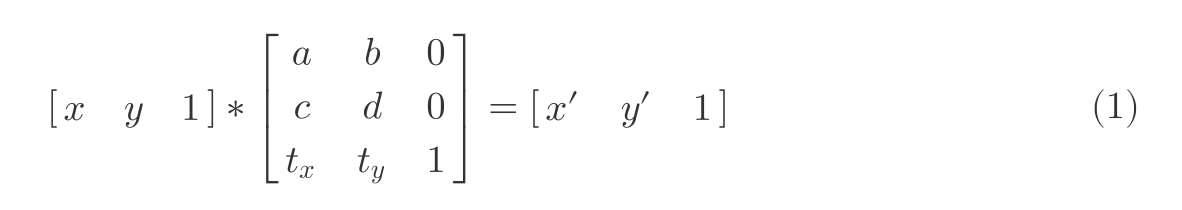
仿射的意思是相对立的侧边始终保持平行。
使用transform来实现动画效果:
[UIView animateWithDuration:0.3 animations:^{
self.captureView.transform = CGAffineTransformMakeScale(0.5f, 0.5f);
});
frame其实是虚拟的一个属性
frame = center + bounds + transform
对UIView做了transform,实际上center和bounds不会变,仅仅多了一个transform。
所以,通过UIView的transform来实现frame的改变,在界面重新布局之后会无效。
通过NSLayoutConstraint的contant变化来做动画
需要执行layoutIfNeeded方法, 必不可少 。
- (void)viewFilteredAnimation {
[UIView animateWithDuration:2.0 animations:^{
_widthViewFiltered.constant = MTScreenWidth;
[self.view layoutIfNeeded];
} completion:^(BOOL finished) {
_lbTitle.hidden = NO;
}];
}
xib中autolayout的生效时机
在viewDidLoad和viewWillAppear中,不会生效。 因为window是在ViewDidAppear之后才有的,那时autolayout才生效。 但在viewDidAppear之前,依然有机会通过代码调整layout:viewDidLayoutSubviews会调用多次来调整。
initWithNibName:bundle: 非storyboard初始化(包含xib和代码)
initWithCoder: 使用storyboard初始化
awakeFromNib 使用xib加载完成
loadView 加载视图的操作,在viewDidLoad之前执行。View在此加载或创建,赋值给UIViewController的view属性。
一些方法的调用顺序:
+load
+initialize
-init
-loadView
-isViewLoaded多次
-viewDidLoad
-isViewLoaded多次
-viewWillAppear:
-isViewLoaded多次
-viewWillLayoutSubviews
-viewDidLayoutSubviews
-isViewLoaded多次
-viewDidAppear:
使用NSLayoutConstraint添加约束
NSLayoutConstraint
前提是两个View要有关系,归属于一个父View,或者直接是父子View的关系。尽量不要越级。
所以先addSubview,再添加约束。 translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints属性要设置为NO。
[self.previewContainer addSubview:_videoMaskViewWhenTakingPhoto];
_videoMaskViewWhenTakingPhoto.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;
NSLayoutConstraint *top = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:_videoMaskViewWhenTakingPhoto
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeTop
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:self.previewContainer
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeTop
multiplier:1
constant:0];
NSLayoutConstraint *bottom = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:_videoMaskViewWhenTakingPhoto
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeBottom
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:self.previewContainer
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeBottom
multiplier:1
constant:0];
NSLayoutConstraint *leading = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:_videoMaskViewWhenTakingPhoto
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeLeading
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:self.previewContainer
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeLeading
multiplier:1
constant:0];
NSLayoutConstraint *trailing = [NSLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:_videoMaskViewWhenTakingPhoto
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeTrailing
relatedBy:NSLayoutRelationEqual
toItem:self.previewContainer
attribute:NSLayoutAttributeTrailing
multiplier:1
constant:0];
[NSLayoutConstraint activateConstraints:@[top, bottom, leading, trailing]];
使NSLayoutConstraint生效
addConstraint:和addConstraints:等已经弃用,在iOS 11.2中遇到过layout不生效的情况。 使用activateConstraints:即可。
[NSLayoutConstraint activateConstraints:@[top, bottom, leading, trailing]];
使用VFL
总之,VFL这套布局的语法也很晦涩(其实是不会,也懒得去学了)。。。
调试Autolayout的异常
可以通过添加全局的symbolic断点来调试Autolayout的异常
-
添加UIViewAlertForUnsatisfiableConstraints的Symbol断点
-
添加对应的action
对于OC:
po [[UIWindow keyWindow] _autolayoutTrace]
对于Swift:
expr -l objc++ -O -- [[UIWindow keyWindow] _autolayoutTrace]
如图:
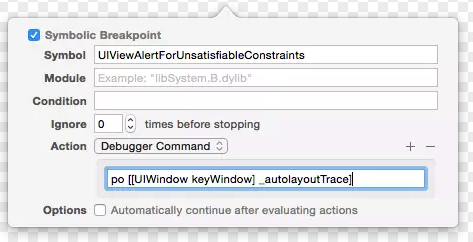
这样,遇到autolayout的异常问题,就会停在断点,然后通过LLDB进行调试了。
界面刷新的一些方法
- setNeedsDisplay 需要更新页面,但不会立刻更新
- layoutIfNeeded 立刻更新页面
- layoutSubviews 重写布局
- setNeedsUpdateConstraints 需更新约束,但不立刻开始
- updateConstraintsIfNeeded 立刻更新约束
- updateConstraints 更新约束
Masonry源码
使用方法
[aView addSubview:bView];
[bView mas_makeConstraints:^ (MASConstraintMaker *maker) {
maker.top.equalTo(aView);
maker.leading.equalTo(aView);
maker.width.equalTo(aView);
maker.height.equalTo(aView);
}];
构建一个 MASConstraintMaker 对象,传入mas_makeConstraints的block中,构建约束规则。
约束规则
先看每一条约束语句:
在 MASConstraintMaker.m 中,可以看到 maker.top.equalTo(aView); 语句最终会调用到 **- (MASConstraint )constraint:(MASConstraint )constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute 方法,在其中构建一个 MASViewConstraint 对象,添加到 MASConstraintMaker 对象的 constraints 属性(NSMutableArray)中,
- (MASConstraint *)addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
return [self constraint:nil addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
}
- (MASConstraint *)top {
return [self addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:NSLayoutAttributeTop];
}
- (MASConstraint *)constraint:(MASConstraint *)constraint addConstraintWithLayoutAttribute:(NSLayoutAttribute)layoutAttribute {
MASViewAttribute *viewAttribute = [[MASViewAttribute alloc] initWithView:self.view layoutAttribute:layoutAttribute];
MASViewConstraint *newConstraint = [[MASViewConstraint alloc] initWithFirstViewAttribute:viewAttribute];
if ([constraint isKindOfClass:MASViewConstraint.class]) {
//replace with composite constraint
NSArray *children = @[constraint, newConstraint];
MASCompositeConstraint *compositeConstraint = [[MASCompositeConstraint alloc] initWithChildren:children];
compositeConstraint.delegate = self;
[self constraint:constraint shouldBeReplacedWithConstraint:compositeConstraint];
return compositeConstraint;
}
if (!constraint) {
newConstraint.delegate = self;
[self.constraints addObject:newConstraint];
}
return newConstraint;
}
总结一句话,执行了 mas_makeConstraints: 方法后,会构建一个 MASConstraintMaker 对象,然后分别根据4个约束语句构建4个 MASViewConstraint 对象,将其添加到 MASConstraintMaker 对象的 constraints 属性中。这样,所有的约束规则即交给 MASConstraintMaker 对象来管理了。
约束生效
接下来,看Masonry如何使这些约束规则生效的:
在 UIView+MASAdditions.m 中,关键在于调用 MASConstraintMaker 对象的 install 方法。
- (NSArray *)mas_makeConstraints:(void(^)(MASConstraintMaker *))block {
self.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = NO;
MASConstraintMaker *constraintMaker = [[MASConstraintMaker alloc] initWithView:self];
block(constraintMaker);
return [constraintMaker install];
}
再看 MASConstraintMaker.m 中:
- (NSArray *)install {
if (self.removeExisting) {
NSArray *installedConstraints = [MASViewConstraint installedConstraintsForView:self.view];
for (MASConstraint *constraint in installedConstraints) {
[constraint uninstall];
}
}
NSArray *constraints = self.constraints.copy;
for (MASConstraint *constraint in constraints) {
constraint.updateExisting = self.updateExisting;
[constraint install];
}
[self.constraints removeAllObjects];
return constraints;
}
取出 constraints 数组中的每一个 MASViewConstraint 对象,执行其 install 方法,该方法的完整代码如下:
- (void)install {
if (self.hasBeenInstalled) {
return;
}
if ([self supportsActiveProperty] && self.layoutConstraint) {
self.layoutConstraint.active = YES;
[self.firstViewAttribute.view.mas_installedConstraints addObject:self];
return;
}
MAS_VIEW *firstLayoutItem = self.firstViewAttribute.item;
NSLayoutAttribute firstLayoutAttribute = self.firstViewAttribute.layoutAttribute;
MAS_VIEW *secondLayoutItem = self.secondViewAttribute.item;
NSLayoutAttribute secondLayoutAttribute = self.secondViewAttribute.layoutAttribute;
// alignment attributes must have a secondViewAttribute
// therefore we assume that is refering to superview
// eg make.left.equalTo(@10)
if (!self.firstViewAttribute.isSizeAttribute && !self.secondViewAttribute) {
secondLayoutItem = self.firstViewAttribute.view.superview;
secondLayoutAttribute = firstLayoutAttribute;
}
MASLayoutConstraint *layoutConstraint
= [MASLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:firstLayoutItem
attribute:firstLayoutAttribute
relatedBy:self.layoutRelation
toItem:secondLayoutItem
attribute:secondLayoutAttribute
multiplier:self.layoutMultiplier
constant:self.layoutConstant];
layoutConstraint.priority = self.layoutPriority;
layoutConstraint.mas_key = self.mas_key;
if (self.secondViewAttribute.view) {
MAS_VIEW *closestCommonSuperview = [self.firstViewAttribute.view mas_closestCommonSuperview:self.secondViewAttribute.view];
NSAssert(closestCommonSuperview,
@"couldn't find a common superview for %@ and %@",
self.firstViewAttribute.view, self.secondViewAttribute.view);
self.installedView = closestCommonSuperview;
} else if (self.firstViewAttribute.isSizeAttribute) {
self.installedView = self.firstViewAttribute.view;
} else {
self.installedView = self.firstViewAttribute.view.superview;
}
MASLayoutConstraint *existingConstraint = nil;
if (self.updateExisting) {
existingConstraint = [self layoutConstraintSimilarTo:layoutConstraint];
}
if (existingConstraint) {
// just update the constant
existingConstraint.constant = layoutConstraint.constant;
self.layoutConstraint = existingConstraint;
} else {
[self.installedView addConstraint:layoutConstraint];
self.layoutConstraint = layoutConstraint;
[firstLayoutItem.mas_installedConstraints addObject:self];
}
}
看其中最关心的布局相关代码:
MASLayoutConstraint *layoutConstraint
= [MASLayoutConstraint constraintWithItem:firstLayoutItem
attribute:firstLayoutAttribute
relatedBy:self.layoutRelation
toItem:secondLayoutItem
attribute:secondLayoutAttribute
multiplier:self.layoutMultiplier
constant:self.layoutConstant];
layoutConstraint.priority = self.layoutPriority;
layoutConstraint.mas_key = self.mas_key;
...
if (existingConstraint) {
// just update the constant
existingConstraint.constant = layoutConstraint.constant;
self.layoutConstraint = existingConstraint;
} else {
[self.installedView addConstraint:layoutConstraint];
self.layoutConstraint = layoutConstraint;
[firstLayoutItem.mas_installedConstraints addObject:self];
}
MASLayoutConstraint 是 NSLayoutConstraint 的子类。 可以看到,对于已有的约束,会直接对其 constant 赋值进行更新;对于新的约束,会调用 addConstraint: 方法来添加约束。
至此,我们已经看到了Masonry的布局代码是如何生效的,最终也是调用 NSLayoutConstraint 的相关方法。
SnapKit源码
使用SnapKit来更新约束,要添加updateConstraints 而使用remake,则会先移除掉已添加的snp约束。
使用方法
self.view.addSubview(box)
box.backgroundColor = UIColor.red
box.snp.makeConstraints { (make) -> Void in
make.top.equalTo(self.view).offset(100)
make.leading.equalTo(self.view).offset(100)
make.width.height.equalTo(50)
}
box.snp.makeConstraints { xxx } 是Swift特色的代码样式,理解这句就要先看下边几处关键代码。
// ConstraintView.swift
public typealias ConstraintView = UIView
// ConstraintView+Extensions.swift
public extension ConstraintView {
public var snp: ConstraintViewDSL {
return ConstraintViewDSL(view: self)
}
}
// ConstraintDSL.swift
public protocol ConstraintDSL {
var target: AnyObject? { get }
func setLabel(_ value: String?)
func label() -> String?
}
public protocol ConstraintBasicAttributesDSL : ConstraintDSL {
}
public protocol ConstraintAttributesDSL : ConstraintBasicAttributesDSL {
}
// ConstraintViewDSL.swift
public struct ConstraintViewDSL: ConstraintAttributesDSL {
...
public func makeConstraints(_ closure: (_ make: ConstraintMaker) -> Void) {
ConstraintMaker.makeConstraints(item: self.view, closure: closure)
}
...
}
约束规则
以 make.top.equalTo(self.view).offset(100) 为例,
// ConstraintMaker.swift
public class ConstraintMaker {
public var top: ConstraintMakerExtendable {
return self.makeExtendableWithAttributes(.top)
}
......
internal func makeExtendableWithAttributes(_ attributes: ConstraintAttributes) -> ConstraintMakerExtendable {
let description = ConstraintDescription(item: self.item, attributes: attributes)
self.descriptions.append(description)
return ConstraintMakerExtendable(description)
}
}
SnapKit在这里,引入了 ConstraintDescription 用于描述每一条约束规则,将其添加到 ConstraintMaker 对象的 descriptions 属性(ConstraintDescription数组)中。 因此,这一系列的约束规则,实际上会对应构建一个个ConstraintDescription对象,存于ConstraintMaker中。
然后,从ConstraintMaker的descriptions对象中,解析得出每一条实际的Constraint对象。
// ConstraintMaker.swift
public class ConstraintMaker {
...
internal static func makeConstraints(item: LayoutConstraintItem, closure: (_ make: ConstraintMaker) -> Void) {
let maker = ConstraintMaker(item: item)
closure(maker)
var constraints: [Constraint] = []
for description in maker.descriptions {
guard let constraint = description.constraint else {
continue
}
constraints.append(constraint)
}
for constraint in constraints {
constraint.activateIfNeeded(updatingExisting: false)
}
}
...
}
所以,
box.snp.makeConstraints { (make) -> Void in
make.top.equalTo(self.view).offset(100)
make.leading.equalTo(self.view).offset(100)
make.width.height.equalTo(50)
}
这段代码的目的也是类似:构建一个 ConstraintMaker 对象,传入 box.snp.makeConstraints 的闭包中,解析并构建每一条约束规则。 最后,调用activateIfNeeded方法来应用这些约束规则。
约束生效
与Masonry类似,我们来看看关键的布局代码。
在 Constraint.swift 中:
internal func activateIfNeeded(updatingExisting: Bool = false) {
guard let item = self.from.layoutConstraintItem else {
print("WARNING: SnapKit failed to get from item from constraint. Activate will be a no-op.")
return
}
let layoutConstraints = self.layoutConstraints
if updatingExisting {
var existingLayoutConstraints: [LayoutConstraint] = []
for constraint in item.constraints {
existingLayoutConstraints += constraint.layoutConstraints
}
for layoutConstraint in layoutConstraints {
let existingLayoutConstraint = existingLayoutConstraints.first { $0 == layoutConstraint }
guard let updateLayoutConstraint = existingLayoutConstraint else {
fatalError("Updated constraint could not find existing matching constraint to update: \(layoutConstraint)")
}
let updateLayoutAttribute = (updateLayoutConstraint.secondAttribute == .notAnAttribute) ? updateLayoutConstraint.firstAttribute : updateLayoutConstraint.secondAttribute
updateLayoutConstraint.constant = self.constant.constraintConstantTargetValueFor(layoutAttribute: updateLayoutAttribute)
}
} else {
NSLayoutConstraint.activate(layoutConstraints)
item.add(constraints: [self])
}
}
这一段代码的逻辑几乎与Masonry的一样了。
可以看到,对于已有的约束,会直接对其 constant 赋值进行更新;对于新的约束,会调用 NSLayoutConstraint.activate(layoutConstraints) 方法来添加约束。
FlexBox
Autolayout实际上是通过解方程的方式来计算各个view的frame。采用Cassowary算法来专门计算这些布局关系。因此autolayout在布局复杂的情况下,性能是非常低的。
Cassowary是个解析工具包,能够有效解析线性等式系统和线性不等式系统,用户的界面中总是会出现不等关系和相等关系,Cassowary开发了一种规则系统可以通过约束来描述视图间关系。约束就是规则,能够表示出一个视图相对于另一个视图的位置。