
new 可以实现一个对象继承构造函数的属性以及方法
举个例子:
function Parent(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Parent.prototype.sayName = function(){
console.log(`my name is ${this.name}`)
}
let child = new Parent('js',18);
console.log(child.name); // js
console.log(child.age); // 18
child.sayName(); // my name is js
从这个案例,可以看到实例child
1.继承了构造函数里面的属性
2.可以访问到构造函数prototype中的属性
通过下面这个图来直观感受一下,这里涉及到js原形以及原型链,先提前补脑一下
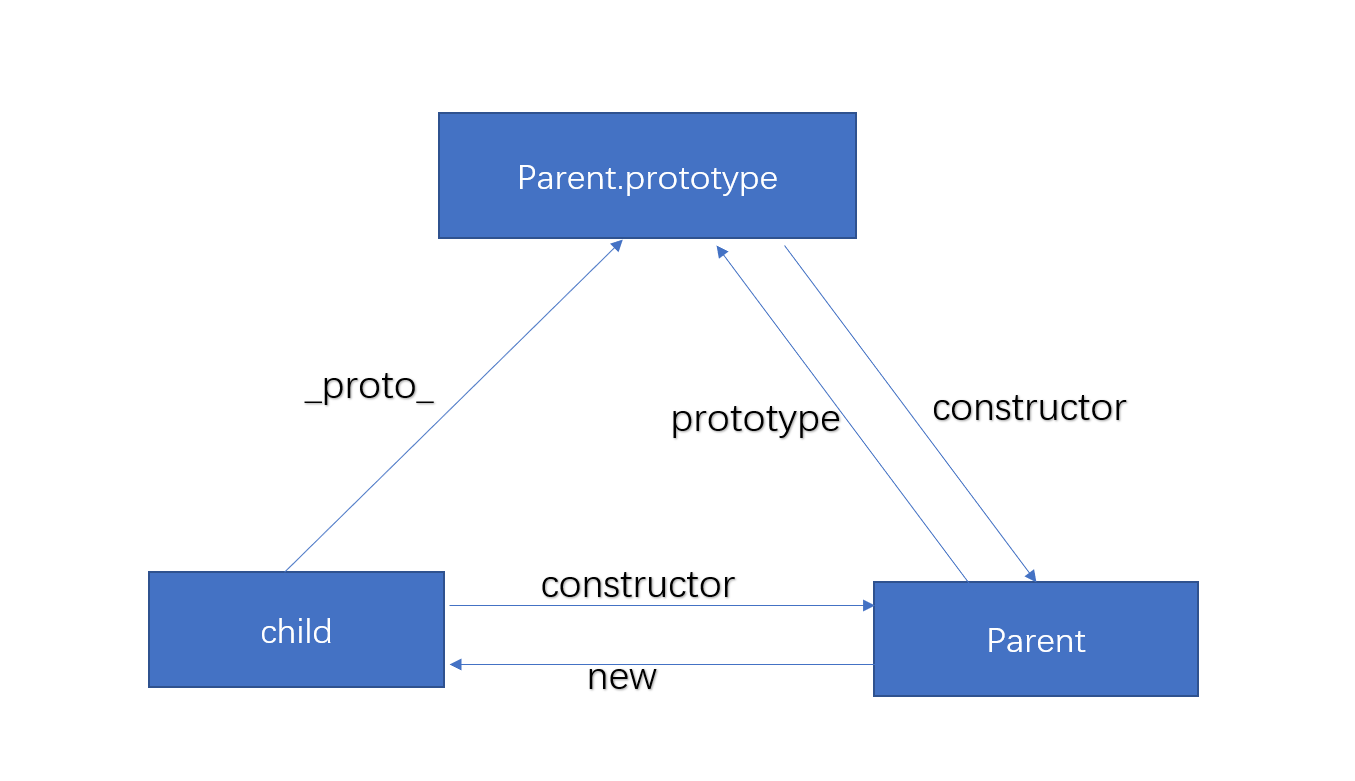
child.constructor === Parent //true
child._proto === Parent.prototype //true
Parent.prototype.constructor === Parent //true
接下来按照刚刚的例子结合上面的这张图片来实现new 内部是怎么的实现过程:
function newFactory(){
let obj = new Object(),
context = Array.prototype.shift.call(arguments);
obj.__proto__ = context.prototype;
context.apply(obj,arguments);
return obj;
}
- 首先通过new Object()新建一个对象 obj;
- 取出第一个参数,就是我们要传入的构造函数。因为 shift 会修改原数组,所以 arguments 会被去除第一个参数.
- 讲obj的原形指向构造函数
- 使用apply改变构造函数的this指向,这样obj就可以访问到构造函数的属性
接下来测试一下
function Parent(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Parent.prototype.sayName = function(){
console.log(`my name is ${this.name}`)
}
function newFactory(){
let obj = new Object(),
context = Array.prototype.shift.call(arguments);
obj.__proto__ = context.prototype;
context.apply(obj,arguments);
return obj;
}
let child = newFactory(Parent,'js','18')
console.log(child.name); // js
console.log(child.age); // 18
child.sayName(); // my name is js
到这一步我们已经完成了80%,因为还有种情况我们没有考虑到,当构造函数有返回值的时候,实例化的对象会怎么?
function Parent(name,age){
this.age = age;
this.sex = 'boy'
return {
name:name,
address:'china'
}
}
var child = new Parent('js','18')
console.log(child.name); // js
console.log(child.age); // undefined
console.log(child.sex); // undefined
console.log(child.address); // china
通过上面这个案例,可以看出当构造函数返回了一个对象的化,实例child只能访问到返回对象的属性,那如果返回的是基本类型呢?
function Parent(name,age){
this.age = age;
this.sex = 'boy'
return 'china';
}
var child = new Parent('js','18')
console.log(child.name); // undefined
console.log(child.age); // 18
console.log(child.sex); // boy
console.log(child.address); // undefined
从这个案例可以看出来当构造函数返回值是基本类型的时候,跟没有返回值一样。
终极版 四大步骤:
1、创建一个空对象,并且 this 变量引用该对象,// let obj = new Object();
2、继承了函数的原型。// obj.proto = func.prototype;
3、属性和方法被加入到 this 引用的对象中。并执行了该函数func// func.call(target);
4、新创建的对象由 this 所引用,并且最后隐式的返回 this 。// 如果func.call(target)返回的res是个对象或者function 就返回它
function newFactory(){
let obj = new Object(),
context = Array.prototype.shift.call(arguments);
obj.__proto__ = context.prototype;
let res = context.apply(obj,arguments);
if ((typeof res === "object" || typeof res === "function") && res !== null) {
return res;
}
return obj;
}