认真看完这篇文章, 您可以自己封装一个简易但功能相对齐全的Promise, 还可以加深对Promise的理解
建议 : 看这篇文章之前希望您
- 了解ES6的语法 [ 阮一峰老师的ES6入门 ]
- 了解Promises/A+规范 [ Promises/A+ ]
- 会使用Promise
文章较长, 代码连贯性较强, 从简单开始入手, 读者可以按需选读
一. 最简单的Promise
class Promise {
constructor (executor) {
if (typeof executor !== 'function')
throw new TypeError(`Promise resolver ${executor} is not a function`)
/* 默认状态 */
this.state = 'pending'
this.value = undefined
this.reason = undefined
/*
状态函数 resolve, reject
1.pending -> fulfilled, pending -> rejected
2.把数据储存到Promise实例上 this.value = value, this.reason = reason
*/
const resolve = value => {
if (this.state === 'pending') {
this.state = 'fulfilled'
this.value = value
}
}
const reject = reason => {
if (this.state === 'pending') {
this.state = 'rejected'
this.reason = reason
}
}
executor(resolve, reject)
}
then (onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.state === 'fulfilled') {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}
if (this.state === 'rejected') {
onRejected(this.reason)
}
}
}
ps : 测试工具为vsCode的Quokka插件


根据Promise的状态函数res和rej,对应执行then中的处理函数onFulfilled和onRejected
二. 异步的Promise
1. then()为异步
我们都知道,Promise中的then函数的代码是异步执行的,而我们写的这个并不是,可以验证一下
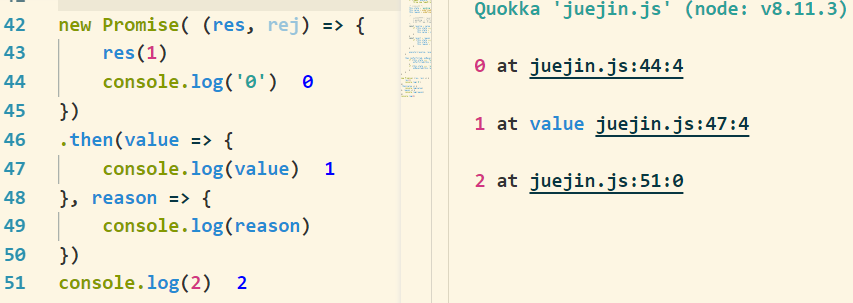
显然这段代码是同步执行的,而我们想要的输出顺序是 0 2 1,所以我们可以使用setTimeout模拟这个异步
class Promise {
constructor (executor) { ... }
then (onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.state === 'fulfilled') {
/* 使用setTimeout模拟异步 */
setTimeout(() => {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}, 0);
}
if (this.state === 'rejected') {
setTimeout(() => {
onRejected(this.reason)
}, 0);
}
}
}
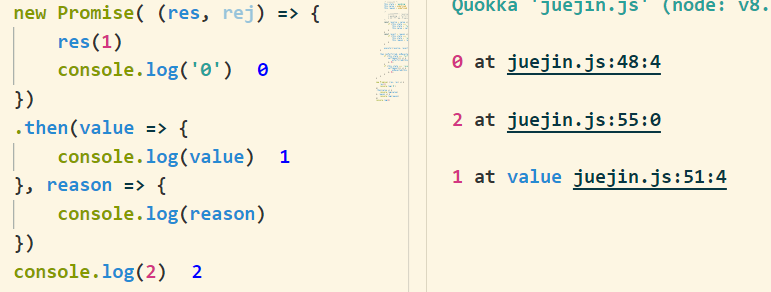
2. 状态函数异步执行

res/rej为异步执行时, 我们可以看到then是没有反应的左边灰色小方块表明这行代码没有执行
为什么呢? 那是因为当执行到then函数的时候,res为异步执行,所以状态还是pending,而我们的then函数里面还没有对状态为pending的处理, 修改一下代码
class Promise {
constructor (executor) {
...
/* 状态函数异步执行时, 处理函数的存储列表 */
this.resolveCallBackList = []
this.rejectCallBackList = []
const resolve = value => {
if (this.state === 'pending') {
...
/* 如果有, 则执行处理函数列表里的函数 */
this.resolveCallBackList.length > 0
&& this.resolveCallBackList.forEach(e => e())
}
}
const reject = reason => {
if (this.state === 'pending') {
...
this.rejectCallBackList.length > 0
&& this.rejectCallBackList.forEach(e => e())
}
}
...
}
then (onFulfilled, onRejected) {
...
/* 状态为pending时, 把处理函数存储对相应的列表 */
if (this.state === 'pending') {
onFulfilled && this.resolveCallBackList.push( () => {
onFulfilled(this.value)
})
onRejected && this.rejectCallBackList.push( () => {
onRejected(this.reason)
})
}
}
}

这样, 状态函数异步执行的时候也可以处理了, 可以简单理解为, 当状态为pending时, 把处理函数onFulfilled/onRejected存起来, 等状态函数res/rej执行时, 自动执行对应的处理函数
三. Promise的错误捕捉
当发生错误时, Promise不会报错, 而是由失败的处理函数then函数的第二个函数捕捉错误并处理, 如果我们自己写的Promise发生错误的话, 毫无意外是直接报错的, 就像这样
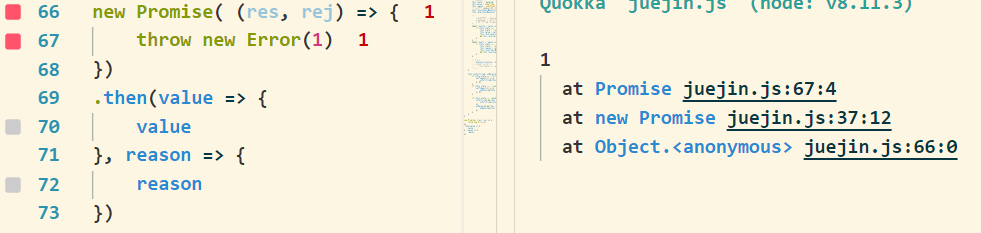
既然执行时发生错误, 那么我们就可以使用try/catch去捕获错误
class Promise {
constructor (executor) {
...
/* 使用try/catch捕获错误, 并执行reject, 改变状态为rejected */
try {
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
this.state === 'pending' && reject(error)
}
}
then (onFulfilled, onRejected) { ... }
}

四. then函数详解
then函数有两个特性
- then函数执行完返回一个新的Promise实例
- then函数能链式调用
1. then的链式调用
new Promise(res => res(0))
.then(value => {
console.log(value) // 0
return `1 fulfilled`
})
.then(value => {
console.log(value) // 1 fulfilled
})
then函数执行后返回一个Promise实例, 该Promise实例的状态由then决定, 下一个then函数根据返回的这个Promise实例执行相应的处理函数, 画个图

then的执行依赖于上一个then执行返回的Promise实例, 而这个Promise实例的数据由上一个then的处理函数onFulfilled/onRejected的执行和其返回值决定
2.then的处理函数返回值不是一个Promise实例
如果按照字面意思去写代码
class Promise {
constructor (executor) { ... }
then (onFulfilled, onRejected) {
/* 一个新的Promise实例 */
const newPromise = new Promise ( (res, rej) => {})
...
return newPromise
}
}
如果这样写, 是没意义的, 返回的Promise实例的状态永远为pending, 因为没有执行状态函数res/rej, 因此也无法进行then函数的链式调用

因为new Promise(executor)的executor函数是同步执行的, 所以我们可以这样写
class Promise {
constructor (executor) { ... }
then (onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const newPromise = new Promise ( (res, rej) => {
/*
这部分的处理函数是同步执行的, 因此可以放在里面执行
同时还能通过res/rej改变返回的Promise实例的状态
*/
if (this.state === 'fulfilled') {
setTimeout(() => {
/* 拿到处理函数执行后的返回值 */
const value = onFulfilled(this.value)
/* 改变返回的Promise实例的状态并把数据传过去 */
res(value)
}, 0);
}
if (this.state === 'rejected') {
setTimeout(() => {
const reason = onRejected(this.reason)
res(reason)
}, 0);
}
if (this.state === 'pending') {
onFulfilled && this.resolveCallBackList.push( () => {
const value = onFulfilled(this.value)
res(value)
})
onRejected && this.rejectCallBackList.push( () => {
const reason = onRejected(this.reason)
res(reason)
})
}
})
return newPromise
}
}

then的链式调用完成了
ps : then的处理函数返回值不是一个Promise实例时, 无论fullfilled还是rejected, 都是执行下一个then函数的onFulfilled
3.then的处理函数返回值是一个Promise实例
当then的处理函数返回值是一个Promise实例时, 则下一个then函数的执行, 全部由这个Promise实例决定, 所以我们需要使用checkReturnValueIfPromise函数去判断一下返回值的类型并处理对应的情况
class Promise {
constructor (executor) { ... }
/*
promise -> Promise对象
target -> then的处理函数的返回值
res/rej -> 要返回的Promise实例的状态函数
*/
checkReturnValueIfPromise (promise, target, res, rej) {
if (target instanceof promise) {
/*
如果是Promise实例
则调用then函数,根据Promise实例的状态执行对应的处理函数
从而改变要返回的Promise实例的状态
如果下面的代码不能理解, 也可以写成这样
target.then( value => {
res(value)
}, reason => {
rej(reason)
} )
*/
target.then(res, rej)
} else {
res(target)
}
}
then (onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const newPromise = new Promise ( (res, rej) => {
if (this.state === 'fulfilled') {
setTimeout(() => {
const value = onFulfilled(this.value)
/* 调用检测函数并做相关处理 */
this.checkReturnValueIfPromise(Promise, value, res, rej)
}, 0);
}
if (this.state === 'rejected') {
setTimeout(() => {
const reason = onRejected(this.reason)
this.checkReturnValueIfPromise(Promise, reason, res, rej)
}, 0);
}
if (this.state === 'pending') {
onFulfilled && this.resolveCallBackList.push( () => {
const value = onFulfilled(this.value)
this.checkReturnValueIfPromise(Promise, value, res, rej)
})
onRejected && this.rejectCallBackList.push( () => {
const reason = onRejected(this.reason)
this.checkReturnValueIfPromise(Promise, reason, res, rej)
})
}
})
return newPromise
}
}


五. 一些Promise上的方法 (直接上代码)
对了, 还有一个与then类似的方法catch, 这个方法是专门处理rejected状态的, 代码也就只有一句话
class Promise {
constructor () { ... }
then () { ... }
catch (onRejected) {
this.then(undefined, onRejected)
}
}
1. Promise.resolve
返回一个fulfilled状态的Promise实例
class Promise {
constructor () { ... }
then () { ... }
catch () { ... }
static resolve (value) {
return new Promise( res => res(value))
}
}
2. Promise.reject
返回一个rejected状态的Promise实例
class Promise {
constructor () { ... }
then () { ... }
catch () { ... }
static resolve () { ... }
static reject (reason) {
return new Promise( (undefined, rej) => rej(reason))
}
}
3. Promise.race
接收一个Promise实例的数组promiseArray, 返回一个Promise实例, 返回的Promise实例由promiseArray中执行最快的Promise实例决定
class Promise {
constructor () { ... }
then () { ... }
catch () { ... }
static resolve () { ... }
static reject () { ... }
static race (promiseArray) {
return new Promise ( (res, rej) => {
promiseArray.forEach( promise => {
promise.then(res, rej)
})
})
}
}

4. Promise.all
功能描述太长了, 不懂的可以去看 阮一峰老师对于Promise.all的介绍
class Promise {
constructor () { ... }
then () { ... }
catch () { ... }
static resolve () { ... }
static reject () { ... }
static race () { ... }
static all (promiseArray) {
let count = 0,
resultArray = []
return new Promise( (res, rej) => {
promiseArray.forEach( promise => {
promise.then( value => {
count++
resultArray.push(value)
if (count === promiseArray.length) {
res(resultArray)
}
}, reason => {
rej(reason)
})
})
})
}
}


六. 结语
谢谢浏览我的文章, 希望你能学到东西