启动指令
php artisan queue:work
启动文件
namespace Illuminate\Queue\Console;
use Illuminate\Queue\Worker;
use Illuminate\Support\Carbon;
use Illuminate\Console\Command;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\Job;
use Illuminate\Queue\WorkerOptions;
use Illuminate\Queue\Events\JobFailed;
use Illuminate\Queue\Events\JobProcessed;
use Illuminate\Queue\Events\JobProcessing;
class WorkCommand extends Command
{
...
/**
* @var \Illuminate\Queue\Worker
*/
protected $worker;
public function __construct(Worker $worker)
{
parent::__construct();
$this->worker = $worker;
}
public function handle()
{
if ($this->downForMaintenance() && $this->option('once')) {
return $this->worker->sleep($this->option('sleep'));
}
$this->listenForEvents();
$connection = $this->argument('connection')
?: $this->laravel['config']['queue.default'];
$queue = $this->getQueue($connection);
$this->runWorker(
$connection, $queue
);
}
...
}
我们先从构造函数和 handle() 方法开始分析,这是入口。
片段一:判断是否维护模式或者
--force强制启动
if ($this->downForMaintenance() && $this->option('once')) {
return $this->worker->sleep($this->option('sleep'));
}
片段二:通过事件绑定在控制台输出信息
$this->listenForEvents();
protected function listenForEvents()
{
$this->laravel['events']->listen(JobProcessing::class, function ($event) {
$this->writeOutput($event->job, 'starting');
});
$this->laravel['events']->listen(JobProcessed::class, function ($event) {
$this->writeOutput($event->job, 'success');
});
$this->laravel['events']->listen(JobFailed::class, function ($event) {
$this->writeOutput($event->job, 'failed');
$this->logFailedJob($event);
});
}
片段三:通过配置文件中配置的驱动获取对应驱动的队列名,如果没有则返回
default
$connection = $this->argument('connection') ?: $this->laravel['config']['queue.default'];
$queue = $this->getQueue($connection);
protected function getQueue($connection)
{
return $this->option('queue') ?: $this->laravel['config']->get(
"queue.connections.{$connection}.queue", 'default'
);
}
片段四:传入连接驱动和队列名称到
runWorker方法运行任务。
$this->runWorker(
$connection, $queue
);
这里是启动的重点,我们传入的 $connection = 'redis' $queue = 'default',继续分析
protected function runWorker($connection, $queue)
{
// "这里的 $this->laravel['cache'] 是 Illuminate\Cache\CacheManager 类的实例。
(是在 app.providers.Illuminate\Cache\CacheServiceProvider::class 注册的)
$this->laravel['cache']->driver() 返回 Illuminate\Cache\Repository 类的实例。"
// "框架通过 CacheManager 对很多存储管理进行了统一。
可以通过修改 app.config.cache.default 和 `app.config.cache.stores 中的值来修改存储驱动。"
// "将获取的驱动赋值给 workder 的 cache成员"
$this->worker->setCache($this->laravel['cache']->driver());
// "当 worker 对象拥有了cache对象之后便拥有了操作对应数据的能力 !"
return $this->worker->{$this->option('once') ? 'runNextJob' : 'daemon'}(
$connection, $queue, $this->gatherWorkerOptions()
);
}
继续运行
return $this->worker->{$this->option('once') ? 'runNextJob' : 'daemon'}(
$connection, $queue, $this->gatherWorkerOptions()
);
这里传入的参数分别是,可以看出都是对队列消费的一些基本设置。
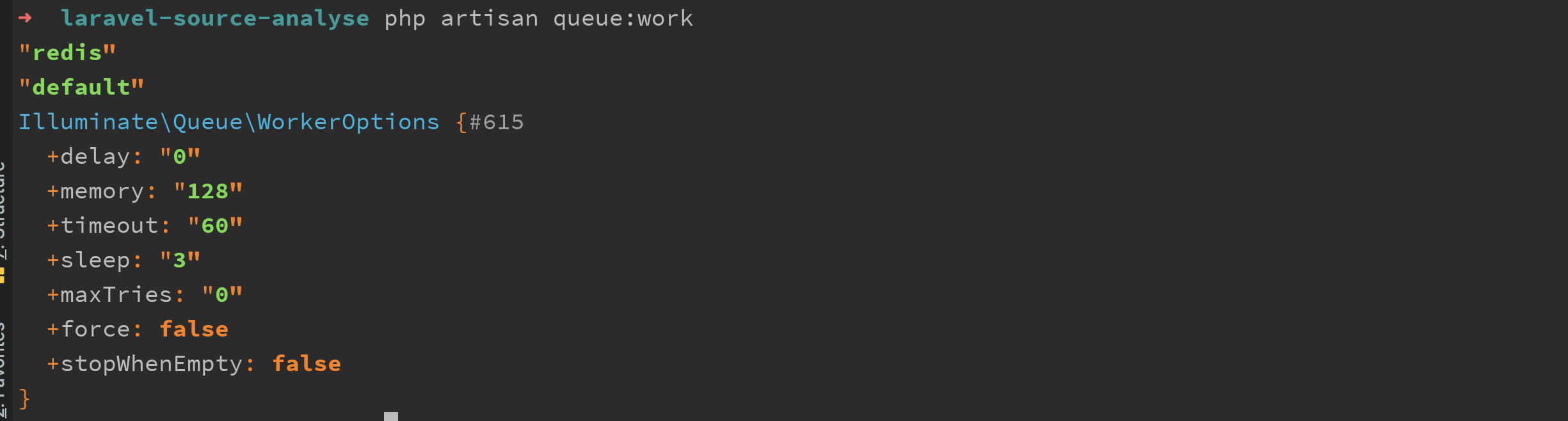
当运行模式非 --once 的情况下就会以 daemon 的方式运行。
我们看
\Illuminate\Queue\Worker 对象的 daemon 方法即可
守护进程模式
public function daemon($connectionName, $queue, WorkerOptions $options)
{
if ($this->supportsAsyncSignals()) {
$this->listenForSignals();
}
$lastRestart = $this->getTimestampOfLastQueueRestart();
while (true) {
if (! $this->daemonShouldRun($options, $connectionName, $queue)) {
$this->pauseWorker($options, $lastRestart);
continue;
}
$job = $this->getNextJob(
$this->manager->connection($connectionName), $queue
);
if ($this->supportsAsyncSignals()) {
$this->registerTimeoutHandler($job, $options);
}
if ($job) {
$this->runJob($job, $connectionName, $options);
} else {
$this->sleep($options->sleep);
}
$this->stopIfNecessary($options, $lastRestart, $job);
}
}
进程参数设定
先设置进程的一些管理参数
if ($this->supportsAsyncSignals()) { // extension_loaded('pcntl'); 是否支持 'pcntl' 拓展,支持多进程的拓展。
$this->listenForSignals();
}
protected function listenForSignals()
{
// "PHP7.1信号新特性 -- 开启异步信号处理"
pcntl_async_signals(true);
// "安装信号处理器,后面可以传入相应的信号来终止或其他操作"
pcntl_signal(SIGTERM, function () {
// "SIGTERM 终止进程 软件终止信号"
$this->shouldQuit = true;
});
pcntl_signal(SIGUSR2, function () {
// "SIGUSR2 终止进程 用户定义信号2"
$this->paused = true;
});
pcntl_signal(SIGCONT, function () {
// "SIGCONT 忽略信号 继续执行一个停止的进程"
$this->paused = false;
});
}
关于
pcntl的用法可以参考 PCNTL
信号可以参考对照表
接着看,从 cache 中获取上一次重启的时间戳
$lastRestart = $this->getTimestampOfLastQueueRestart();
循环任务执行
判断是否终止运行
if (! $this->daemonShouldRun($options, $connectionName,$queue)) {
// "$opions 就是 调用artisan 传入的参数
$connectionName 我用了redis驱动,所有就是 'redis'
$queue 这里没有传入队列则是 'default'"
$this->pauseWorker($options, $lastRestart);
continue;
}
下面代码一共三个判断:
1.是否是关站模式并且非强制运行。
2.是否有外部传入的暂停信号
3.是否有绑定 Looping 事件执行并返回结果
如果符合条件则暂停或者发送终止信号。
主要功能是为了控制是否继续执行任务。
protected function daemonShouldRun(WorkerOptions $options, $connectionName, $queue)
{
return ! (($this->manager->isDownForMaintenance() && ! $options->force) ||
$this->paused ||
$this->events->until(new Events\Looping($connectionName, $queue)) === false);
}
获取待运行的 Job
// "$this->manager->connection($connectionName) 是 Illuminate\Queue\RedisQueue 对象
$queue : 'default'"
$job = $this->getNextJob(
$this->manager->connection($connectionName), $queue
);
继续看 getNextJob
protected function getNextJob($connection, $queue)
{
try {
foreach (explode(',', $queue) as $queue) {
if (! is_null($job = $connection->pop($queue))) {
return $job;
}
}
} catch (Exception $e) {
// "异常处理主要是报告异常"
// "设置 '$this->shouldQuit = true;' 后续就会终止"
$this->exceptions->report($e);
$this->stopWorkerIfLostConnection($e);
$this->sleep(1);
} catch (Throwable $e) {
$this->exceptions->report($e = new FatalThrowableError($e));
$this->stopWorkerIfLostConnection($e);
$this->sleep(1);
}
}
上面分析过了 $connection 是 RedisQueue 对象,所有展开 RedisQueue 的 pop 方法,获取要执行的任务对象。
public function pop($queue = null)
{
$this->migrate($prefixed = $this->getQueue($queue));
if (empty($nextJob = $this->retrieveNextJob($prefixed))) {
return;
}
[$job, $reserved] = $nextJob;
if ($reserved) {
return new RedisJob(
$this->container, $this, $job,
$reserved, $this->connectionName, $queue ?: $this->default
);
}
}
迁移延迟队列
在 pop 的过程中首先迁移延迟队列的相关数据
protected function migrate($queue)
{
// "这里是不是很熟悉了,上一章存储端分析的时候延迟"
// "队列就是用的这个key来存的"
// "将延迟的队列迁移到主队列"
$this->migrateExpiredJobs($queue.':delayed', $queue);
// "将过期队列迁移到主队列"
if (! is_null($this->retryAfter)) {
$this->migrateExpiredJobs($queue.':reserved', $queue);
}
}
继续看如何迁移到主队列的
public function migrateExpiredJobs($from, $to)
{
return $this->getConnection()->eval(
LuaScripts::migrateExpiredJobs(),
2,
$from,
$to,
$this->currentTime()
);
}
public static function migrateExpiredJobs()
{
return <<<'LUA'
if(next(val) ~= nil) then
redis.call('zremrangebyrank', KEYS[1], 0, #val - 1)
for i = 1, #val, 100 do
redis.call('rpush', KEYS[2], unpack(val, i, math.min(i+99, #val)))
end
end
return val
LUA;
}
最终通过 eval 命令使用 Lua 解释器执行脚本。
请看 Redis Eval
真香,这仅仅是把延迟任务切回主队列,继续!
检索数据
从队列检索下一个 Job
if (empty($nextJob = $this->retrieveNextJob($prefixed))) {
return; // 没有数据就返回
}
展开检索代码
protected function retrieveNextJob($queue)
{
// "默认值是 null"
if (! is_null($this->blockFor)) {
return $this->blockingPop($queue);
}
// "这段是直接通过 lua 从 redis lpop出对象,"
// "在lua中完成封装,执行逻辑和 blockingPop 相似"
return $this->getConnection()->eval(
LuaScripts::pop(), 2, $queue, $queue.':reserved',
$this->availableAt($this->retryAfter)
);
}
我们主要看 blockingPop 的代码
protected function blockingPop($queue)
{
// "以阻塞的方式弹出队列的第一个元素"
$rawBody = $this->getConnection()->blpop($queue, $this->blockFor);
// "解析获取的数据,同时再封装一个重试对象并写入有序集合。"
if (! empty($rawBody)) {
$payload = json_decode($rawBody[1], true);
$payload['attempts']++;
$reserved = json_encode($payload);
$this->getConnection()->zadd($queue.':reserved', [
$reserved => $this->availableAt($this->retryAfter),
]);
return [$rawBody[1], $reserved];
}
return [null, null];
}
检索完成之后回到 pop 中继续执行
public function pop($queue = null)
{
$this->migrate($prefixed = $this->getQueue($queue));
if (empty($nextJob = $this->retrieveNextJob($prefixed))) {
return;
}
// "到这里了!"
[$job, $reserved] = $nextJob;
if ($reserved) {
return new RedisJob(
$this->container, $this, $job,
$reserved, $this->connectionName, $queue ?: $this->default
);
}
}
我们来看看 $nextJob 是什么

最后调用
return new RedisJob(
$this->container, $this, $job,
$reserved, $this->connectionName, $queue ?: $this->default
);
看看 Illuminate\Queue\Jobs\RedisJob 的构造函数
public function __construct(Container $container, RedisQueue $redis, $job, $reserved, $connectionName, $queue)
{
$this->job = $job;
$this->redis = $redis;
$this->queue = $queue;
$this->reserved = $reserved;
$this->container = $container;
$this->connectionName = $connectionName;
$this->decoded = $this->payload();
}
这应该是最后一层封装,最后要返回给最外层的任务对象。
运行 Job
回到 Worker 对象中
...
$job = $this->getNextJob(
$this->manager->connection($connectionName), $queue
);
// "刚刚我们从 redis 中拿到了封装好的 $job 对象,继续执行"
// "$job 就是 Illuminate\Queue\Jobs\RedisJob 对象"
// "是否支持 pcntl 拓展,异步模式传递信号"
if ($this->supportsAsyncSignals()) {
// "设置超时信号处理"
$this->registerTimeoutHandler($job, $options);
}
继续注册超时信号控制
protected function registerTimeoutHandler($job, WorkerOptions $options)
{
pcntl_signal(SIGALRM, function () {
$this->kill(1);
});
pcntl_alarm(
max($this->timeoutForJob($job, $options), 0)
);
}
总算要到运行 Job 的部分了
if ($job) {
$this->runJob($job, $connectionName, $options);
} else {
// "不存在 $job 则睡眠,最低睡眠1秒"
$this->sleep($options->sleep);
}
解析 runJob
到这一步我们已经拿到了所有的对象,接下来就是把 对象用起来!
protected function runJob($job, $connectionName, WorkerOptions $options)
{
try {
return $this->process($connectionName, $job, $options);
} catch (Exception $e) {
// "异常处理和上部分的一样,"
// "设定停止信号,在循环的结尾会检测信号"
// "因此我们不需要分析这段"
$this->exceptions->report($e);
$this->stopWorkerIfLostConnection($e);
} catch (Throwable $e) {
$this->exceptions->report($e = new FatalThrowableError($e));
$this->stopWorkerIfLostConnection($e);
}
}
展开
$this->process($connectionName, $job, $options);
继续展开
public function process($connectionName, $job, WorkerOptions $options)
{
try {
// "触发任务执行前的绑定事件,从队列删除任务"
$this->raiseBeforeJobEvent($connectionName, $job);
// "标记超过最大重试次数的任务"
$this->markJobAsFailedIfAlreadyExceedsMaxAttempts(
$connectionName, $job, (int) $options->maxTries
);
$job->fire();
// "触发任务执行后的绑定事件"
$this->raiseAfterJobEvent($connectionName, $job);
} catch (Exception $e) {
$this->handleJobException($connectionName, $job, $options, $e);
} catch (Throwable $e) {
$this->handleJobException(
$connectionName, $job, $options, new FatalThrowableError($e)
);
}
}
$job->fire()
$job => Illuminate\Queue\Jobs\RedisJob 继承了 Illuminate\Queue\Jobs\Job
所以调用了抽象父类的 fire() 方法
public function fire()
{
$payload = $this->payload();
[$class, $method] = JobName::parse($payload['job']);
($this->instance = $this->resolve($class))->{$method}($this, $payload['data']);
}
我们看看 $payload 的结构实际就是 json_decode($job, true)
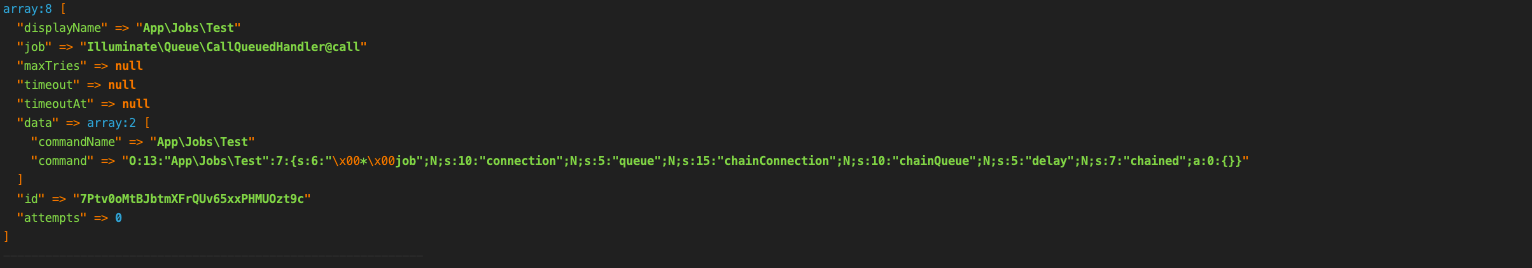
转换后的[$class, $method] 分别是 Illuminate\Queue\CallQueuedHandler 和 call
最后就是从容器中解析出 Illuminate\Queue\CallQueuedHandler 对象并且调用 call 方法,展开方法
public function call(Job $job, array $data)
{
try {
$command = $this->setJobInstanceIfNecessary(
$job, unserialize($data['command'])
);
} catch (ModelNotFoundException $e) {
return $this->handleModelNotFound($job, $e);
}
$this->dispatcher->dispatchNow(
$command, $this->resolveHandler($job, $command)
);
if (! $job->hasFailed() && ! $job->isReleased()) {
$this->ensureNextJobInChainIsDispatched($command);
}
if (! $job->isDeletedOrReleased()) {
$job->delete();
}
}
先看看 $command 获取的是什么
protected function setJobInstanceIfNecessary(Job $job, $instance)
{
if (in_array(InteractsWithQueue::class, class_uses_recursive($instance))) {
$instance->setJob($job);
}
return $instance;
}
打印 class_uses_recursive($instance)
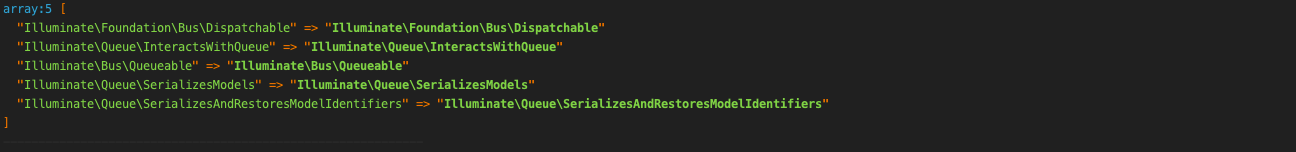
接着就调用了 $instance->setJob($job);
这里的 $instance 就是对应我们自己编写的任务对象。
执行完之后最终 $command 返回的就是自己编写的类

将 RedisJob 和 $command 传给 dispatchNow 方法
$this->dispatcher 是 Illuminate\Bus\Dispatcher 对象
$this->dispatcher->dispatchNow(
$command, $this->resolveHandler($job, $command)
);
最后的真像
public function dispatchNow($command, $handler = null)
{
if ($handler || $handler = $this->getCommandHandler($command)) {
$callback = function ($command) use ($handler) {
// "划重点,要考!"
return $handler->handle($command);
};
} else {
$callback = function ($command) {
return $this->container->call([$command, 'handle']);
};
}
return $this->pipeline->send($command)->through($this->pipes)->then($callback);
}
其实费了那么大的力气,最后就是调用 $command->handle
回头看看 job 的定义
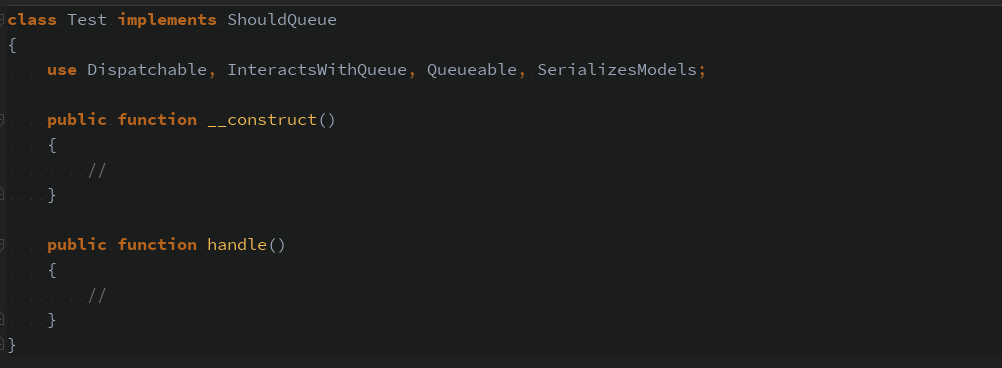
就像烟火过后一样,消失于无形。
最后
整体分析下来感觉使用 pcntl 拓展来做异步信号控制和进程中断来实现终止循环是一个亮点!
至此完成了任务队列消费端的分析,后续有机会分析 Horizon
是如何消费队列的哈~