核心配置文件
一、创建配置层config,其下放置核心配置文件configuration.xml 例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="" value=""/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="UNPOOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/micro_message"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
//映射到SQL配置文件
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/imooc/config/sqlxml/Message.xml"/>
<mapper resource="com/imooc/config/sqlxml/Command.xml"/>
<mapper resource="com/imooc/config/sqlxml/CommandContent.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
与数据库交互最重要的对象SqlSession:
作用: 1、向SQL语句传入参数 2、执行SQL 3、获取执行SQL语句的结果 4、事务控制
如何得到SqlSession: 1、通过配置文件获取数据库连接相关信息 2、通过配置信息构建SqlSessionFactory 3、通过SqlSessionFactory打开数据库会话
数据库访问
二、创建真正与数据库交互的数据访问层db,其下创建一个类专门访问数据库 例:DBAccess.java
package com.imooc.db;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
//访问数据库类
public class DBAccess {
public SqlSession getSqlSession() throws IOException {//抛出异常在dao层处理
// 通过配置文件获取数据库连接信息
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("com/imooc/config/Configuration.xml");
// 通过配置信息构建一个SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
// 通过sqlSessionFactory打开一个数据库会话
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
return sqlSession;
}
}
数据交互
三、Dao层与数据交互 例:MessageDao.java
package com.imooc.dao;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import com.imooc.bean.Message;
import com.imooc.db.DBAccess;
// 和message表相关的数据库操作
public class MessageDao {
//根据查询条件查询消息列表
public List<Message> queryMessageList(String command,String description) {
DBAccess dbAccess = new DBAccess();
//保证符合泛型
List<Message> messageList = new ArrayList<Message>();
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
//由于parameterType只接受一个参数,所以讲command、description两个属性封装成一个对象
Message message = new Message();
message.setCommand(command);
message.setDescription(description);
sqlSession = dbAccess.getSqlSession();
// 通过sqlSession执行SQL语句,查询一个则是select,多个就是selectList
messageList = sqlSession.selectList("Message.queryMessageList", message);
} catch (IOException e) {//处理数据访问层抛出的异常
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
return messageList;
}
//单条删除
public void deleteOne(int id) {
DBAccess dbAccess = new DBAccess();
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = dbAccess.getSqlSession();
// 通过sqlSession执行SQL语句
sqlSession.delete("Message.deleteOne", id);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
//多条删除
public void deleteBatch(List<Integer> ids) {
DBAccess dbAccess = new DBAccess();
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = dbAccess.getSqlSession();
// 通过sqlSession执行SQL语句
sqlSession.delete("Message.deleteBatch", ids);
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
}
SQL语句配置文件
四、在配置层下创建SQL配置层sqlConfig,其中存放dao层下文件中使用的SQL语句配置文件
调用SQL语句的方法是:mapper标签的namespace.对应语句标签(增删查改)的id
例:Message.xml(每个实体类都对应一个配置文件)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="Message">
<resultMap type="com.imooc.bean.Message" id="MessageResult">//type:数据库中字段对应java中的类
<id column="ID" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>//主键使用id标签,否则使用result标签
<result column="COMMAND" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="command"/>
<result column="DESCRIPTION" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="description"/>
<result column="CONTENT" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="content"/>
</resultMap>
//通过parameter接收dao层中传递的参数,parameter=包名.类型名
<select id="queryMessageList" parameterType="String" resultMap="MessageResult">
select ID,COMMAND,DESCRIPTION,CONTENT from MESSAGE
//条件检索
<where>
<if test="command != null and !"".equals(command.trim())">
and COMMAND=#{command}
</if>
<if test="description != null and !"".equals(description.trim())">
and DESCRIPTION like '%' #{description} '%'
</if>
</where>
</select>
<delete id="deleteOne" parameterType="int">
delete from MESSAGE where ID = #{_parameter}
</delete>
<delete id="deleteBatch" parameterType="java.util.List">
delete from MESSAGE where ID in(
<foreach collection="list" item="item" separator=",">
#{item}
</foreach>
)
</delete>
</mapper>
动态SQL拼接
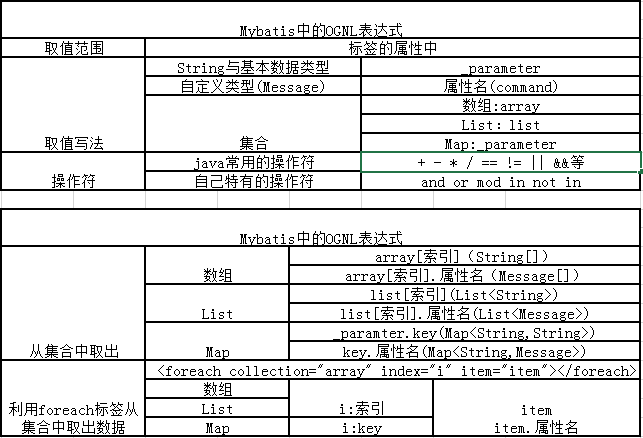
五、动态SQL拼接 使用if、foreach、choose进行动态拼接,mybatis配置文件中使用ognl(表达式语言),ognl中能直接使用java对象的方法。使用例:
<select id="queryMessageList" parameterType="com.imooc.bean.Message" resultMap="MessageResult">
select ID,COMMAND,DESCRIPTION,CONTENT from MESSAGE
<where>
<if test="command != null and !"".equals(command.trim())">
and COMMAND=#{command}
</if>
<if test="description != null and !"".equals(description.trim())">
and DESCRIPTION like '%' #{description} '%'
</if>
</where>
</select>
<delete id="deleteBatch" parameterType="java.util.List">
delete from MESSAGE where ID in(
<foreach collection="list" item="item" separator=",">
#{item}
</foreach>
)
</delete>
一对多关系配置
六、一对多关系配置
举例:
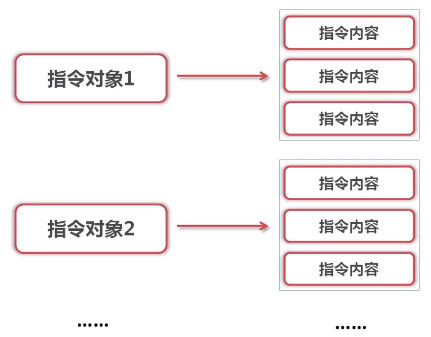
要实现一条指令对应多条内容,数据库表中需要两个表,一个为指令表,作为主表,一个为内容表,作为子表。内容表中需要指令id这一指令表主键进行关联。在项目文件中,建立对应表的实体类,指令表实体类Command中还需要包含子表实体类CommandContent的列表。在xml配置文件中配置一条能查询出这个主表的实体类的SQL语句。因为要查询出主表的实体,sql语句需要写在主表的xml配置文件中,将查出的数据填充到主表的属性中,同时填充子表的列表。配置文件:
Command.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="Command">
<resultMap type="com.imooc.bean.Command" id="Command">
<id column="C_ID" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="NAME" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="DESCRIPTION" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="description"/>
<collection property="contentList" resultMap="CommandContent.Content"/>
</resultMap>
<!--注意:1、column属性对应查询列表的列名,若查询列表中列名取了别名,那么对应column也要填写别名;2、因为前缀无效,a.ID和b.ID在查询出的结果集再去掉前缀以后,这两列的列名是一致的,所以这两个ID至少有一个要去别名,并且不能与其他列名重复-->
<select id="queryCommandList" parameterType="com.imooc.bean.Command" resultMap="Command">
select a.ID C_ID,a.NAME,a.DESCRIPTION,b.ID,b.CONTENT,b.COMMAND_ID
from COMMAND a left join COMMAND_CONTENT b on a.ID=b.COMMAND_ID
<where>
<if test="name != null and !"".equals(name.trim())">
and a.NAME=#{name}
</if>
<if test="description != null and !"".equals(description.trim())">
and a.DESCRIPTION like '%' #{description} '%'
</if>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>
CommandContent.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="CommandContent">
<resultMap type="com.imooc.bean.CommandContent" id="Content">
<id column="ID" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="CONTENT" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="content"/>
<result column="COMMAND_ID" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="commandId"/>
</resultMap>
</mapper>
注意:要在核心配置文件中引入这两个xml文件
然后再在Dao层创建与数据交互的CommandDao.java文件
package com.imooc.dao;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import com.imooc.bean.Command;
import com.imooc.db.DBAccess;
public class MessageDao {
//根据查询条件查询指令列表
public List<Command> queryCommandList(String command,String description) {
DBAccess dbAccess = new DBAccess();
List<Command> commandList = new ArrayList<Command>();
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
Command command = new Command();
command.setName(name);
command.setDescription(description);
sqlSession = dbAccess.getSqlSession();
// 通过sqlSession执行SQL语句,查询一个则是select,多个就是selectList
commandList = sqlSession.selectList("Command.queryCommandList", command);
} catch (IOException e) {//处理数据访问层抛出的异常
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
return commandList;
}
}
最后在service中调用dao
package com.imooc.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.imooc.bean.Message;
import com.imooc.dao.MessageDao;
import com.imooc.bean.Command;
import com.imooc.dao.CommandDao;
import com.imooc.util.Iconst;
/**
* 查询相关的业务功能
*/
public class QueryService {
public List<Message> queryMessageList(String command,String description) {
MessageDao messageDao = new MessageDao();
return messageDao.queryMessageList(command, description);
}
/**
* 通过指令查询自动回复的内容
* @param command 指令
* @return 自动回复的内容
*/
public String queryByCommand(String command) {
CommandDao commandDao = new CommandDao();
List<command> commandList;
if(Iconst.HELP_COMMAND.equals(command)) {
commandList = commandDao.queryCommandList(null, null);//无条件检索
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < commandList.size(); i++) {
if(i != 0) {
result.append("<br/>");
}
result.append("回复[" + commandList.get(i).getName() + "]可以查看" + commandList.get(i).getDescription());
}
return result.toString();
}
commandList = commandDao.queryCommandList(command, null);
if(commandList.size() > 0) {
List<CommandContent> contentList = commandList.get(0).getContentList();
int i = new Random().nextInt(contentList.size());
return contentList.get(i);
}
return Iconst.NO_MATCHING_CONTENT;
}
}
其中
package com.imooc.util;
/**
* 通用的常量定义
*/
public interface Iconst {
//当指令没有匹配的自动回复内容时,用此内容代替。
public static final String NO_MATCHING_CONTENT = "客官,你没按套路出牌……我听不懂你在说什么哎!";
public static final String HELP_COMMAND = "帮助";
}
使用log4j调试动态SQL
七、使用log4j调试动态SQL 导入log4j.jar包,创建log4j.properties配置文件(放置根目录下,省去写加载log4j的方法) log4j配置文件:
#配置日志级别和输出的位置, 级别不小于debug的输出形式才会输出,输出日志的级别:debug < info < warn < error。mybatis源码中日志输出使用的是debug,所以此处使用debug
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,Console
log4j.appender.Console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
#配置布局方式
log4j.appender.Console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
#自定义输出内容的格式
log4j.appender.Console.layout.ConversionPattern=%d [%t] %-5p [%c] - %m%n
#为某个特定的包(org.apache)下面去配其他不同的级别
log4j.logger.org.apache=INFO
自定义输出内容的格式
%d 产生日志的时间
%t 产生日志所处于线程的线程名称
%p 输出的日志级别
-5输出的字符至少占5位字符,不足5位将会用空格补齐
负号指的是补齐的空格在右边,如果没有负号,补齐的空格将在左边
%c 你输出的日志所属于的那个类的全名,包括包名
%m 指的是你输出的时候附加的信息将会出现在这个位置
%n 指的是换行
常用标签
八、常用标签
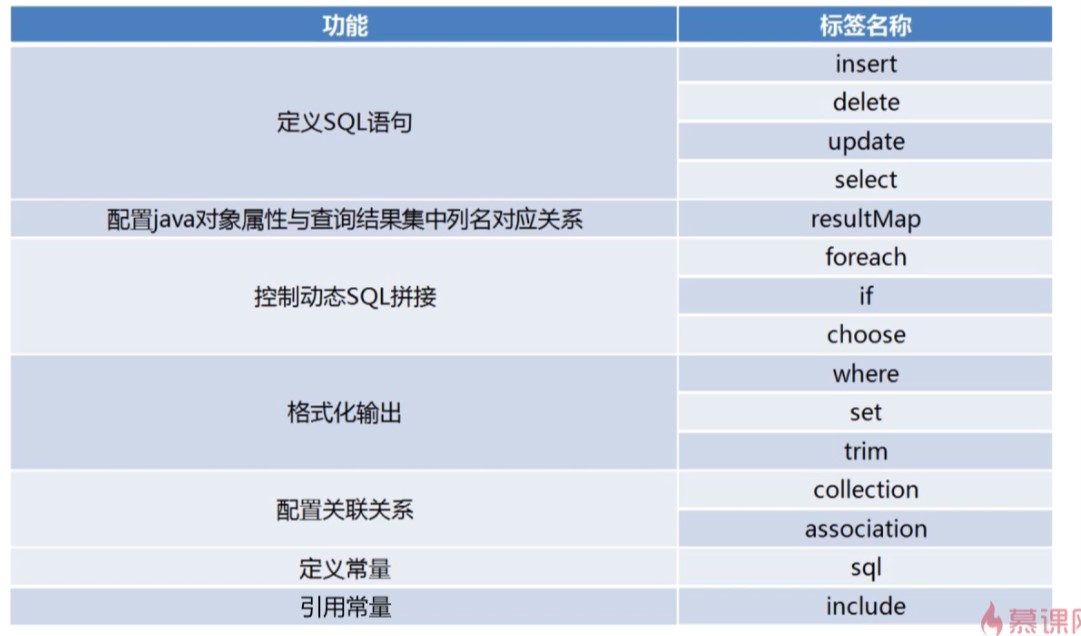
参考
慕课课程《通过自动回复机器人学Mybatis---基础版》