一直在使用ThreadLocal,都是按部就班的去使用它的函数方法,当人问起的时候也就只是知道它内部维护了一个Map,属于线程私有,适用于每一个线程一个实例的访问。再往深里就不知道了,也没有深入去了解它具体内部是怎么实现的。今天我要把它搞清楚!!!
贴出get方法的代码
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
}
最直观的感觉就是它内部就是保存了一个Map集合,使用当前线程作为Key,然后获取对象Value,用这种方式达到线程隔离的目的。上面的代码是1.8版本的 ,get方法获取当期线程,去除线程内部的ThreadLocal类型变量,根据当期的ThreadLocal 查找到对应的ThreadLocalMap.Entry,如果不为空,返回内部存放的对象值,否则就调用初始化方法。 那么ThreadLocalMap类中是怎么存储所有变量的呢?
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
根据Hash值求出,key对应的table数组的下标。
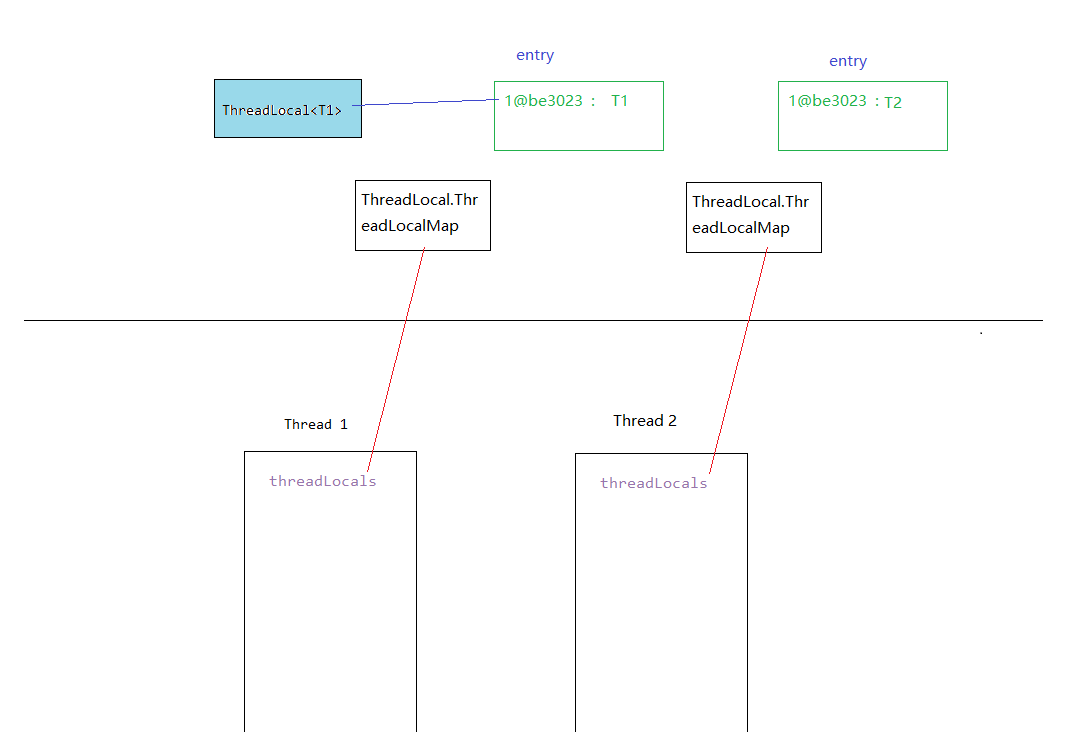
到这儿,源码中我们可以读到,实际存放的对象是保存在当前线程内部的ThreadLocalMap变量中,以<K,V>形式存储,K = ThreadLocal ,传入的对象 = value (initialValue 中可以初始化默认值)
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
这里也是需要注意一下的,当期Entry是将ThreadLocal作为弱引用来存储的,如果一个ThreadLocal没有外部强引用引用它,那么系统GC的时候,这个ThreadLocal就会被系统给回收掉,进而ThreadLocalMap内部就会出现以null为Key的Entry,当然nullkey对应的value值也无法获取。如果当期线程不结束,那这些无用的强引用就无法回收。从而造成内存泄漏的问题。
所以就有建议说是要讲ThreadLocal变量定义成为private static ,由于一直存在着ThreadLocal的强引用,也就能保证任何时候对应的弱引用能访问到Entry中的value值。
与线程同步机制的比较 在同步机制中,通过对象的锁保证同一时间只会有一个线程访问变量。这时该变量是多个线程所共享的使用同步机制就要去程序必须非常缜密的分析什么时候对变量进行读写,什么时候锁定和释放对象,程序设计的难度是非常大的。
ThreadLocal是从另外一个角度去解决并发问题。它为每一个线程都提供了一个独立的变量副本