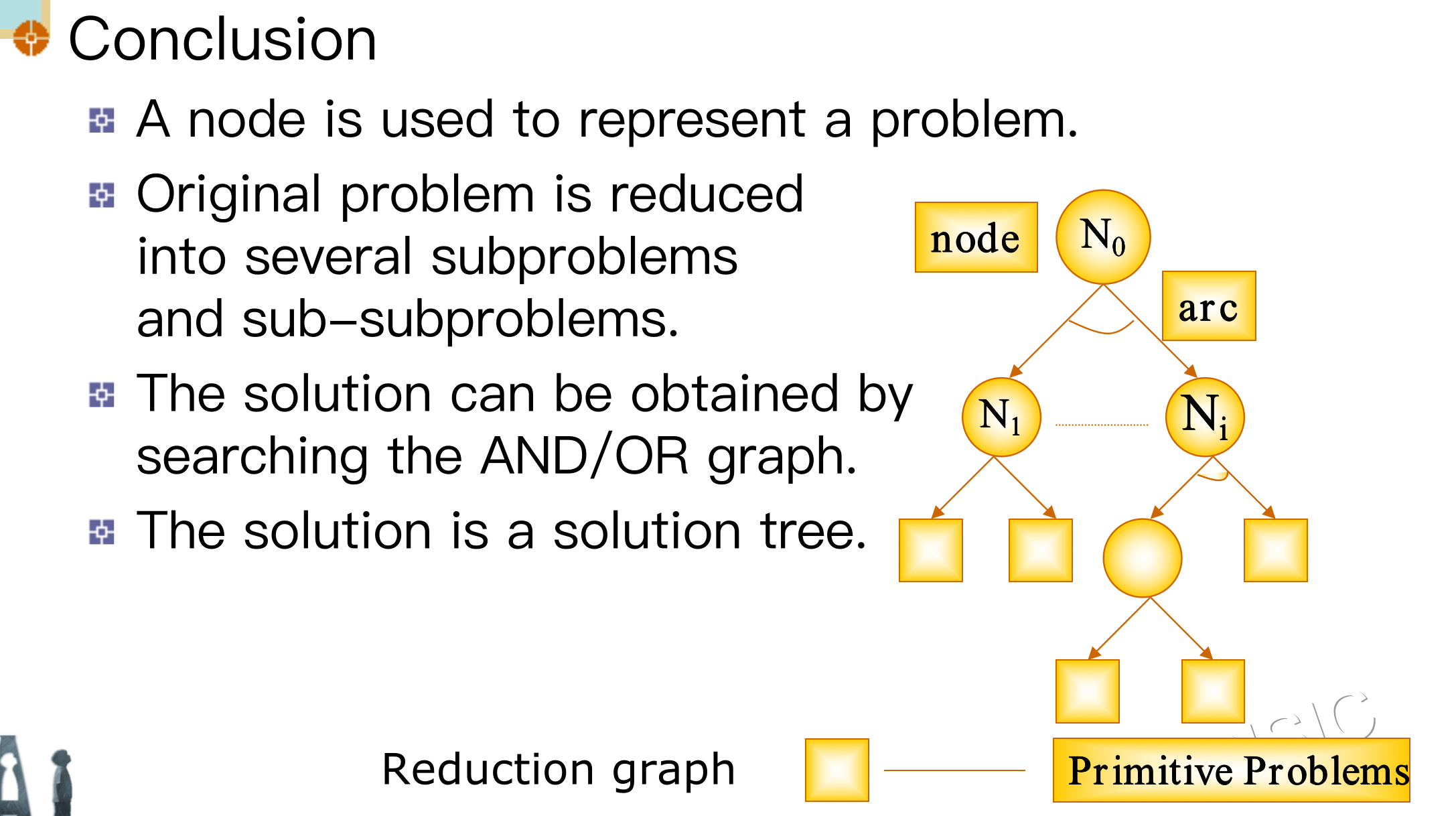
0 知识
啥是知识啊
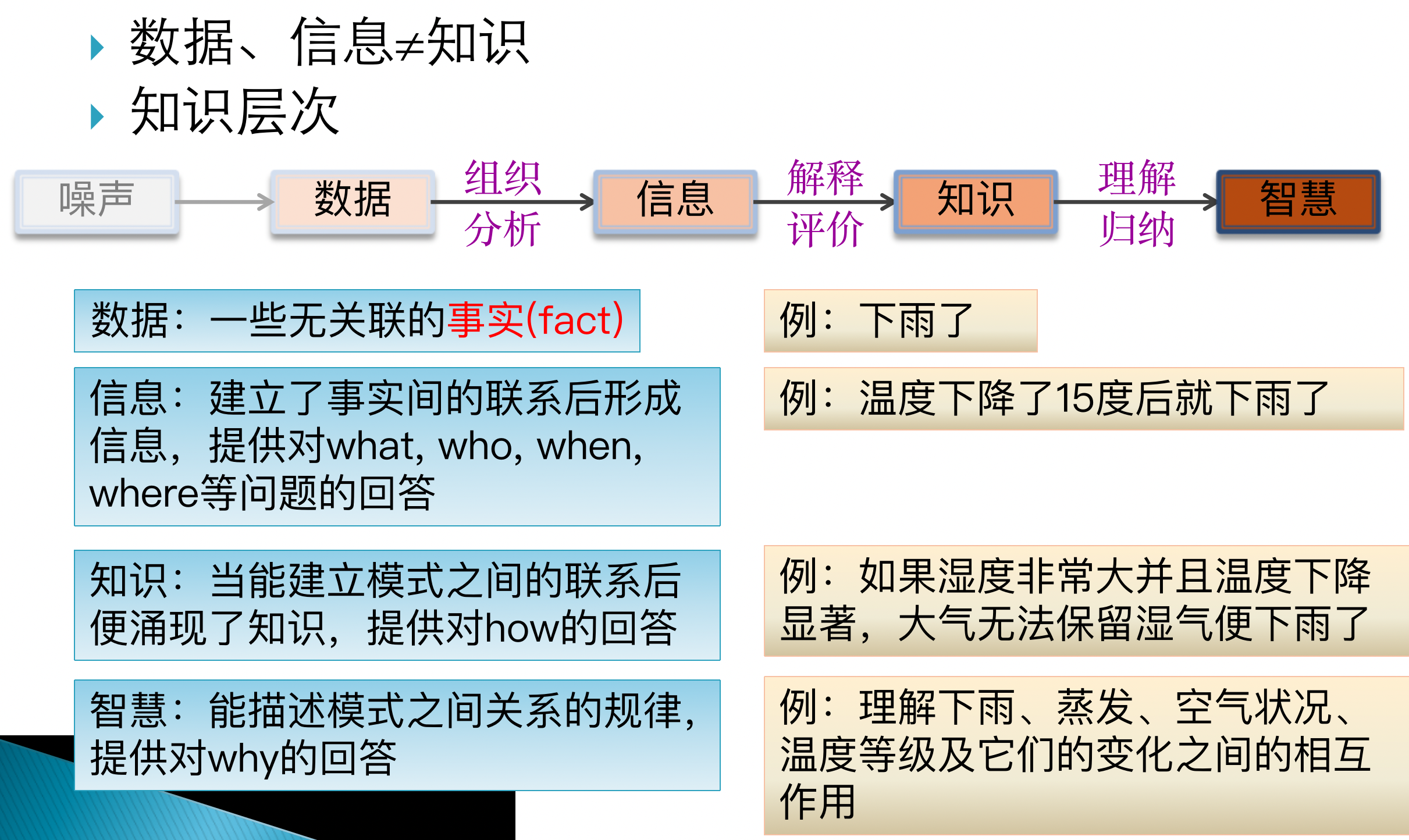
知识的属性

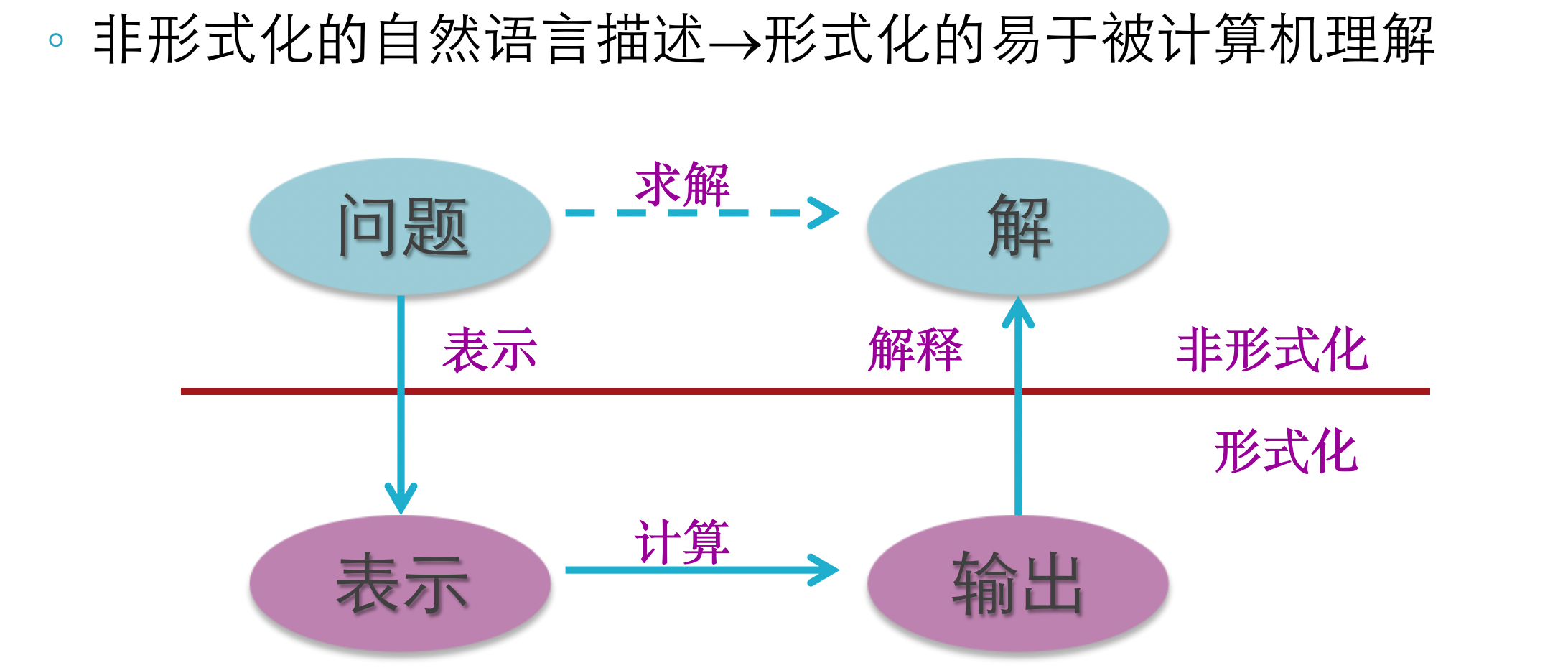
知识表示

-
知识表示的过程
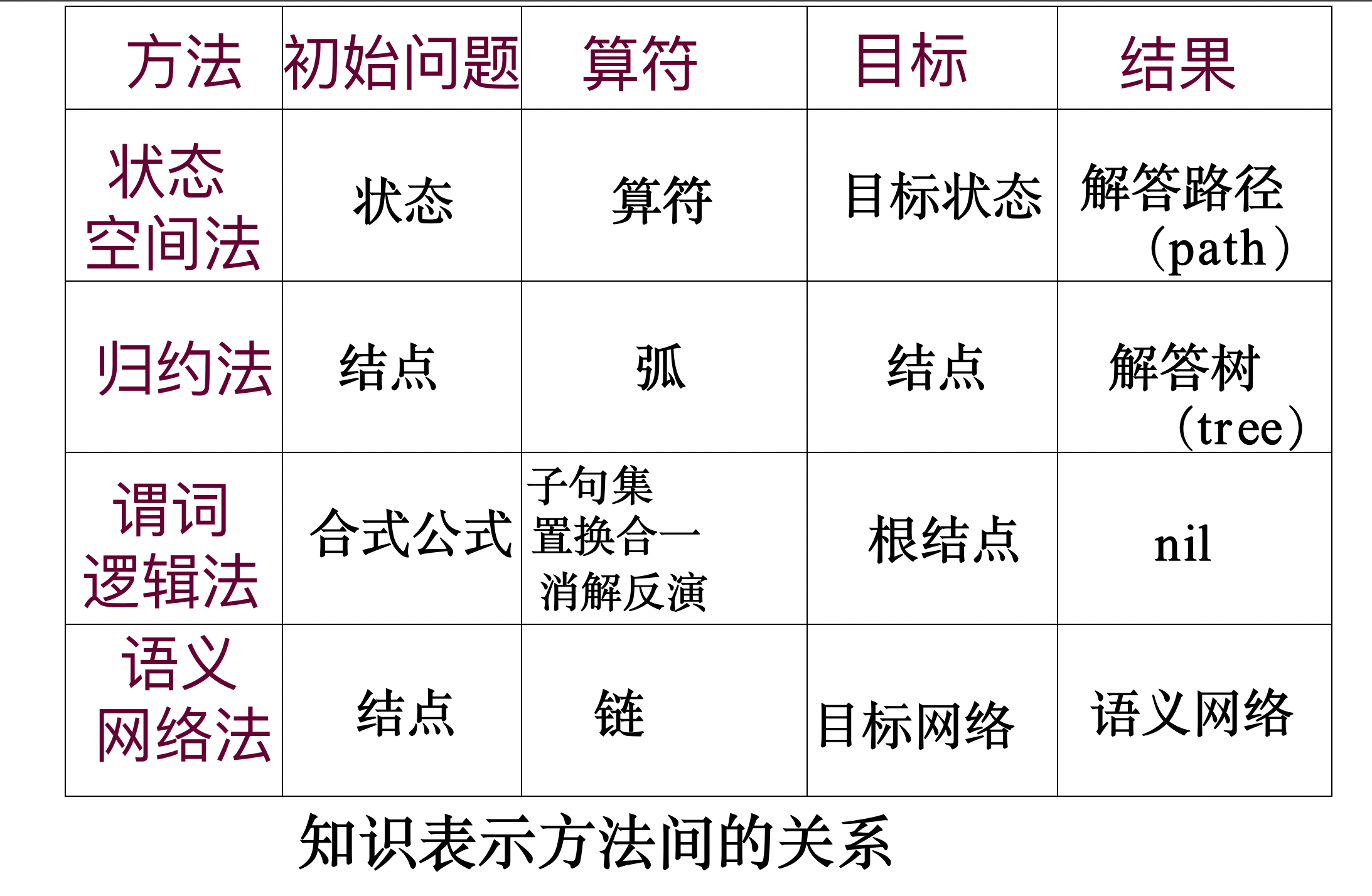
Basic Methodologies� 主要知识表示方法

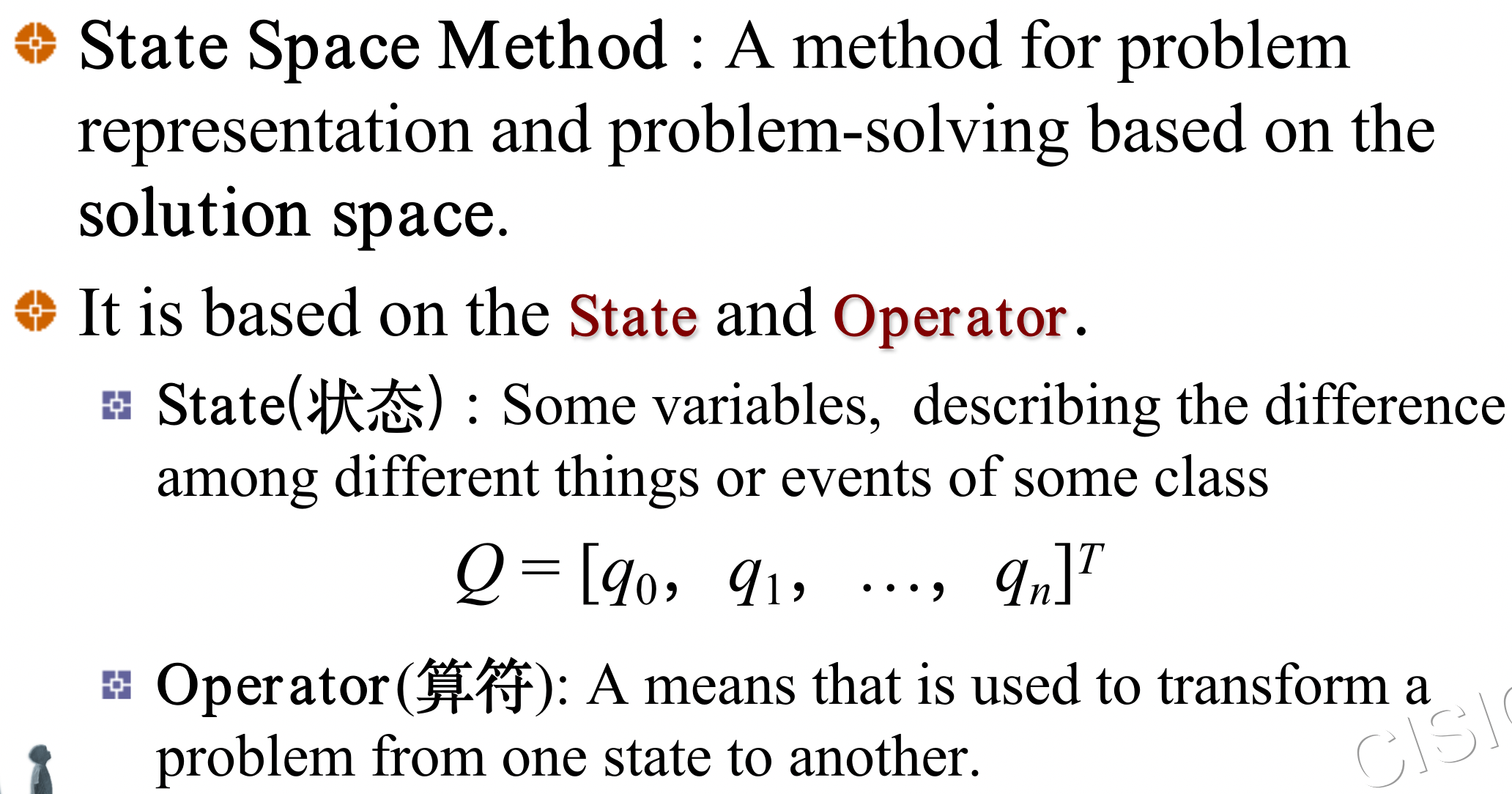
1 State Space Representation 状态空间表示
1.1 状态问题描述
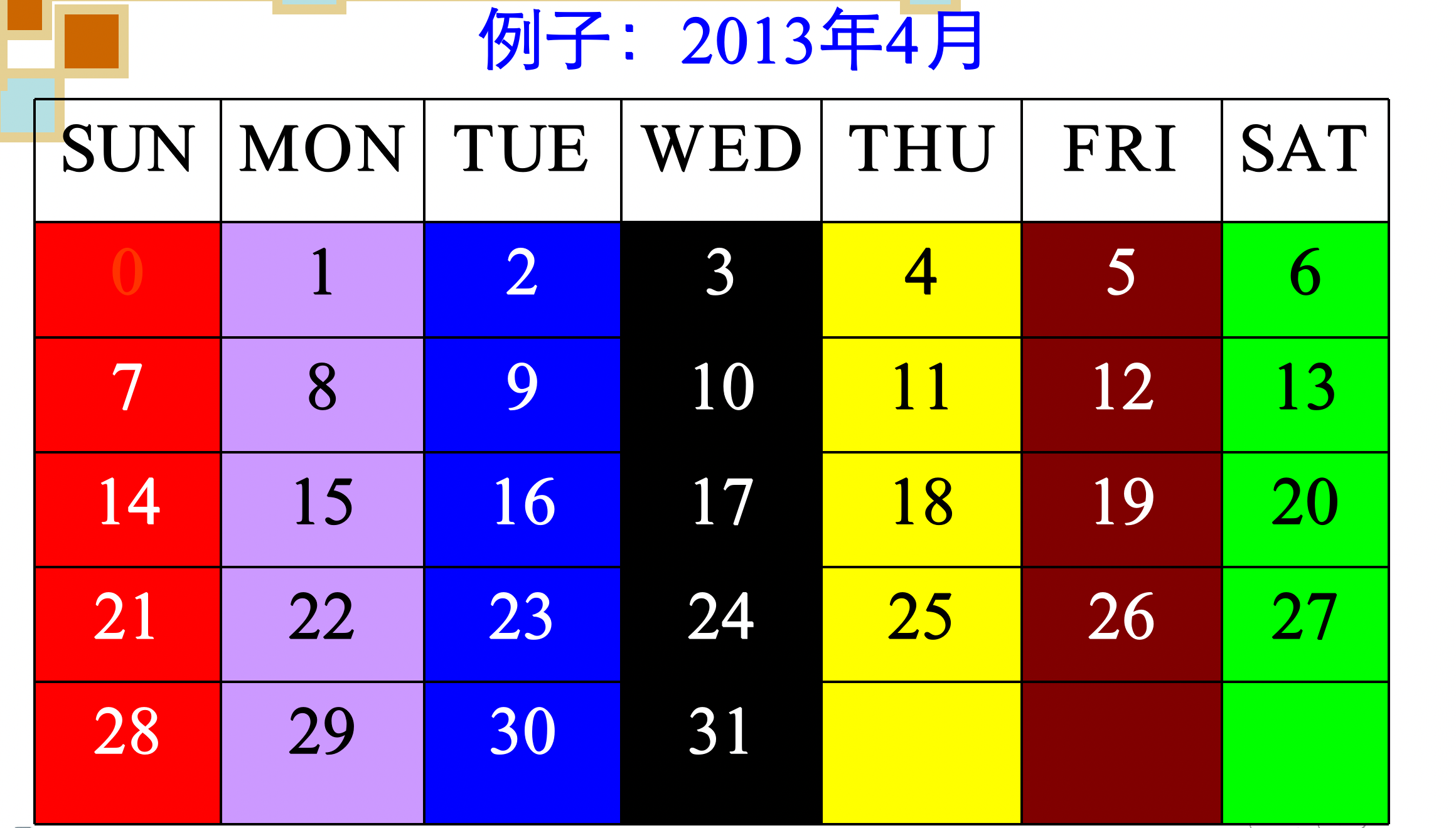
1.1.1 月历魔柱
1.1.2 8 Puzzle Problem (8数码难题)
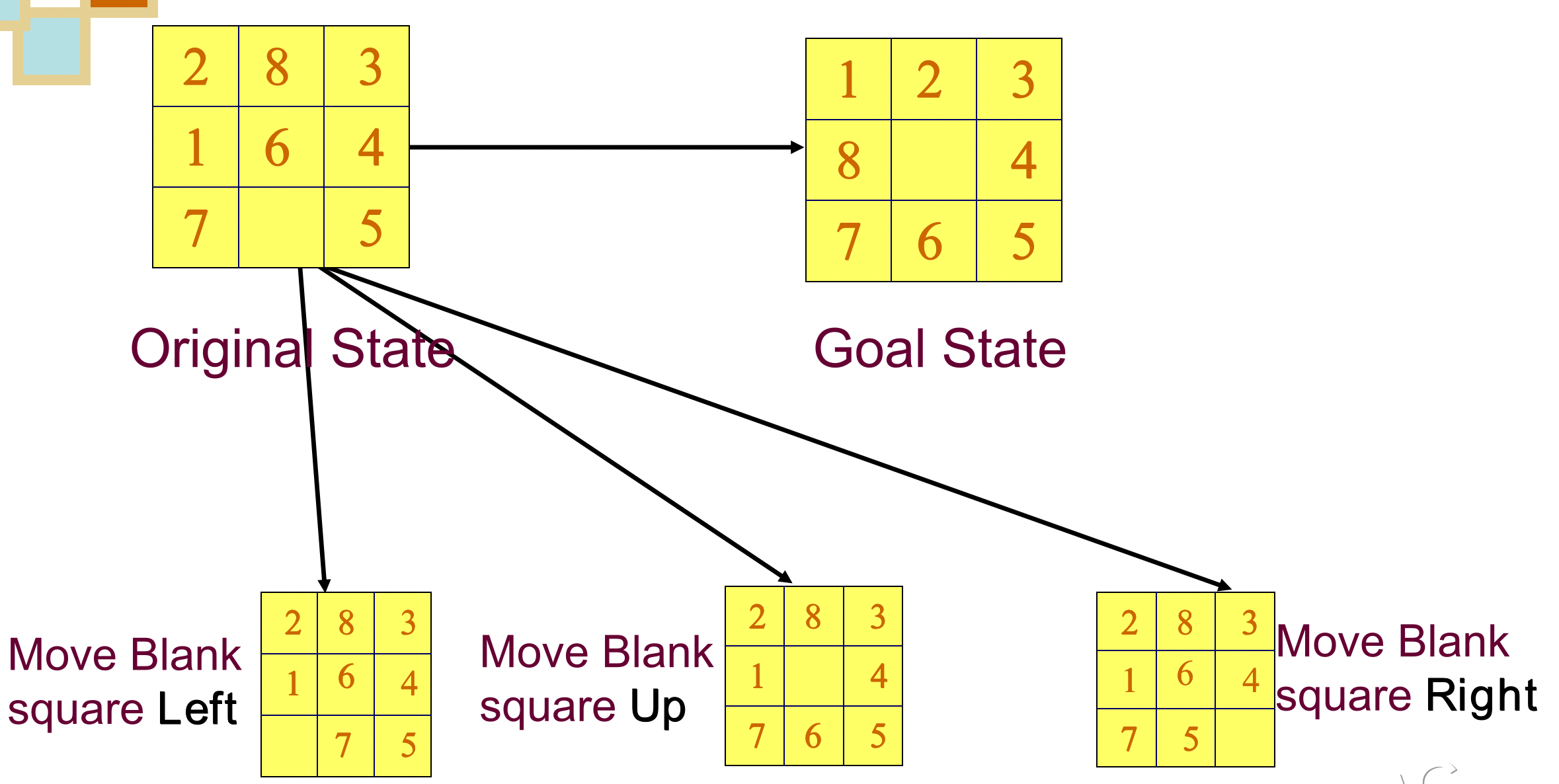
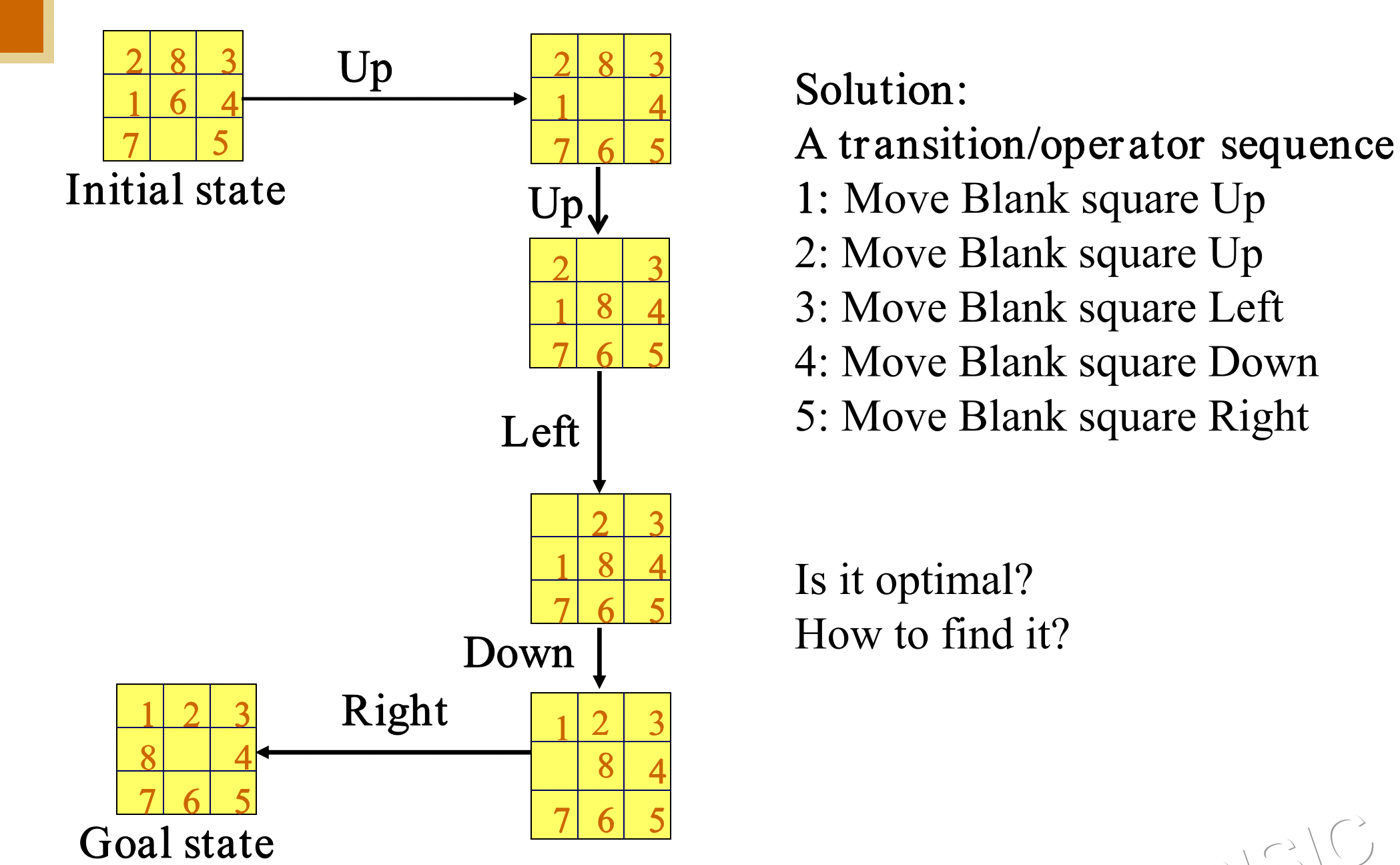
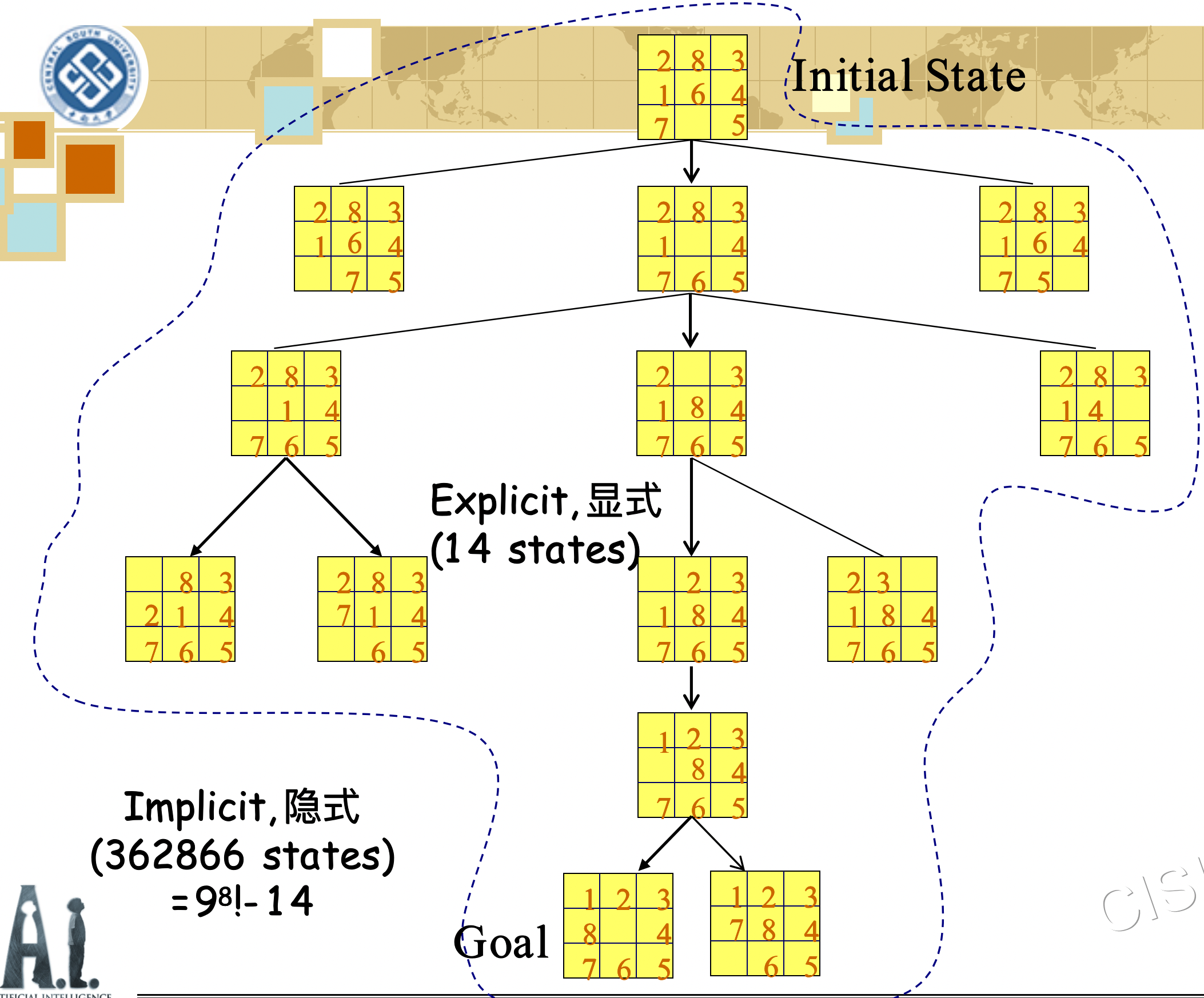
1.1.3 15 Puzzle Problem (15数码难题)
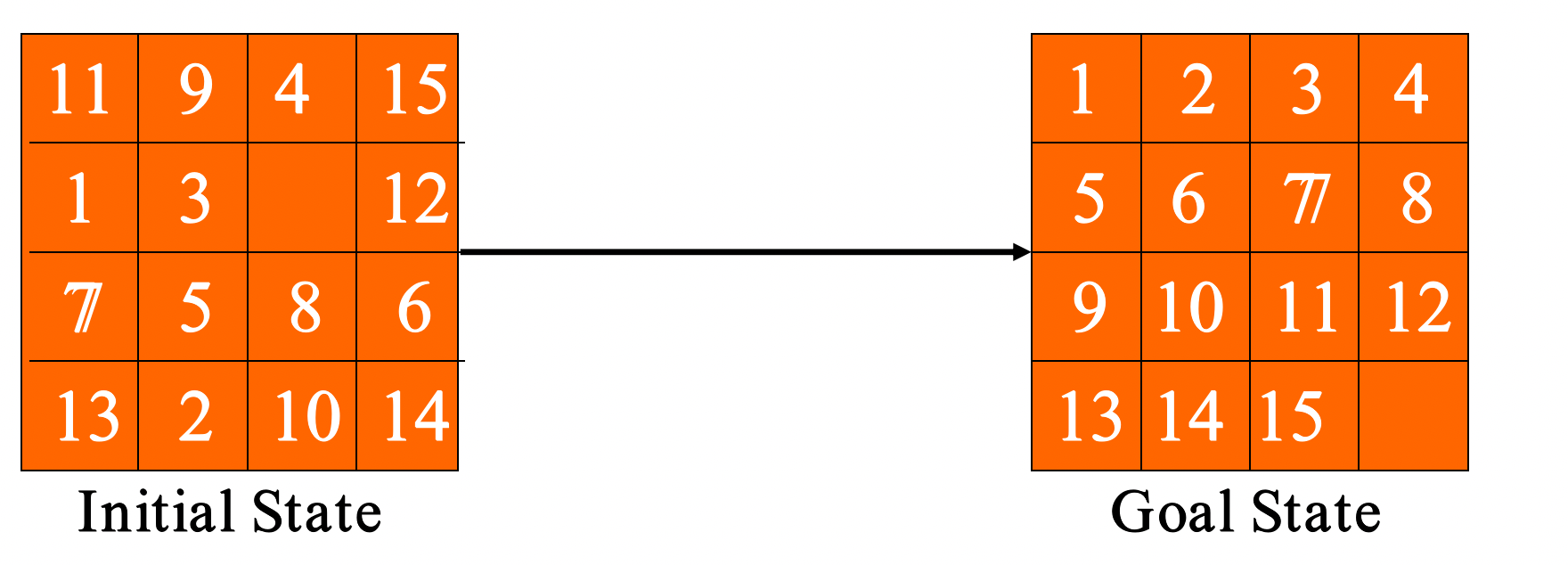
15-puzzle problem

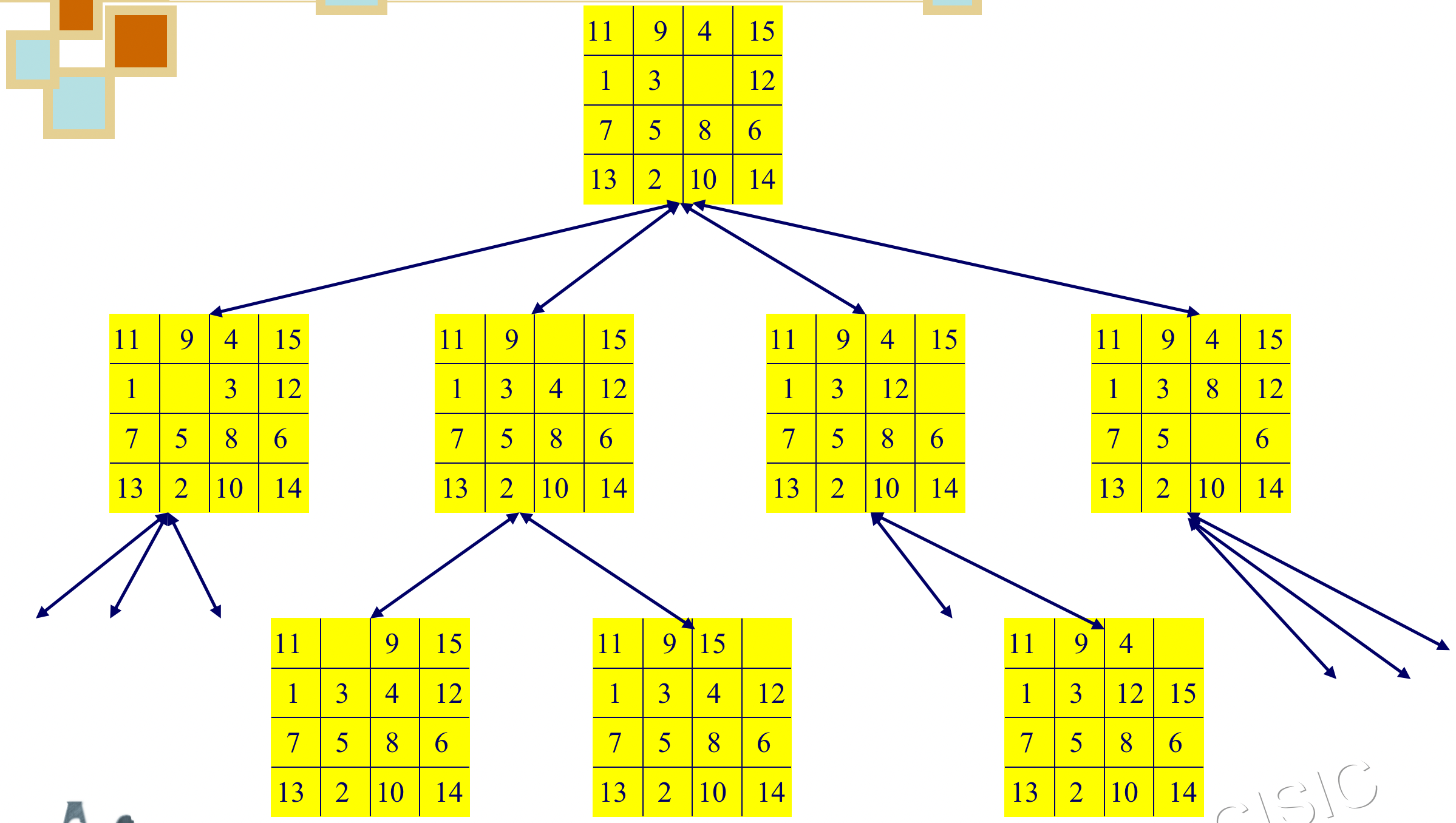
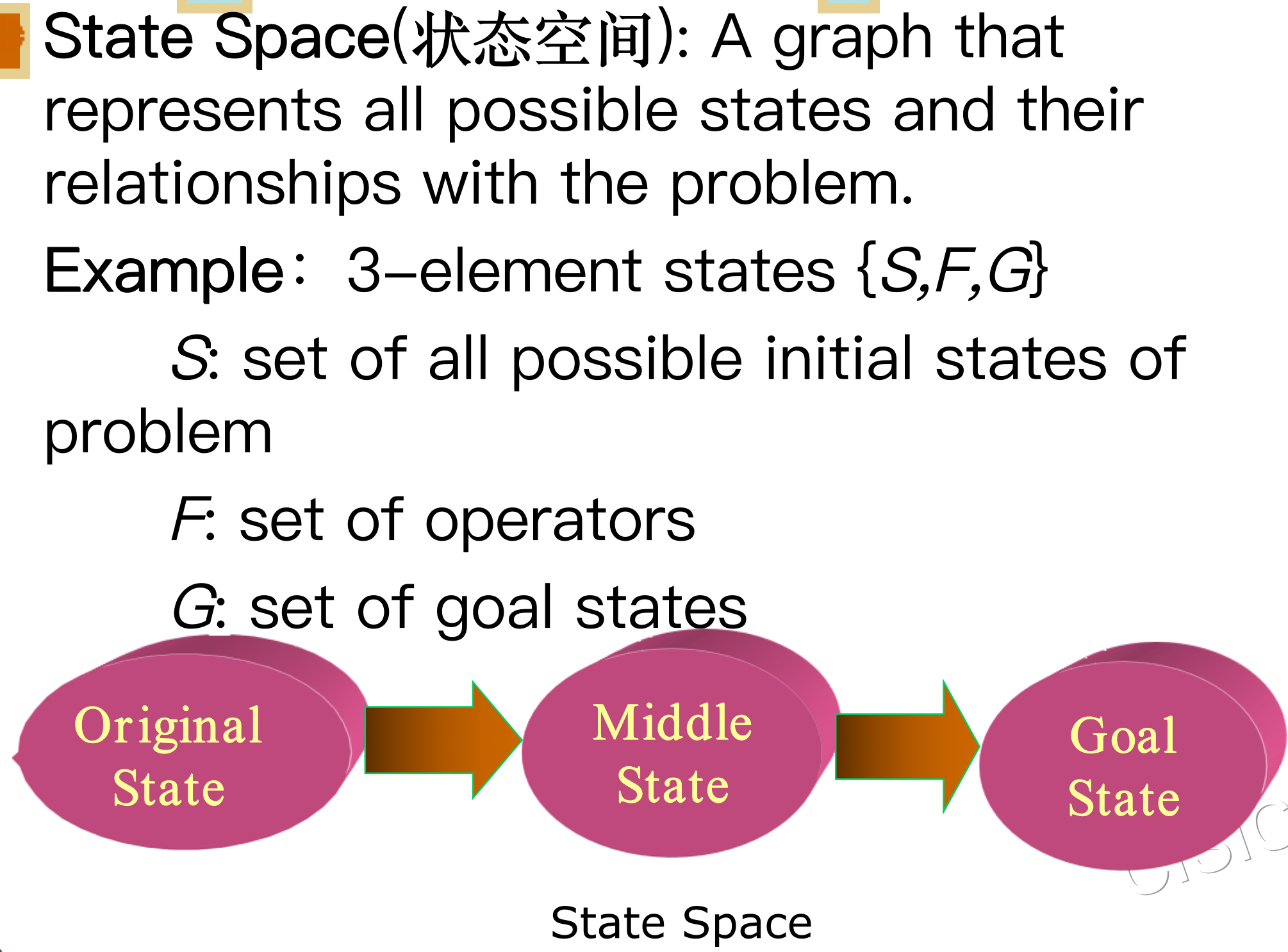
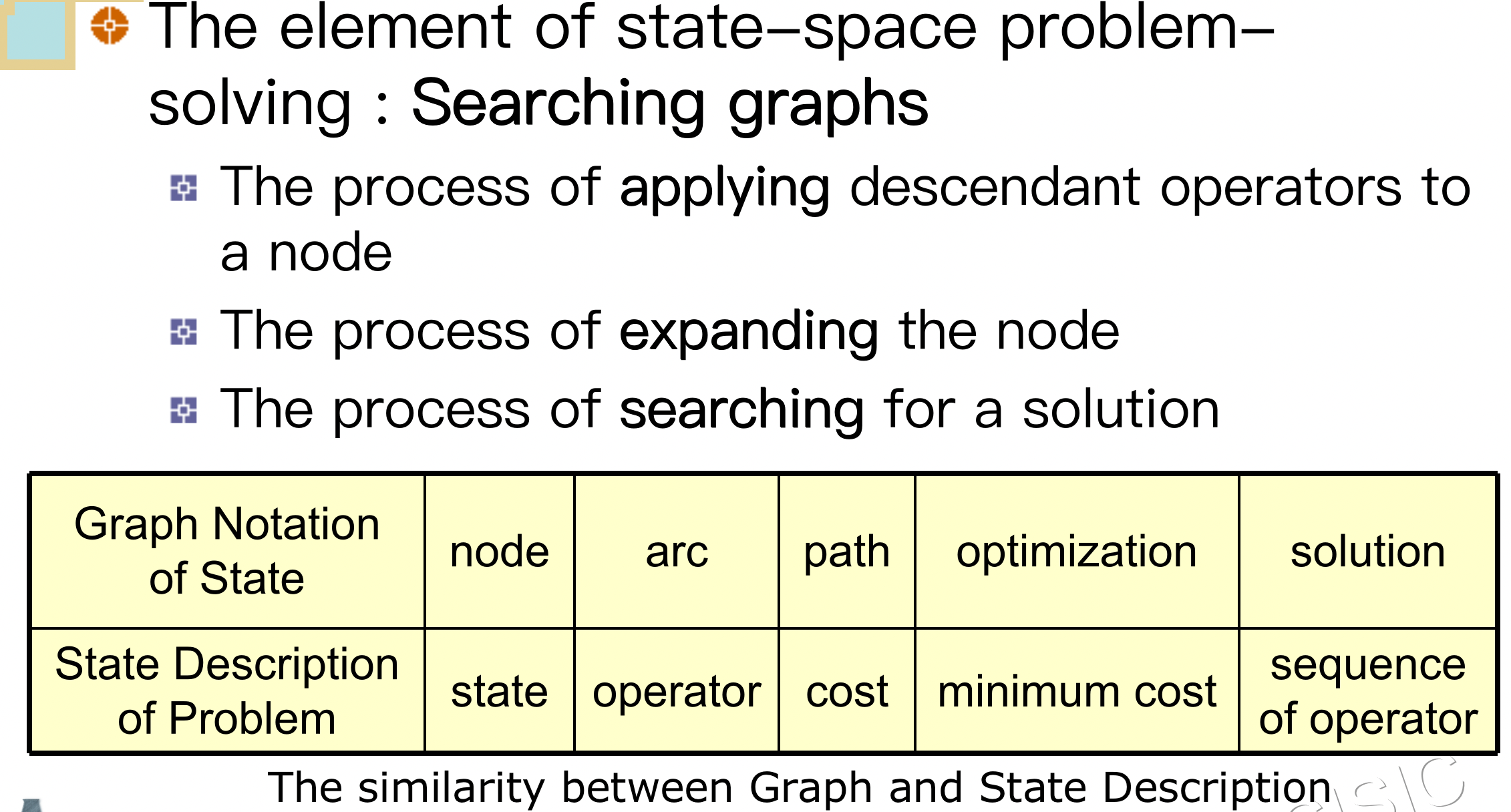
1.2 Graph Notion of State 状态图示法

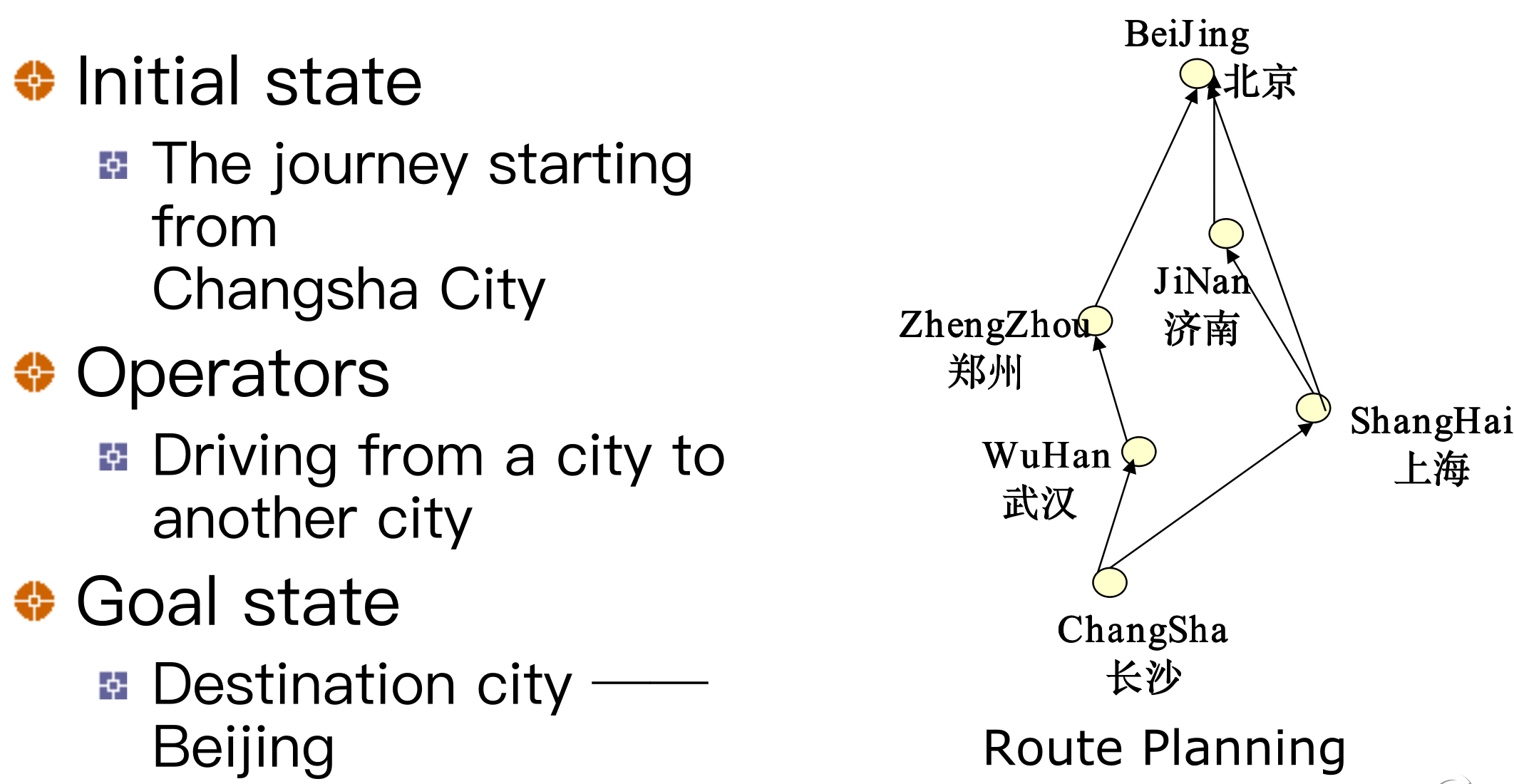
Example 1 – Route Planning 例1 路线规划
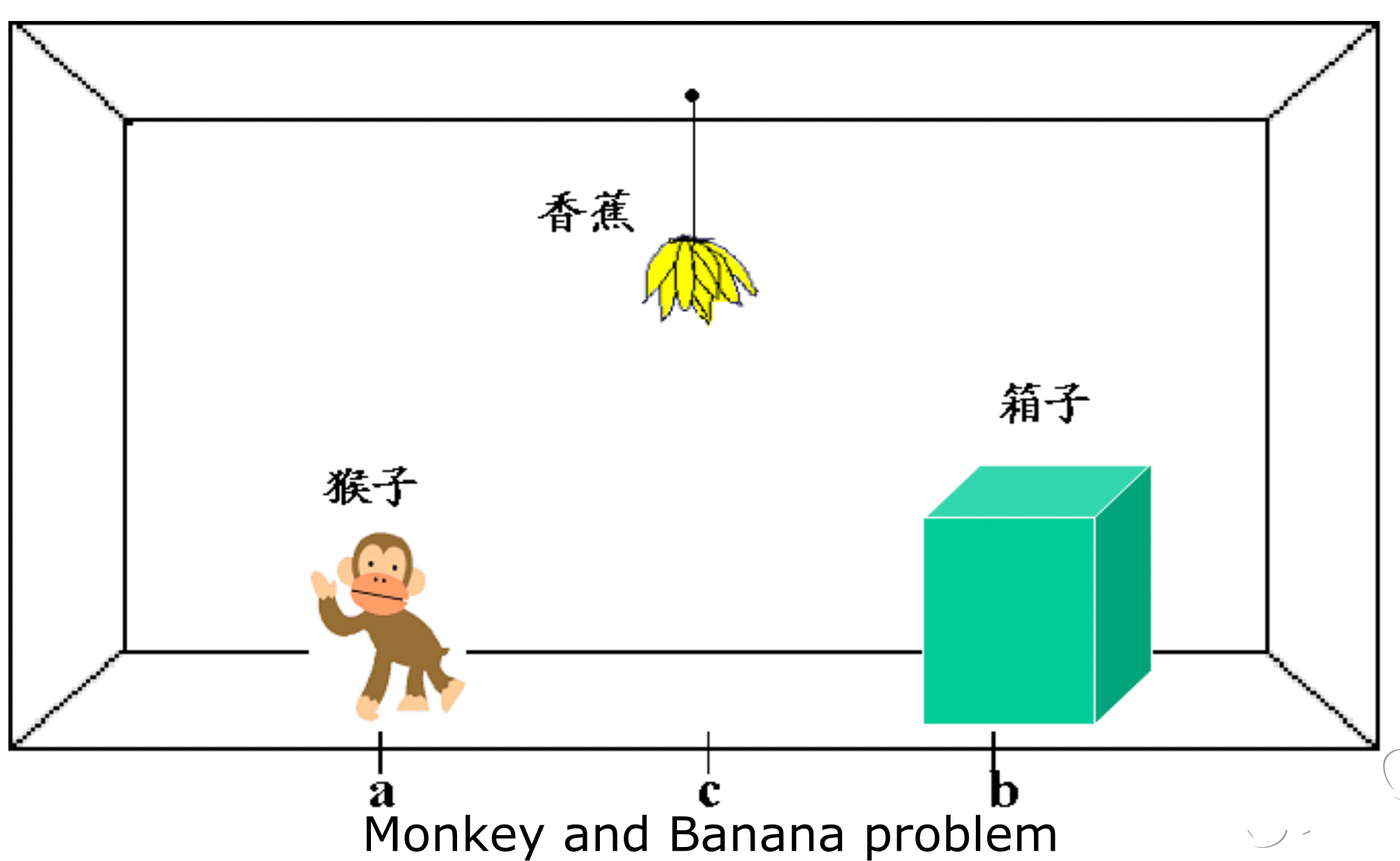
Example 2 – Monkey & Banana� 例2 猴子与香蕉问题



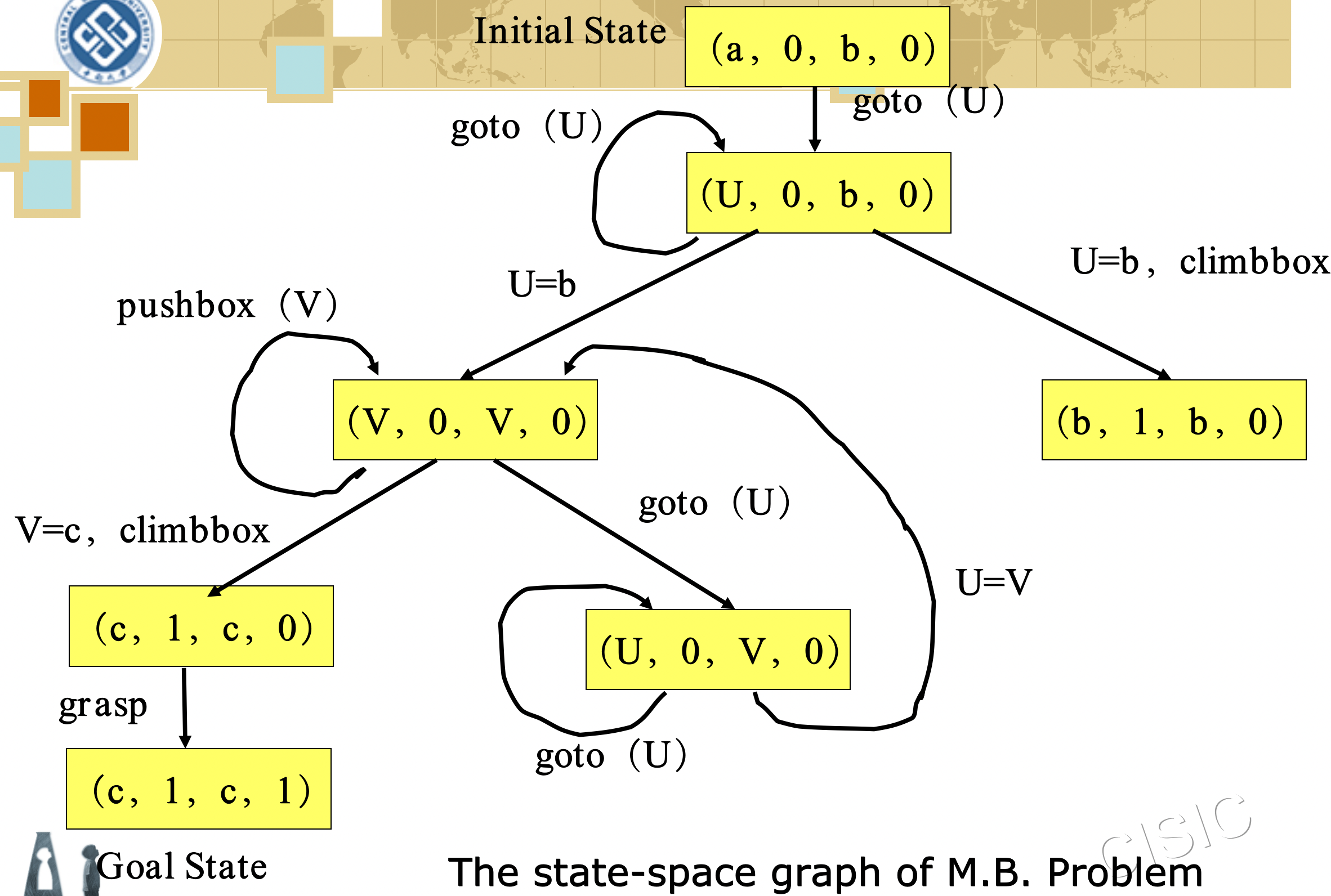
Example 3 Missionaries& Cannibals

-
状态及其表示

-
状态的转换

-
传教士野人问题状态空间图
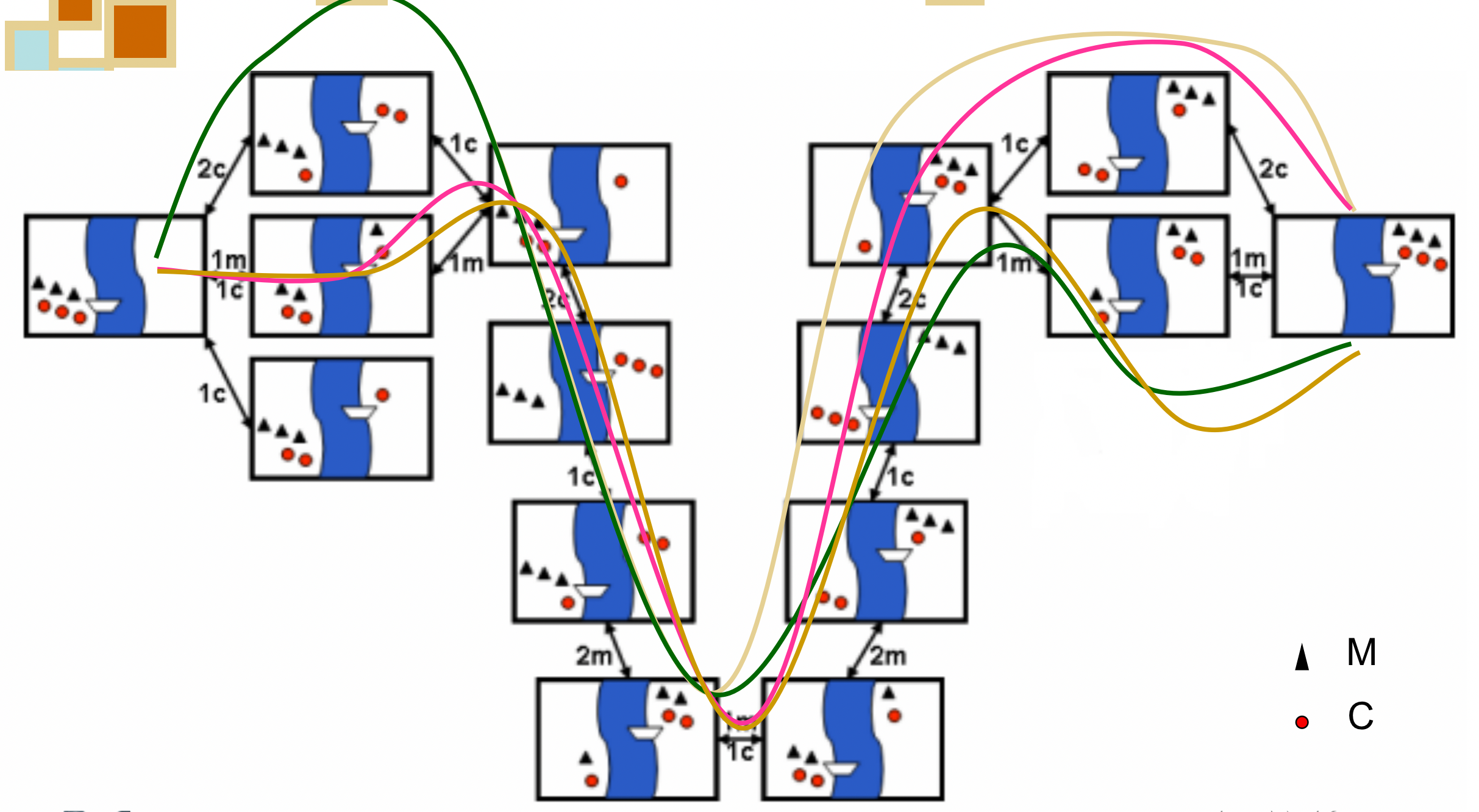
2 Problem Reduction 问题归约法
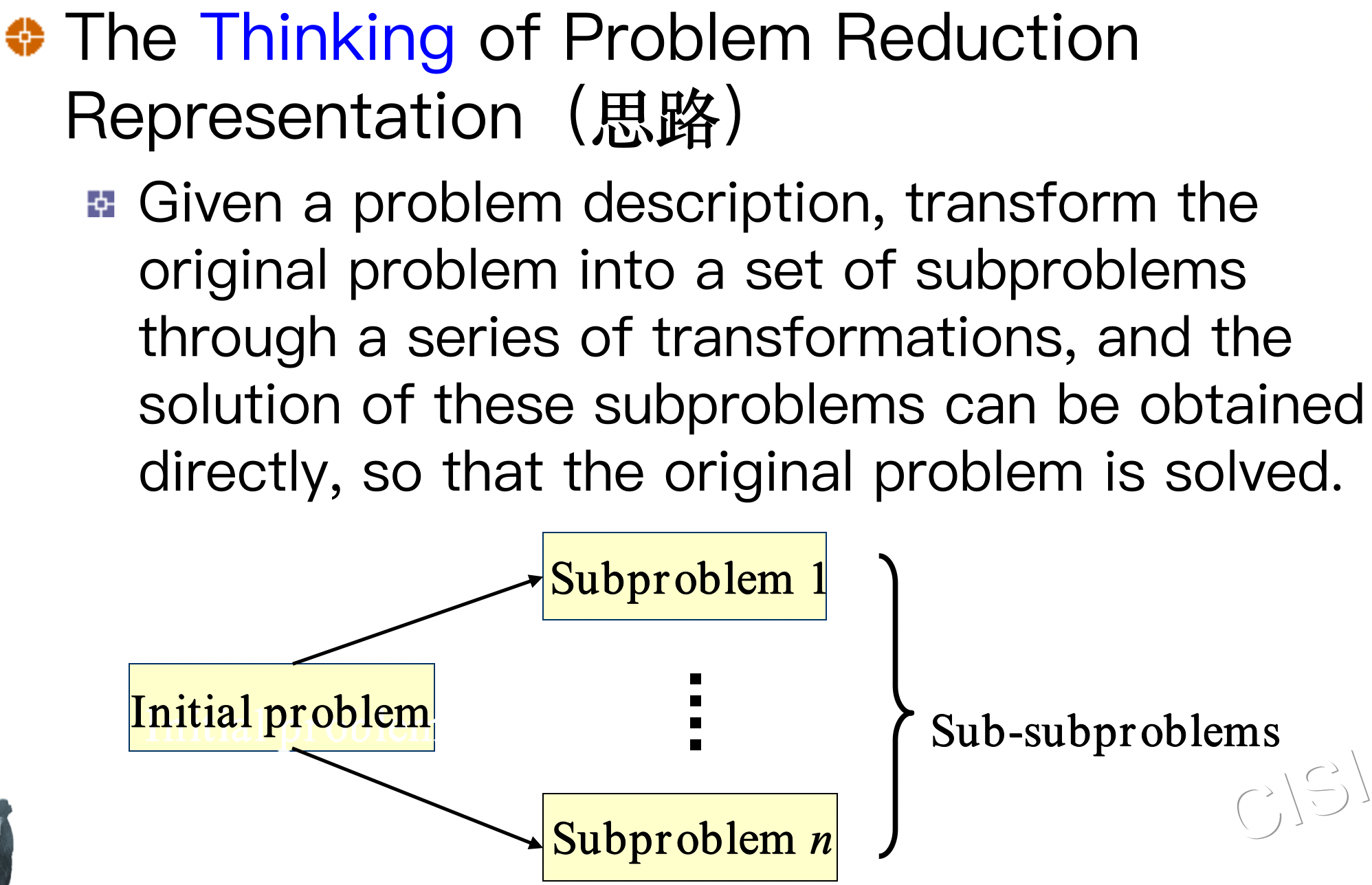

Working Mechanism-Reduction 变换机理-归约

Tower of Hanoi Puzzle( THP)(梵塔难题)
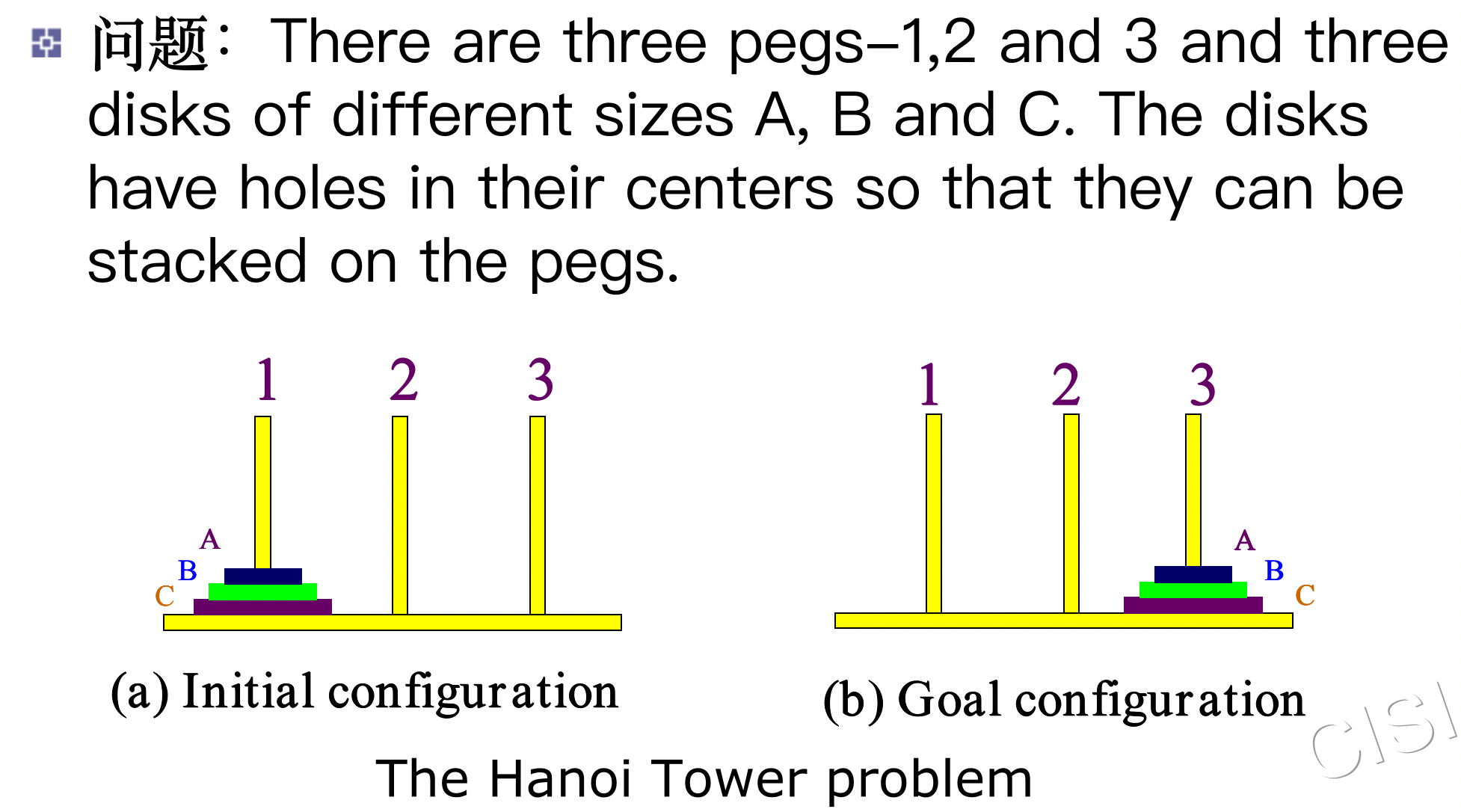
Three disk Hanoi-Tower(3圆盘梵塔难题)

Constrain Conditions(约束条件)

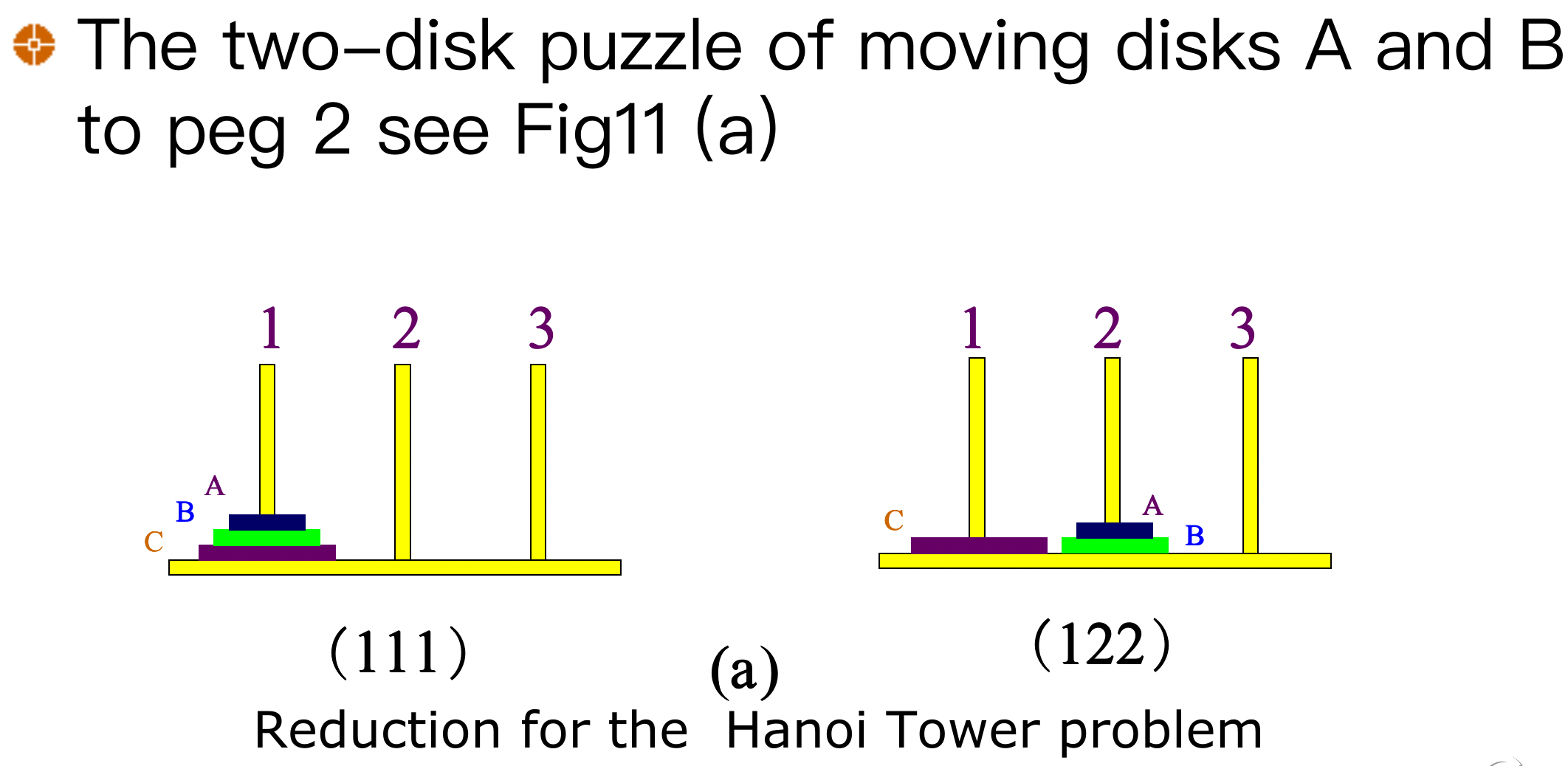
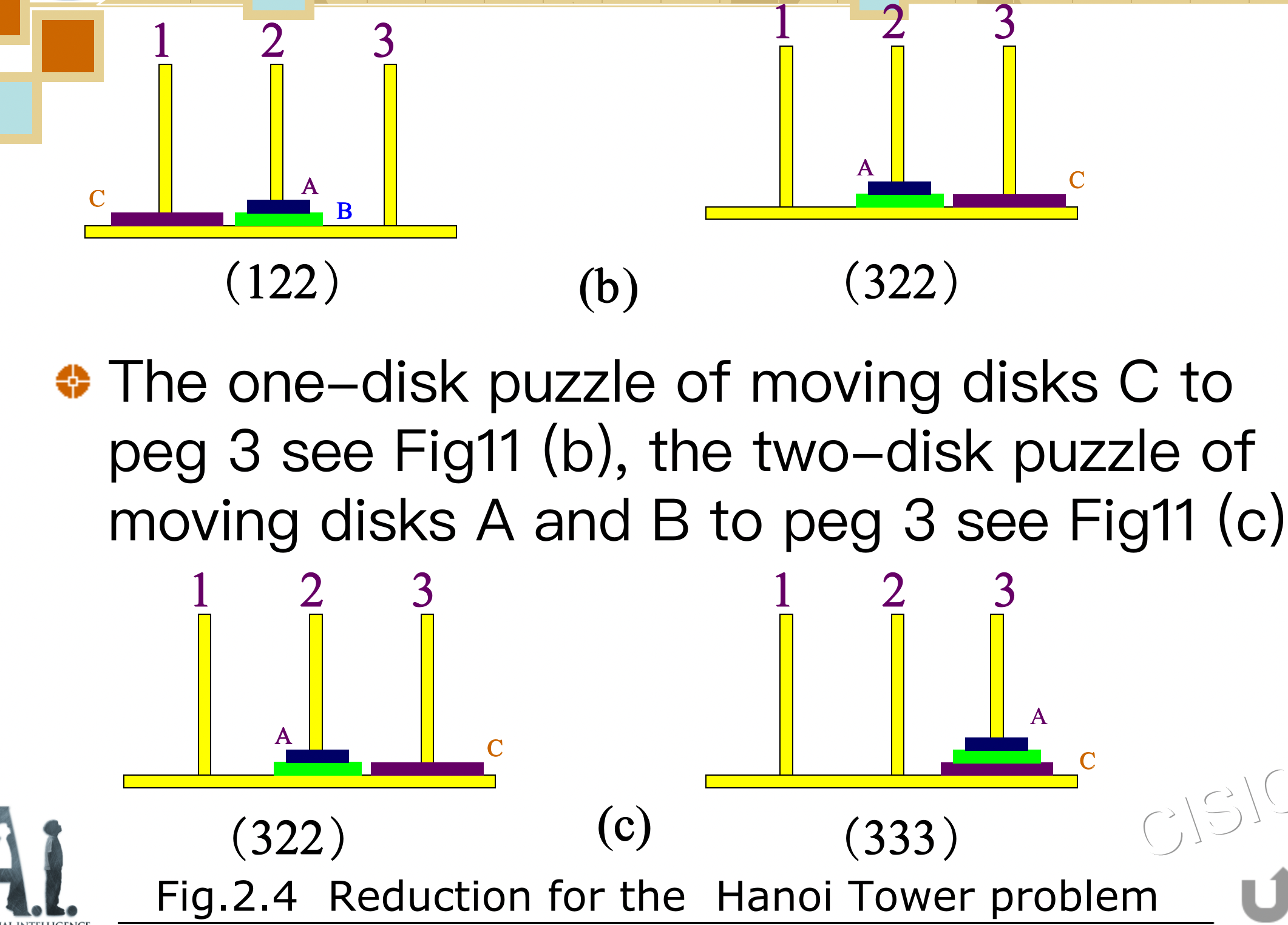
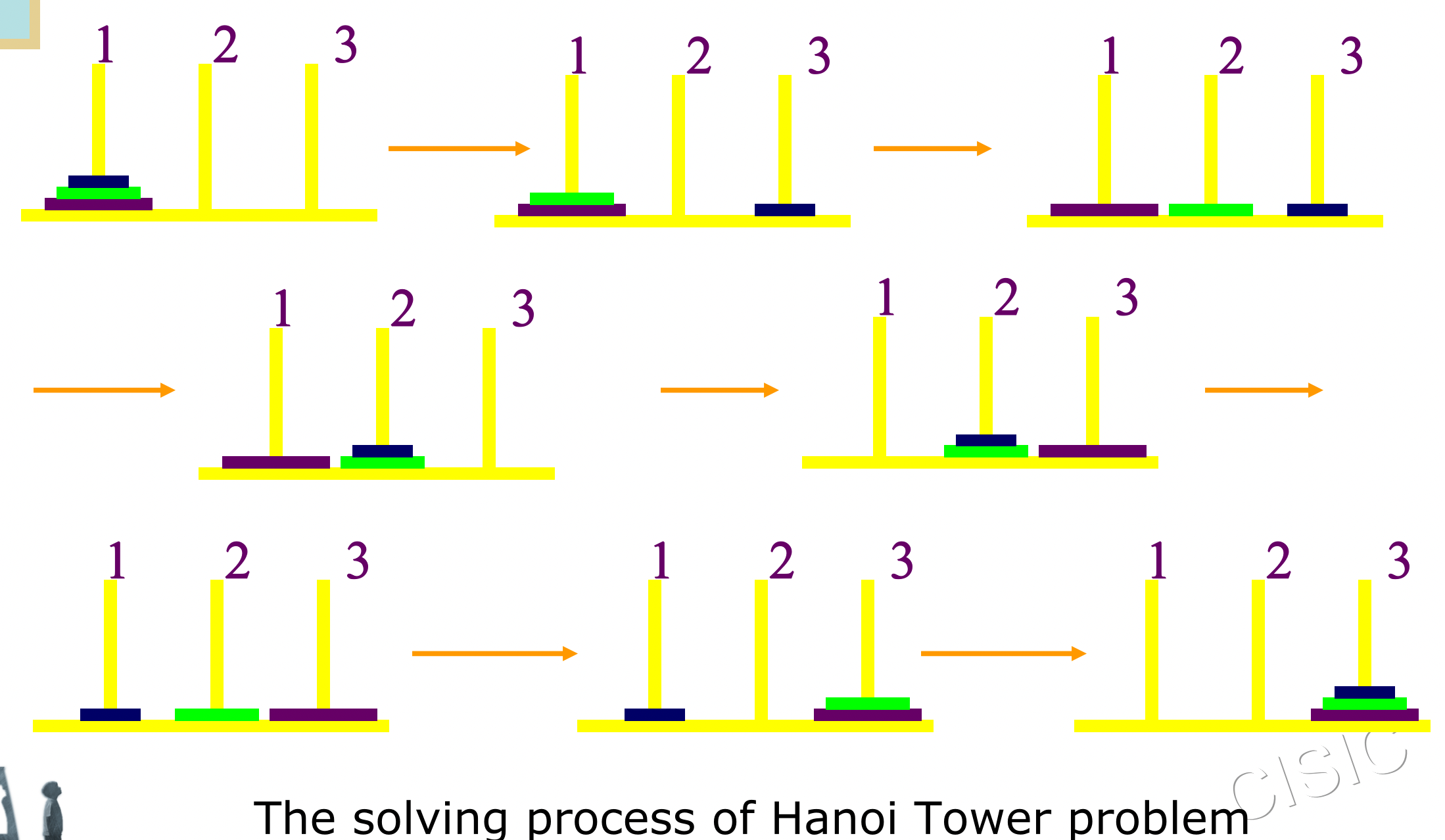

Four-disk Hanoi Tower
2.2 AND/OR Graph Representation� 与或图表示
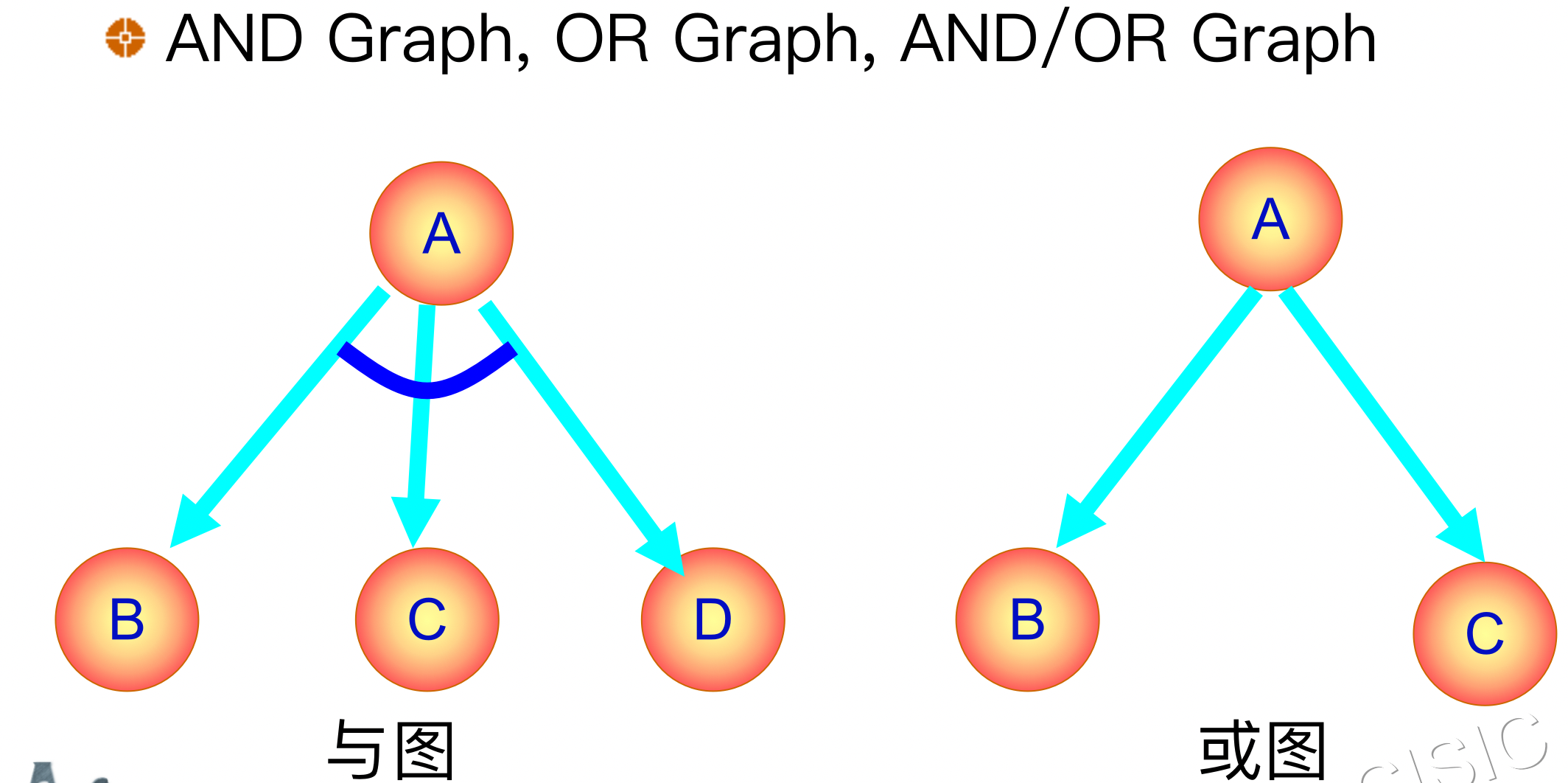
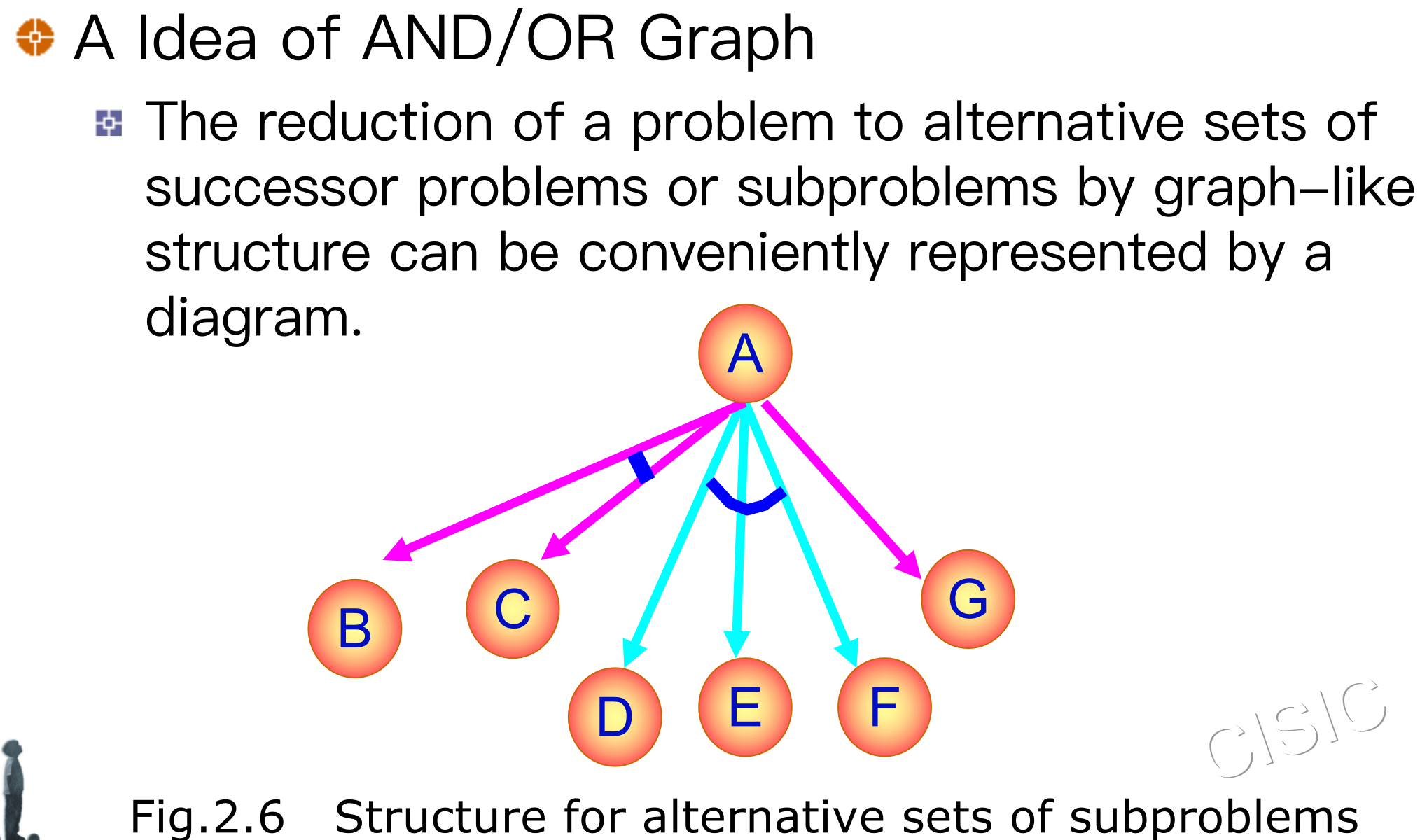
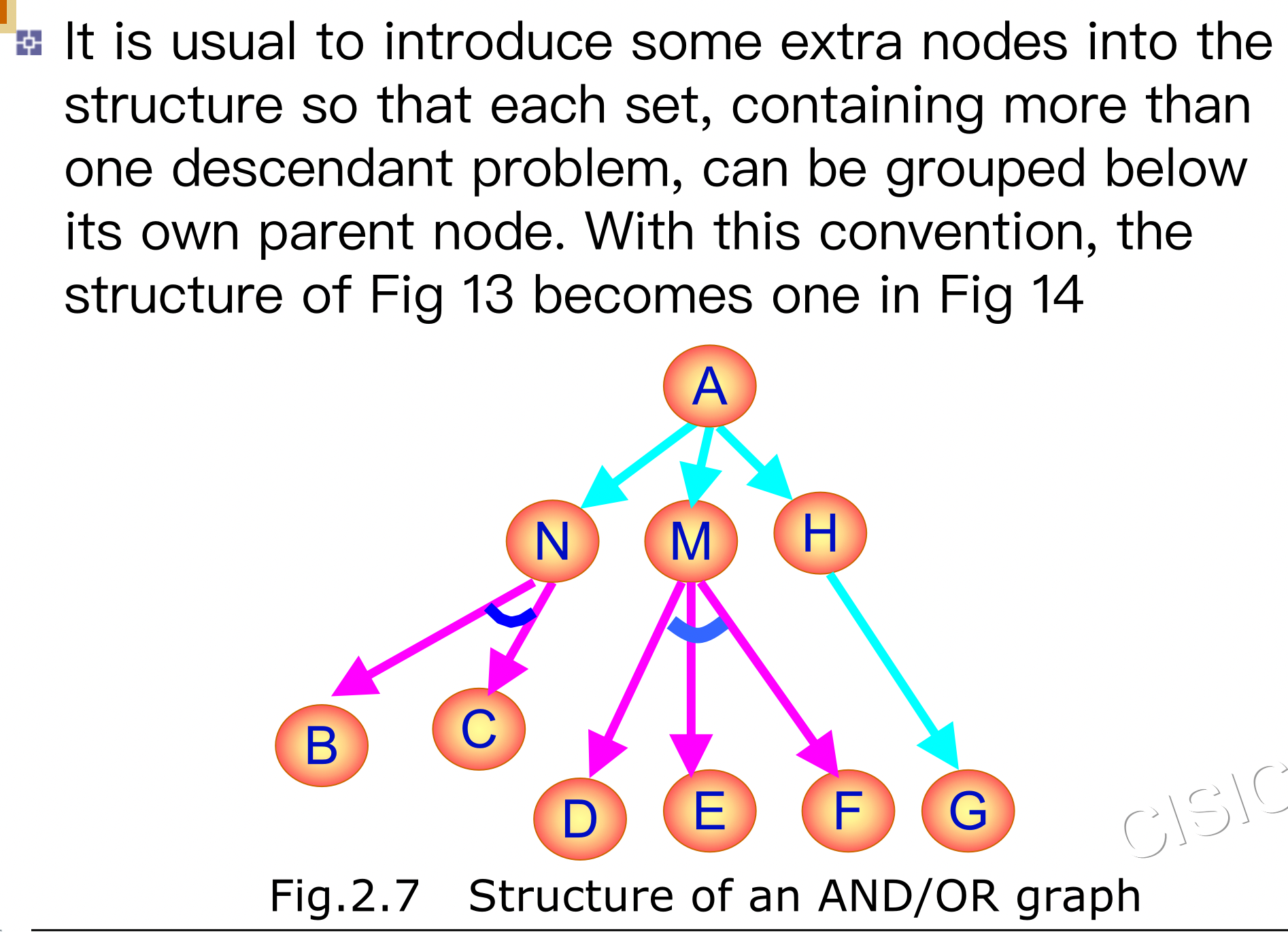
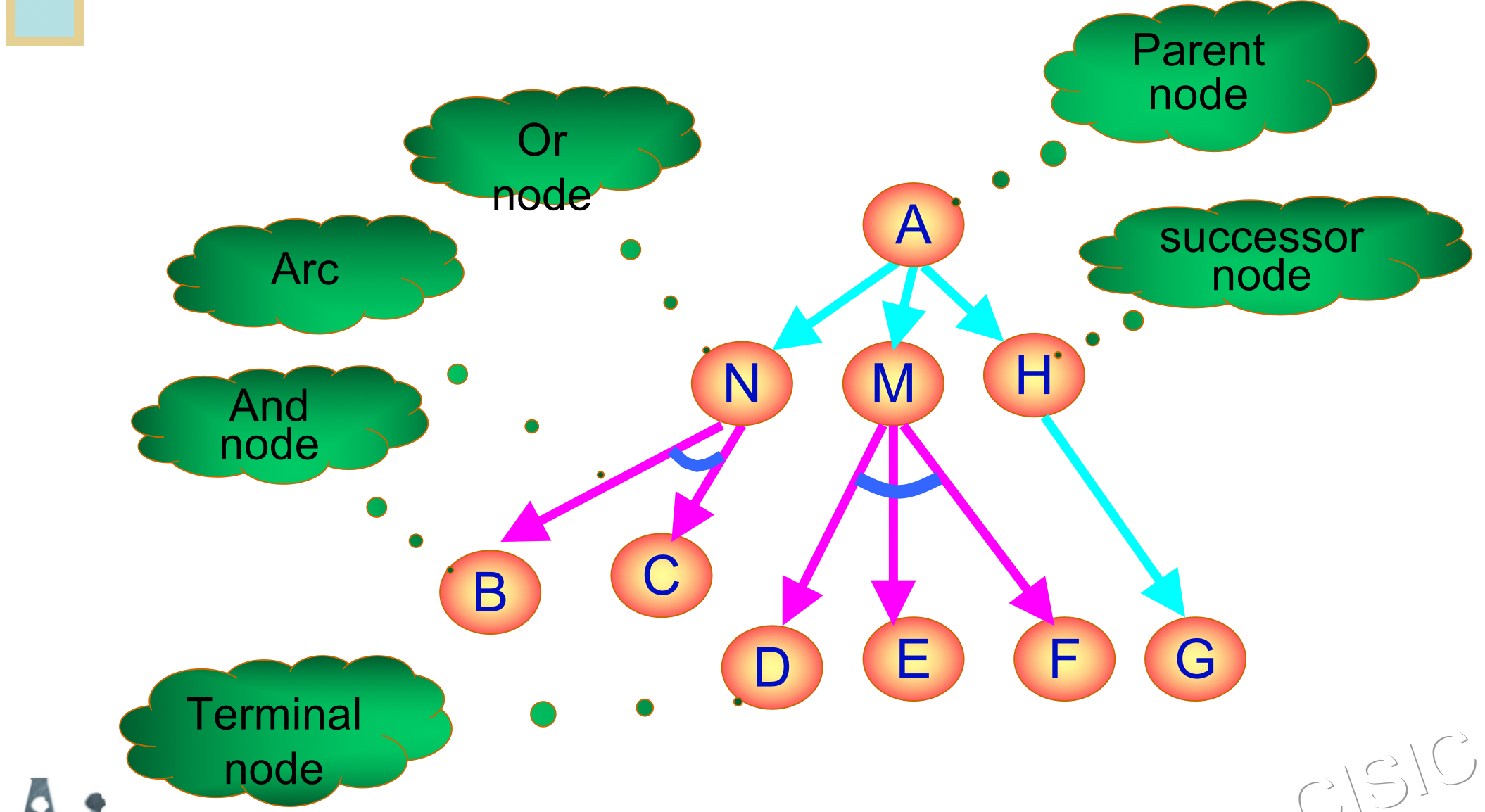
某些术语
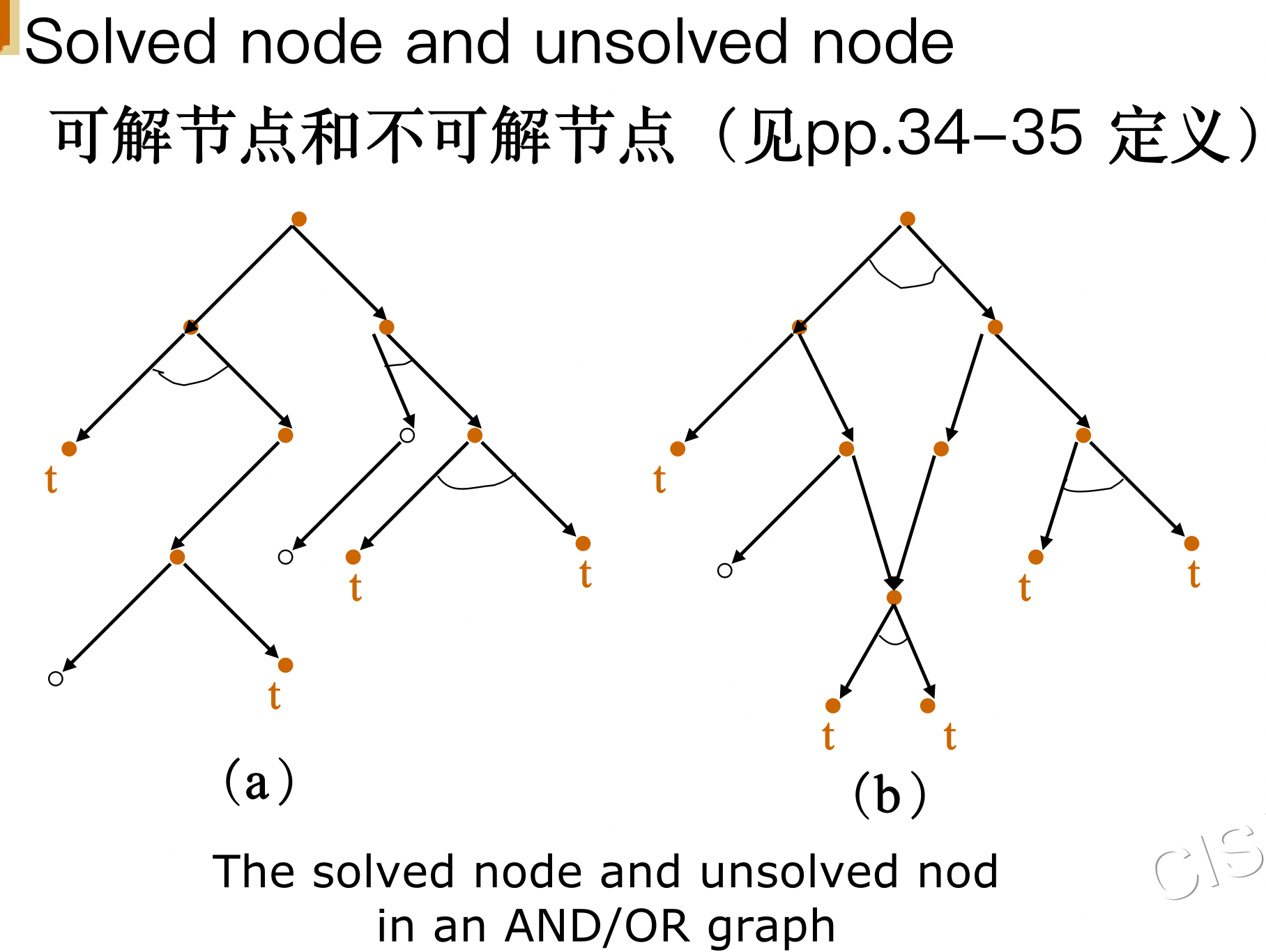

-
AND/OR Graph Representation� 3圆盘问题(注意数据结构)
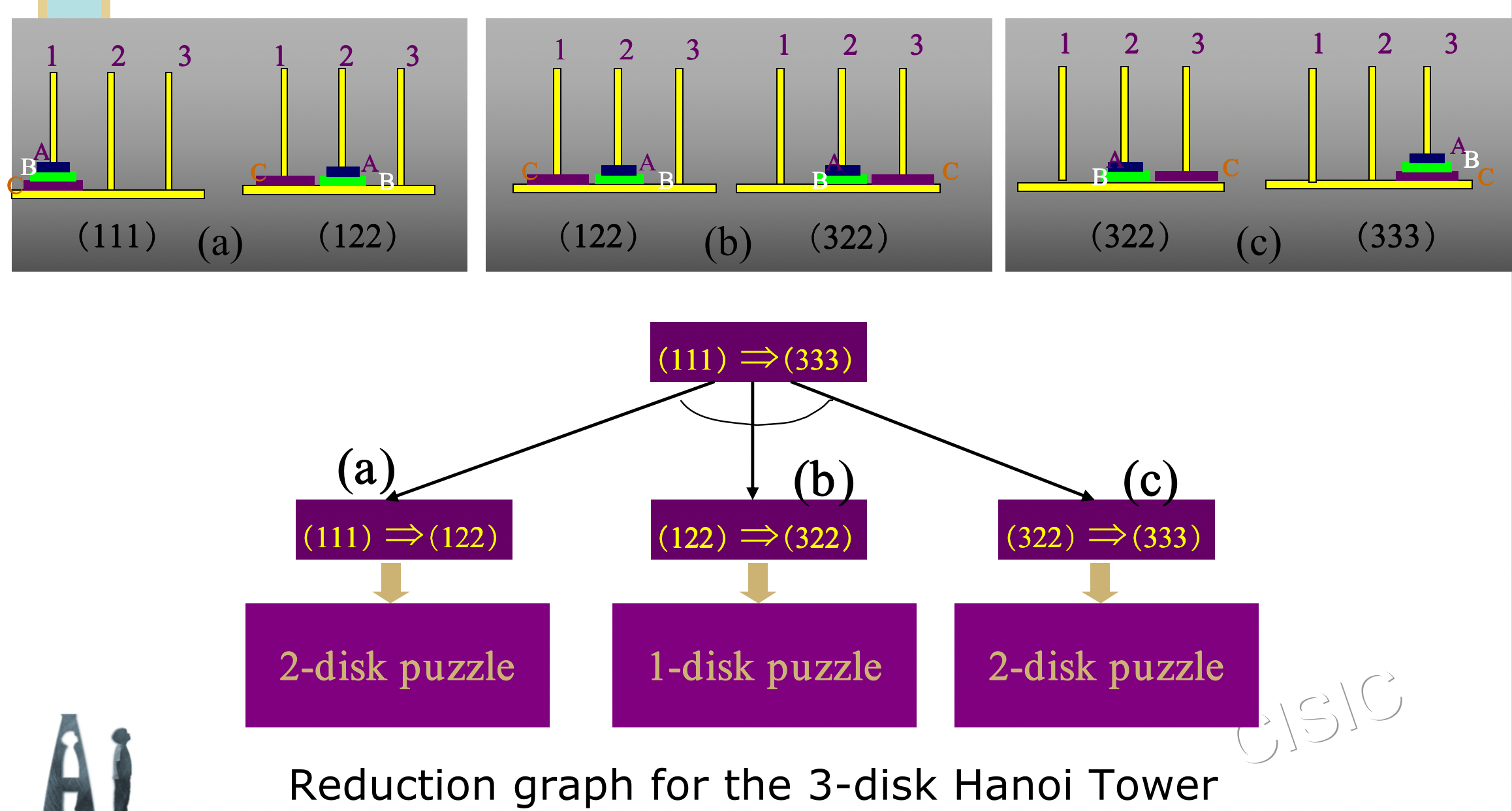
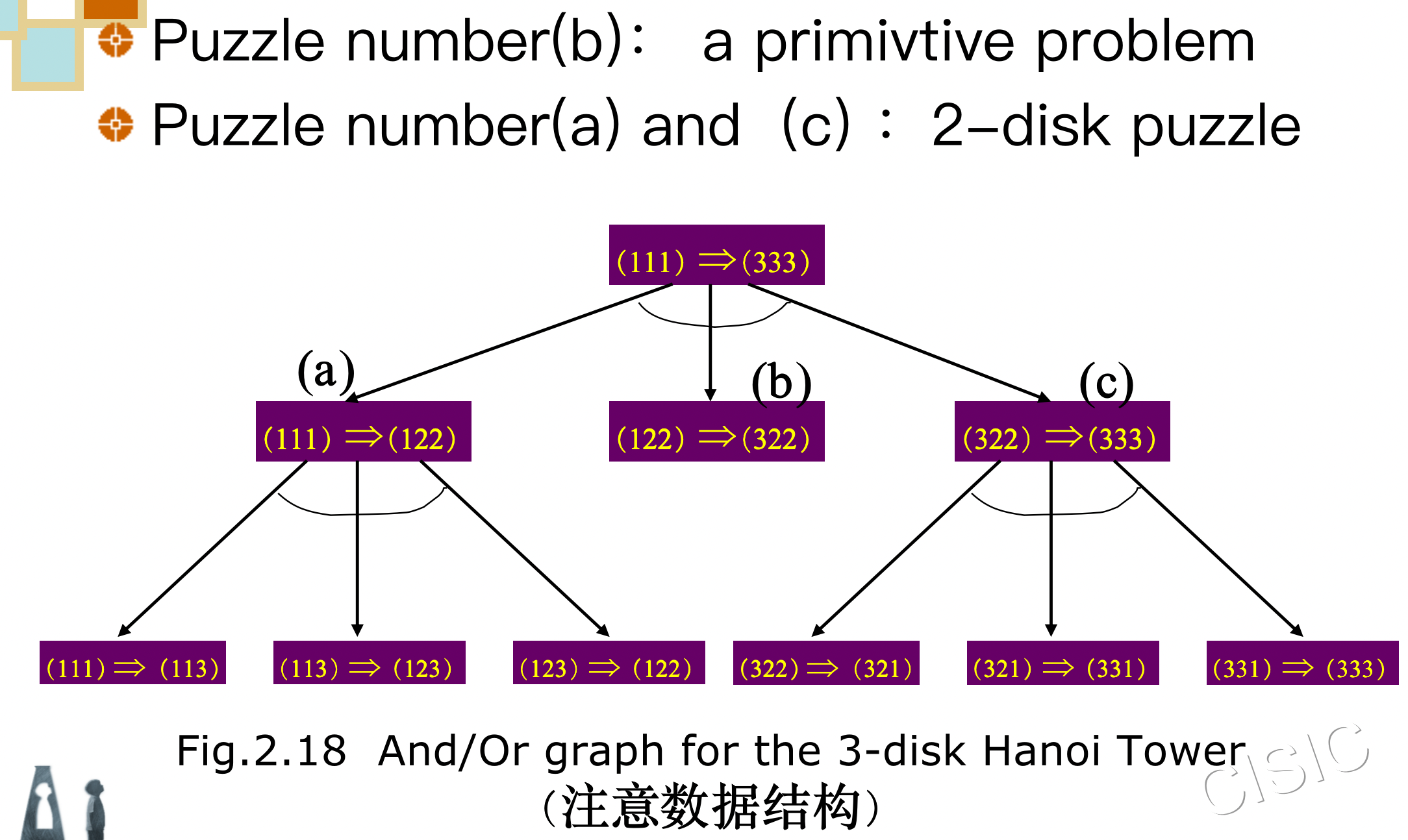
-
AND/OR Graph Representation� 4圆盘问题
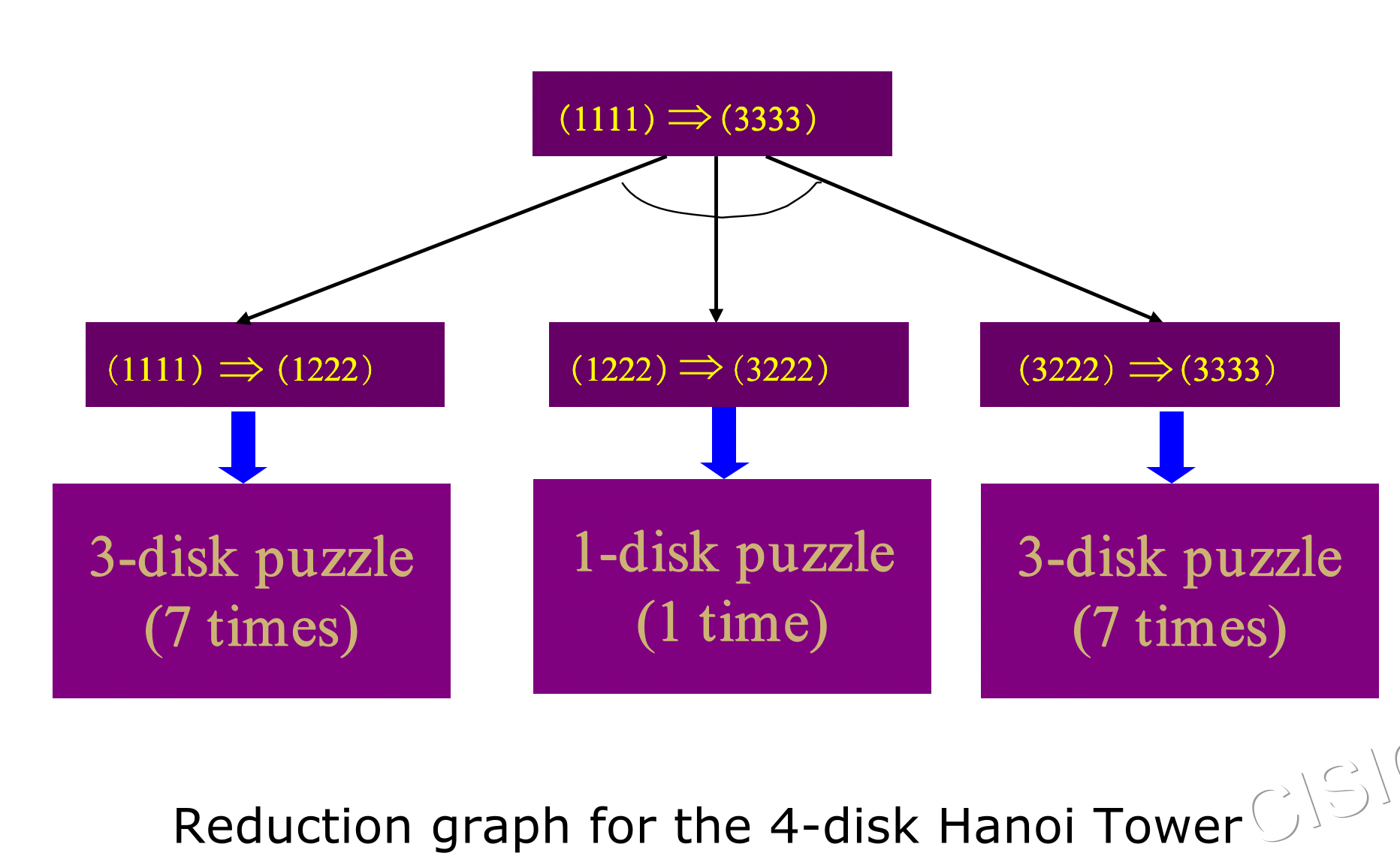
-
小结

3 Predicate Logic(谓词逻辑法)

3.1 Predicate Calculus(谓词演算)
1. 语法和语义 (Syntax and Semantics)
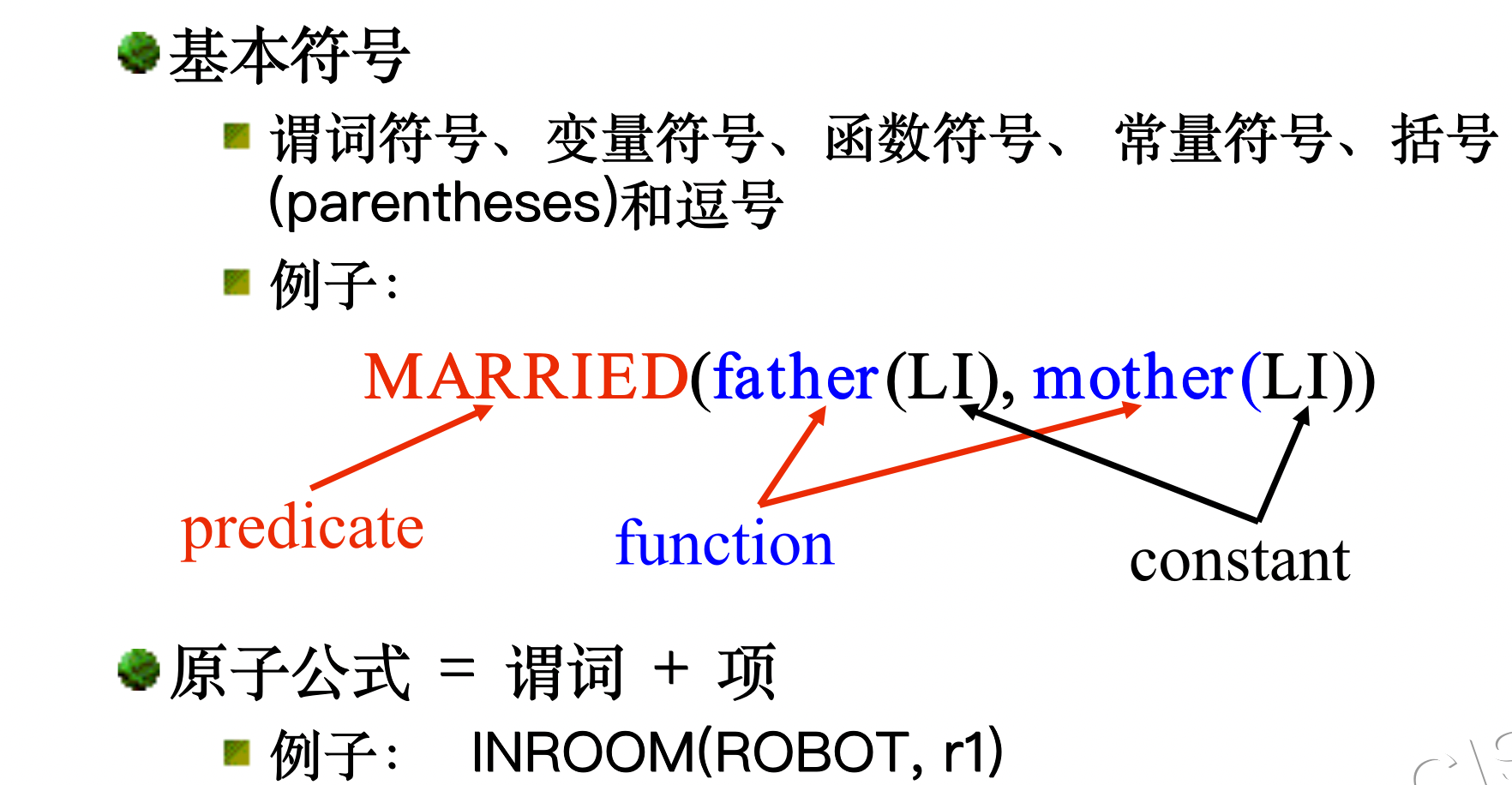
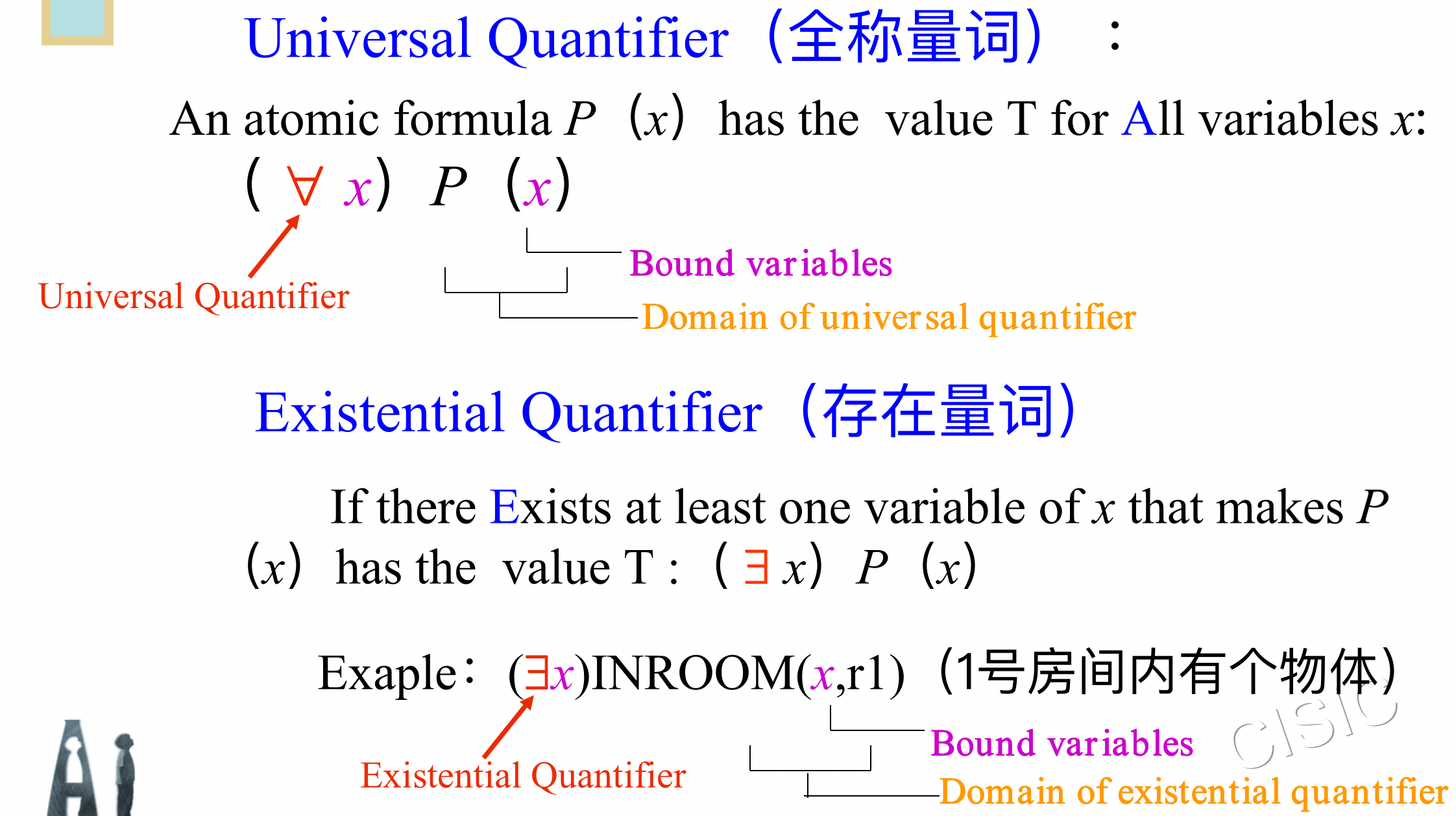
2. 连词和量词(Connectives & Quantifiers)



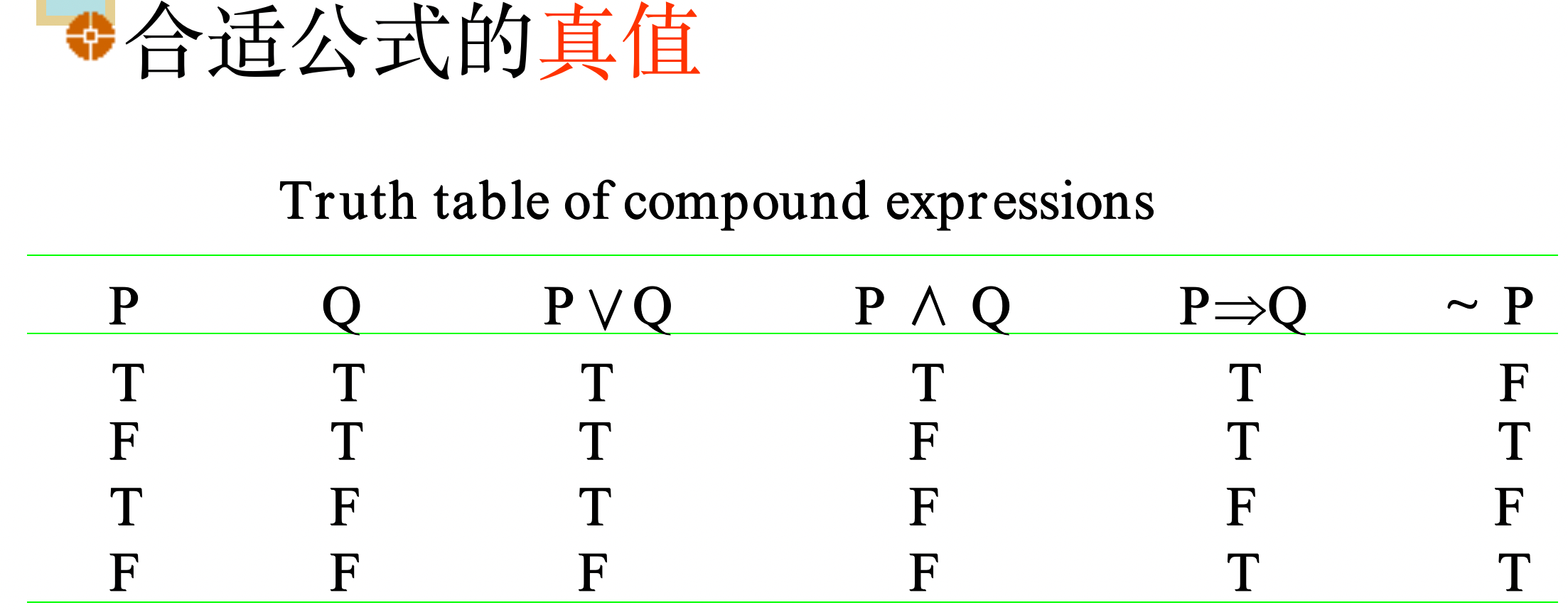
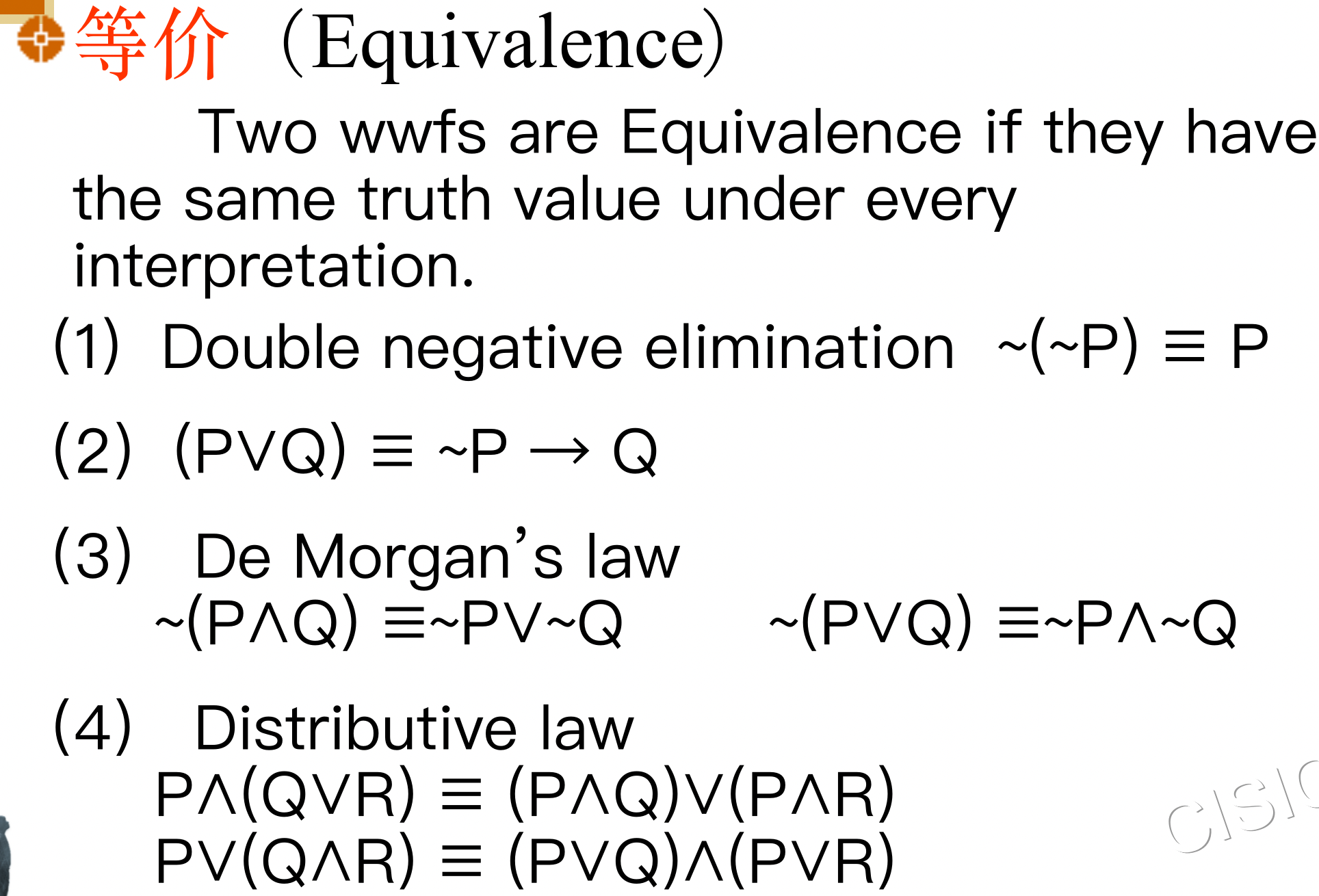
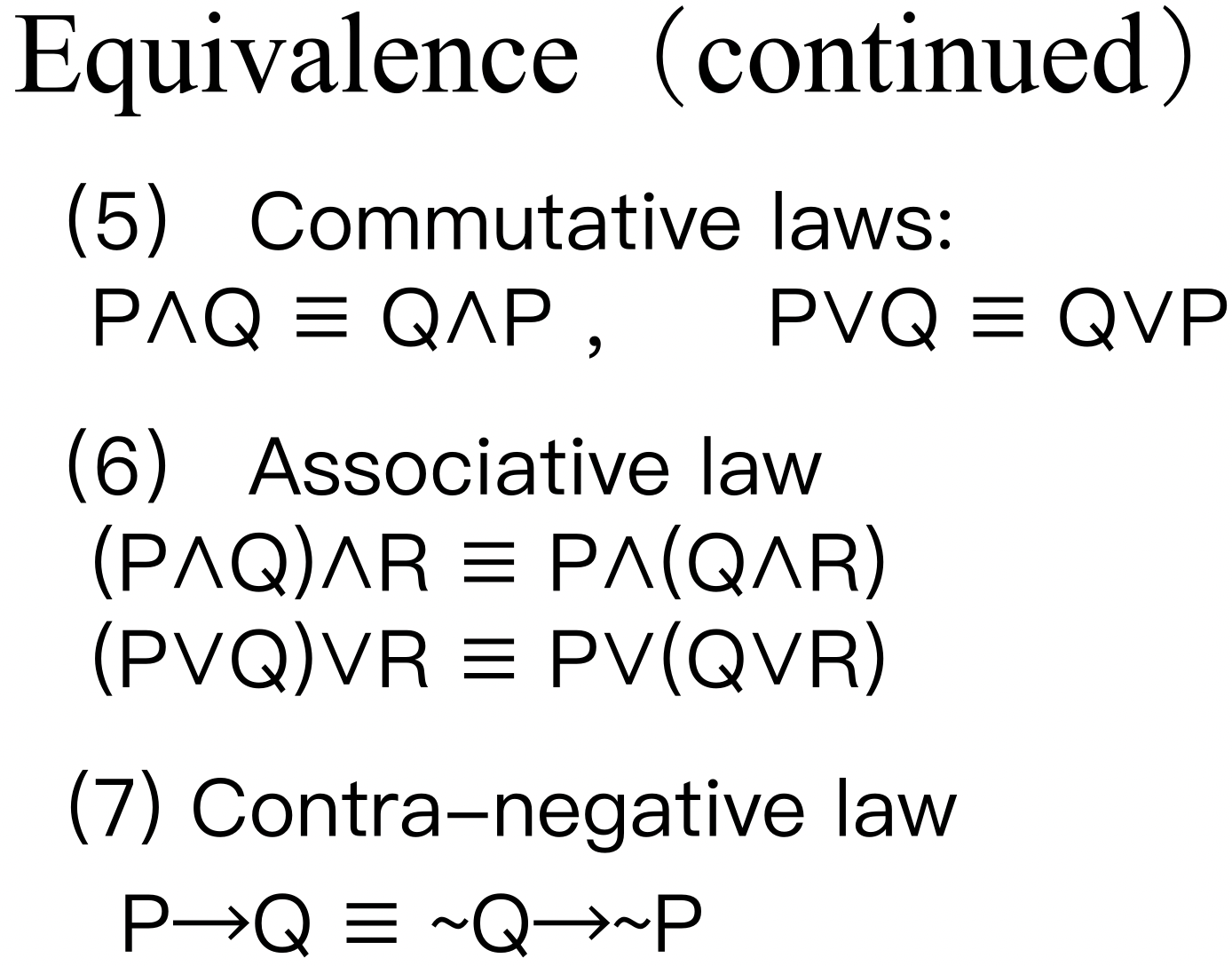
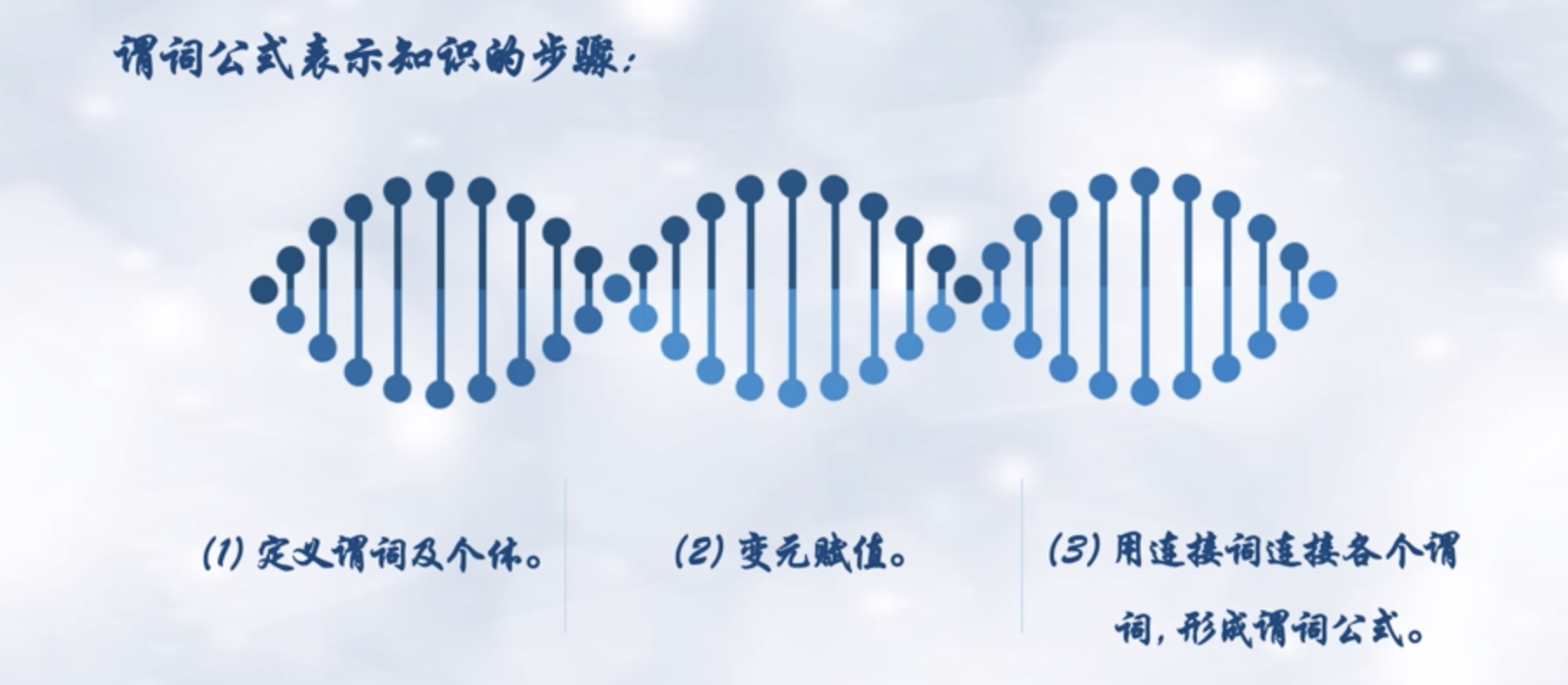
3.2 Predicate Formula (谓词公式)




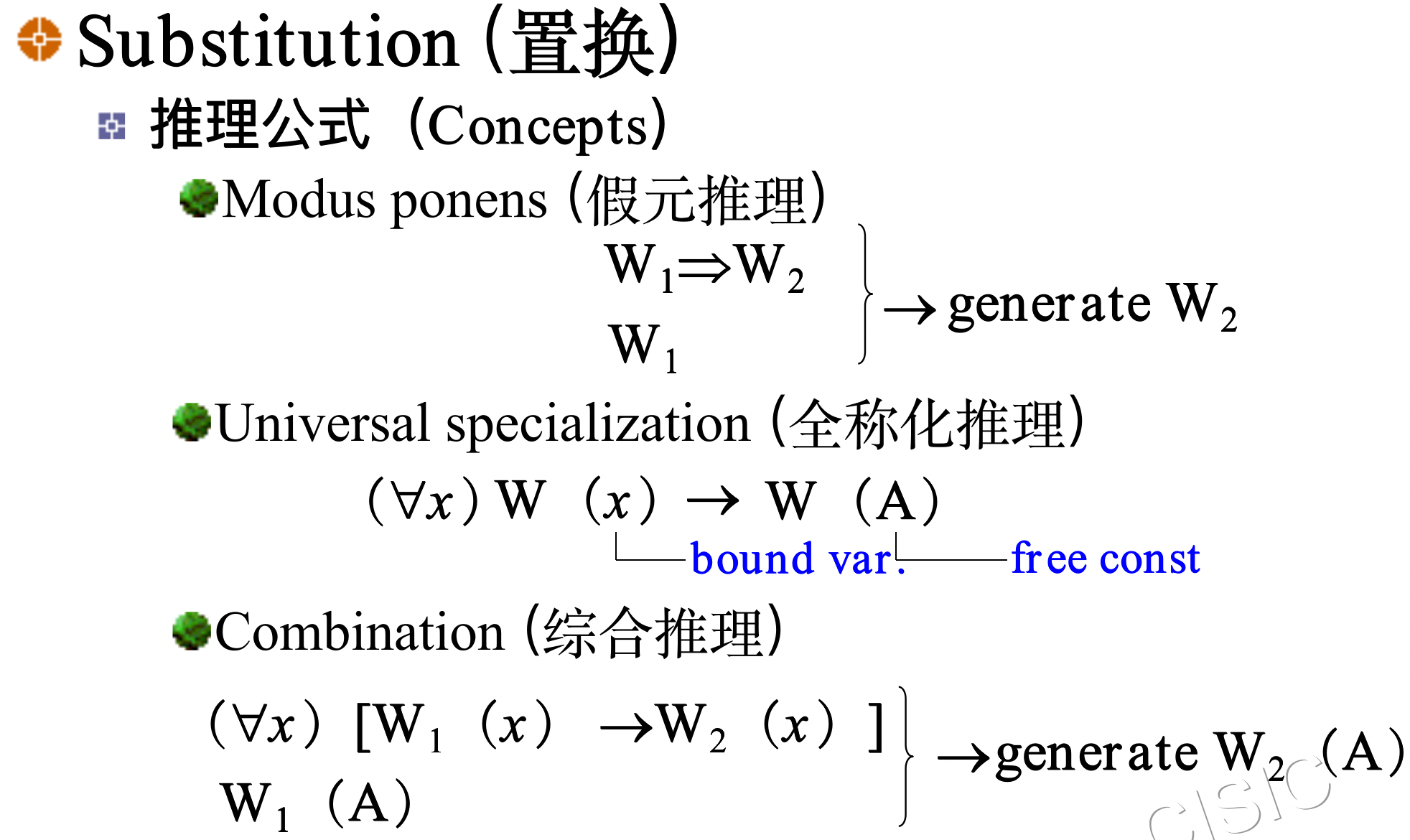
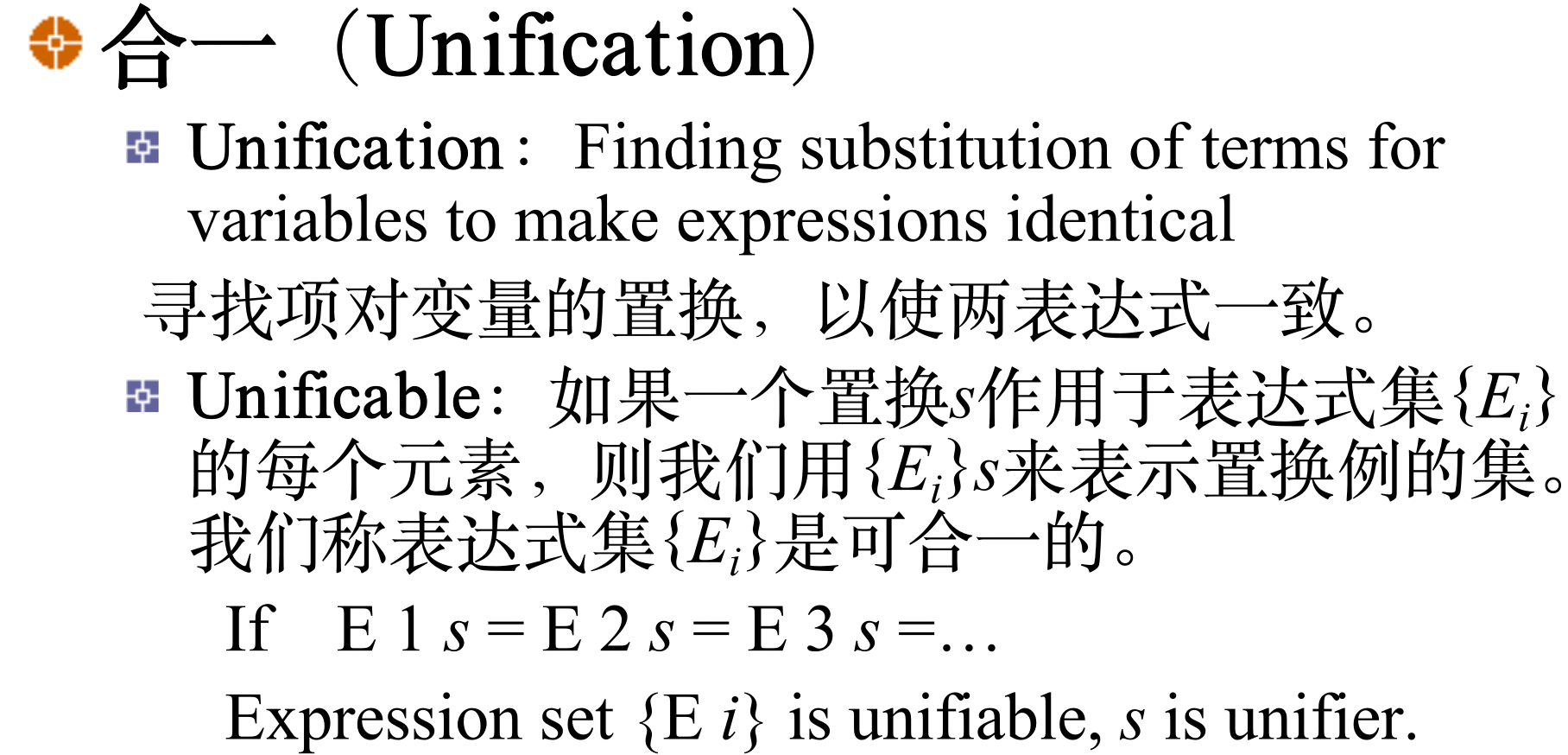
3.3. Substitution and Unification 置换与合一

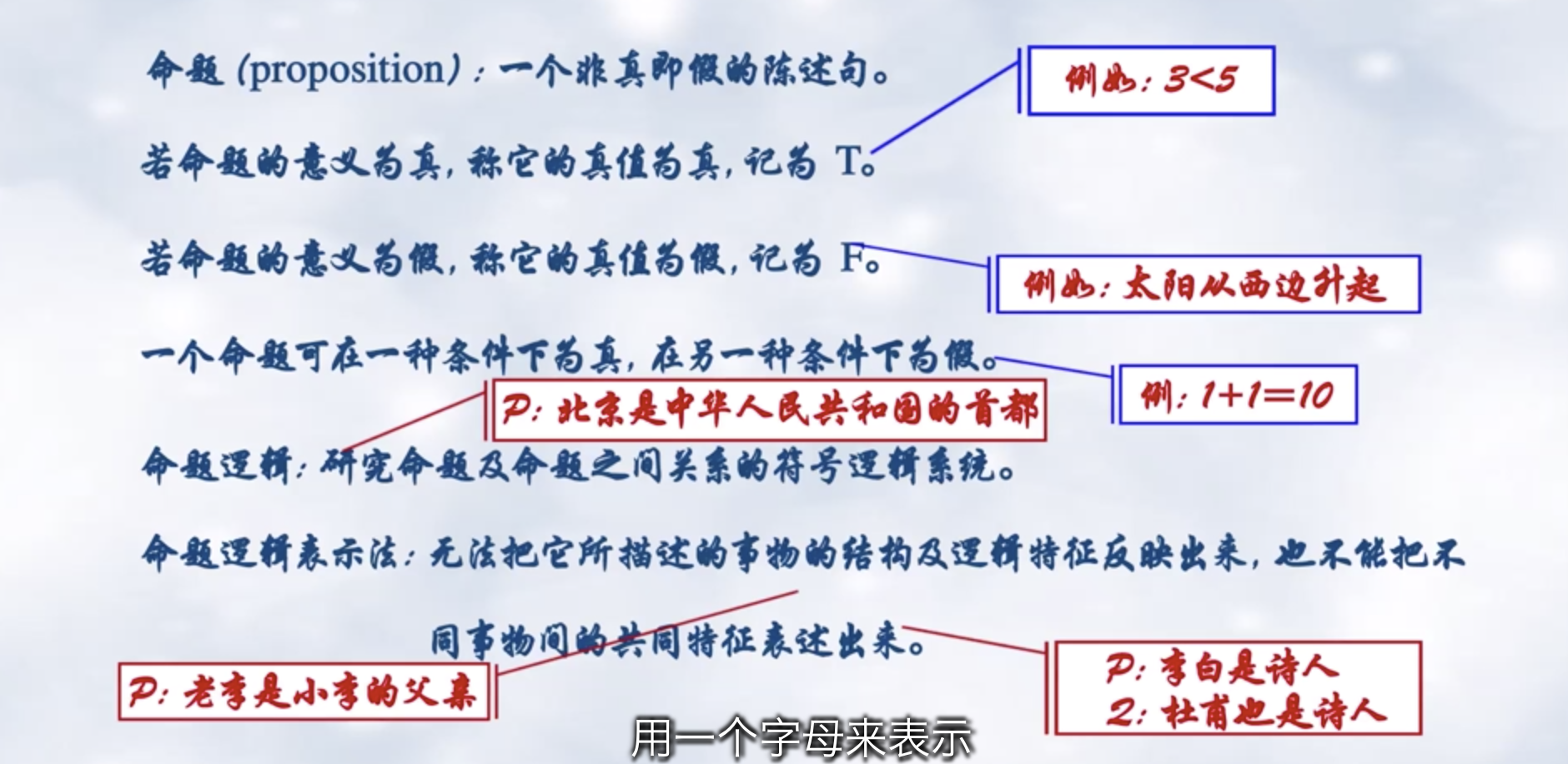
1 命题逻辑
无法刻画个体之间的关系
因此有了谓词逻辑
2 谓词逻辑

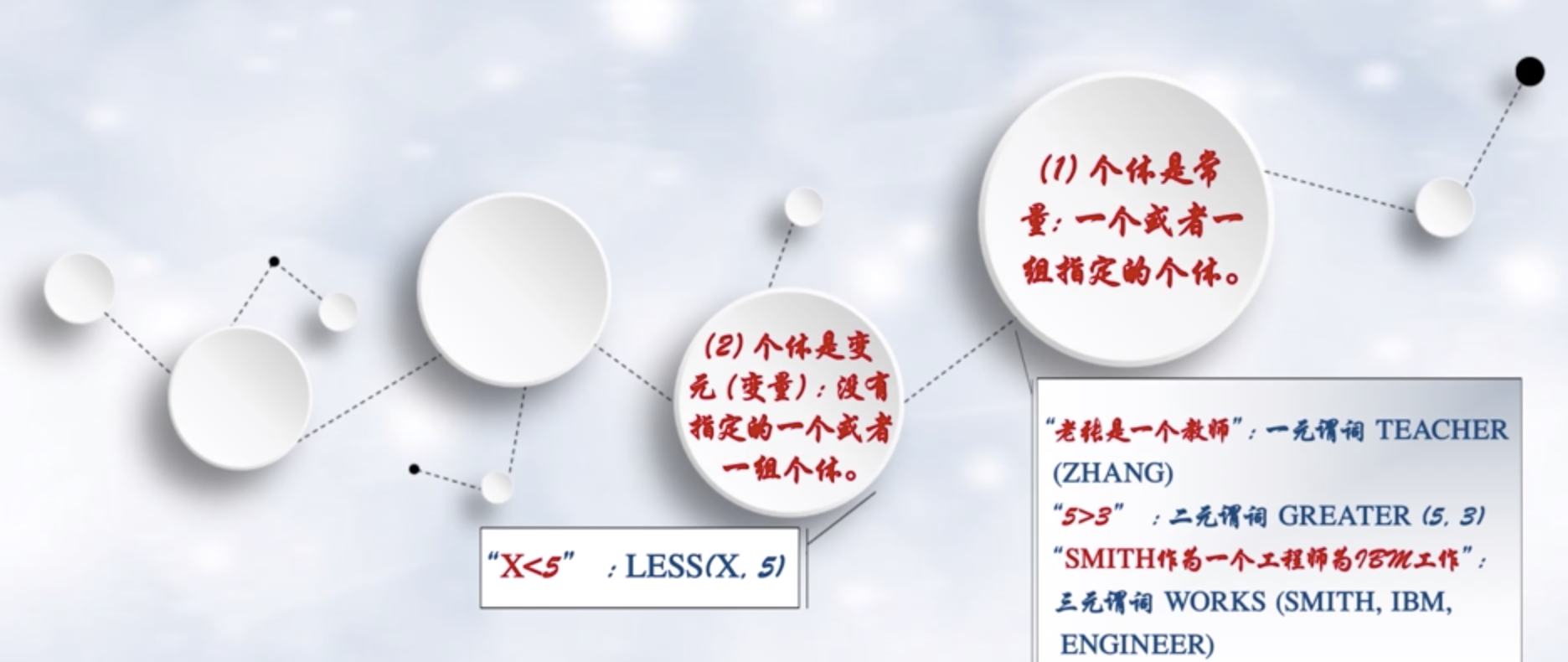
二阶谓词不讨论
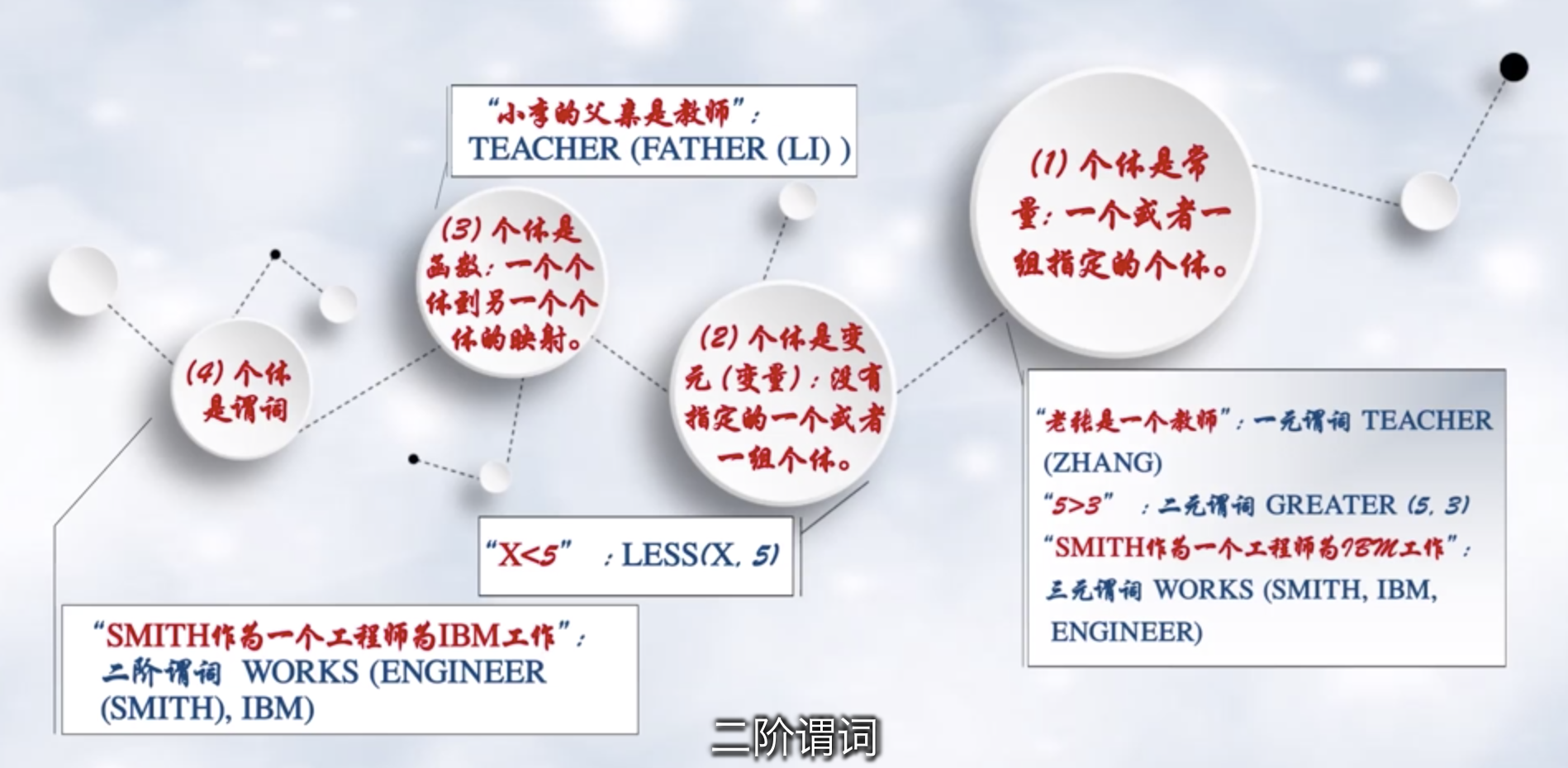
3 一阶谓词逻辑知识表示方法

一阶谓词逻辑特点
不能表示不确定的知识,会产生组合爆炸

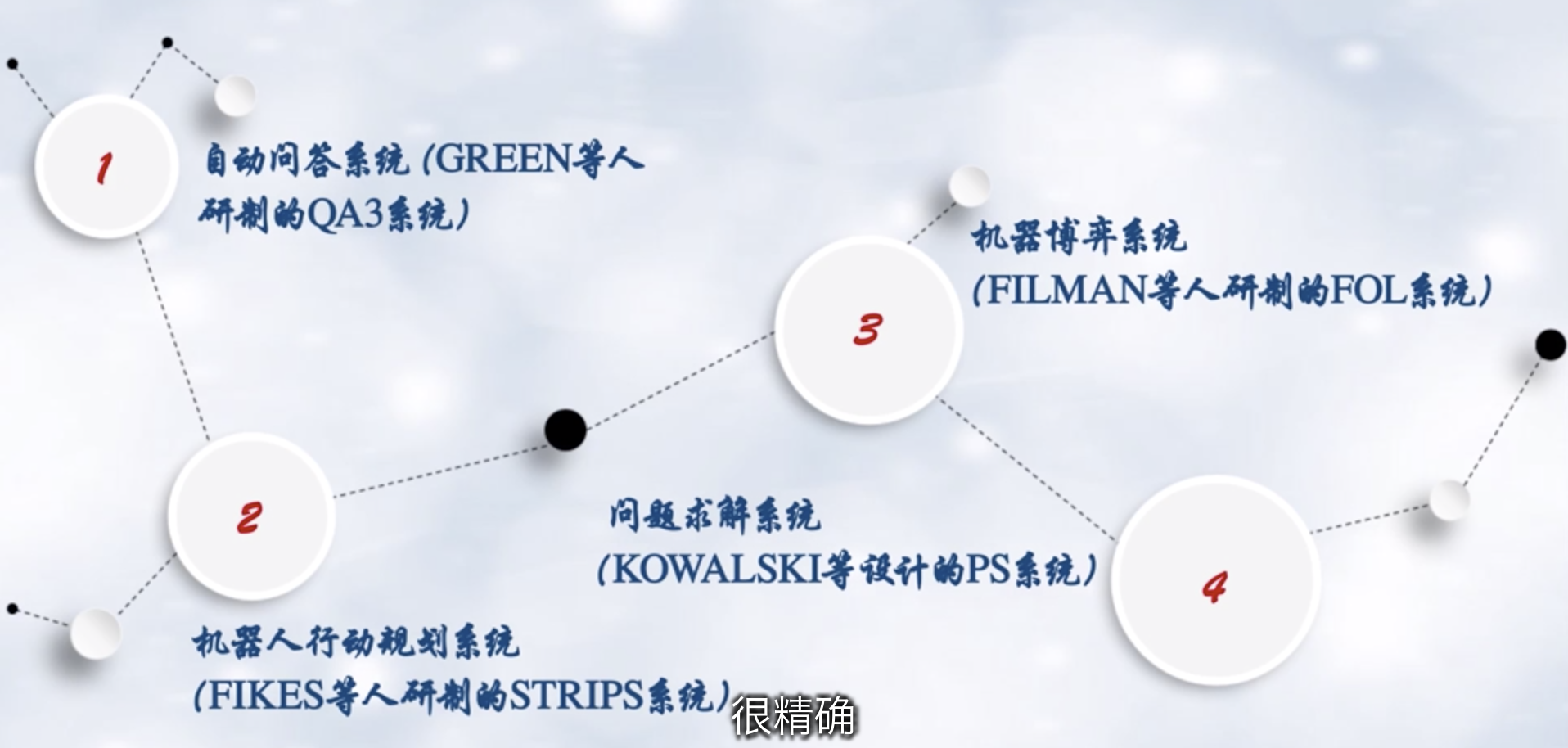
4 Semantic Network Representation 语义网络法


4.1 Representation of Two-Element Semantic Network (二元语义网络的表示)

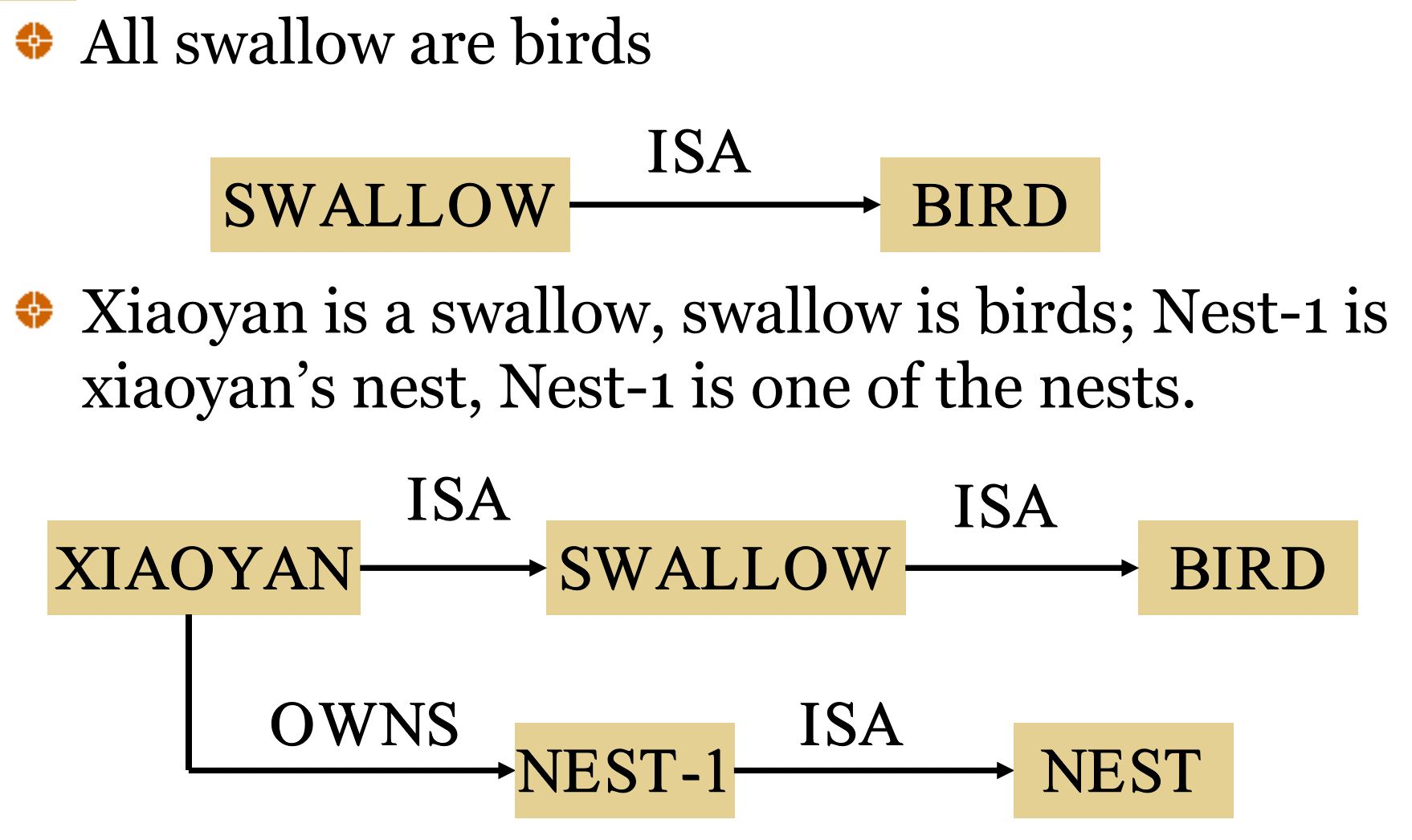

-
谓词逻辑与语义网络等效
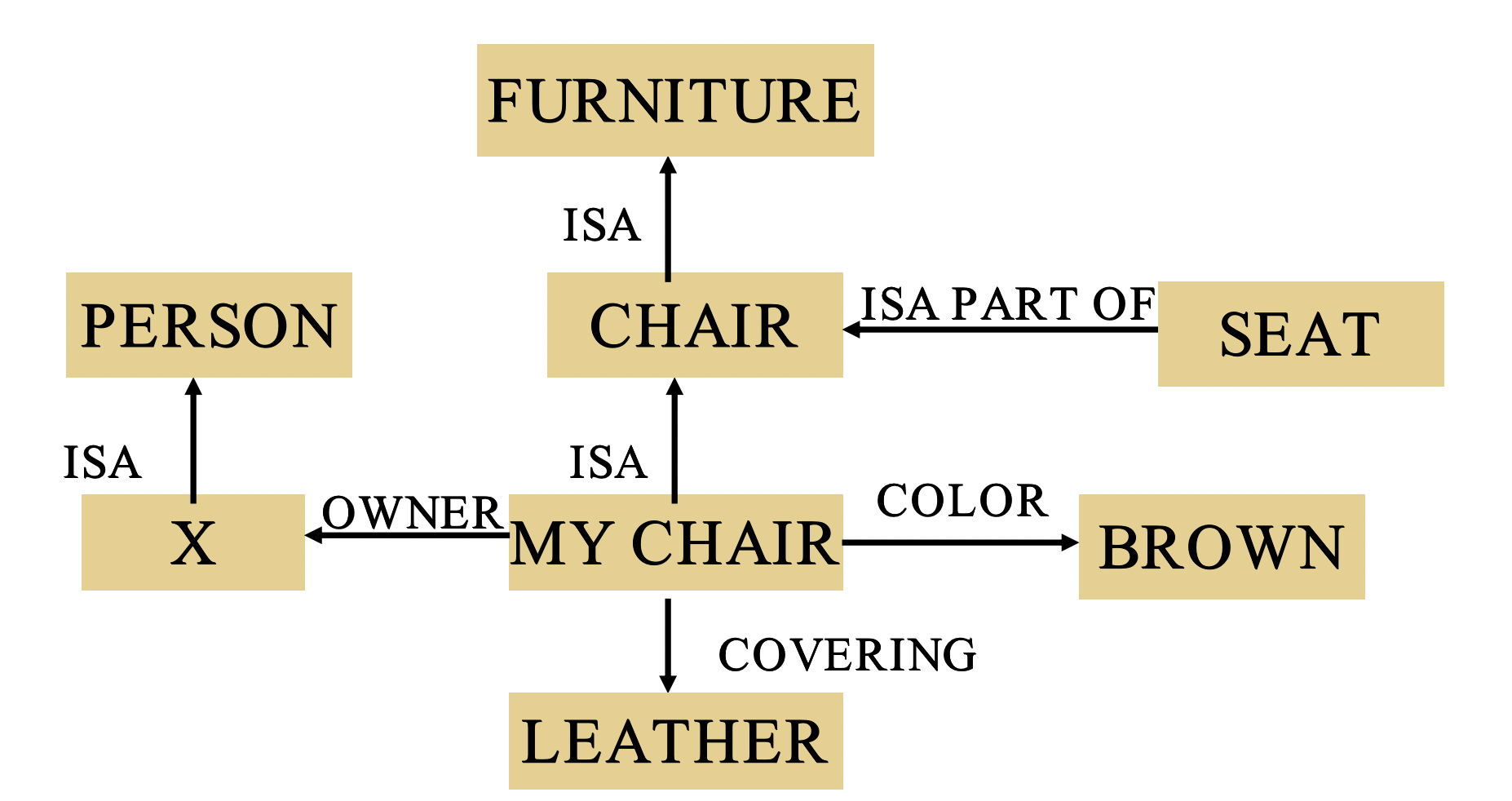
4.2 Representation of Multi-Element Semantic Network(多元语义网络的表示)

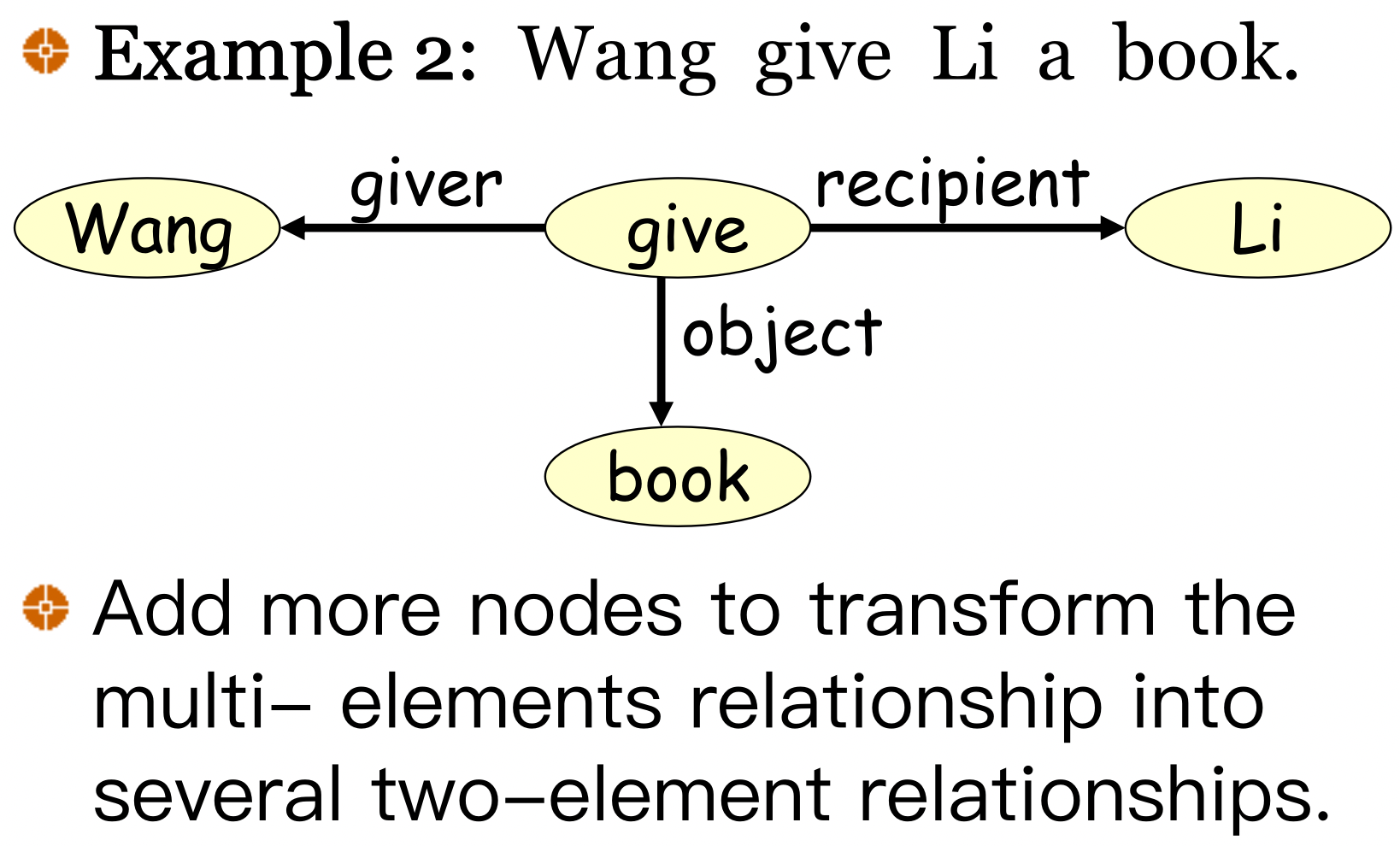
把多元关系转化为一组二元关系的组合,或二元关系的合取
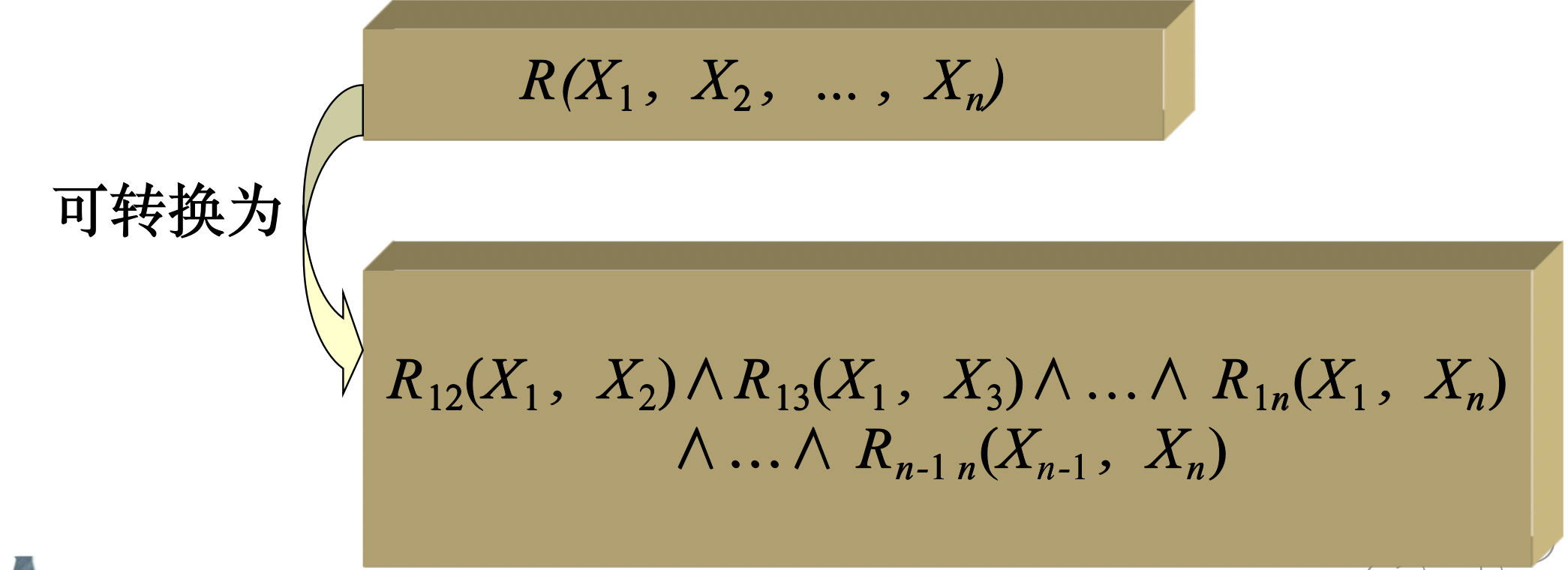
4.3 Inference Processv

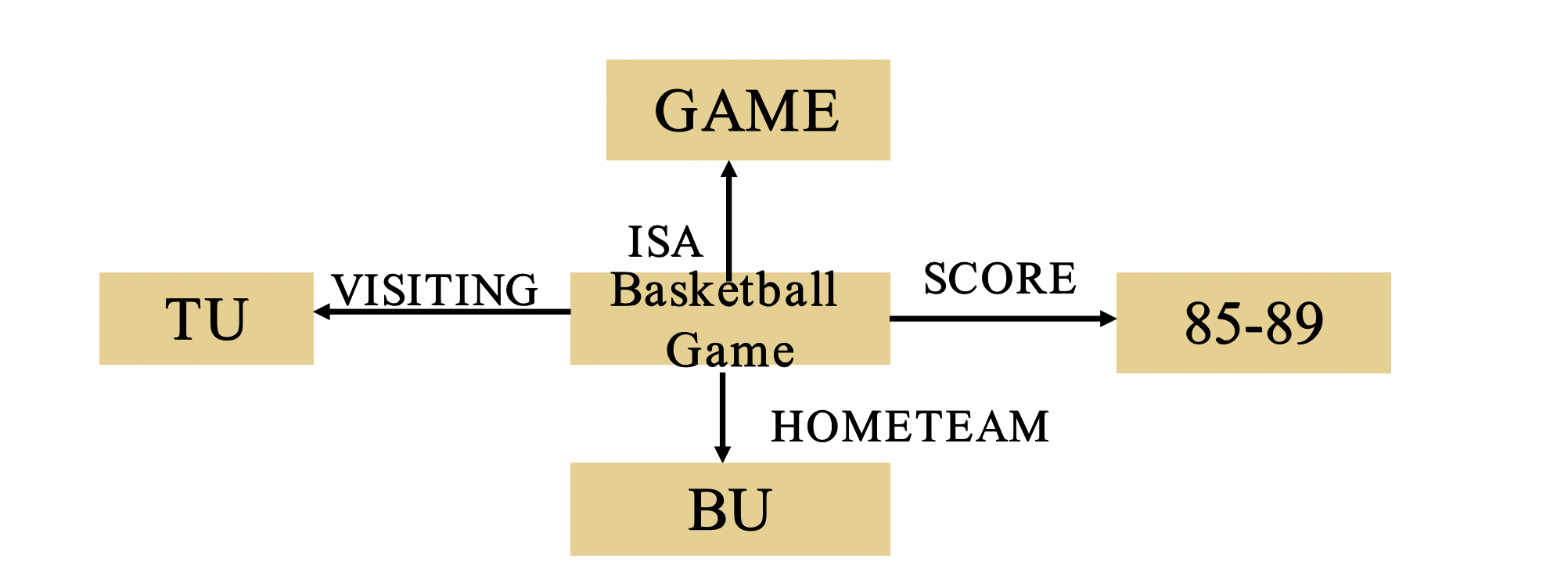
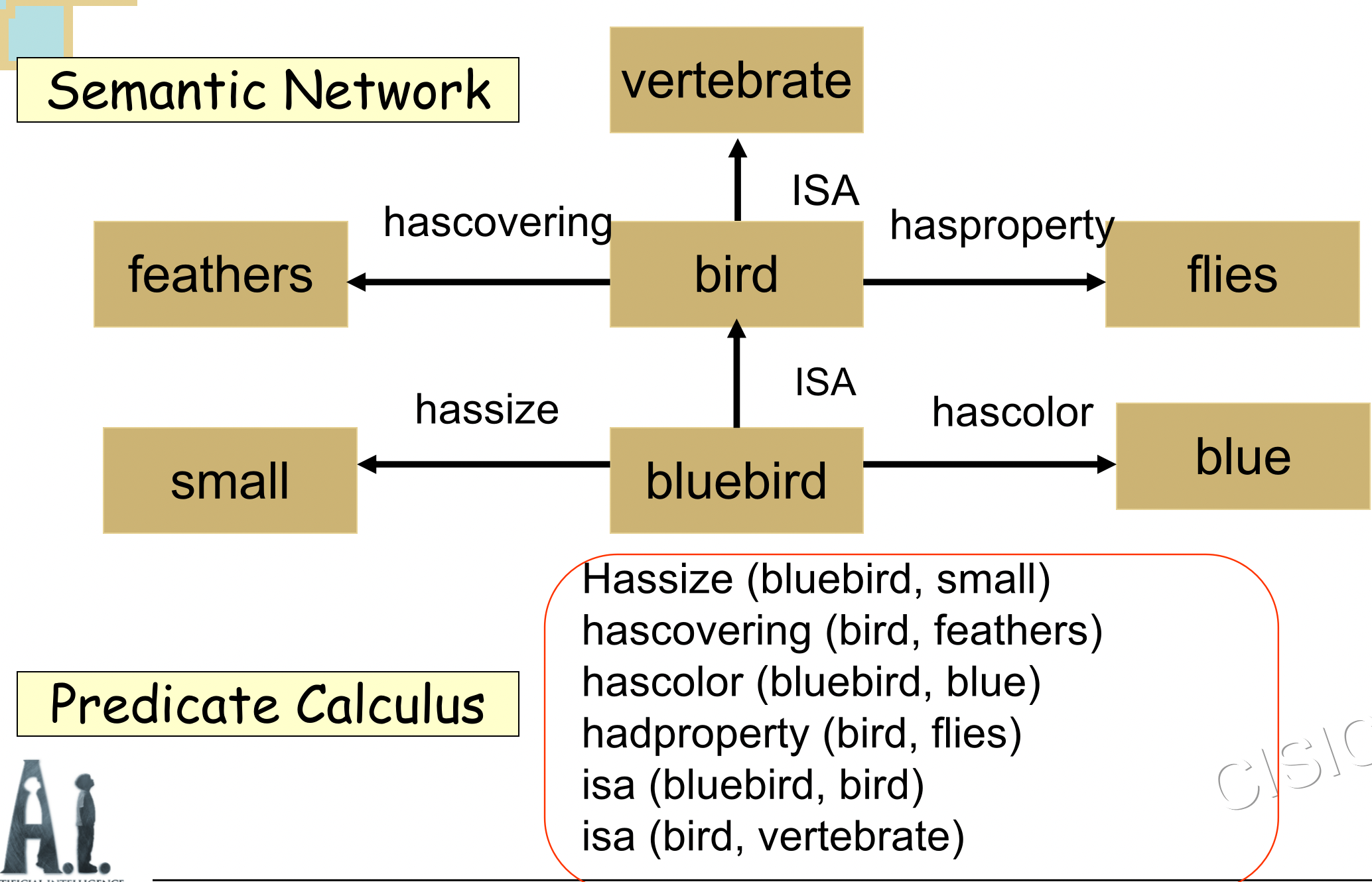
Semantic Network
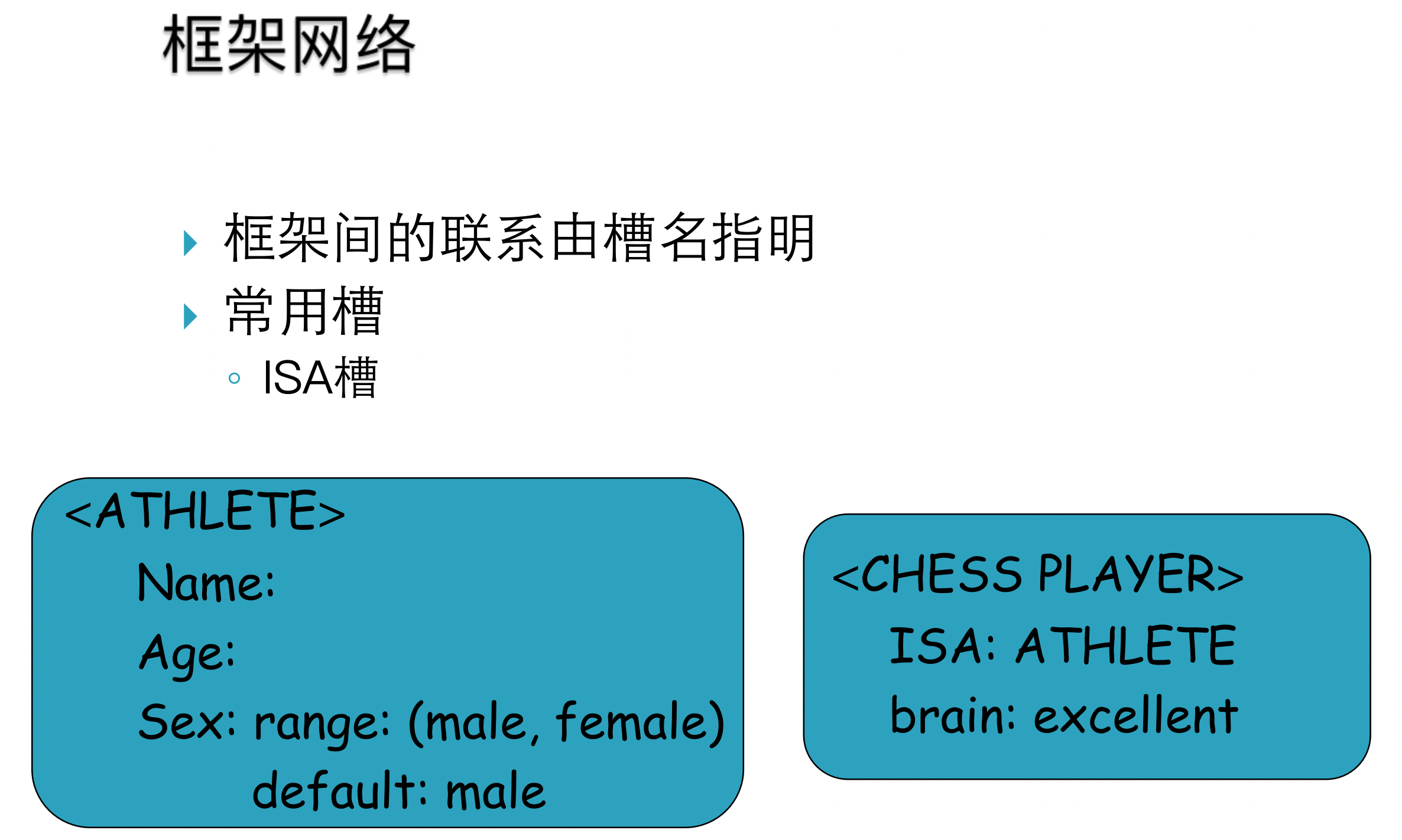
Inheritance(继承)

Three methods for inheritance
-
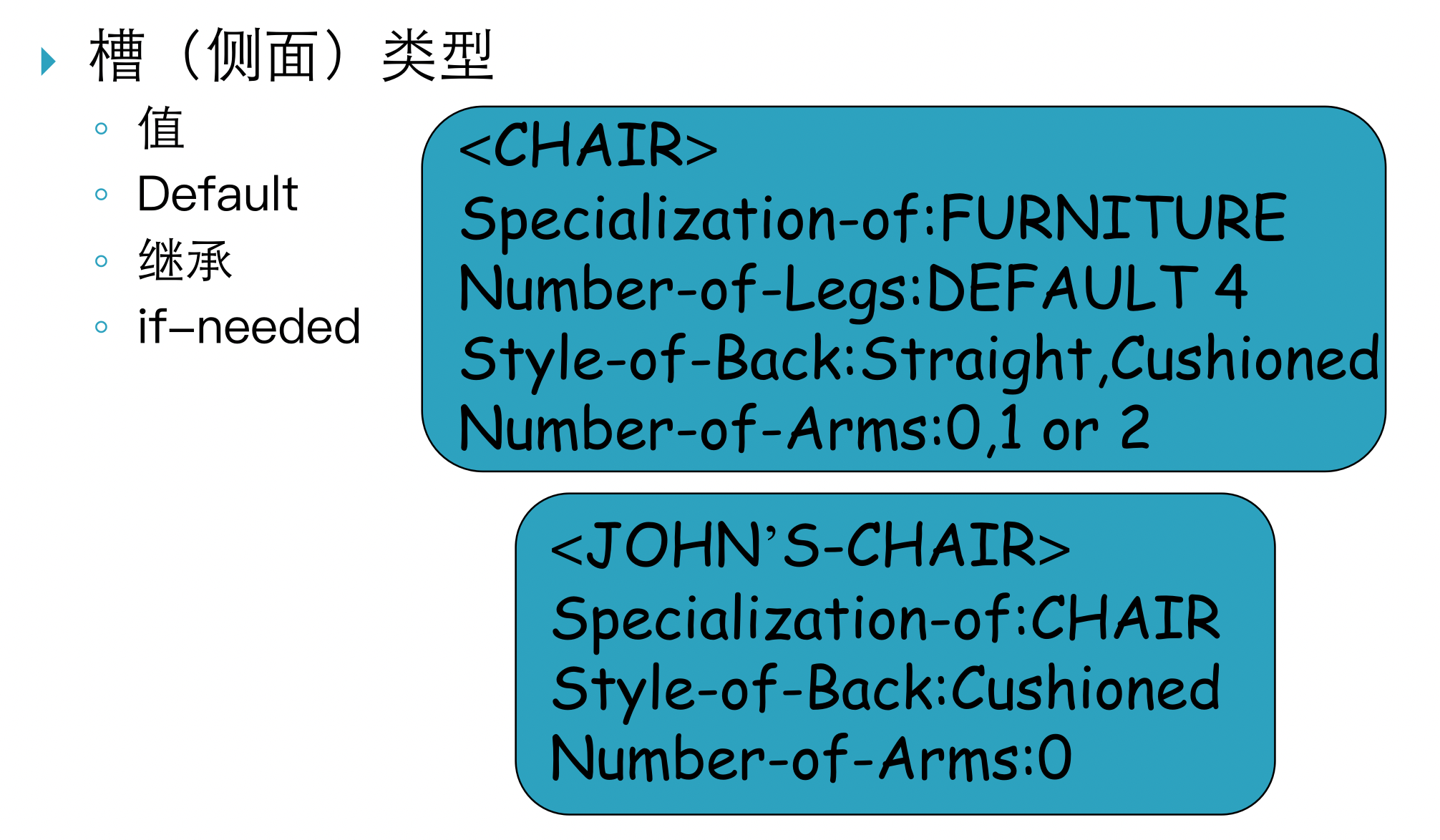
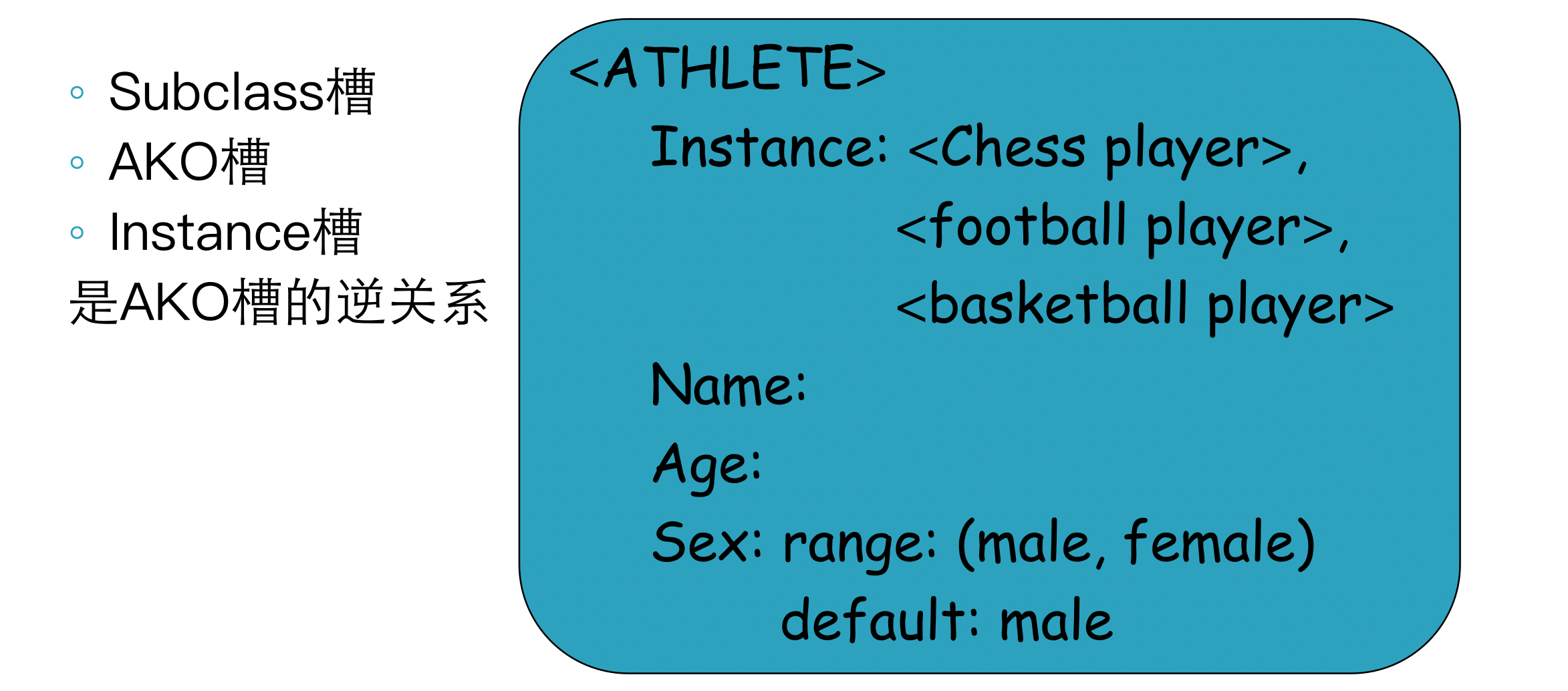
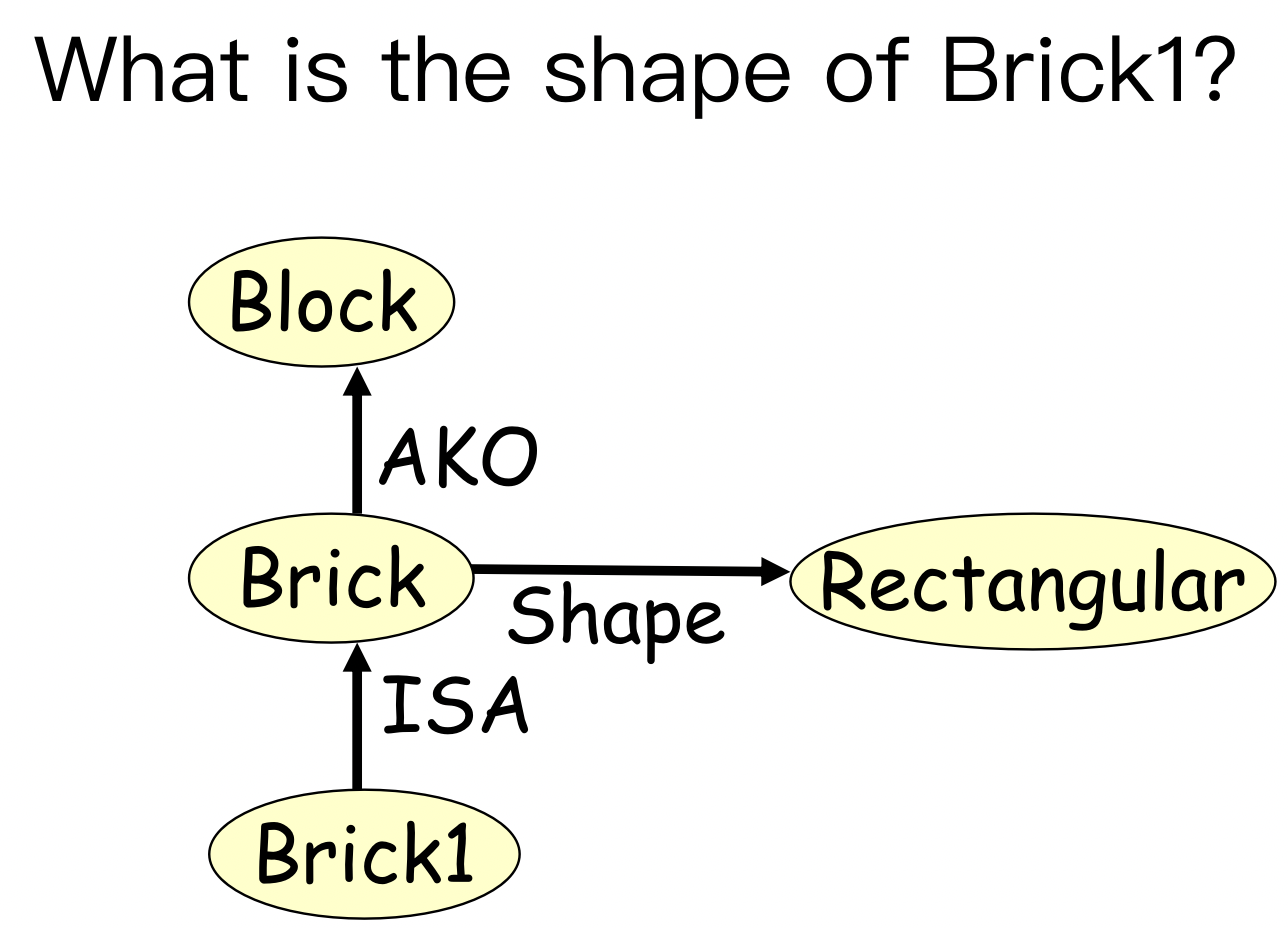
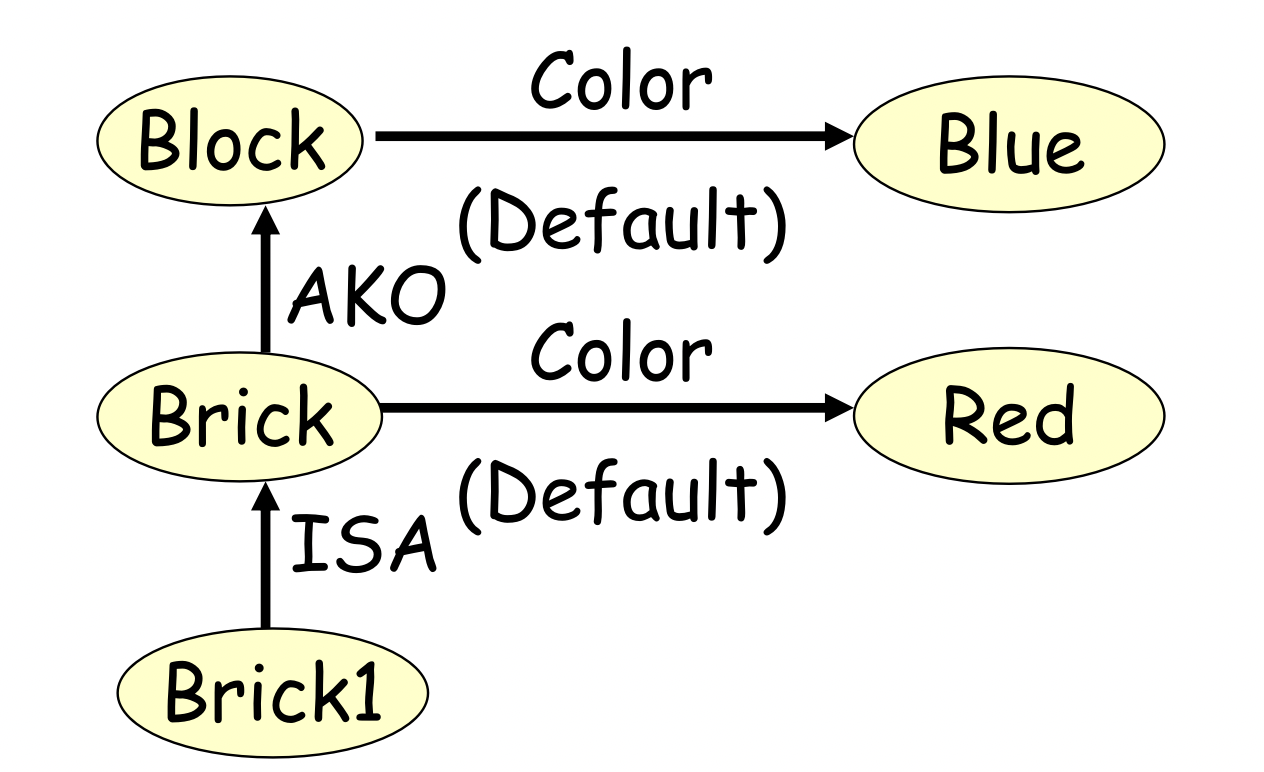
值继承: is-a, AKO(a kind of)
-
如果 -需要”继承:if-needed (it can not inherit from the ancestors,we get it from other programs )
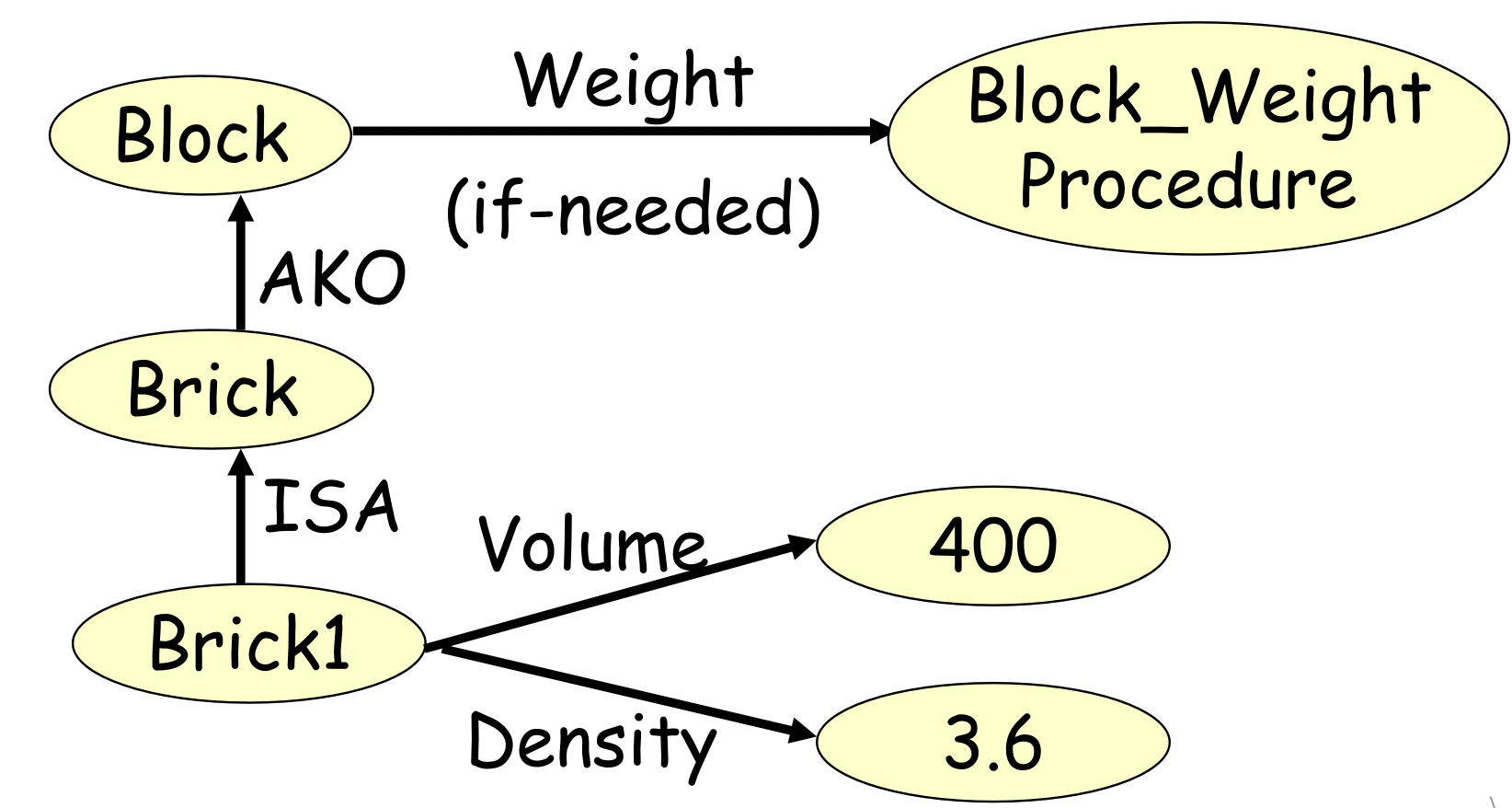
-
缺省继承:Default—it is mostly the truth
Exp: the birds can fly
Matching(匹配)
当涉及由几个部分组成的事物时,必须考虑值的传递问题。
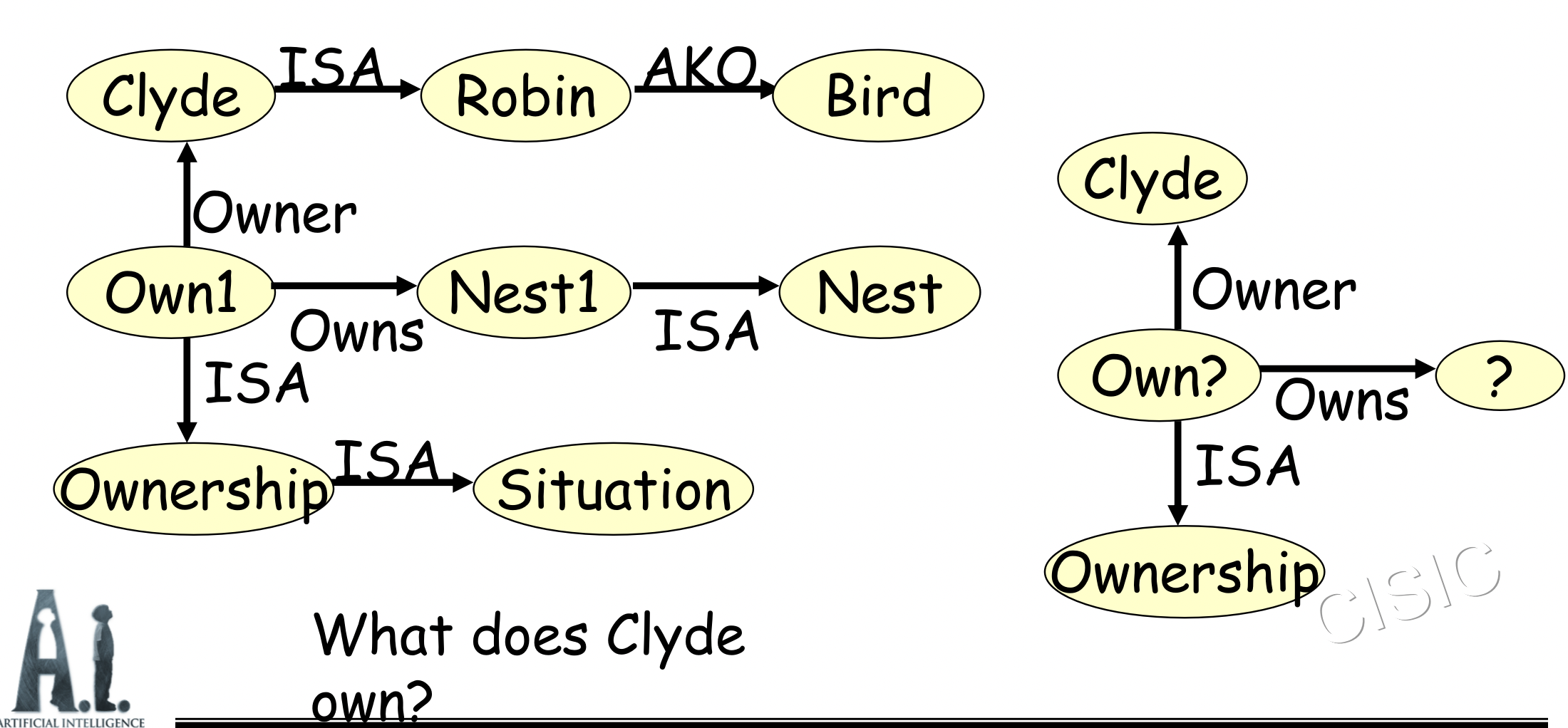
Example 1:
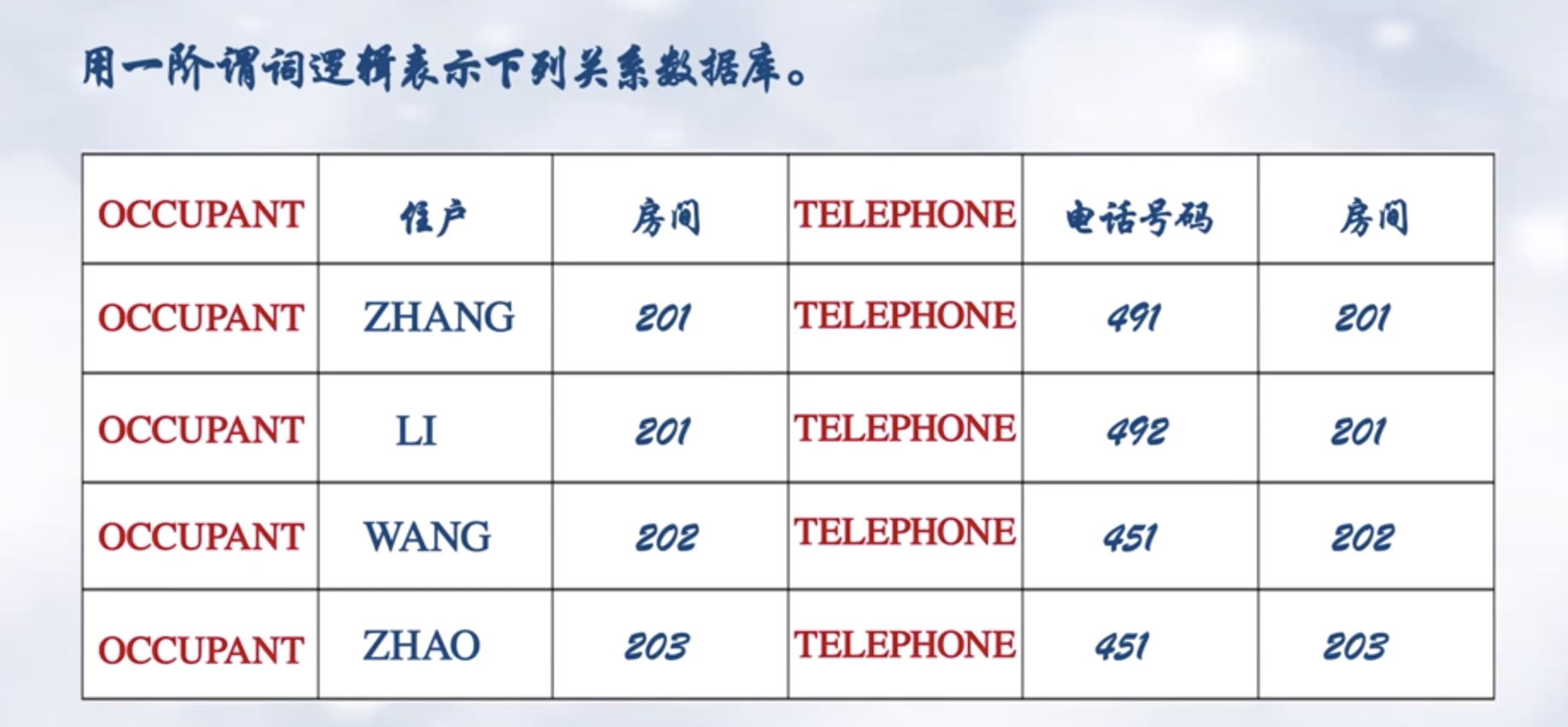
Use semantic networks to represent the followings:

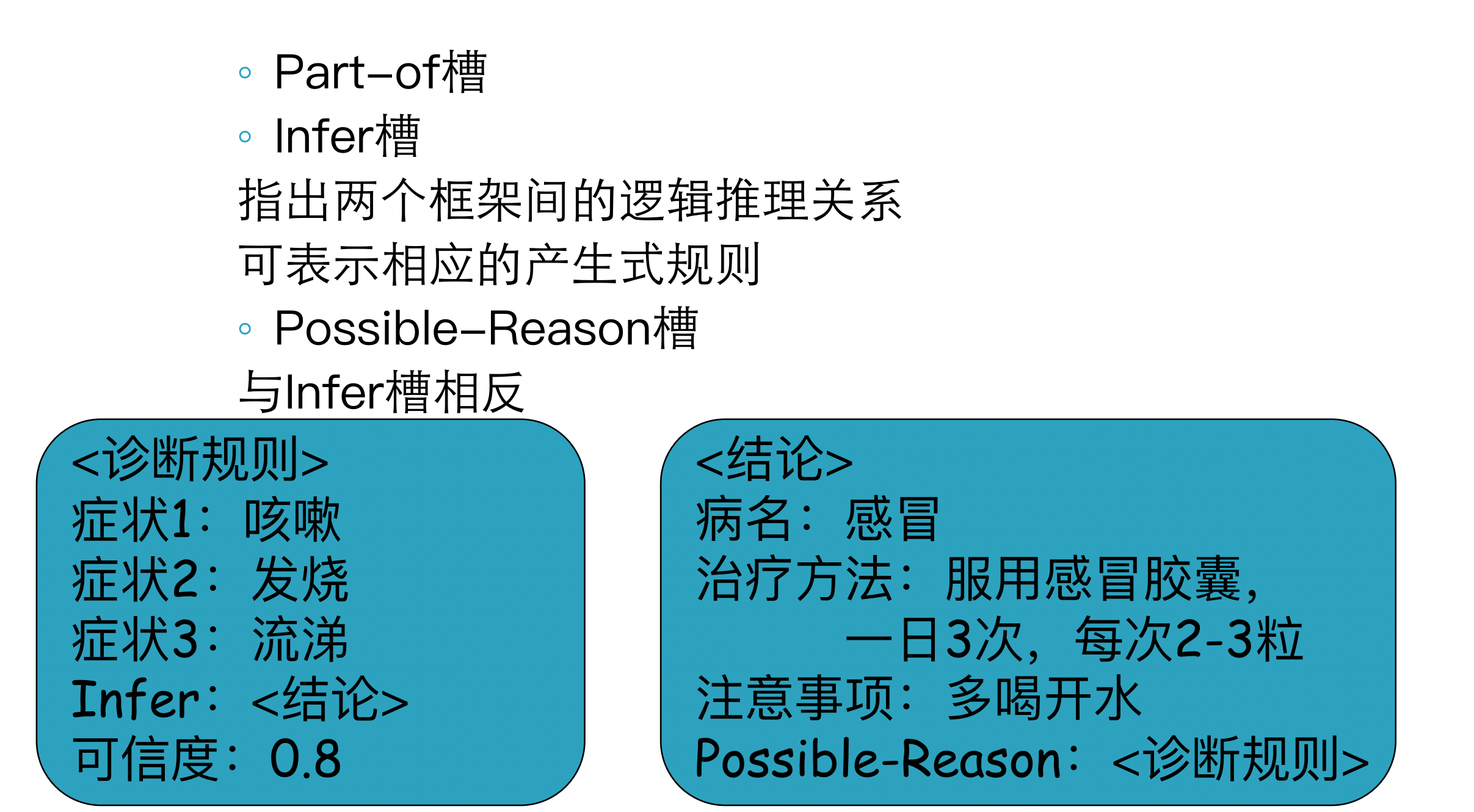
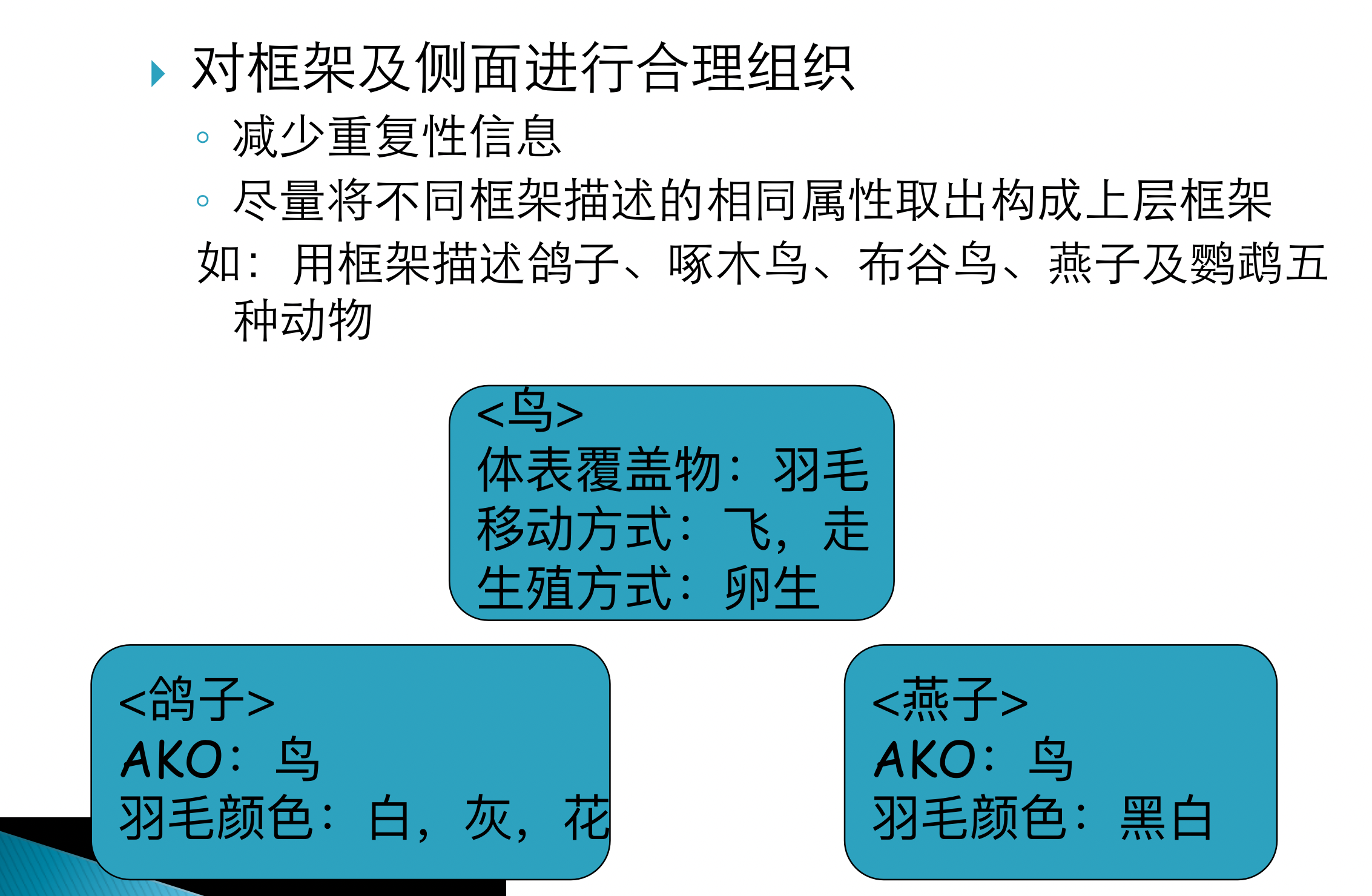
5 Frame (框架)

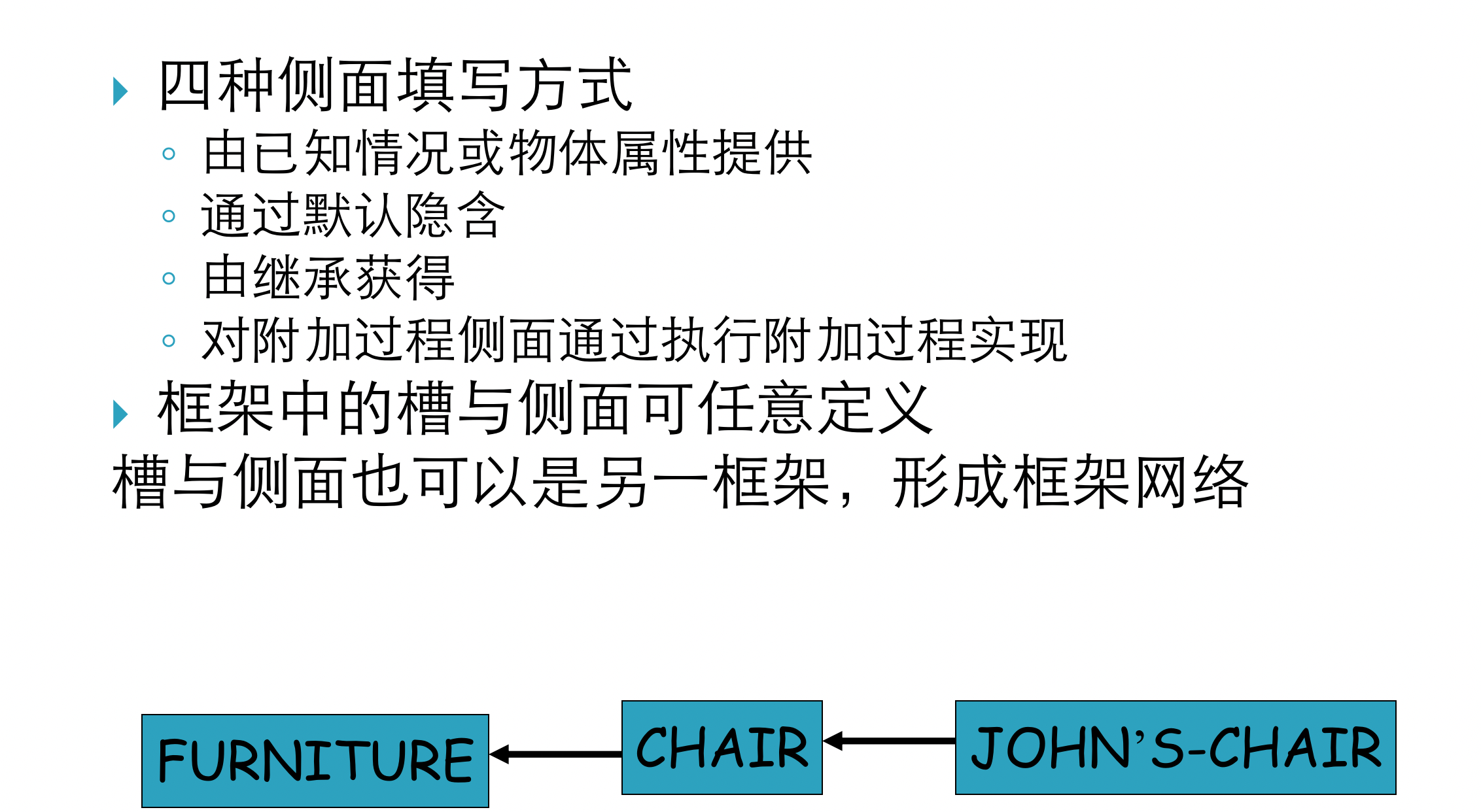
框架的结构

例:描述“大学教师”的框架